ADH II wk 2 pt 1 Cardiac Rhythms
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
SALI stands for in EKG
Septal
Anterior
Lateral
Inferior
Septal EKG for what
V1, V2
Anterior EKG for what
V3, V4
Lateral EKG for what
V5, V6, VL
Inferior EKG for what
II, III, AVF
P wave purpose
Atria depolarization (SA node)
QRS wave purpose
ventricular depolaraziton
T wave purpose
Ventricular repolarization
Small box time
0.04
9 steps for ECG analysis (H, R, P, P, Q, S, T, Q, I)
calculate heart rate
Determine if heart rhythm is regular
assess P waves
Measure PR interval
Measure duration of QRS complex
Assess ST segment
Observe for change in T wave
Measure length of QT interval
Interpret the rhythm
How to calculate test strip
count QRS (heartbeat) x 10 = bpm
How to measure is heart rhythm is regular or not
measure the distance of the R - R (peak) intervals
How to assess for P waves
determine if P way is present before each QRS
(see if the P’s are the same)
How to measure PR interval
Normal Duration
start of P wave to start of QRS complex
0.12-0.20
(see if PR intervals are consistent)
How to measure QRS complex
normal duration
how many boxes should normal height be
start of QRS complex to start if ST segment (start and end of hump)
0.06-0.10
less than 3 t
Where is ST segment located
After QRS right before T wave
How to assess ST segment
what does elevated or depressed isoelectric line indicate
see if it went back to isoelectric line
some myocardial or cardiac ischemia (ST elevation)
How to assess for changed in T wave
What are 2 irregular shapes for T wave
look for shape and height
inverted and peaked
Inverted T wave can indicate what
Electrolyte issues like hypokalemia
Cardiac Perfusion problems like ischemia, PE
Peaked T wave can indicate what
Electrolyte issues like hyperkalemia
How to measure QT interval
what should max time of QT interval be
start of QRS to end of T wave
0.45 seconds
can lead to lethal dysrhythmias
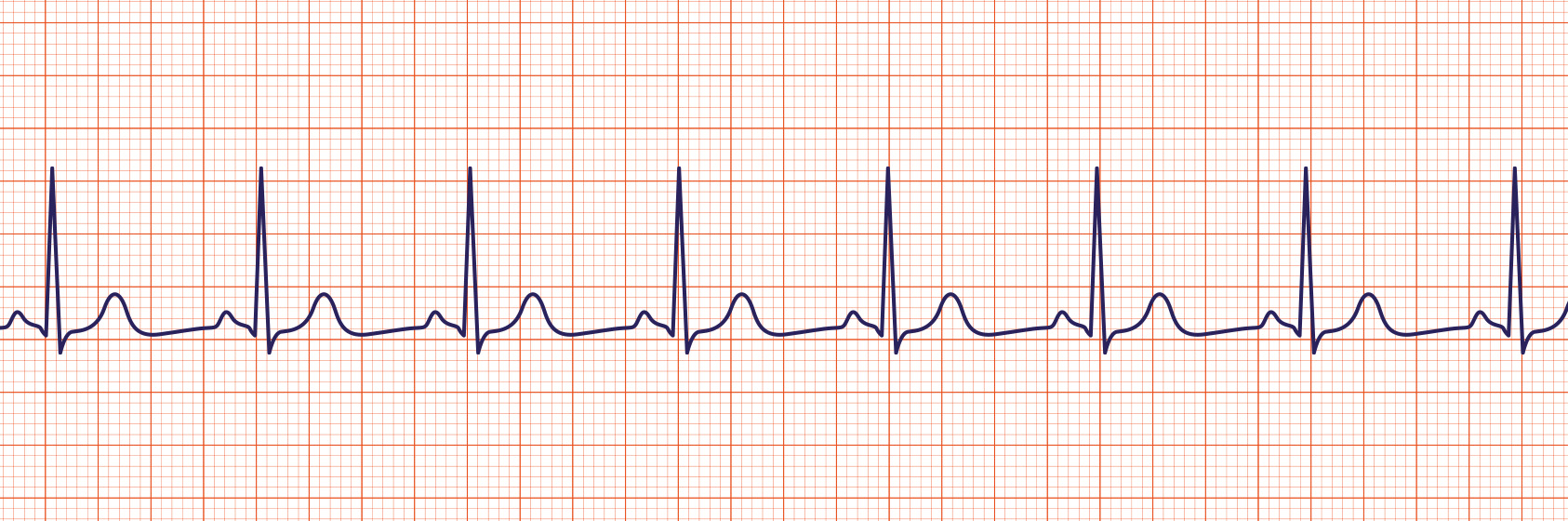
Sinus Rhythm
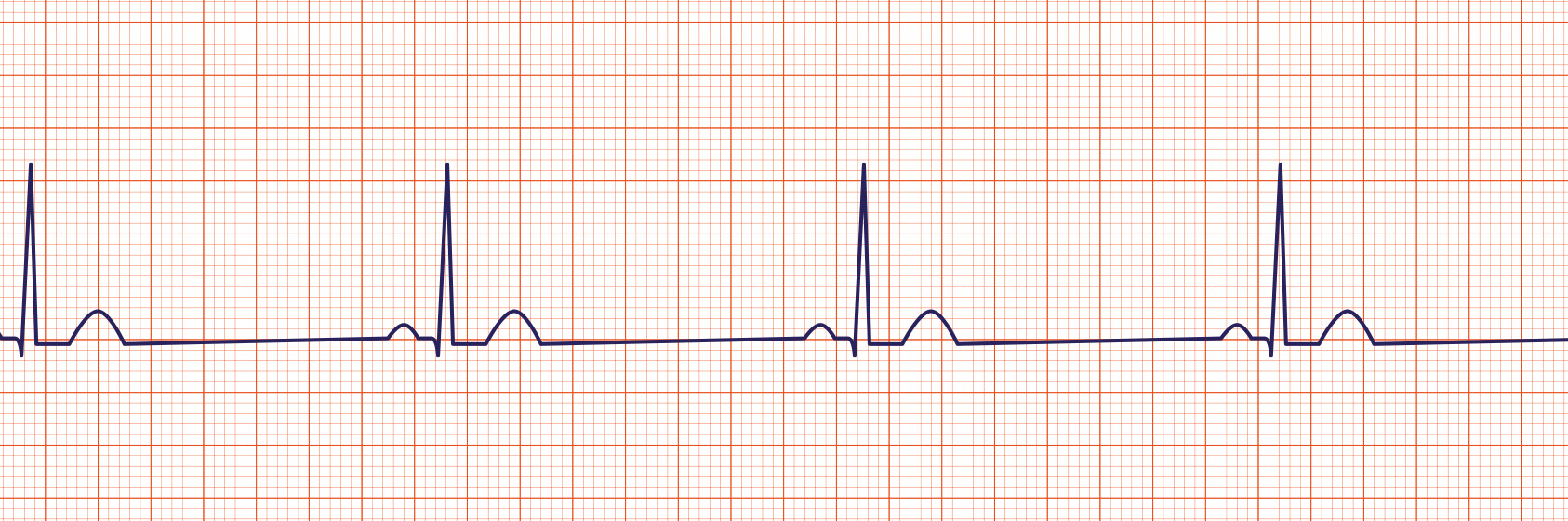
Sinus Brady
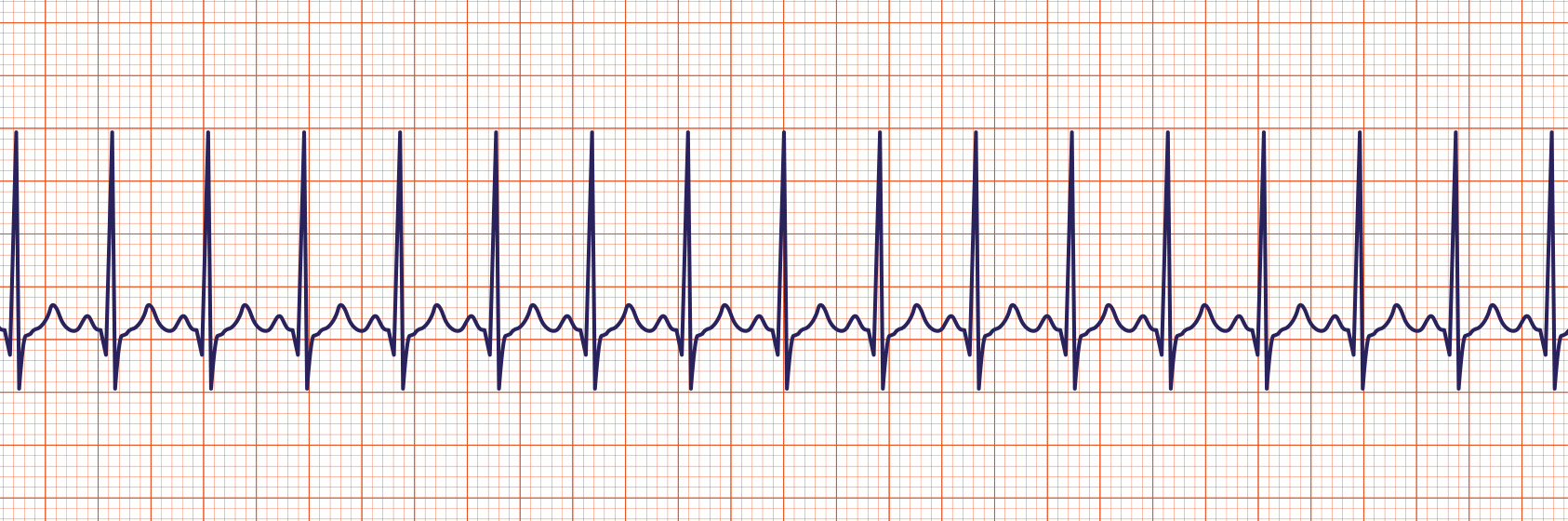
Sinus Tachy
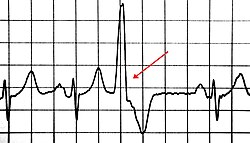
premature ventricular contraction PVC
(no p wave before it, can be "Benign" until has patterns)
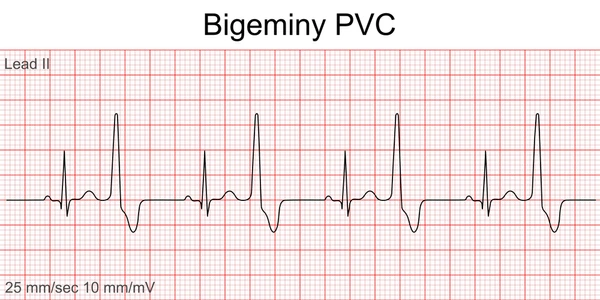
What is bigeminy
consistent irregular heart rhythm that hits every other complex (1 gap)
2nd in the biz bigeminy
What is Trigenimy
consistent irregular heart rhythm that hits every 3rd complex (2 gap)
3rd in the biz = trigenimy

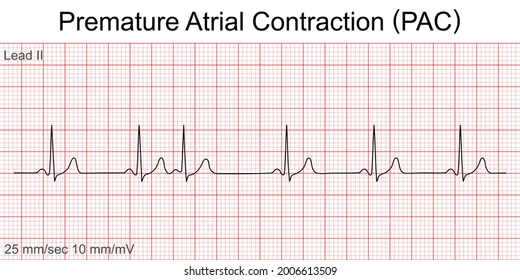
sinus rhythm with premature atrial contraction (PAC)
Benign can’t feel
How are PAC and PVC different
PVC dont derive from atrium (no atrial depolarization P wave, wide and bizzar)
PAC dont derive from ventricles

sinus rhythm w/ first degree atrial ventricular (AV block)
pt are asymp (wait and watch)
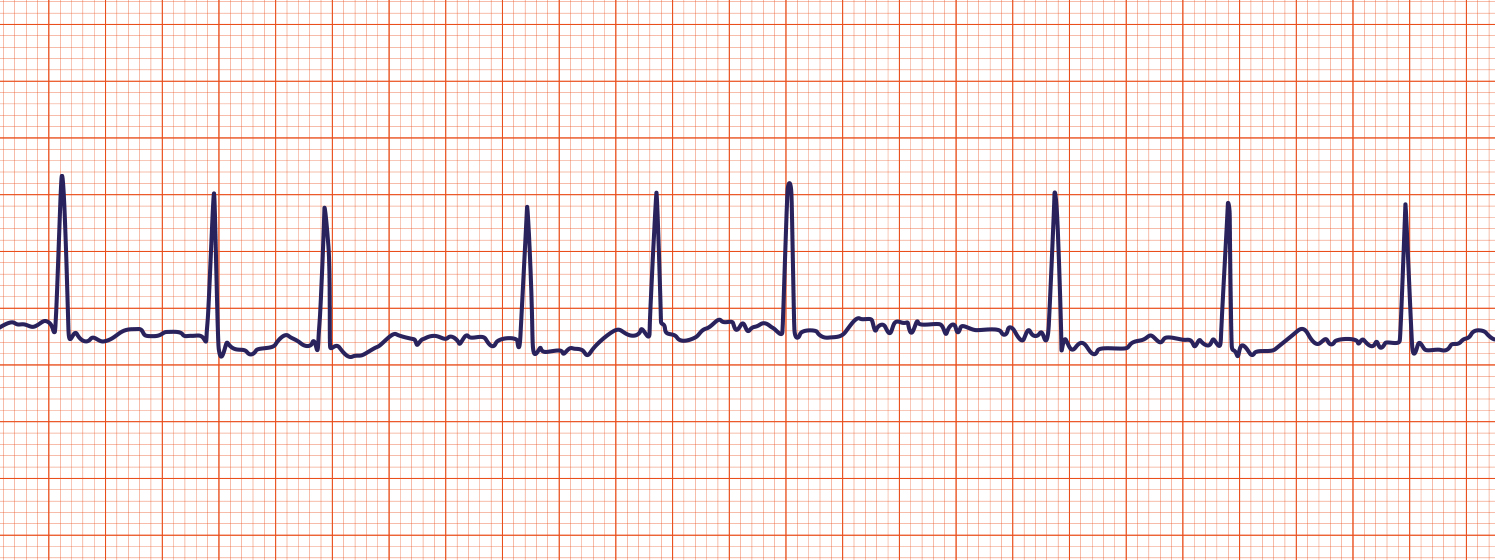
Atrial fibrillation (A- Fib)
Quiver in isoelectric line = p waves
if more than 100 bpm = a fib w/ rapid ventricular response
may need anticoaglate or anti platelet
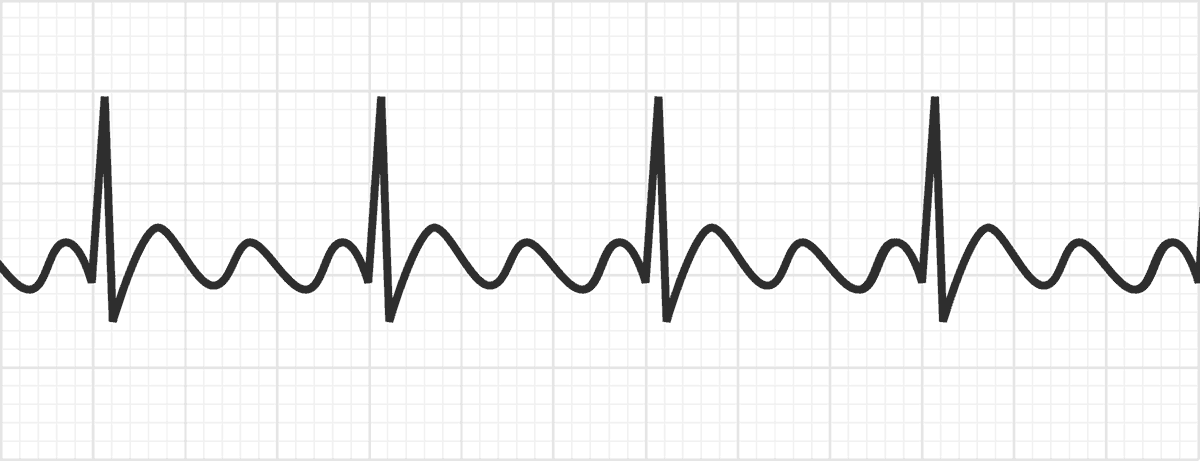
Atrial flutter
Saw tooth like P waves
Asymp (can lead to A fib)
Mostly regular
How to manage a fib and a flutter
Anti arrythmics Meds
Ca channel blockers
Beta Blockers
Synchronized cardioversion if less than 24 hours (shock w/ electrcity) when they are conscious
What can A fib lead to
blood statsis can lead to clothes
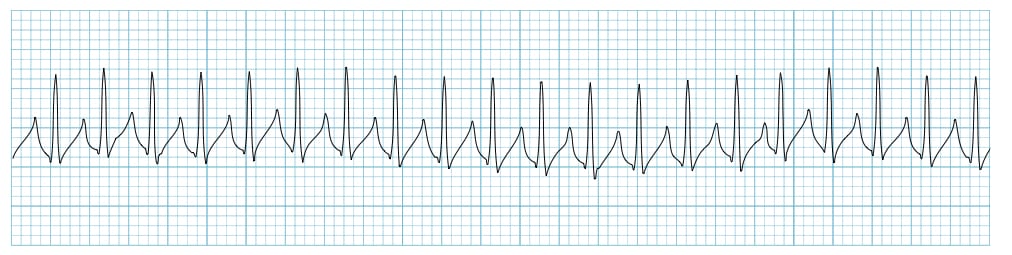
supra ventricular tachycardia (SVT)
no P wave
rate greater than 150
supra ventricular tachycardia (SVT) management least invase to mose
first see if stable or unstable
check vagal maneuver
Meds adenosine: temp stops heart has fast half life
Synchronized Cardioversion (electricity) when they are conscious

Ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach)
Emergency
V tach management if pulse is present
synchronized cardioversion
ventricular antiarrhythmics medications (amiodarone, lidocaine)
V tach management if pulse is not present
defibrillate
ACLS protocal (CPR, epi, amiodarone, lidocaine)
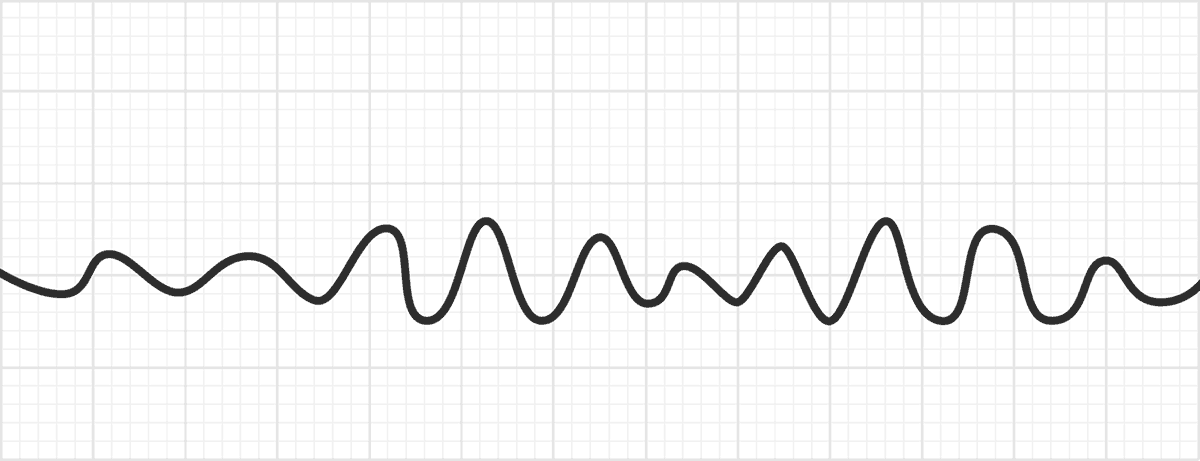
Ventricular Fibrillation (V Fib)
Ventricular Fibrillation (V Fib) management
(pt is most likley unconsciousness)
defibrillate
ACLS protocal (CPR, epi, amiodarone, lidocaine)
Pulseless electrical activity PEA
heart shows organized electrical signals on an ECG, but the heart muscle doesn't contract effectively to pump blood
Pulseless electrical activity PEA management
CPR and epi q 3-5 min
(not a stackable rhythm
Only shockable rhythm in a code
V tach
V Fib
Pulseless electrical activity PEA 5 H’s
Hypovolemia
Hpoxia
Hydrogen ion
Hypokalemia/ Hyperkaelmia
Hypothermia
Pulseless electrical activity PEA 5 T’s
Tension peumonthroax
Trauma
Tamponade
Thrombosis (pulomonary)
Thromobosis (coronary)
What will code rhythm turn into if we do nothing
asystole (flat line)
When your PR interval gets long and long and drops
now you have a winky block
Pr get longer and longer
(2nd degree AV [heart] block type 1)
![<p>now you have a winky block</p><p>Pr get longer and longer</p><p>(2nd degree AV [heart] block type 1)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bf2e84b2-7a68-4fcb-9bfa-5f39a4fc48a4.png)
How to determine the severity of any rhythm
if pt is symptomatic or not
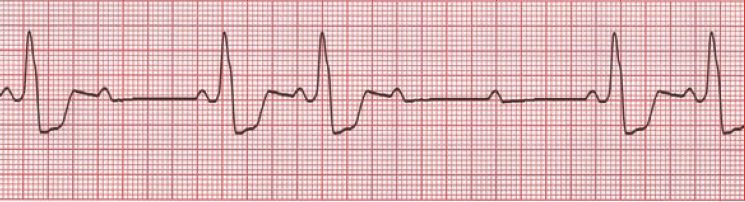
If some P’s dont get thorugh (no QRS)
then you have a mobitz 2
Pr are constant
(second degree heart block type 2)
How to manage block
identify underlying cause to prevent from becoming higher degree block
check if pt is symptom
If pt is bradycardic (low HR) and hypotensive (low BP) give meds
atropine
dopamine
pace (electricity)
if R and P disagree then you have a
3rd degree and you need electricity
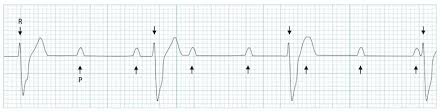
3rd degree heart block (complete heart block)
3rd degree heart block management
need a permeant pacemaker (electricity) to support