Exam 1: Equine Juvenile Orthopedics
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
angular limb deformity
deviation of the appendicular skeleton in the frontal plane
abnormal angulation refers to the direction of deviation of the limb distal to the involved area or joint in relation to the midline
Valgus
abnormal angulation AWAY from midline
knock knee, angle is OUT
Varus
abnormal angulation towards midline
bow legged
angle is IN
conservative treatment angular limb deformities
stall rest
splints and tube casts
corrective hoof trimming
surgical treatments angular limb deformities
growth acceleration = periosteal transection and stripping
growth slowing = transphyseal bridging
corrective osteotomies/ostoectomy
stall rest for angular limb deformities
cuboidal bone hypoplasia = 4-6 weeks, repeat radiographs at 2 week intervals
periarticular laxity and normal cuboidal bone ossification = 15 min controlled exercise, swimming if possible
physeal and diaphyseal growth disturbances= 4-6 weeks, surgery if no improvement
hoof trimming for valgus
trim lateral, causing inside of the foot the contact the ground first during the procress of placing weight and rotates medially
do not trim heel bulb
hoof trimming varus
trim medial
do not trim heel bulb
periosteal elevation
causes growth acceleration
performed on the short side concave aspect of bone
repeatable
good cosmetic results
no overcorrection possible
commonly performed laterally in carpal valgus
periosteal elevation postop care
light bandages for 10-12 days
stall rest 4-6 weeks
corrective hoof trimming every 2 weeks
observatio/rads
sites for transphyseal bridging
distal radius
distal tibia
distal mc III,Mt II
techniques for transphyseal bridging
transphyseal staples
transphyseal screws
screws and figure 8 cerclage wires
screws and small bone plates
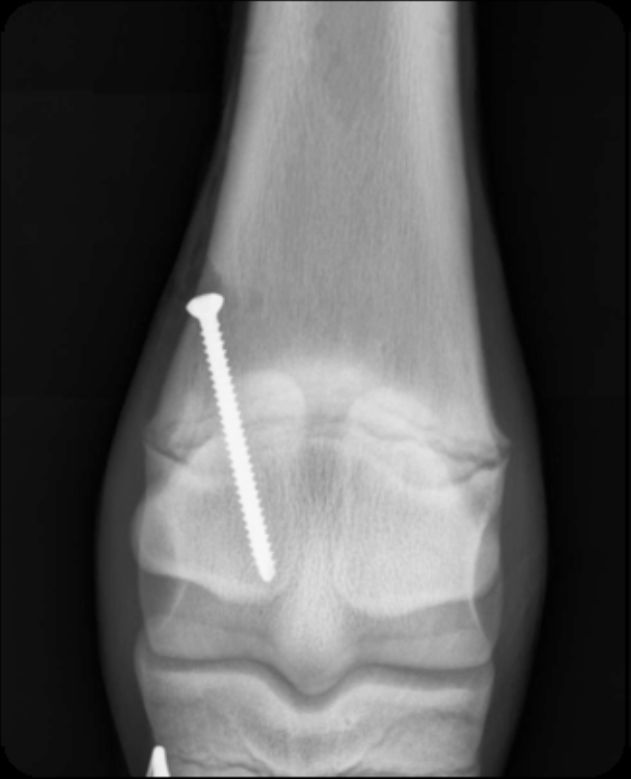
use of transphyseal screw
most common technique
single cortical screw placed THROUGH physis
performed on distal radius, tibia, distal MC/Mt 3
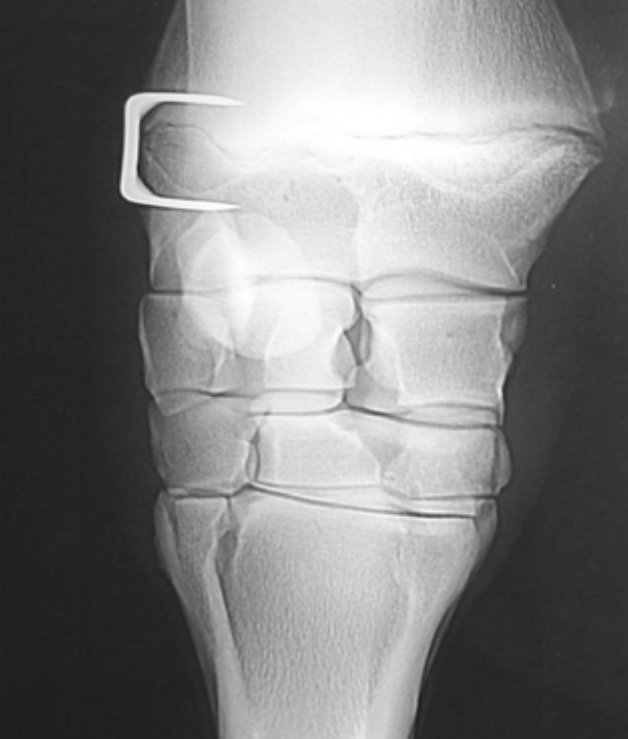
use of staple for transphyseal bridging
commonly used in the carpus
single staple screw placed across physis
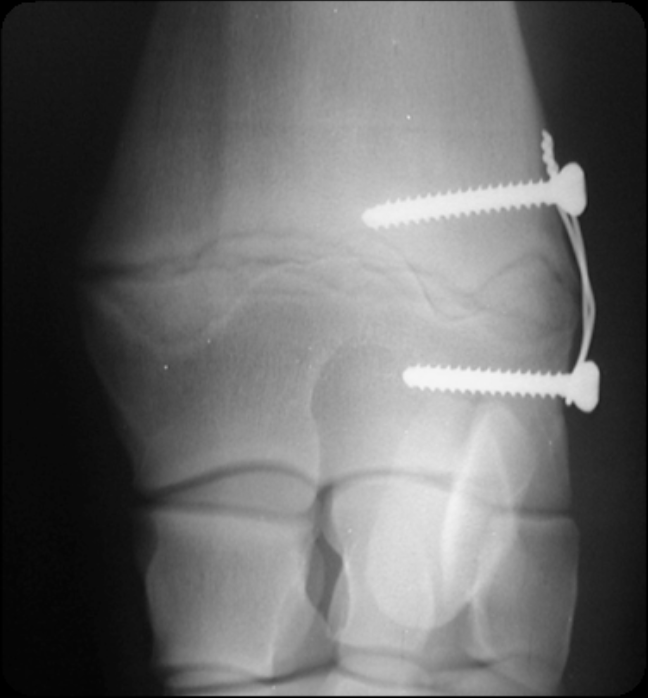
transphyseal bridging using screw and wire
commonly used in the carpus
two scres placed on either side of the physis, held with a figure 8 cerclage wire across physis
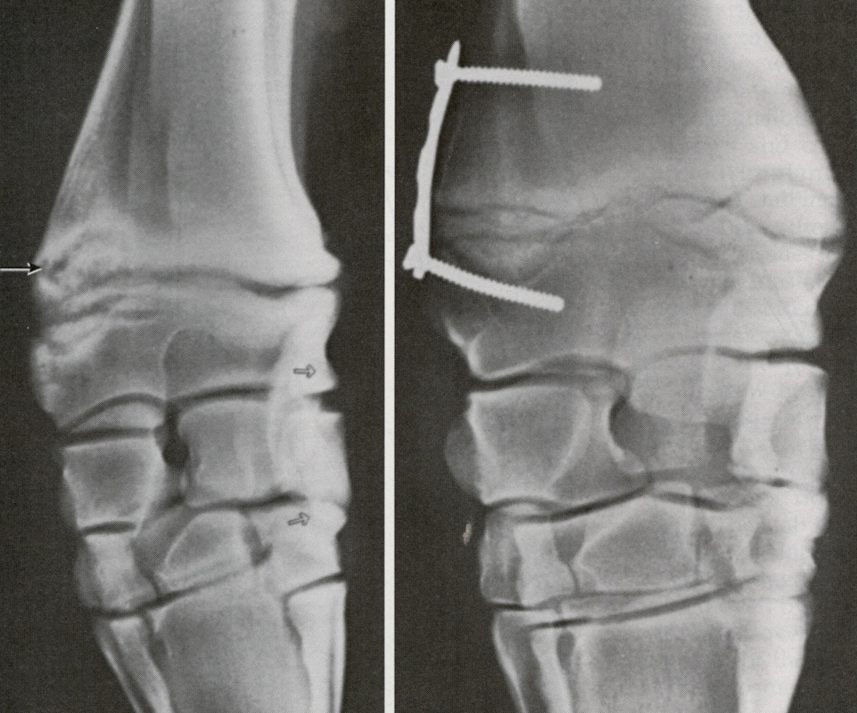
transphyseal screw and plate
commonly used in the carpus
used for more severe angulation
transphyseal bridging post operative care
light bandages for 10-12 days
stall rest for 6 weeks
corrective hood trimming every 2 weeks
with all types of implants monitor foals daily to determine extent of change
lack of minitoring can lead to over-correction
screw removal 2-4 wks post implantation or when limb is at the desirable position
some screws can be reset or replaced if not enough change in 4 weeks
corrective osteotomy techniques
foals with closed growth plates and severe diaphyseal deformities
metaphyseal/diaphyseal deformities
prolonged recovery and higher cost
horizontal wedge, step sagittal, rotational, frontal
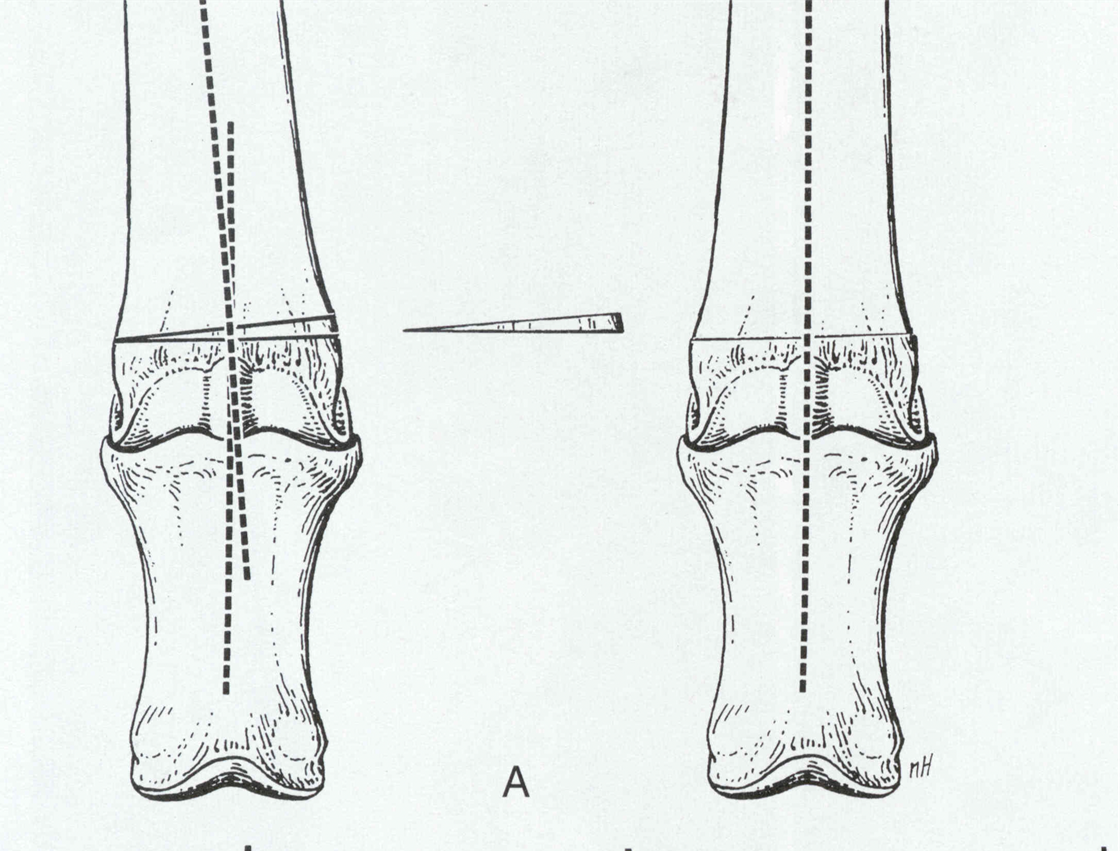
wedge ostectomy
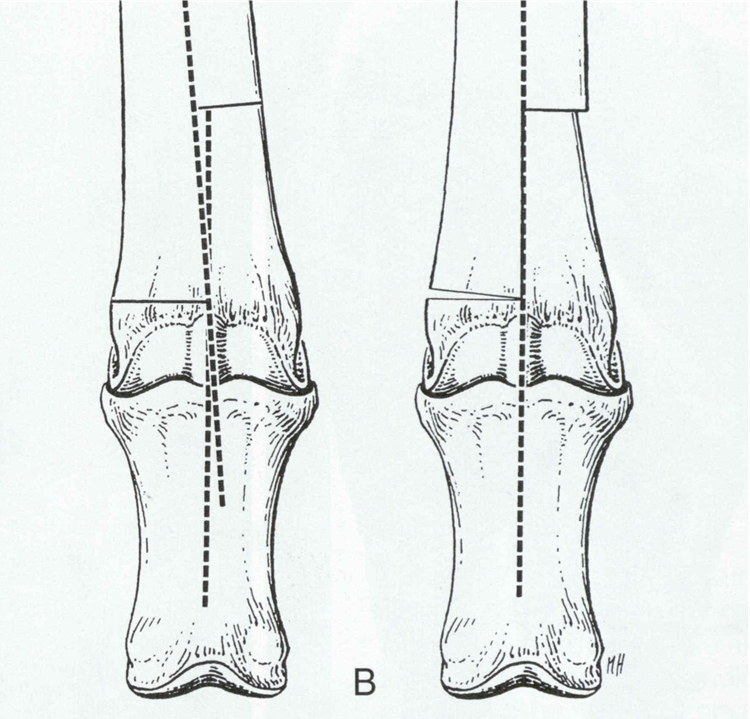
step ostectomy saggital
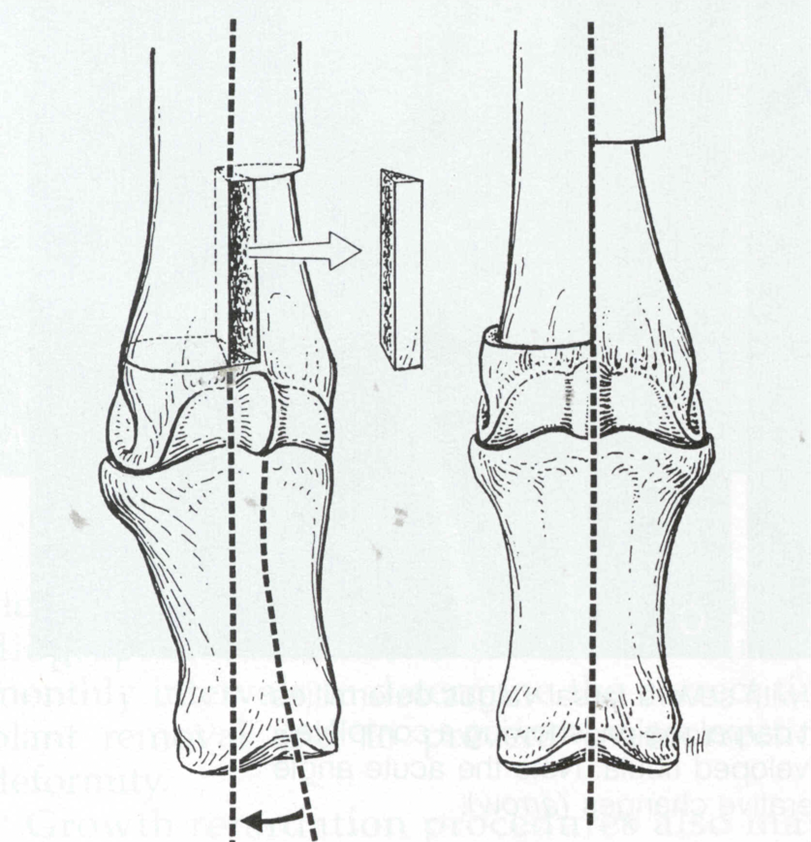
step ostectomy rotational
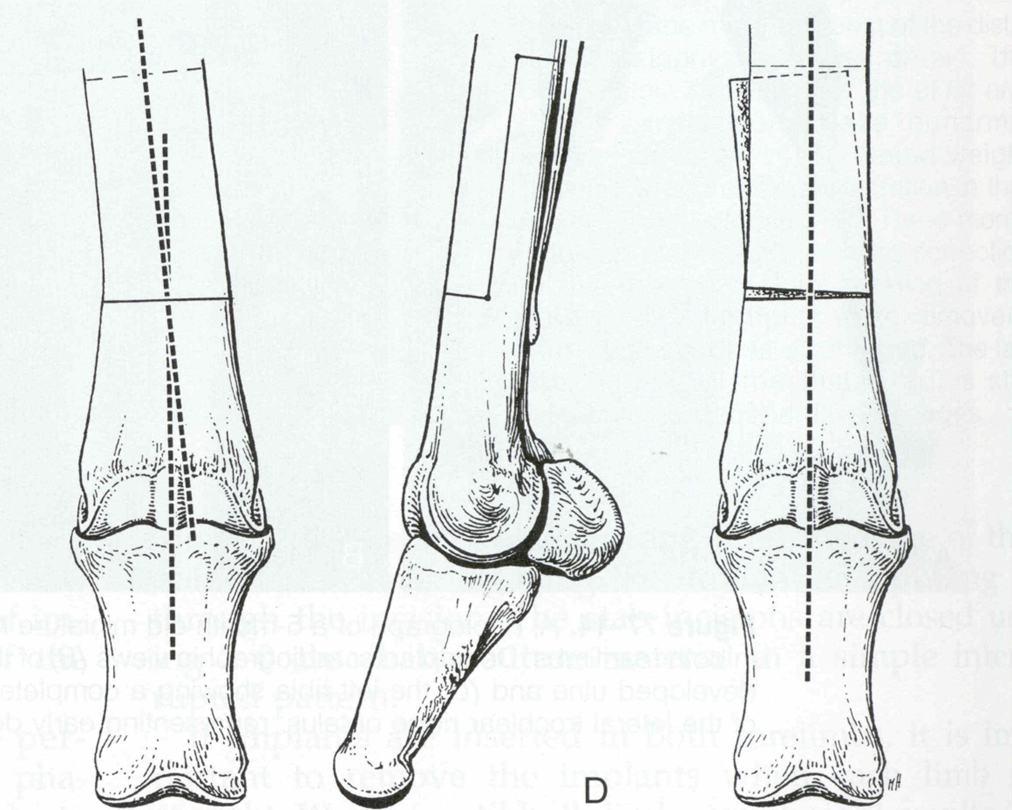
step ostectomy frontal
prognosis for angular limb deformities
periosteal transection = limb straightening achieved in 60%
transphyseal bridge = 80% of carpal and 27% of fetlock successful
trasal valgus= 52%
incomplete ossification >30%
early recognition is key
flexural deformity
deviation of a limb in the sagittal plane
persistent hyperflexion or hyperextention of a joint
classified according to joint involved and age of onset
most often observed in forelimbs
usually bilateral unless pain associated
conservative management flexural deformity of the DIP joint
restrict protein and caloric intake, balanced trace minerals
increased exercise
corrective trimming reducing heel length
extended toe shoe or acrylic
etiology flexural deformity of DIP joint
contracture of DDF tendon, club foot
multifactorial
rapidly growing foals 2-8mo
rarely present at birth
high plane of nutrition
functional shortening of DDF muscle tendon unit
flexural deformity of DIP inferior check ligament desmotomy
all stage II or stage I with no response to conservative tx
lengthening of DDF musculo-tendionous unit
infections, scarring, recurrence
87% of horses treated athletically sound
flexureal deformity of DIP deep digital flexor tenotomy
severe stage II deformities
cases unnresponsive to ICL desmotomy
salvage procedure, corrective shoeing to prevent DIP subluxation
flexural deformity DIP prognosis
ICL desmotomy= good for stage I, guarded to fair for stage II, minimal scarring if <1yr
DDF tenotomy- poor for athletic soundness
congenital flexural deformity of metacarpophalangeal joint
contracture of SDF tendon, flexural deformity of the fetlock
unequal lengthening of SDF muscle tendon unit and bones of limb
DDF tendon and suspensory appear to be involved in some cases
flexural deformity of metacarpophalangeal joint- congenital- conservative management
exercise or physical therapy
light weight bandages
splits or casts
oxytestracycline- binds Ca which is used by myofibroblasts involved in contraction
flexural deformity of the metacarpophalangeal- congenital- surgical management
cases unresponsive to conservative therapy
SCL desmotomy
ICL desmotomy
transection of SDF tendon
transection of suspensory ligament
SCL desmotomy post op care and px
reduced/controlled activity until deformity corrected
bandages for 12-15 days
cast or splint for 10-14 days
good px if limb can be straightened manually, better than carpus
flexural deformity of metacarpophalangeal- acquired- etiology
multifactorial
high energy/protein diet
quarter horses
excessive or lack of exercise
pain = physitis in distal radius, OCD in shoulder or fetlock, fractures ect
flexural deformity of metacarpophalangeal- acquired- diagnosis
horses between 8 and 18mo
rapidly growing horses
mostly forelimbs, hindlimbs can also be affected
palpation of involved structures
rads showing changes in fetlock and distal interphalangeal joints
flexural deformity of metacarpophalangeal- acquired- conservative management
corrective shoeing with elevated heel and toe extension- loads SDF and suspensory but little value if ddf also involved
reduce protein and energy intake, balance trace minerals
NSAIDs
bandages, splints, casts- heel to proximal cannon bone or higher
flexural deformity of metacarpophalangeal- acquired- surgical management
moderate to severe cases unresponsive to conservative
SCL desmotomy if SDF only affected structure
SCL and ICL desmotomy of SDF and DDf affected
salvage= SDF tenotomy, suspensory desmotomy, DDF tenotomy
flexural deformity of metacarpophalangeal- acquired- complications and prognosis
pressure sores, recurrence, failure to respond
px good if fetlock angle can be corrected manually
px poor if suspensory involved or joint capsule contracted
flexural deformity of the carpus- etiology
usually bilateral, almost always congenital
uterine malpositioning
teratogenic factors first 3 months= toxic weeds, viral infections
palmar ligament, palmar carpal joint capsule restricting carpal extension
flexural deformity of the carpus-treatment
exercise
physical therapy
casts, bandaging and splinting (PCV splints, sleeve casts if manually correctable, monitor for slipping, rotation, pressure sores)
oxytetracycline
surgery to release palmar carpal capsule in severe cases unresponsive to splinting
ruptured common digital extensor tendon
common congenital disorder, not truly a flexural deformity
swelling in the tendon sheath at dorsolateral aspect of carpus
rupture of CDE often secondary to carpal flexural deformity
bowlegged and “over the knees” stance
flexor tendon laxity etiology
unknown
known factors include systemic disease, lack of exercise, pre/dysmaturity, secondary to bandaging and casting
mainly hind limbs but may involve all 4
foot rocks back and heel on heel, toe off ground
abrasions palmar/plantar on pastern and fetlock
flexor tendon laxity- treatment
corrective hoof trimming
heel extensions
forced controlled exercise
light bandaging- excessive will make worse!!
osteochondrosis
failure of endochondral ossificaton causing thickening or retention of growth plates
diagnosis when defective cartilage growth in the articular-epiphyseal complex is found
sites of osteochondrosis
stifle, tarsus, fetlock, shoulder
physitis
cervical vertebral malformation aka wobblers
osteochondrosis prognosis varies due to ?
location of lesion
duration of lesion
severity of lesion
concurrent DJD
owner compliance
etiologies of stifle osteochondrosis
OCD in lateral trochlear ridge, medial trochlear ridge, lateral facet of patella
cysts in medical femoral condyle, patella
treatment stifle osteochondrosis
arthroscopic debridement
60% athletic function
treatment stifle subchondral bone cyst
arthroscopic guided injection of steroids
packing with bone cement and stem cells
arthroscopic currettage
locations for tarsal OCD
distal intermediate ridge of the tibia (DIRT)
lateral trochlear ridge of the talus
medial malleous of tibia
medial trocheal ridge of the talus
treatment of lateral trochlear ridge OCD
arthroscopic debridement
good prognosis
fetlock osteochondrosis
OCD of dorsal distal MC3- stagittal ridge
P1 osteochondral fragments- dorsal, palmar/plantar
types of sagittal ridge fetlock osteochondrosis
1= defect or flattening, can attempt conservative treatment
2= defect or flattening with fragmentation
3= defect or flattening with or without fragmentation, loose bodies
P1 fragments fetlock osteochondrosis
dorsal are not usually OCD but traumatic
Palmar/plantar may be OCD lesions
axial fragments can cause lameness and need to be removed
abaxial fragments are not always signfificant
treatment fetlock osteochondrosis
arthroscopic debridement for proximal P1 chips, MC3 sagittal ridge lesions, palmar/plantar P1 fragmentgs
\
treatment fetlock sobchondral bone cysts
found i P1, MC3
curettage ± stem cells, bone graft, injection of steroids
causes of shoulder osteochondrosis
glenoid or humeral head subchondral bone cysts- treat if lame, depends on location
OCD of humeral head or glenoid- guarded to poor px
osteochondrosis post surgical care
stall rest and hand walking → increased hand walking → round pen turn out → small paddoc
swimming
60 days to 6 months off before resuming work
NSAIDs
intraarticular steroids
hyaluronic acid
PSGAGS
oral supplemets