AP Pre-calculus S1 FINALS!!
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
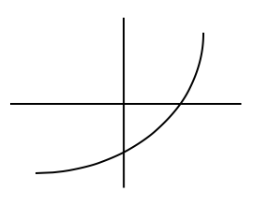
Graph of f
Graph of f is INCREASING ←→ Rate of change of f is POSITIVE
Graph of f is CONCAVE UP ←→ Rate of change of f is INCREASING
The graph of f is INCREASING at an INCREASING RATE
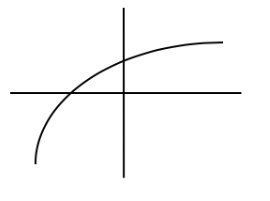
Graph of g
Graph of g is INCREASING ←→ Rate of change of g is POSITIVE
Graph of g is CONCAVE DOWN ←→ Rate of change of g is DECREASING
The graph of g is INCREASING at an DECREASING RATE
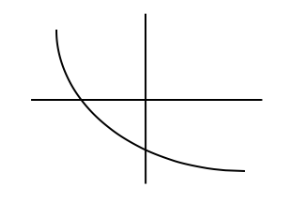
Graph of h
Graph of h is DECREASING ←→ Rate of change of h is NEGATIVE
Graph of h is CONCAVE UP ←→ Rate of change of h is INCREASING
The graph of h is DECREASING at an INCREASING RATE
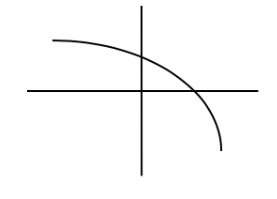
Graph of k
Graph of k is DECREASING ←→ Rate of change of k is NEGATIVE
Graph of k is CONCAVE DOWN ←→ Rate of change of k is DECREASING
The graph of k is DECREASING at an DECREASING RATE
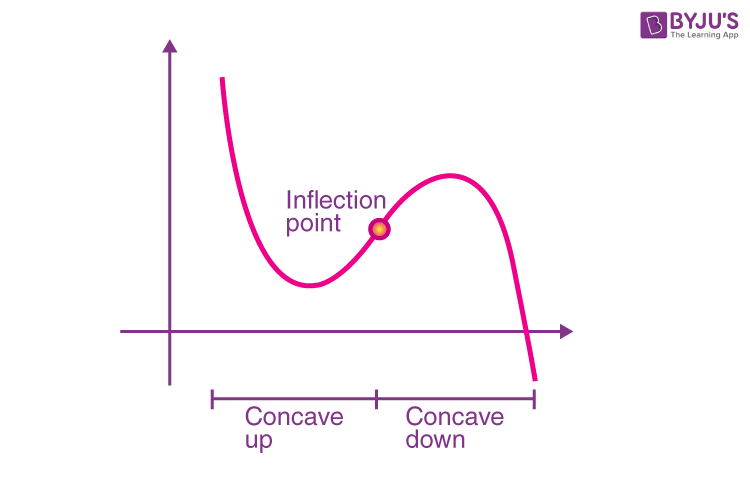
Points of inflection
Points where graph of f changes from concave up to concave down (or vice versa)
Average rate of change definition
slope between two points
The rate of change of f definition
slope of the graph at a single point
Average rate of change of a function over the interval [a,b] (a<x<b) is given by
AROC = f(b) - f(a) / (b-a)
Phrase to start a function explanation
“Over equal-length input-value intervals”
FUNCTIONS : if the differences in outputs are increasing, the function is ____
concave up
FUNCTIONS : if the differences in outputs are decreasing, the function is ____
concave down
FUNCTIONS : For a polynomial of the nth degree, the nth differences in output will be
constant
(quadratic function: 2nd differences are constant)
Complex Zeros
solutions (or roots) of polynomial equations that are complex numbers
Always comes in pairs!!!
If x=-2+4i is a zero, then so is x=-2-4i
Multiplicity
If a factor is repeated n times, it has a multiplicity of If
If a zero has an even multiplicity, the graph will bounce off the x-axis at that zero
The end behavior of a polynomial function is determined by
the leading term (highest degree)
What end behavior do you determine first?
Right and then left
Left end behavior
As x values decrease without bound, the y values of f(x)…
Even degree - goes in same direction as right
Odd degree- goes in opposite direction as right
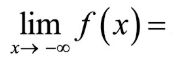
Right end behavior
As x values increase without bound, the y values of f(x)…
Leading term positive - y goes to infinity
Leading term negative - y goes to negative infinity
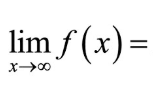
Even functions
Graphs have symmetry over y-axis
f(-x) = f(x)
Odd functions
Graphs have symmetry over the origin
f(-x) = -f(x)
Solving Polynomial Inequalities: -2(x+3)(x-1)²(x-4)<0
Put all terms on one side and factor
Create sign chart with all zeros marked
Check one value from each side of the zeros (far right interval usually easiest to check) for + or -
Each successive interval on the sign chart will alternate signs unless the zero has an even multiplicity
Zeros at = -3,1,4
Solution = (-inf, -2) u (4,inf)
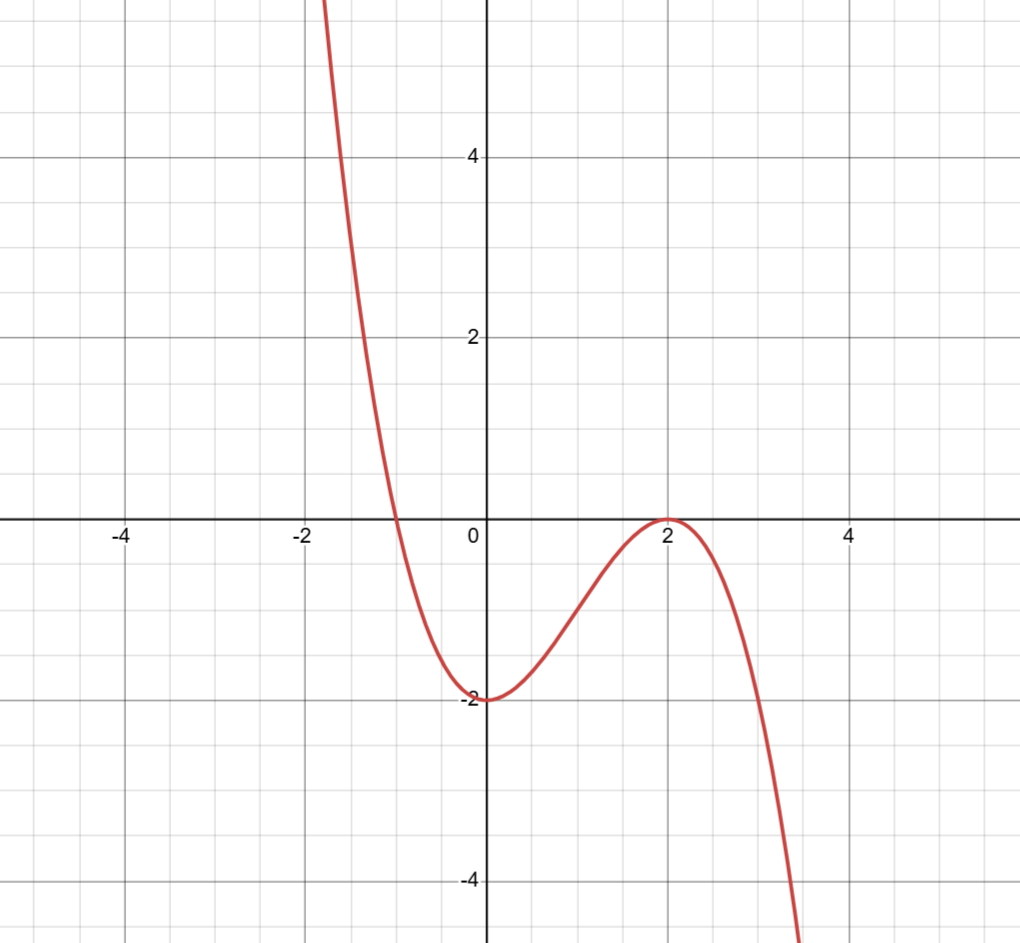
f(x) = -0.5(x+1)(x-2)²
Explain the properties of the graph and function
Zeros at x=-1 and x=2
Bounce at x=2 because (x-2)² has multiplicity of 2 which is even
Leading term = -0.5x³
Negative leading term → right side goes down
Odd degree → left opposite of right, left goes up
Left End Behavior = As x decreases without bound, the graph of f increases without bound
Right End Behavior = As x increases without bound, the graph of f decreases without bound
f\left(x\right)=\frac{x^4+x^3+5}{-2x^3-4x+1}
Find properties
N > D (Top Heavy)
No horizontal asymptotes
N = D+1 → Slant asymptote
End behavior → slanting line
y=\frac{x^4}{-2x^3}\to y=-\frac12x ← solve for slant/oblique asymptote
Left: \lim_{x\to-\infty}f\left(x\right)=\infty
Right : \lim_{x\to\infty}f\left(x\right)=-\infty
g\left(x\right)=\frac{-2x^3+3x+4}{5x^3-x+2}
Find properties
N=D (Same degree)
Horizontal asymptote
HA : y=\frac{-2x^3}{5x^3}\to y=-\frac25
End Behavior - Use horizonal asymptote
Left : \lim_{x\to-\infty}g\left(x\right)=-\frac25
“As inputs decrease without bound, the outputs become arbitarilty close to -2/5”
Right : \lim_{x\to\infty}g\left(x\right)=-\frac25
“As inputs increase without bound, the outputs become arbitrarily close to -2/5”
h\left(x\right)=\frac{2x^2+x-3}{x^4-x+2}
Find properties
N<D (Bottom Heavy)
Horizontal asymptote
HA : y=0
End Behavior - Use horizontal asymptote
Left : \lim_{x\to-\infty}h\left(x\right)=0
Right : \lim_{x\to\infty}h\left(x\right)=0
Rational Functions : Zeros
Numerator equals 0 AND denominator NOT equal 0
Rational Functions : Holes
Denominator equals 0 AND cancels out with the numerator (numerator has equal or larger multiplicity)
Rational Functions : Vertical Asymptotes
Denominator equals 0 AND does NOT cancel out with numerator (denominator has larger multiplicity)
r\left(x\right)=\frac{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+3\right)^2\left(x-1\right)\left(x-4\right)^4}{\left(x+3\right)^2\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x-4\right)^3}
Find zeroes, holes, and vertical asymptotes
Zero : x=-5
Holes : x=-3 + x=4
Vertical asymptotes : x=1
Factors in the denominator will never be a zero of the function.
Factors in the denominator always are a location of a hole or vertical asymptote
Limit Notation + In words (Verbally)
Left End Behavior
\lim_{x\to-\infty}f\left(x\right)=
The end behavior of f as x decreases without bound
Right End Behavior
\lim_{x\to\infty}f\left(x\right)=
The end behavior of f as x increases without bound
Arithmetic Sequence
Linear Functions
Sequence : a_{n}=a_{k}+d\left(n-k\right)
Geometric Sequences
Exponential Functions
Sequence : g_{n}=g_{k}r^{\left(n-k\right)}
Exponent Properties
b^{m}b^{n}
\left(b^{m}\right)^{n}
b^{-n}
b^{\left(\frac{1}{k}\right)}
b^{\left(m+n\right)}
b^{\left(mn\right)}
\frac{1}{b^{n}}
\sqrt[k]{b}
Exponential Functions are always…
increasing or always decreasing, and their graphs are always concave up or always concave down
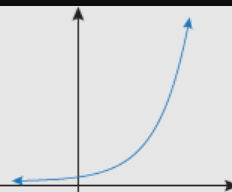
Exponential Function Property?
y=a\cdot b^{x}
a=1, b>1
Exponential Growth
Increasing at an increasing rate
\lim_{x\to\infty}ab^{x}=\infty
\lim_{x\to-\infty}ab^{x}=0
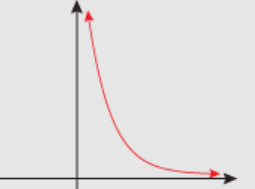
Exponential Function Property?
y=a\cdot b^{x}
a=1, 0<b<1
Exponential Decay
Decreasing at an increasing rate
\lim_{x\to\infty}ab^{x}=0
\lim_{x\to-\infty}ab^{x}=\infty
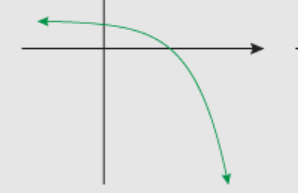
Exponential Function Property?
y=a\cdot b^{x}
a=-1, b>1
Exponential Growth
Decreasing at an decreasing rate
\lim_{x\to\infty}ab^{x}=-\infty
\lim_{x\to-\infty}ab^{x}=0
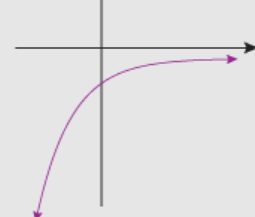
Exponential Function Property?
y=a\cdot b^{x}
a=-1, 0<b<1
Exponential Decay
Increasing at an increasing rate
\lim_{x\to\infty}ab^{x}=0
\lim_{x\to-\infty}ab^{x}=-\infty
Exponential function with natural base e is
f\left(x\right)=e^{x}
Additive and Multiplicative Transformations
g\left(x\right)=a\cdot b^{\left(cx+h\right)}+k
Vertical dilation by a factor of a units. If a<0, the graph reflects over the x-axis
Horizontal dilation by a factor of c units. If c<0, the graph reflects over the y-axis
Horizontal translation of -h units
Vertical translation of k units
Exponential Function Manipulation
f\left(x\right)=2^{x+3}
g\left(x\right)=3^{x-2}
y=9^{2x}
k\left(x\right)=9\cdot4^{x} (turn 4 →16)
f\left(x\right)=8\cdot2^{x}
g\left(x\right)=\frac19\cdot3^{x}
y=81^{x}
k\left(x\right)=9\cdot16^{\frac{x}{2}}
Every horizontal translation of an exponential function
f\left(x\right)=b^{x+h} is equivalent to
a vertical dilation of the exponential function
f\left(x\right)=ab^{x} where a=b^h
If a quantity doubles every day (d), then
f\left(d\right)=2^{d} gives the quantity after d days. An equivalent form,
f\left(d\right)=\left(2^7\right)^{\frac{d}{7}} indicates the quantity increases by a factor of 2^7 every week.
Regression Model : Residual Formula
Actual Value — predicted value
If the residual plot has no pattern,
the model is appropriate
Use a linear model when
the data reveals a relatively constant rate of change
Use a quadratic model when
the rates of change are increasing/decreasing at a relatively constant rate
Data generally follows a u shaped pattern
Use an exponential model when
the output values are roughly proportional.
Each successive output is approximately the result of repeated multiplication
What do inverse functions do?
they will “undo” a function. If you plug x into a function and then plug the output into the inverse function, we should end up with x again
Two functions are inverses only if
f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)=x and g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=x
A continuous function will only have an inverse function if
it is strictly increasing or strictly decrasing
Log form of b^{a}=c
\log_{b}c=a
b>0, b does not equal 1
Common logarithm
Log base 10 = do not write the base
Log base e = write Ln instead
general form of logarithmic function
f\left(x\right)=a\log_{b}x
b>0, b does not equal 1, a does not equal 0
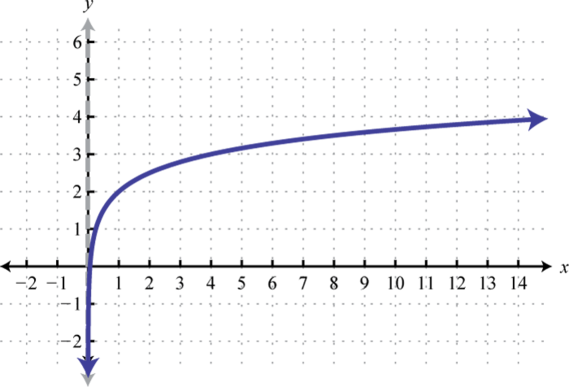
Logarithmic Property?
f\left(x\right)=a\log_{b}x
a>0, b>1
a does not equal 0, b does not equal 1, b>0
increasing at a decreasing rate
\lim_{x\to\infty}\log_{b}\left(ax\right)=\infty
\lim_{x\to0+}\log_{b}\left(ax\right)=-\infty
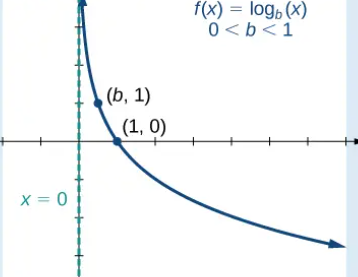
Logarithmic Property?
f\left(x\right)=a\log_{b}x
a>0, 0<b<1
a does not equal 0, b does not equal 1, b>0
decreasing at an increasing rate
\lim_{x\to\infty}\log_{b}\left(ax\right)=-\infty
\lim_{x\to0+}\log_{b}\left(ax\right)=\infty
Properties of Logarithms
\log_{b}\left(a\right)+\log_{b}\left(b\right)
n\log_{b}\left(x\right)
\frac{\log_{a}\left(x\right)}{\log_{a}\left(b\right)} where a>0 and a does not equal 1
\log_{b}\left(ab\right)
\log_{b}\left(x^{n}\right)
\log_{b}\left(x\right)