lecture 13
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
decision making
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Why is all clinical data considered imperfect?
All clinical data contains some degree of uncertainty, including diagnostic test results, patient history, and physical examination findings.
What is Bayes' Theorem and why is it important in medical diagnosis?
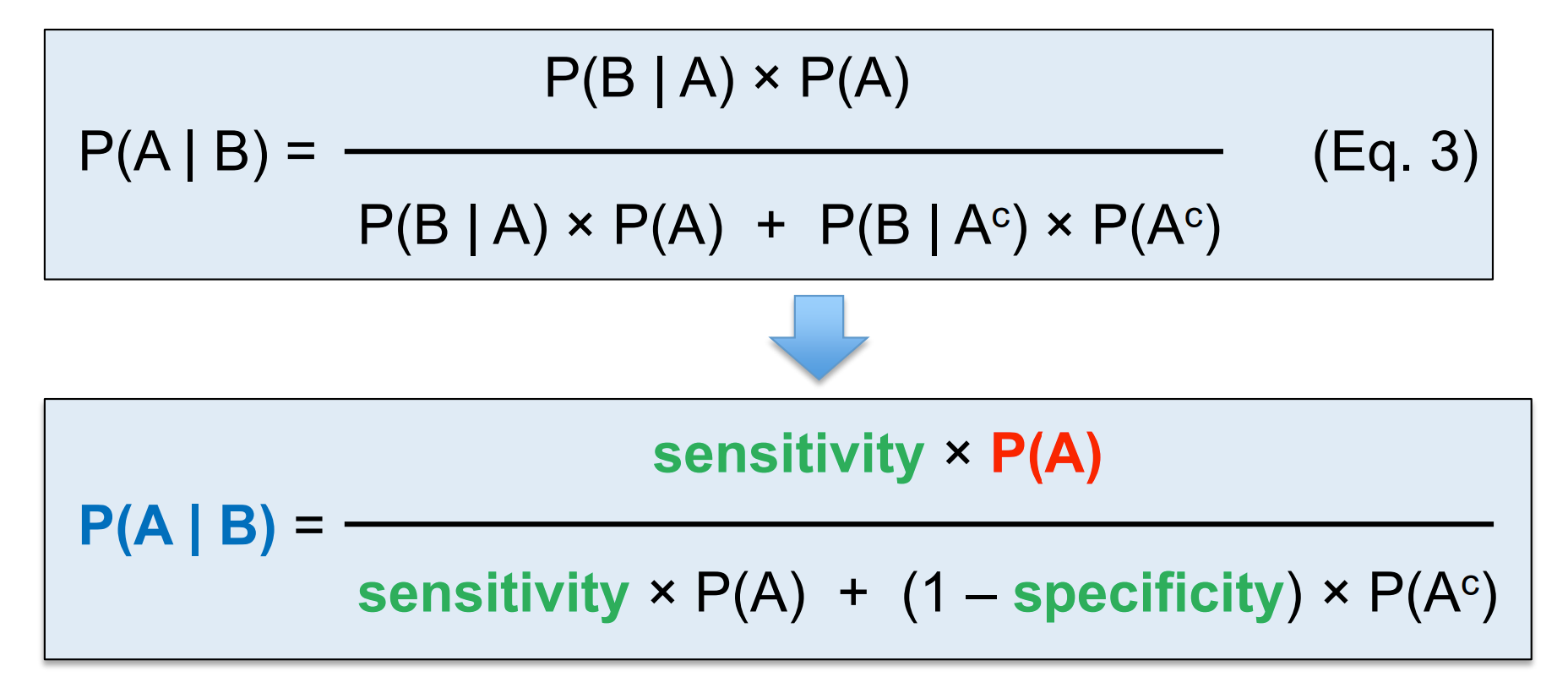
Bayes' Theorem is a formula that updates probability estimates based on new evidence: P(A|B) = [P(B|A) × P(A)] ÷ P(B). It allows clinicians to calculate the probability of disease given a test result.
What is the expanded form of Bayes' Theorem used in clinical contexts?
P(disease|positive test) = [sensitivity × P(disease)] ÷ [sensitivity × P(disease) + (1-specificity) × P(no disease)]
What are the three stages of the diagnostic process?
1) Initial judgment (establishing prior probability),
2) Information gathering (performing tests), and
3) Probability update (calculating posterior probability).
What is prior probability in medical diagnosis?
The estimated probability that a patient has a disease before any diagnostic tests are performed, based on epidemiology, symptoms, and risk factors.
What is posterior probability in medical diagnosis?
The updated probability estimate of a patient having a disease after considering test results, calculated using Bayes' theorem.
how to improve posterior probability?
By increasing specificity and (or) increasing sensitivity
can you explain the stage one initial judgment and where it is derived from?
Making an initial assessment about disease likelihood(Establishing the prior probability) Based on epidemiology, clinical experience, patient symptoms
can you explain the stage two diagnostic process and where it is derived from?
Collecting additional information through diagnostic tests. Primary goal: reducing uncertainty about patient's condition Considering test reliability (sensitivity and specificity)
can you explain the stage three diagnostic process and where it is derived from?
Calculating posterior probability using Bayes' theorem
what is the Bayes formula and the extended one?