Genetics Exam 3-Gene Control
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Structural Genes
encoding proteins
Regulatory Genes
encoding products that interact with other sequences and affect the transcription and translation of these sequences
Regulatory elements
DNA sequences that are not transcribed but play a role in regulating other nucleotide sequences
How do bacteria respond to environmental changes in regards to genes
turn them on and off
In eukaryotic cells, gene regulation brings about
cell differentiation
Constitutive expression
continuously expressed under normal cellular conditions
Positive control
stimulate gene expression
Negative control
inhibit gene expression
Domains
~60–90 amino acids, responsible for binding to DNA, forming hydrogen bonds with DNA
Motif
within the binding domain, a simple structure that fits into the major groove of the DNA
Distinctive types of DNA-binding proteins based on the
motif
Major types of motifs
Helix-turn-helix
Zinc finger
Steroid receptor
Leucine zipper
Helix-loop-helix
Homeodomain
Helix-turn-helix Location
Bacterial regulatory proteins; related motifs in eukaryotic proteins
Helix-turn-helix Characteristic
Two alpha helices
Helix-turn-helix Binding Site in DNA
Major groove
Zinc finger Location
Eukaryotic regulatory and other proteins
Zinc finger Characteristics
Loop of amino acids with zinc at base
Zinc Finger Binding Site in DNA
Major groove
Leucine zipper location
Eukaryotic transcription factors
Leucine zipper Characteristics
Helix of leucine and a basic arm; two leucines interdigitate
Leucine zipper Binding Site in DNA
Two adjacent major grooves
Operon
promoter + operator + structural genes
Regulatory gene
DNA sequence–encoding products that affect the operon function but are not part of the operon
Inducible Operons
Transcription is usually off and needs to be turned on
Repressible operons
Transcription is normally on and needs to be turned off
Negative inducible operons
The control at the operator site is negative. Molecule binding is to the operator, inhibiting transcription. Such operons are usually off and need to be turned on
Inducer
small molecule that turns on the transcription
Negative repressible operons
The control at the operator site is negative. But such transcription is usually on and needs to be turned off
Corepressor
small molecule that binds to the repressor and makes it capable of binding to the operator to turn off transcription
In positive transcriptional control, the regulatory protein involved is an
activator
How does positive control work
binds to DNA and stimulates transcription
The lac operon is a ___ operon
negative inducible
What is the inducer of the lac operon
allolactose
lacl
repressor encoding gene
lacP
operon promoter
lacO
operon operator
Structural genes lac operon
lacZ
LacY
lacA
LacZ
encoding ß-galactosidases
LacY
encoding permease
LacA
encoding transacetylase
Does repression of the lac operon completely stop transcription?
no
Catabolite Repression
using glucose when available and repressing the metabolite of other sugars
Is catabolite repression a positive or negative control
positive
cAMP
adenosine-3′, 5′-cyclic monophosphate
The concentration of cAMP is inversely proportional to
the level of available glucose
Low glucose means cAMP levels are high, cAMP binds to CAP, the CAP-cAMP complex binds to DNA, increasing the efficiency of polymerase binding, and results are
high rates of transcription and translation of the structural genes
High glucose means low levels of cAMP, cAMP is less likely to bind to CAP, RNA polymerase cannot bind to DNA as efficiently so
transcription rate is low
The trp operon is a ____ operon
negative repressible operon
What are the five structural genes of the trp operon
trpE
trpD
trpC
trpB
trpA
What do the structural genes function to do
these five enzymes convert chorismate to tryptophan
When tryptophan is low: the trp repressor is normally inactive, so it does not bind to the operator so
transcription does not take place
When tryptophan is high: tryptophan binds to the repressor, making it active
the trp repressor binds to the operator and shuts transcription off
Attenuation
affects the continuation of transcription, not its initiation
This action terminates the transcription before it reaches the structural genes
Attenuator
a specific DNA sequence within a bacterial operon that causes premature termination of transcription
Antiterminator
genetic process that allows RNA polymerase to bypass termination signals and continue transcribing RNA
What causes the change between humans and apes despite our very similar genomes
a small number of regulatory sequences
For eukaryotic cells, each gene has its own ___ and must be transcribed separately
promoter
For eu, DNA must unwind from the histone before
transcription
How are transcription and translation separated in eukaryotes
through time and space
Changes in chromatin structure affect the
expression of genes
DNase I hypersensitive sites
more open chromatin configuration site, upstream of the transcription start site
Histone modification
Addition of methyl groups to the histone protein tails
Addition of acetyl groups to histone proteins
Chromatin remodeling complexes reposition the ___ allowing transcription factors and RNA polymerase to bind to promoters and initiate transcription
nucleosomes
The ___ of histone proteins alters ____
and permits some transcription factors to bind to DNA
acetylation; chromatin structure
Flowering locus C (FLC) gene
encodes a regulatory protein that represses the activity of other genes that affect flowering
Flowering locus D (FLD) gene
encodes a deacetylase enzyme, which removes acetyl groups from histone proteins in the chromatin surrounding FLC
Which species if the FLD and FLC gene found in
Arabidopsis
Chromatin remodeling complexes
bind directly to DNA sites and reposition nucleosomes
Chromatin immunoprecipitat ion (ChIP) can be used to identify
DNA-binding sites of a specific protein and locations of modified histone protein
Transcription in eukaryotes is regulated by
transcription factors
Transcription factors can stimulate and stabilize
basal transcription apparatus at core promoter
Mediator
interact with transcription factors and RNA Polymerase
Transcription factors allow for the regulation of galactose metabolism through
GAL4
Where does the GAL4 bind to
UASG site
What does the GAL4 do
controls transcription of genes in galactose metabolism
Enhancer
DNA sequence stimulating transcription a distance away from promoter
Silencer
DNA sequence with an inhibitory effect on the transcription of distant genes
silencers are position and orientation independent, and they contain binding sites for transcription factors that decrease transcription.
true
Insulator
DNA sequence that blocks or insulates the effect of enhancers
Insulator function
cause loops of chromatin that form interacting regions of genes and regulatory elements
Insulators and their binding proteins
may help create “neighborhoods” of regulatory elements and genes that physically interact but insulated from regulatory elements in other neighborhoods
An insulator blocks the action of an ____ on a promoter when the insulator lies between the enhancer and the promoter
enhancer
Alternative splicing in drosophila XX genotype
XX embryos and active Sxl gene produce a protein that causes pre-mRNA to be spliced at the downstream 3’ site
This produces tra protein
Tra and Tra-2 proteins direct female specific splicing of dsx pre-mRNA, producing a protein that makes a female
Alternative splicing in drosophila XY genotype
Sxl gene is not activated
tra pre-mRNA is spliced at upstream site, producing a nonfunctional protein
without tra, male specific splicing of dsx protein produces a male phenotype
Degradation of RNA
5’ cap removal
shortening of Poly-A tail
degradation of 5’ UTR, coding sequence, and 3’ UTR
Dicer and RISC
RNA-induced silencing complex
Dicer function
cleaves and processes double-stranded RNA
produce single-stranded siRNAs or miRNAs 21 to 25 nucleotides long
combine with proteins to form a RISC
The RNA component of RISC pairs with
complementary base sequences in specific mRNA molecules (often sequences in the 3’ UTR of the mRNA)
Small interfering RNAs base-pair perfectly with
mRNAs
microRNAs often form
less-than-perfect pairings
Mechanisms of gene regulation by RNA interference
RNA cleavage
Inhibition of translation
Transcriptional silencing
Silencer-independent degradation of mRNA
RNA cleavage
RISC containing an siRNA, pair with mRNA molecules and cleavage to the mRNA
Transcriptional silencing
altering chromatin structure
RNA silencing leads to the degradation of ___ or to the ___ of translation and transcription
mRNA; inhibition
The control of development by RNA interference
miRNA molecules are key factors in controlling development in animals, including humans and
plants
RNA crosstalk
Different RNA molecules that share binding sites for miRNAs may compete among themselves for
available miRNAs
The availability of ribosomes, charged tRNAs, and initiation and elongation factors may affect the rate of translation
true
Translation of some mRNAs is regulated by proteins that bind to the 5’ and 3’ untranslated regions of the mRNA
true
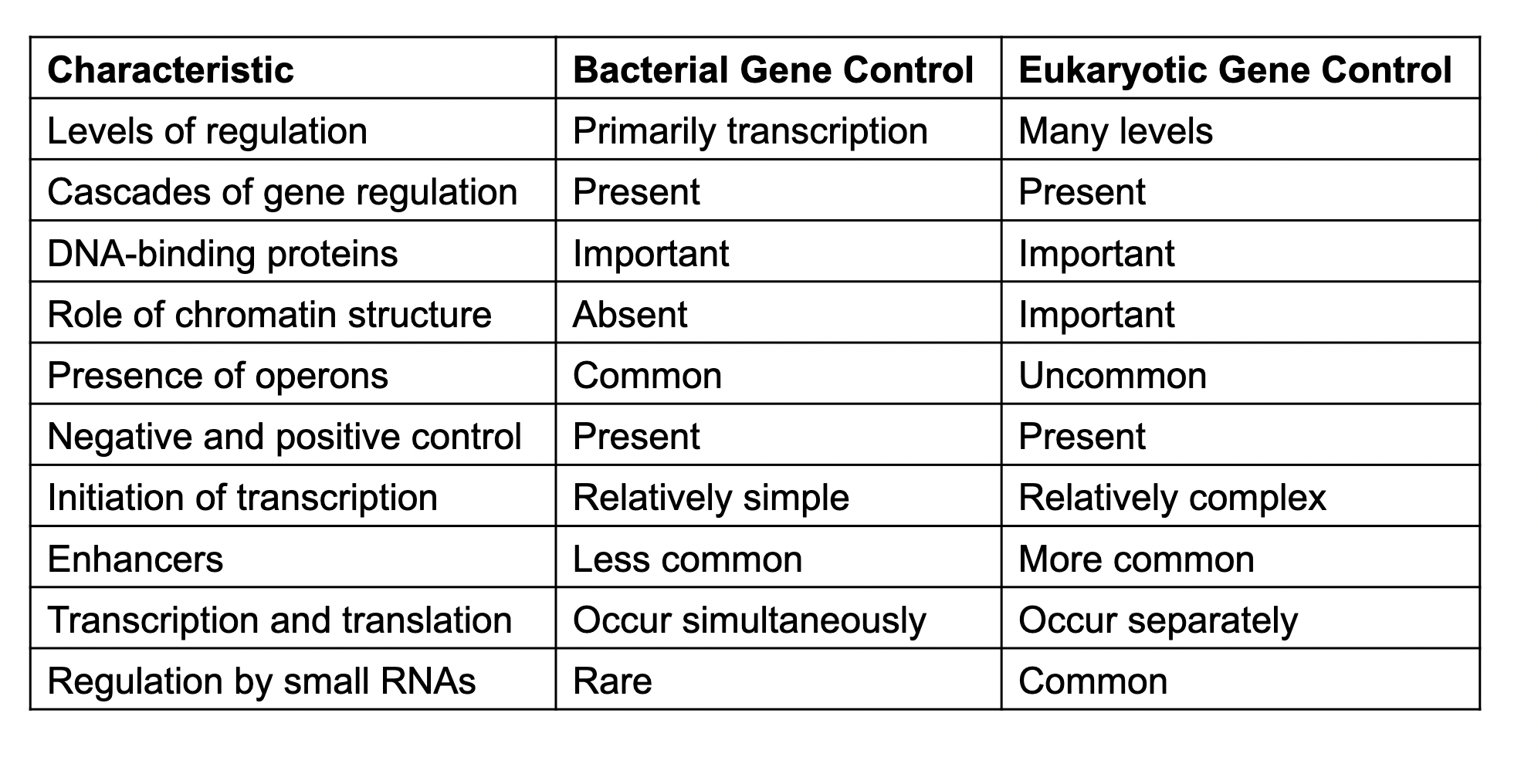
Bacterial and Eukaryotic gene control comparison
see chart