Chapter 3: Chemistry of Life; part 2: Lipids
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Are lipids hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic
What are lipids soluble in?
In non-polar solvents
note (water is polar)
What are the 5 types of Lipids?
Fats (triglycerides)
Phospholipids
Carotenoids
Steroids
Waxes
The main biological functions of lipids include:
- Energy storage
- Signaling (hormones)
- Structural components of cell membranes
What is the structure of lipids?
• Mainly hydrocarbon-containing regions
• few oxygens (polar or ionic groups)
What is the consistency of lipids?
greasy/oily
What is the most abundant type of lipid in living organisms?
Triacylglycerols (fats).
Why are fats considered an economical form of energy storage?
They yield more than twice the energy per gram compared to carbohydrates.
Which macromolecules can be enzymatically converted into fats?
Carbohydrates and proteins.
Where are fats stored in animals/humans? and where in plants?
In adipose (fat) tissue in animals and humans
In seeds and fruits in plants
What is the major form of energy storage in the human body?
Fat (triacylglycerols)
How many kilocalories are typically stored in the body as fat? As protein? As carbohydrate?
100,000 kcal for fats
25,000 kcal for protein
650 kcal for carbs
How long could fat reserves sustain a person during starvation?
Approximately 30 days
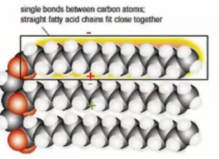
saturated vs unsaturated fatty acid
• Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds between the
individual carbon atoms of the fatty acid chain. Are solid at room temp.
•Unsaturated fatty acids have at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain. Are liquid at room temp.
Which bond connects fatty acids to glycerol to from fats?
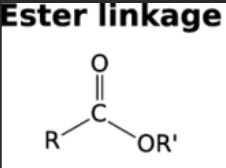
Why are saturated fats solid at room temperature ?

What is the function of Phospholipids?
Main cell membrane component (Phospholipid bilayer)
The structure of Phospholipid is
• glycerol
• 2 fatty acids
• phosphate group
Is the phospholipid bilayer amphipathic, and why?
Yes, Head: Hydrophilic and Tails: Hydrophobic
Why are carotenoids classified as lipids?
They are insoluble in water
oily consistency
What are Carotenoids? and what are they derived from?
Carotenoids are yellow, orange, and red plant pigments
Derived from isoprene units
2 roles of carotenoids are
plays a role in photosynthesis
(β-carotene) can be converted to vit A (visual pigment)
What Are Steroids?
Steroids are organic compounds with a structure of carbon atoms arranged in four rings. Steroids are synthesized from isoprene units.
Examples: Cholesterol, Bile salts (digestive juice
secreted by the liver), some hormones
What is the function of Cholesterol?
Maintains cell membrane fluidity and permeability (For humans and animals, cholesterol in not present in plants)