Chapter 14 Rivers & Streams
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
stream
a ribbon of water that flows in a channel
trough
a trough dug into the ground surface by flowing water
headwaters
the beginning point of a stream
mouth
The outlet of a stream where it discharges into another stream, a lake, or a sea.
flood
an event during which the volume of water in a stream becomes so great that it covers areas outside the stream’s normal channels
sheetwash
a film of water less than a few mm thick that covers the ground surface during heavy rains
runoff
when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate the soil
downcutting
extra water flow erodes and deepens the river channel
headward erosion
the process by which a stream channel lengthens up its slope as the flow of water increases
tributaries
a smaller stream that flows into a larger stream
drainage network
an array of interconnecting streams that together drain an area
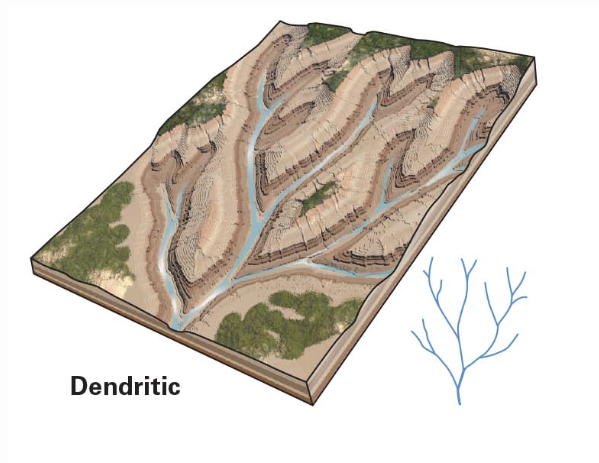
dendritic
fairly uniform substrate
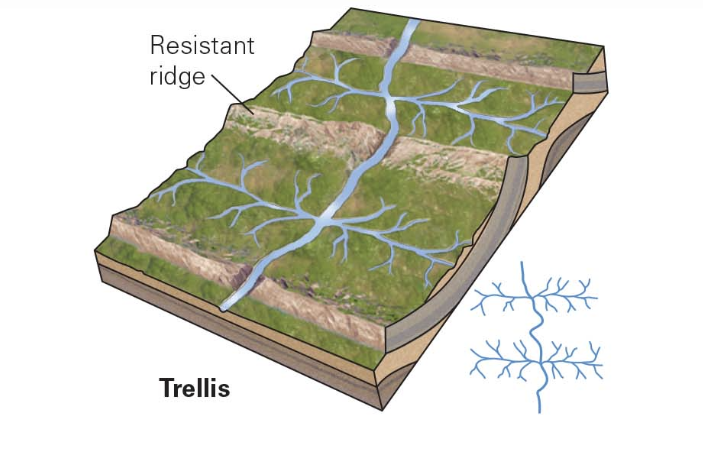
trellis
landscape of parallel ridges and valleys
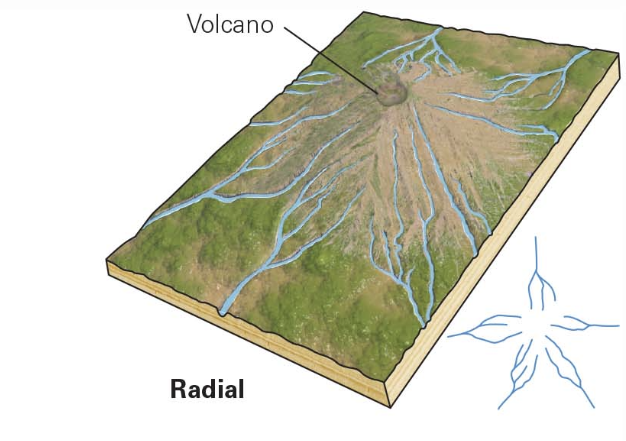
radical
cone-shaped mountain
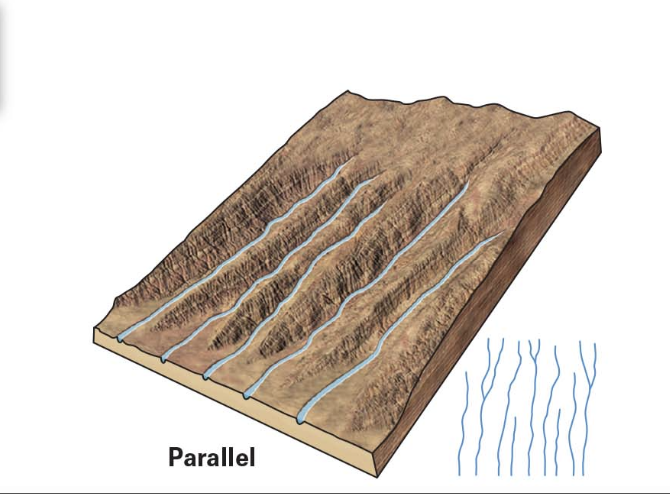
parallel
steep uniform slope
rectangular
rectangular grid of fractures (joints), breaking up the ground

watershed
the region that collects water that feeds into a given drainage network
drainage divide
a ridge that separates one watershed from another
permanent streams
stream that flows year-round
Permanent streams exist bc
lies below the water table or because more water is supplied from upstream than can infiltrate the ground
ephemeral streams
flowing water for only part of the year bc stream bed exists below water table or meltwater exceeds the rate at which it infiltrates the ground
uplift
the upward movement of earth’s surface
subsidence
the sinking movement of earth’s surface
relief
the difference in elevation between adjacent high and low regions on the land surface
downslope movement
The tumbling or sliding of rock and sediment from higher elevations to lower ones.
discharge
volume of water in a conduit
conduit
channel of water
hydrologic water cycle
Evaporation > Transpiration > Sublimation > Condensation > Transportation > Precipitation > Deposition > Infiltration > Runoff > Groundwater flow
evaporation
Liquid water heats up and turns into water vapor
transpiration
Plants release water vapor from their leaves
sublimation
Solid ice changes directly into water vapor
condensation
Water vapor cools and turns into liquid droplets
transportation
Wind moves water vapor or clouds
precipitation
Water falls to Earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
deposition
Water vapor turns directly into solid ice
infilitration
Water soaks down into the soil
runoff
Water flows over land into streams, rivers, and lakes
groundwater flow
Water moves underground through rock and soil
relative humidity
(amount of water vapor in air)/
(amount of water vapor air can hold)
rain shadow
area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region
vadose zone
unsaturated zone above the water table, containing both air and water
hydraulic gradient
difference in the hydraulic head over a distance
hydraulic head
level of water in a well, measuring energy at a point
darcy’s law
flow of a fluid through a porous medium