AP Econ Final
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
Which of the following is a defining characteristic of a market economy?
Responses
A
Private ownership of resources
B
Equitable distribution of income
C
Taxation of personal income
D
Reliance on public goods
E
Government-guided resource allocation
A
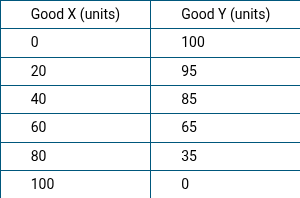
The table above shows the maximum possible output combinations of good X and good Y that Microland can produce by using all of its available resources and technology.
As the production of good X increases, what happens to the opportunity cost of producing good X?
Responses
A
It decreases, because the production of good Y decreases by greater amounts.
B
It decreases, because the production of good Y increases by smaller amounts.
C
It remains constant, because the production of good X increases by the same amount.
D
It increases, because the production of good Y decreases by greater amounts.
E
It increases, because the production of good Y increases by smaller amounts.
D
An increase in the supply of good X resulted in an increase in the price and quantity of good Y. It can be concluded that good Y is
Responses
A
an inferior good
B
a luxury good
C
a normal good
D
a substitute for good X
E
a complement for good X
E
Which of the following will shift the supply curve for apples to the right?
Responses
A
An increase in consumers’ income
B
An increase in the price of apples
C
An increase in the wages of apple pickers
D
A decrease in the rental price for apple harvesting equipment
E
A decrease in the demand for oranges, a substitute in consumption
D
Which of the following relationships among the price elasticity of demand, change in price, and change in total revenue is consistent?
Responses
A
Price Elasticity Of Demand | Change In Price | Change inTotal Revenue |
|---|---|---|
Elastic | Increase | Increase |
B
Price Elasticity Of Demand | Change In Price | Change in Total Revenue |
|---|---|---|
Elastic | Decrease | Decrease |
C
Price Elasticity of Demand | Change in Price | Change in Total Revenue |
|---|---|---|
Unit Elastic | Decrease | Decrease |
D
Price Elasticity of Demand | Change in Price | Change in Total Revenue |
|---|---|---|
Inelastic | Decrease | Increase |
E
Price Elasticityof Demand | Changein Price | Change inTotal Revenue |
|---|---|---|
Inelastic | Decrease | Decrease |
E
Which of the following best describes how a consumer maximizes total utility from the consumption of a bundle of goods and services?
Responses
A
By choosing the quantity of each good such that the quantity demanded of each good is equal to the quantity supplied
B
By choosing the quantity of each good such that the marginal utility from each good is equal to zero
C
By choosing the quantity of each good such that the price is equal to the marginal revenue
D
By choosing the level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost
E
By choosing the combination of goods such that the marginal utility per dollar spent on the last unit of each good is equal
E
The marginal benefit of consuming a good is
Responses
A
the change in average utility that results from consuming one more unit of the good
B
the same as the total benefit
C
equal to the marginal cost of the good
D
the change in total expenditures as a result of buying one more unit of the good
E
the maximum amount a consumer is willing to pay for one more unit of the good
E
The economic concept of total consumer surplus refers to which of the following?
Responses
A
The difference between the quantity of a good or service that people purchase and the amount that they actually consume
B
The overproduction of goods and services relative to the socially optimal level of output
C
The sum of the differences between the prices that consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and the price they actually pay
D
The sum of the differences between the prices that consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and the minimum prices that sellers must receive to offer that quantity
E
The difference between the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of a product at a given price
C
The table below is partially filled in with the different types of costs for a firm.
Quality | Variable Cost | Fixed Cost | Total Cost | Average Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | $0 | $60 |
|
|
1 |
|
| $130 |
|
2 |
|
|
| $90 |
Based on the information in the table, what is the marginal cost of producing the second unit?
Responses
A
$50
B
$60
C
$70
D
$90
E
$180
A
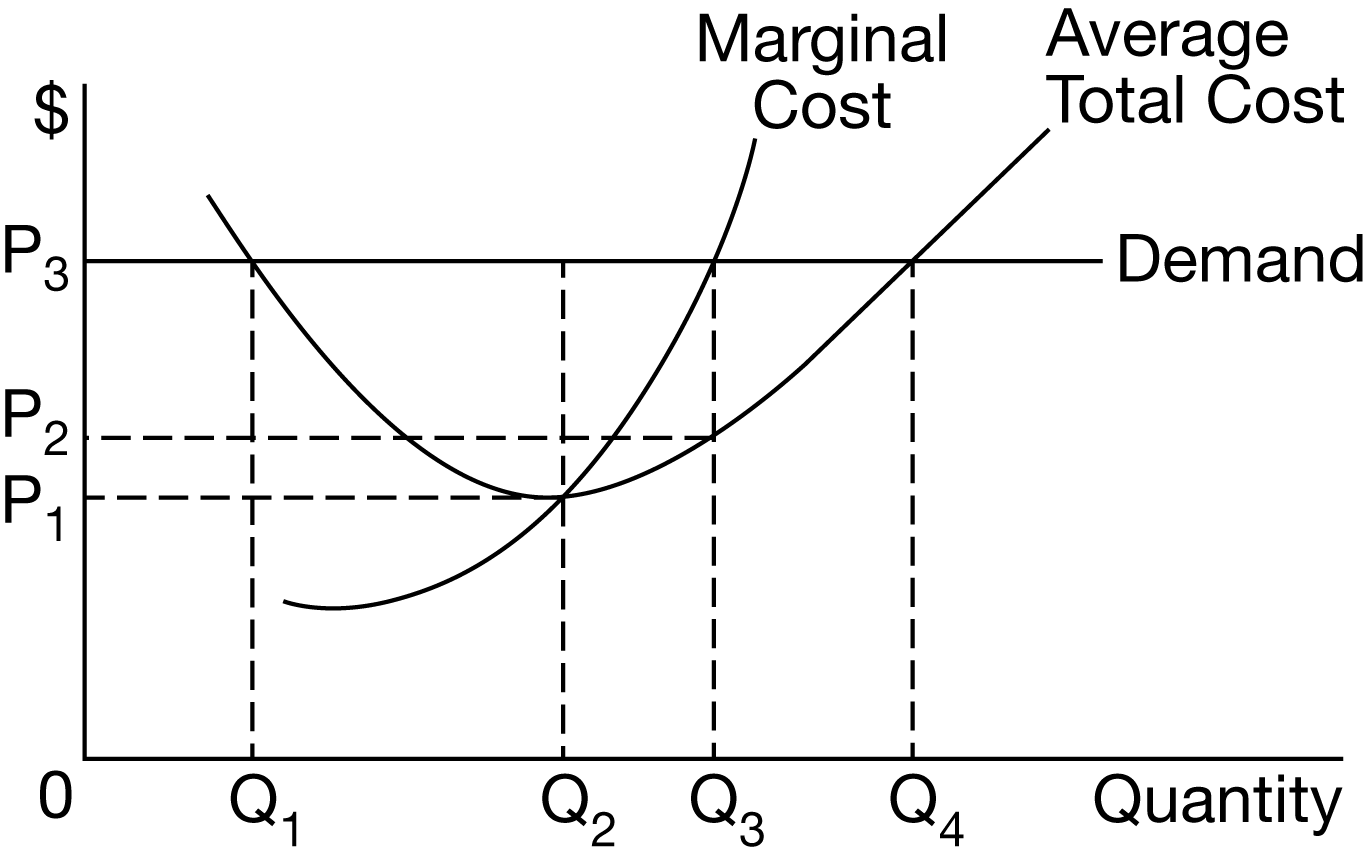
How many units of output should a firm with the cost and demand curves shown above produce to maximize profit?
Responses
A
0
B
Q1
C
Q2
D
Q3
E
Q4
D
Currently, XYZ Corporation can produce 50 units of output using 20 workers and 8 units of capital. Which of the following changes in the number of workers, units of capital, and quantity of output are consistent with constant returns to scale?
Responses
A
Workers | Capital | Output |
|---|---|---|
40 | 8 | 100 |
B
Workers | Capital | Output |
|---|---|---|
40 | 16 | 90 |
C
Workers | Capital | Output |
|---|---|---|
20 | 4 | 25 |
D
Workers | Capital | Output |
|---|---|---|
10 | 4 | 25 |
E
Workers | Capital | Output |
|---|---|---|
10 | 8 | 25 |
D
If the four largest firms in a market produce 88 percent of total industry output, the market is
Responses
A
perfectly competitive
B
a pure monopoly
C
a natural monopoly
D
an oligopoly
E
a monopsony
D
In monopolistic competition, an individual firm’s market power stems from which of the following?
Responses
A
Economies of scale in production
B
The production of a differentiated product
C
The absence of perfectly competitive firms that produce similar products
D
Barriers to entry allowing firms to earn economic profit
E
The maintenance of excess capacity to meet unexpected increase in demand
B
A profit-maximizing firm hires labor in a perfectly competitive market. Labor is the only variable input, and the marginal product of the last worker hired is 10 units per hour.
If the hourly wage is $20, the firm’s marginal revenue
Responses
A
is $2
B
is $20
C
increases as more output is produced
D
increases first and then decreases as more output is produced
E
decreases first and then increases as more output is produced
A
Assume the demand curve for a good is perfectly inelastic and the production of each unit of this good generates external costs. A profit-maximizing firm producing the good in an unregulated free market will
Responses
A
generate deadweight loss because marginal social cost is greater than marginal private cost
B
generate deadweight loss only if marginal costs are constant
C
not generate deadweight loss because the equilibrium quantity is socially optimal
D
not generate deadweight loss unless marginal costs are constant
E
not generate deadweight loss unless fixed costs are zero
C
A linear production possibilities curve indicates which of the following?
Responses
A
Constant opportunity costs
B
Decreasing opportunity costs
C
Increasing opportunity costs
D
Diminishing marginal returns
E
Labor-intensive production
A
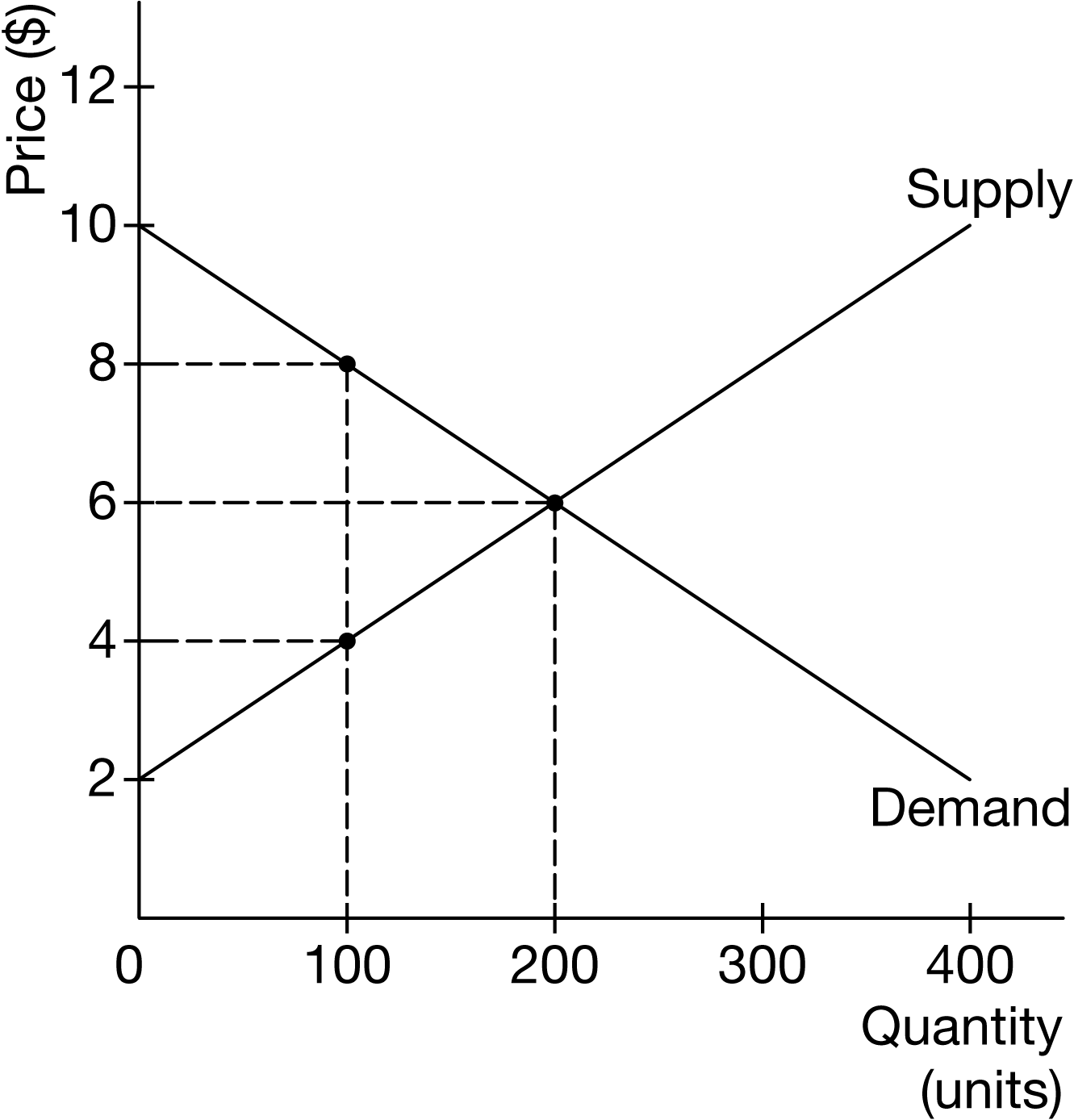
Assume that the government imposes a $4 per-unit tax on sellers of a good in the market described by the graph above.
What are the price paid by buyers, the after-tax price received by sellers, and the deadweight loss?
Responses
A
Price Paid by Buyers | Price Received by Sellers | Deadweight Loss |
|---|---|---|
$8 | $6 | $100 |
B
Price Paid by Buyers | Price Received by Sellers | Deadweight Loss |
|---|---|---|
$8 | $4 | $200 |
C
Price Paid by Buyers | Price Received by Sellers | Deadweight Loss |
|---|---|---|
$6 | $6 | $0 |
D
Price Paid by Buyers | Price Received by Sellers | Deadweight Loss |
|---|---|---|
$4 | $8 | $100 |
E
Price Paid by Buyers | Price Received by Sellers | Deadweight Loss |
|---|---|---|
$4 | $8 | $200 |
B
Which of the following must be true if at the tenth unit of output, marginal cost (MC) is $130 and average total cost (ATC) is $150 ?
Responses
A
ATC of producing the ninth unit is higher than $150.
B
ATC of producing the ninth unit is less than $150.
C
MC of producing the ninth unit is higher than $130.
D
The average variable cost of producing the tenth unit is higher than $150.
E
The average variable cost of producing the tenth unit is equal to $20.
A
Which of the following occurs as a result of the substitution effect of an increase in the price of a normal good?
Responses
A
The demand for the good decreases.
B
The demand for the complementary good increases.
C
The demand for the good becomes more elastic.
D
The quantity demanded of the substitute good decreases.
E
The quantity demanded of the good decreases.
E
Number of Workers | Quantity of Output |
0 | 0 |
1 | 10 |
2 | 25 |
3 | 35 |
4 | 40 |
5 | 42 |
Given the production schedule, what is the maximum number of workers the firm can hire before the effects of diminishing marginal returns set in?
Responses
A
1
B
2
C
3
D
4
E
5
B
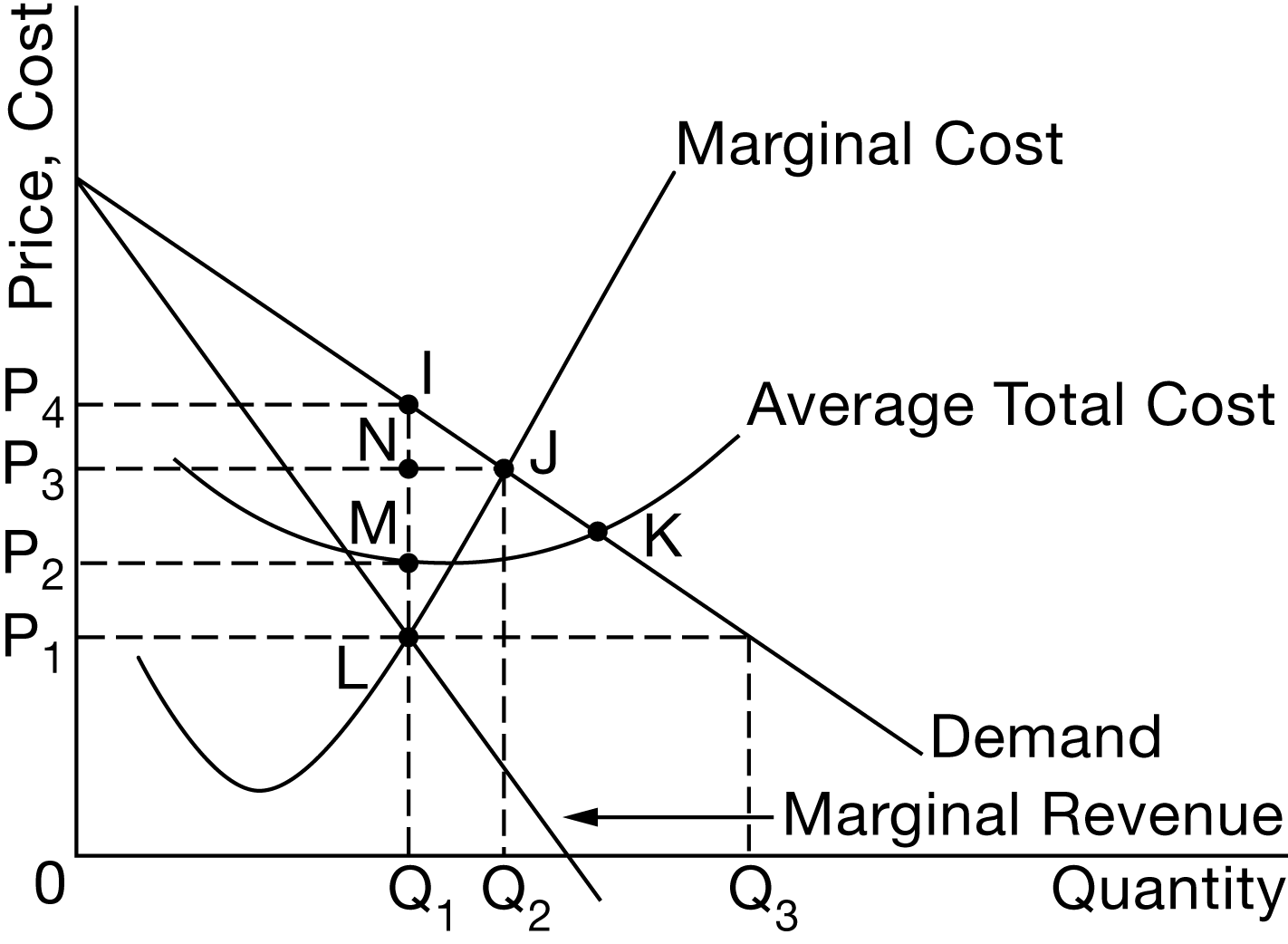
Which of the following combinations of output, price, and economic profit is consistent for the profit-maximizing monopolist depicted in the graph?
Responses
A
Output | Price | Economic Profit |
|---|---|---|
Q1 | P1 | 0P1LQ1 |
B
Output | Price | Economic Profit |
|---|---|---|
Q1 | P4 | P1P4IL |
C
Output | Price | Economic Profit |
|---|---|---|
Q1 | P4 | P2P4IM |
D
Output | Price | Economic Profit |
|---|---|---|
Q2 | P3 | P2P3NM |
E
Output | Price | Economic Profit |
|---|---|---|
Q3 | P1 | P1P2ML |
C
| Town Herald | ||
|
| Do Not Change Subscription Price | Increase Subscription Price |
Daily Voice | Do Not Change Subscription Price | $500,$400 | $200,$700 |
Increase Subscription Price | $600,$300 | $300,$100 | |
The two major newspapers in a city, Daily Voice and Town Herald, are considering whether to raise the subscription price. The first entries in the matrix above show the profits to Daily Voice, and the second entries show the profits to Town Herald.
Which of the following is consistent with the payoff matrix?
Responses
A
Do Not Change Subscription Price is a dominant strategy for Daily Voice.
B
Do Not Change Subscription Price is a dominant strategy for Town Herald.
C
Increase Subscription Price is a dominant strategy for Daily Voice.
D
Increase Subscription Price is a dominant strategy for Town Herald.
E
There are no dominant strategies in the above payoff matrix.
C
If a firm engages in perfect price discrimination, it charges
Responses
A
each customer the highest price the customer is willing to pay
B
each customer the average cost of the product
C
each customer the lowest price the customer is willing to pay
D
different prices to customers based on how old they are
E
different prices to customers based on how many units of output they buy
A
Assume a perfectly competitive firm is currently producing 100 units of output. Its marginal cost is $6 and rising at that output quantity. Its average variable cost is $7 and its average fixed cost is $3.
If the product’s price is $6, which of the following will the firm do in the short run to maximize its profit?
Responses
A
Shut down
B
Produce, but less than 100 units of output
C
Produce more than 100 units of output
D
Continue to produce at exactly 100 units of output
E
Increase its price above $6
A
The following two questions refer to the data in the table below.
A perfectly competitive firm operates with a fixed amount of capital that costs $1,000 per day. Labor is the only variable input. The firm hires labor in a perfectly competitive labor market at $100 per day per worker. The table below shows the firm’s production function.
Number of Workers Hired | Quantity of Output (units) |
0 | 0 |
1 | 10 |
2 | 30 |
3 | 54 |
4 | 75 |
5 | 85 |
6 | 90 |
What is the marginal product of the third worker?
Responses
A
5
B
10
C
20
D
24
E
It cannot be determined from the information given.
D
The following two questions refer to the data in the table below.
A perfectly competitive firm operates with a fixed amount of capital that costs $1,000 per day. Labor is the only variable input. The firm hires labor in a perfectly competitive labor market at $100 per day per worker. The table below shows the firm’s production function.
Number of Workers Hired | Quantity of Output (units) |
0 | 0 |
1 | 10 |
2 | 30 |
3 | 54 |
4 | 75 |
5 | 85 |
6 | 90 |
The firm will maximize profit in the short run if it
Responses
A
shuts down and the price is $10
B
produces 30 units and the price is $4
C
produces 30 units and the price is $10
D
produces 54 units and the price is $4
E
produces 85 units and the price is $10
E
Hours of Labor | Marginal Product |
|---|---|
0 | 0 |
1 | 10 |
2 | 12 |
3 | 9 |
4 | 7 |
5 | 4 |
The table above shows how a firm’s hourly level of output changes as more of the labor input is employed. The firm sells its output and hires labor in perfectly competitive markets. The wage paid to labor is $10 per hour, and the price of the firm’s output is $2 per unit.
Based on the data in the table, the marginal revenue product of the fourth hour of labor is equal to
Responses
A
$4
B
$7
C
$14
D
$26
E
$70
C
Levels of Cleanup | Total Cost of Cleanup ($) | Total Benefit of Cleanup ($) |
|---|---|---|
0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 7 | 45 |
2 | 37 | 80 |
3 | 92 | 105 |
4 | 172 | 125 |
5 | 272 | 140 |
The table above shows the total cost and the total benefit of cleaning up pollution in a community.
Which of the following cleanup levels is socially optimal?
Responses
A
1
B
2
C
3
D
4
E
5
B
The Lorenz curve represents the relationship between
Responses
A
the cumulative percentage of households and the cumulative percentage of income
B
income tax rates and income tax revenues
C
child labor rates and the poverty levels
D
income inequality and education level
E
market structure and the number of firms in the market
A
Antitrust laws are designed to maintain a competitive market environment by
Responses
A
eliminating monopolies wherever they exist
B
preventing monopolies from generating negative externalities
C
limiting practices that increase a firm’s market power
D
imposing price ceilings on products produced by monopolies
E
making charging a price above marginal cost illegal
C
Country | Opportunity Cost of 1 Ton of Apples | Opportunity Cost of 1 Ton of Oranges |
X | 1 ton of oranges | 1 ton of apples |
Y | 2 tons of oranges | 0.5 ton of apples |
The table above shows the opportunity costs of producing apples and oranges in Countries X and Y.
Which of the following can be concluded based on the data given in the table?
Responses
A
Country Y has an absolute advantage in producing both goods.
B
Country Y has a comparative advantage in producing both goods.
C
Country X has an absolute advantage in producing both goods.
D
Country X has a comparative advantage in producing oranges.
E
Country X has a comparative advantage in producing apples.
E
If the price elasticity of supply for pickles is 2 and the price of pickles increases by 10 percent, then the quantity supplied of pickles will increase by
Responses
A
0.2%
B
5%
C
8%
D
12%
E
20%
E
If a 10 percent increase in the price of good X results in a 20 percent decrease in the quantity of good Y demanded, which of the following is true?
Responses
A
Good X and good Y are complementary goods, and the cross-price elasticity is −0.5 .
B
Good X and good Y are substitute goods, and the income elasticity is +2 .
C
Good X and good Y are complementary goods, and the cross-price elasticity is −2 .
D
Good X and good Y are normal goods, and the income elasticity is +2 .
E
Good X and good Y are substitute goods, and the cross-price elasticity is −2 .
C
Which of the following provides a possible explanation for a simultaneous increase in the equilibrium price and the quantity of blueberries in a market?
Responses
A
An increase in the price of strawberries, a substitute
B
An increase in the supply of strawberries, a substitute
C
An increase in the price of farmland used to grow blueberries
D
A decrease in the price of blueberry harvesting equipment
E
Imposition of a price floor in the market for blueberries
A
The table below shows the per-unit prices and marginal utility for the last unit of video games and comic books that Kyle purchased.
| Video Games | Comic Books |
Price per unit | $25 | $10 |
Marginal utility | 50 | 50 |
Kyle spent all of his allocated budget on video games and comic books.
To maximize his utility, Kyle should have purchased
Responses
A
more video games and fewer comic books
B
fewer video games and more comic books
C
fewer of both goods
D
equal amounts of both goods
E
more of both goods
B
A perfectly competitive firm currently produces 1,000 units of output and hires its resources in a perfectly competitive factor market. It uses both labor and capital as inputs. The price of labor is $40; the price of capital is $100. The marginal product of labor is 8 units, and the marginal product of capital is 10 units.
Which of the following must be true?
Responses
A
The firm is currently maximizing its profit.
B
The firm can produce more than 1,000 units without increasing the total cost if it uses more labor and less capital.
C
The firm can produce more than 1,000 units without increasing the total cost if it uses more capital and less labor.
D
The firm can reduce the cost of producing 1,000 units by using less capital and employing the same amount of labor.
E
The firm can reduce the cost of producing 1,000 units by employing less labor and using the same amount of capital.
B
When two firms interact in an oligopolistic market, which of the following statements is true?
Responses
A
If one firm has a dominant strategy, then the other firm does not have a dominant strategy.
B
If one firm has a dominant strategy, then the other firm also has a dominant strategy.
C
Both firms must have dominant strategies.
D
If one firm has a dominant strategy, then there is no Nash equilibrium.
E
If both firms have dominant strategies, then there is a Nash equilibrium.
E
Which of the following is true when a profit-maximizing monopolist produces in the elastic portion of its demand curve?
Responses
A
It can increase total revenue by raising price.
B
It can decrease average total cost by reducing output.
C
Price is equal to marginal revenue.
D
Marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
E
Marginal revenue is positive.
E
The following two questions refer to the cost and revenue conditions of a monopolistically competitive firm shown in the graph below.

MC = marginal cost, ATC = average total cost, AVC =average variable cost, and MR = marginal revenue.
The firm’s profit-maximizing output in the short run is
Responses
A
zero, because P<AVC
B
Q1, because MR=MC
C
Q2, because P=MC
D
Q3, because MC=ATC
E
impossible to determine
A
The following two questions refer to the cost and revenue conditions of a monopolistically competitive firm shown in the graph below.

MC = marginal cost, ATC = average total cost, AVC =average variable cost, and MR = marginal revenue.
Which of the following will the firm do in the long run if market conditions do not change?
Responses
A
It will increase output to Q2 and lower price to P2 to minimize losses.
B
It will increase output to Q3 and raise price to P4 to earn zero economic profit.
C
It will produce Q1 and set price equal to marginal revenue.
D
It will exit the industry.
E
It will build a larger plant to achieve decreasing returns to scale.
D
At the current quantity that a firm is selling, the firm has marginal revenue of $750 and marginal cost of $800. Which of the following is true?
Responses
A
The firm is maximizing profit.
B
The firm’s profits would increase if the firm increased the quantity sold.
C
The firm’s profits would increase if the firm decreased the quantity sold.
D
The firm earns negative economic profit.
E
The firm earns zero accounting profit.
C
Which of the following is true of a monopsony in a labor market?
Responses
A
It faces a labor supply curve that is horizontal at the competitive market equilibrium wage.
B
Its marginal factor (resource) cost is the same as the market supply curve.
C
At its optimal level of employment, it pays a wage rate higher than the competitive market wage rate.
D
The imposition of a minimum wage results in a larger reduction in employment than is true in a competitive market.
E
Its marginal factor (resource) cost curve lies above the labor supply curve because hiring an extra worker means paying more to existing workers.
E
Which of the following indicates that a perfectly competitive firm has hired the profit-maximizing amount of labor?
Responses
A
The total product of labor exceeds the total real wage payments to workers.
B
The average product of labor exceeds the real wage paid to workers.
C
The marginal revenue product of labor is below the wage paid to workers.
D
The marginal revenue product of labor is above the wage paid to workers.
E
The marginal revenue product of labor equals the wage paid to workers.
E
In a competitive market in which the production of a good causes pollution, the socially optimal output is different from the competitive market equilibrium output of that good because the
Responses
A
marginal social benefit is higher than the marginal social cost
B
marginal social benefit is lower than the marginal private cost
C
marginal social cost is higher than the marginal private cost
D
marginal social benefit is higher than the marginal private benefit
E
total social cost is less than the total social benefit
C
Which of the following explains why free-riding can result in a market failure?
Responses
A
More than the socially optimal quantity is produced and consumed.
B
The socially optimal quantity is produced but less than the socially optimal quantity is consumed.
C
Private producers of nonexcludable goods are unable to charge everyone who consumes the good.
D
There is a market surplus of the good.
E
There is no consumer surplus derived from the good.
C
Individual private property rights provide people incentives to
Responses
A
meet societal goals rather than pursue their own self-interest
B
produce goods and services regardless of market demand
C
achieve equitable distribution of goods and services through competitive markets
D
focus only on benefits without regard to costs
E
produce goods and services that are valued in markets
E
Assume the market for disposable coffee cups is in equilibrium and disposable coffee cups are inputs for serving brewed coffee. Which of the following will result in a higher short-run equilibrium price of disposable coffee cups?
Responses
A
A decrease in the supply of coffee
B
A decrease in the number of locations serving brewed coffee
C
An increase in the supply of disposable coffee cups
D
An increase in the demand for brewed coffee
E
An increase in the price of tea, a complement for coffee
D
The equilibrium price for a good with a vertical supply curve and a downward-sloping demand curve is $20. If a binding price floor is set, which of the following will occur?
Responses
A
There will be a shortage of the good.
B
The sum of consumer and producer surpluses will decrease.
C
The equilibrium price of the good will decrease.
D
The quantity sold of the good will remain unchanged.
E
Demand for substitutes for the good will decrease.
B

The graphs above show the individual demand curves for the only two consumers, Adey and Sarah, in the market for popcorn.
As the price of popcorn decreases from $12 to $6, how does the quantity demanded change along the market demand curve?
Responses
A
It increases from 2 to 4 units.
B
It increases from 2 to 5 units.
C
It increases from 2 to 8 units.
D
It increases from 0 to 14 units.
E
It increases from 8 to 14 units.
C
Which of the following is true for a firm that uses labor as a variable input and capital as a fixed input in the short run?
Responses
A
If the marginal product of labor is negative, the average product of labor must also be negative.
B
If the marginal product of labor is rising, the average product of labor must be greater than the marginal product of labor.
C
If the average product of labor is rising, the marginal product of labor must be rising.
D
If the average product of labor is falling, the marginal product of labor must be less than the average product of labor.
E
The average product of labor can never be equal to the marginal product of labor.
D

The graph above shows the cost curves for May’s Fruit Farm, where MC is marginal cost, ATC is average total cost, and AVC is average variable cost.
May’s short-run supply curve includes which of the following points?
Responses
A
TW
B
RST
C
STV
D
STW
E
RSTV
C
The characteristic that causes firms in a perfectly competitive industry to earn zero economic profits in the long run is
Responses
A
firms are price takers
B
firms produce identical products
C
individual firms account for a small fraction of the total market
D
the industry supply curve is horizontal
E
there are no barriers to entry or exit
E
If individual firms in a perfectly competitive market are earning positive economic profits, the number of firms and the price of the product in the market will most likely change in which of the following ways in the long run?
Responses
A
Number of Firms | Price |
|---|---|
Increase | Increase |
B
Number of Firms | Price |
|---|---|
Decrease | Increase |
C
Number of Firms | Price |
|---|---|
Increase | Decrease |
D
Number of Firms | Price |
|---|---|
Decrease | Decrease |
E
Number of Firms | Price |
|---|---|
No change | Decrease |
C
Jamal quits a job that was paying him $30,000 per year and decides to start his own business. He runs his business out of his house in a room he had been renting to his colleague for $12,000 a year. Jamal withdraws the $20,000 in his savings account that had been earning him a 10 percent annual interest to purchase computers and related accessories and equipment for the business. During the first year of operation, Jamal’s business incurred $30,000 in explicit costs and generated $60,000 in total sales.
Jamal’s economic profit is
Responses
A
$30,000
B
$17,000
C
$0
D
−$2,000
E
-$14,000
E
Firms in monopolistic competition do not attain allocative efficiency because at the long-run equilibrium output, which of the following is true?
Responses
A
Price is greater than marginal cost.
B
Marginal cost is greater than minimum average total cost.
C
Marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
D
There is an overallocation of resources to the market.
E
Products are homogeneous.
A
A perfectly competitive firm is producing 10 units of output and sells the product for $5 per unit. At this level of output the average total cost is $4, the average variable cost is $3 and the marginal cost is $7.
What should this firm do to maximize short-run profits?
Responses
A
Increase output until price equals average total cost.
B
Increase output until price equals marginal cost.
C
Leave output unchanged because price is greater than average total cost.
D
Decrease output until price is equal to marginal cost.
E
Decrease output until price is equal to average total cost.
D
Assume accountants and teachers have identical marginal revenue product schedules. Which of the following provides an explanation for why accountants receive higher starting salaries than school teachers?
Responses
A
Accountants have less human capital than school teachers.
B
Accountants have lower opportunity cost than school teachers.
C
Accounting firms provide a more pleasant work environment than schools provide.
D
The supply of accountants is low relative to the supply of teachers.
E
Fewer teaching majors graduate from college each year than accounting majors.
D
Assume that firms providing health-care services to older people operate in a perfectly competitive market. What must happen in the market for health-care workers if there is an increase in the number of older people in a country?
Responses
A
The demand for health-care workers will increase.
B
The marginal factor cost in the health-care industry will decrease.
C
The number of health-care workers will decrease.
D
The quality of health-care services will increase.
E
The wages of health-care workers will decrease.
A
As an unregulated monopolist, City Cable is earning positive economic profits. If the government regulated the firm by requiring it to produce the level of output that allowed the firm to earn zero economic profit, City Cable would set a price that is equal to its
Responses
A
marginal cost
B
marginal revenue
C
average total cost
D
average variable cost
E
total cost
C
A progressive income tax is characterized by
Responses
A
a higher average tax rate at low income levels than at high income levels
B
tax rates that increase total tax revenues
C
marginal tax rates that do not change as income changes
D
marginal tax rates that increase as income increases
E
marginal tax rates that decrease as income increases
D
An outward shift of a production possibilities curve can be caused by
Responses
A
planting a more profitable farm crop
B
improving technology
C
using idle resources
D
changing consumer preferences
E
increasing the minimum wage
B
At a price of $10, the quantity demanded of pizzas is 100 and the quantity supplied is 150. Which of the following statements must be true?
Responses
A
There is a shortage of pizza at a price of $10.
B
The equilibrium price of pizza is below $10.
C
The quantity of pizzas sold will be 150.
D
At equilibrium, fewer than 100 pizzas will be sold.
E
The pizza market is in equilibrium.
B
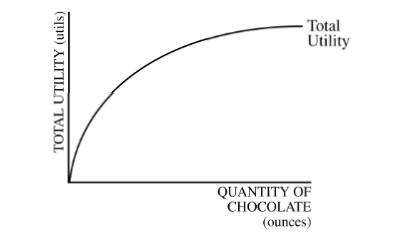
The diagram above shows Sally’s utility function for chocolate.
Her utility function illustrates the principle of
Responses
A
trade-offs when making choices
B
diminishing marginal utility
C
income and substitution effects
D
increasing opportunity cost
E
constrained utility maximization
B
At a perfectly competitive firm’s current output level, average total cost is $15, average variable cost is $10, and marginal cost is $8 and increasing. If the product price is $15, what should this firm do to maximize profits?
Responses
A
Increase the quantity of output produced.
B
Increase the product price.
C
Decrease the product price to increase sales.
D
Shut down immediately.
E
Continue to produce at its current output level.
A
The government must provide public goods such as national defense because
Responses
A
the production of public goods requires economies of scale that the private sector cannot achieve
B
it is generally impossible to exclude individuals who value public goods but do not pay for them
C
public goods cannot be produced in private competitive markets, since they have highly inelastic demand
D
private producers charge a price that is substantially greater than marginal cost
E
no single individual should have to pay for public goods, since they benefit society as a whole
B
Which of the following will increase the demand for pizza, a normal good?
Responses
A
An increase in the cost of producing pizza
B
A decrease in the price of pizza
C
An increase in the price of a complementary product
D
An increase in consumers’ income
E
An increase in the number of restaurants selling pizza
D
Game theory is used to explain
Responses
A
why firms price discriminate
B
how monopolies evolve into oligopolies
C
strategic behavior of firms in oligopoly
D
profit maximization in monopoly
E
price leadership of monopolistic competition
C
If a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market chooses to produce in the short run, then marginal cost is always
Responses
A
greater than or equal to total cost
B
greater than or equal to average total cost
C
greater than or equal to average variable cost
D
greater than or equal to average fixed cost
E
less than average total cost
C
The table above shows the total benefit Tony gets from eating different quantities of apples.
If apples cost $3 each, how many should he buy to maximize his consumer surplus?
Responses
A
1
B
2
C
3
D
4
E
5
D

Given the demand curve, if price decreases from $8 to $4 per unit, total consumer surplus will
Responses
A
increase by $4
B
increase by $8
C
increase by $12
D
increase by $18
E
remain constant at $24
D
Which of the following describes how a market will respond when the scarcity of a good increases?
Responses
A
Consumers will increase their demand for the good
B
Consumers will decrease their demand for the good.
C
The price of the good will increase.
D
The price of the good will decrease.
E
Producers will increase the supply of the good.
C
Suppose that the demand for vegetables is price elastic. If the price of vegetables increases by 5 percent, the quantity of vegetables demanded would
Responses
A
increase by 5 percent
B
increase by more than 5 percent
C
increase by less than 5 percent
D
decrease by more than 5 percent
E
decrease by less than 5 percent
D
The table below lists the monthly individual demand schedules for text messages for the only three buyers in the market: Allison, Bill, and Chang.
Which of the following combinations of price and quantity lies on the market demand curve?
Responses
A
Price | Quantity |
4¢ | 1,000 |
B
Price | Quantity |
8¢ | 350 |
C
Price | Quantity |
12¢ | 200 |
D
Price | Quantity |
16¢ | 270 |
E
Price | Quantity |
20¢ | 0 |
D
Which of the following best explains why a firm’s short-run marginal cost curve shifts down when it purchases new, more efficient equipment and experiences an increase in its total cost?
Responses
A
The situation represents an exception to the law of diminishing returns.
B
The average total cost curve shifts upward as a result of the equipment purchase, and there is a movement up along the marginal cost curve.
C
The equipment purchase is a fixed cost, and the new equipment will cause a reduction in the cost of producing each additional unit.
D
The average variable cost curve shifts upward as a result of the equipment purchase, and the marginal cost curve shifts downward.
E
The marginal cost curve shifts downward because of the law of diminishing returns.
C
Question is based on the chart below for a firm that is perfectly competitive in both the labor and product markets, showing how much daily output a firm can produce using different numbers of workers.
If output sells for $20 per unit, what is the marginal revenue product of the fifth worker?
Responses
A
$2
B
$40
C
$100
D
$115
E
$460
B
Question is based on the chart below for a firm that is perfectly competitive in both the labor and product markets, showing how much daily output a firm can produce using different numbers of workers.
If output sells for $20 per unit and the daily wage is $100 per worker, how many workers should the firm hire to maximize profit?
Responses
A
1
B
2
C
4
D
5
E
6
C

Given the information, the average variable cost of 25 units of output is
Responses
A
$2
B
$6
C
$25
D
$50
E
$75
A
A typical firm in a perfectly competitive constant-cost industry is operating with an economic loss in the short run. When the industry returns to long-run equilibrium, what will happen to the number of firms in the industry, the market price, and the typical firm’s quantity?
Responses
A
Number of Firms | Market Price | Firm’s Quantity |
Decrease | Increase | Increase |
B
Number of Firms | Market Price | Firm’s Quantity |
Decrease | Decrease | Increase |
C
Number of Firms | Market Price | Firm’s Quantity |
Decrease | Increase | Decrease |
D
Number of Firms | Market Price | Firm’s Quantity |
Increase | Increase | Decrease |
E
Number of Firms | Market Price | Firm’s Quantity |
Increase | Decrease | Decrease |
A
The two firms in an industry are deciding whether to advertise. The profit to each firm depends on the other firm’s decision. The first entries in the matrix below indicate the profit earned, in millions of dollars, by Firm A; and the second entries indicate the profits earned, in millions of dollars, by Firm B.
Based on the payoff matrix, which of the following is correct?
Responses
A
Firm A always gets a smaller share of the industry profits.
B
Firm A’s dominant strategy is to advertise.
C
Firm B’s dominant strategy is not to advertise.
D
The dominant strategy for both firms is not to advertise.
E
Neither firm has a dominant strategy.
B
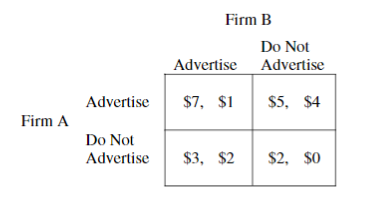
The two firms in an industry are deciding whether to advertise. The profit to each firm depends on the other firm’s decision. The first entries in the matrix below indicate the profit earned, in millions of dollars, by Firm A; and the second entries indicate the profits earned, in millions of dollars, by Firm B.
The combination where Firm A advertises and Firm B does not advertise is Nash equilibrium because
Responses
A
it is best for each firm given what the other firm has chosen
B
the total industry profits are maximized
C
Firm A has an incentive to change its strategy and chooses not to advertise
D
It is the best outcome for Firm B regardless of what firm A does
E
advertising is always the best strategy for Firm A
A

Based on the production possibilities curve for books and pencils shown, what is the opportunity cost of producing a book?
Responses
A
30 pencils
B
10 pencils
C
3 pencils
D
1/3 of a pencil
E
1/10 of a pencil
C
The demand curves X and Y are shown in the graph above.
Which of the following offers the most accurate comparison of the price elasticities of demand curves X and Y at a price of $4?
Responses
A
Demand Curve X | Demand Curve Y |
Perfectly elastic | Perfectly inelastic |
B
Demand Curve X | Demand Curve Y |
Perfectly inelastic | Perfectly elastic |
C
Demand Curve X | Demand Curve Y |
Perfectly inelastic | Relatively elastic |
D
Demand Curve X | Demand Curve Y |
Relatively inelastic | Perfectly elastic |
E
Demand Curve X | Demand Curve Y |
Relatively elastic | Relatively inelastic |
D
An art student spends all of her income on pencils and drawing pads. The student currently buys 30 pencils at $1 each and 10 pads at $5 each.
If the marginal utility of the 30th pencil is 100 utils and the marginal utility of the 10th pad is 400 utils, to maximize utility the student should change her purchases of pencils and pads in which of the following ways?
Responses
A
Pencils | Pads |
Not change | Buy more |
B
Pencils | Pads |
Buy more | Buy more |
C
Pencils | Pads |
Buy more | Buy less |
D
Pencils | Pads |
Buy less | Buy more |
E
Pencils | Pads |
Buy less | Buy less |
C
Assume that the current market equilibrium price for milk is $2.80 per gallon and that 5 million gallons are sold per day. If the government sets a price ceiling of $2.00 per gallon, which of the following is true?
Responses
A
The demand for milk will increase.
B
The supply of milk will decrease.
C
There will be an excess supply of milk in the market.
D
More than 5 million gallons of milk will be sold.
E
Less than 5 million gallons of milk will be sold.
E
Which of the following is most likely to cause the demand curve for nurses to shift to the right?
Responses
A
An increase in the number of nurses graduating from nursing schools
B
An increase in nursing schools’ tuition
C
An increase in the number of hospitals that employ nurses
D
A decrease in the marginal productivity of nurses
E
An improvement in the health of older people
C
In a given year, Jennifer earns $50,000 and spends $40,000. During the same period, Steve earns $30,000 and spends $27,000.
If Jennifer and Steve both must pay a 10 percent sales tax on goods purchased, the sales tax is
Responses
A
a higher percentage of income for Jennifer than for Steve
B
a higher percentage of spending for Steve than for Jennifer
C
progressive with respect to income
D
regressive with respect to income
E
proportional with respect to income
D
A monopolistically competitive firm is currently producing the profit-maximizing level of output. If the price of a variable input increases, which of the following will occur?
Responses
A
The firm will increase its output to increase its revenue.
B
The firm will increase the price of its output by the same amount.
C
The firm’s average total cost and marginal cost curves will shift upward.
D
The firm’s average fixed cost will decrease as it decreases production.
E
The firm’s fixed cost will increase, but its output level will be unaffected.
C
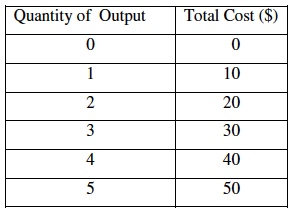
The table below shows the long-run total cost function of a firm.
The firm’s cost function exhibits
Responses
A
diseconomies of scale
B
constant returns to scale
C
economies of scale
D
decreasing marginal cost
E
increasing marginal cost
B
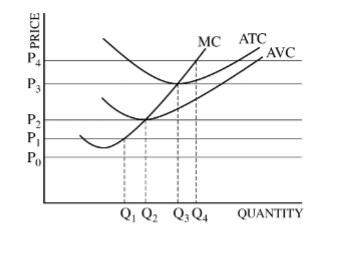
Question is based on the following graph, which shows a firm’s marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC).
In the short run, the firm will
Responses
A
shut down if the price falls below P3
B
continue to produce as long as the price is greater than P1
C
continue to produce as long as the price is greater than P2
D
earn economic profits as long as the price is greater than P2
E
cover its fixed cost as long as the price is less than P3
C
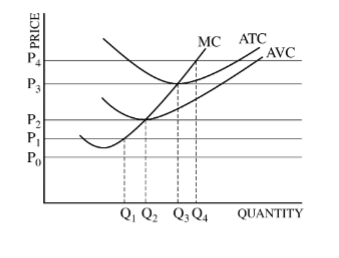
Question is based on the following graph, which shows a firm’s marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC).
The firm’s short-run supply curve is which of the following?
Responses
A
The AVC curve above P1
B
The AVC curve above P2
C
The ATC curve above P3
D
The MC curve above P2
E
The MC curve above P3
B

According to the data, if Mr. X and Ms. Y have the opportunity to trade, which of the following will be mutually beneficial?
Responses
A
Ms. Y sells shoes to and buys bread from Mr. X.
B
Ms. Y sells bread to and buys shoes from Mr. X.
C
Ms. Y sells both bread and shoes to Mr. X.
D
Ms. Y buys both bread and shoes from Mr. X.
E
Ms. Y and Mr. X do not trade with each other.
A
If the government eliminates an effective minimum wage in a competitive labor market, which of the following is true?
Responses
A
Minimum wage workers will experience no change in hourly pay.
B
Minimum wage workers will experience a decrease in hourly pay.
C
The number of people employed will decrease because people do not want to work for low wages.
D
There will be an excess demand for workers.
E
There will be an increase in the supply of workers.
B
Carmen consumes both entertainment and medical care. For Carmen, entertainment is a normal good, and the income elasticity of her demand for medical care is zero.
If Carmen’s income increases, which of the following will be the immediate impact on her consumption?
Responses
A
Entertainment: Increase; Medical care: Increase
Entertainment | Medical care |
Increase | Increase |
B
Entertainment | Medical care |
Increase | No change |
C
Entertainment | Medical care |
No change | Increase |
D
Entertainment | Medical care |
Increase | Decrease |
E
Entertainment | Medical care |
Decrease | Increase |
B
Assume that a perfectly competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium. If industry demand for the product increases, how will this firm’s price, output, and profit change in the short run?
Responses
A
Price | Output | Profit |
Increase | Increase | Increase |
B
Price | Output | Profit |
Increase | Decrease | Decrease |
C
Price | Output | Profit |
Increase | Increase | Decrease |
D
Price | Output | Profit |
No change | Decrease | Decrease |
E
Price | Output | Profit |
Decrease | Increase | Increase |
A
One difference between oligopolies and monopolistically competitive markets is that
Responses
A
there is no deadweight loss in monopolistically competitive markets, but there is in oligopolies
B
the products sold in monopolistically competitive markets are identical
C
oligopolies have fewer barriers to entry
D
firms maximize profits in monopolistically competitive markets but not in oligopolies
E
there are fewer firms in oligopolistic markets than in monopolistically competitive ones
E
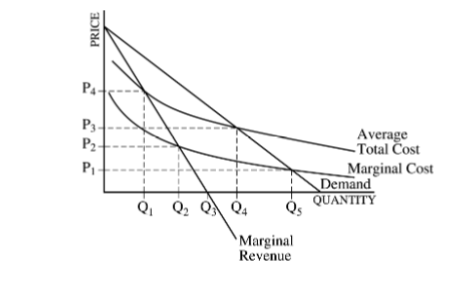
The question refers to the following diagram of a natural monopolist.
The firm shown in the diagram qualifies as a natural monopoly because
Responses
A
the demand curve is downward sloping
B
the demand curve lies above the marginal revenue curve
C
the average total cost is decreasing in the relevant range of market demand
D
the firm can maximize profit with any output level it chooses
E
marginal revenue is positive at the profit-maximizing output level
C
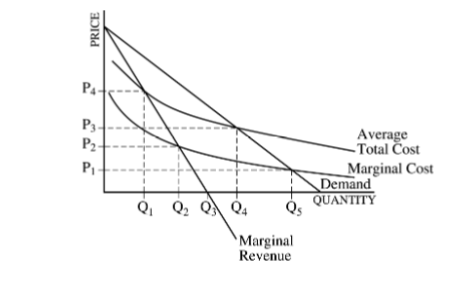
The question refers to the following diagram of a natural monopolist.
If government regulated the natural monopoly to produce the output resulting in zero economic profit, then the output would be
Responses
A
Q1
B
Q2
C
Q3
D
Q4
E
Q5
D
Which of the following characteristics is prevalent in oligopolies?
Responses
A
Allocative efficiency
B
Low barriers of entry
C
Consideration of rivals’ reactions
D
No deadweight loss
E
Zero economic profit
C
A firm uses capital and labor in its production process. The marginal product for the last unit of labor is 5, the marginal product for the last unit of capital is 10, and the wage is $10.
At what cost of hiring each unit of capital would the firm be minimizing the cost of the current output?
Responses
A
$5
B
$10
C
$15
D
$20
E
$50
D
Which of the following must be true if a profit-maximizing monopolistically competitive firm continues to operate in the short run while incurring a loss?
Responses
A
Marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price is greater than average total cost.
B
Marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price is greater than average variable cost.
C
Marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price is less than average variable cost.
D
Price equals both marginal cost and marginal revenue.
E
Price is less than marginal revenue, but greater than average variable cost.
B