AP HUG Chapter 11 Vocab - Service and Industry
5.0(1)Studied by 15 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Last updated 10:26 PM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Industrial Revolution
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods (starting in Great Britain)
2
New cards
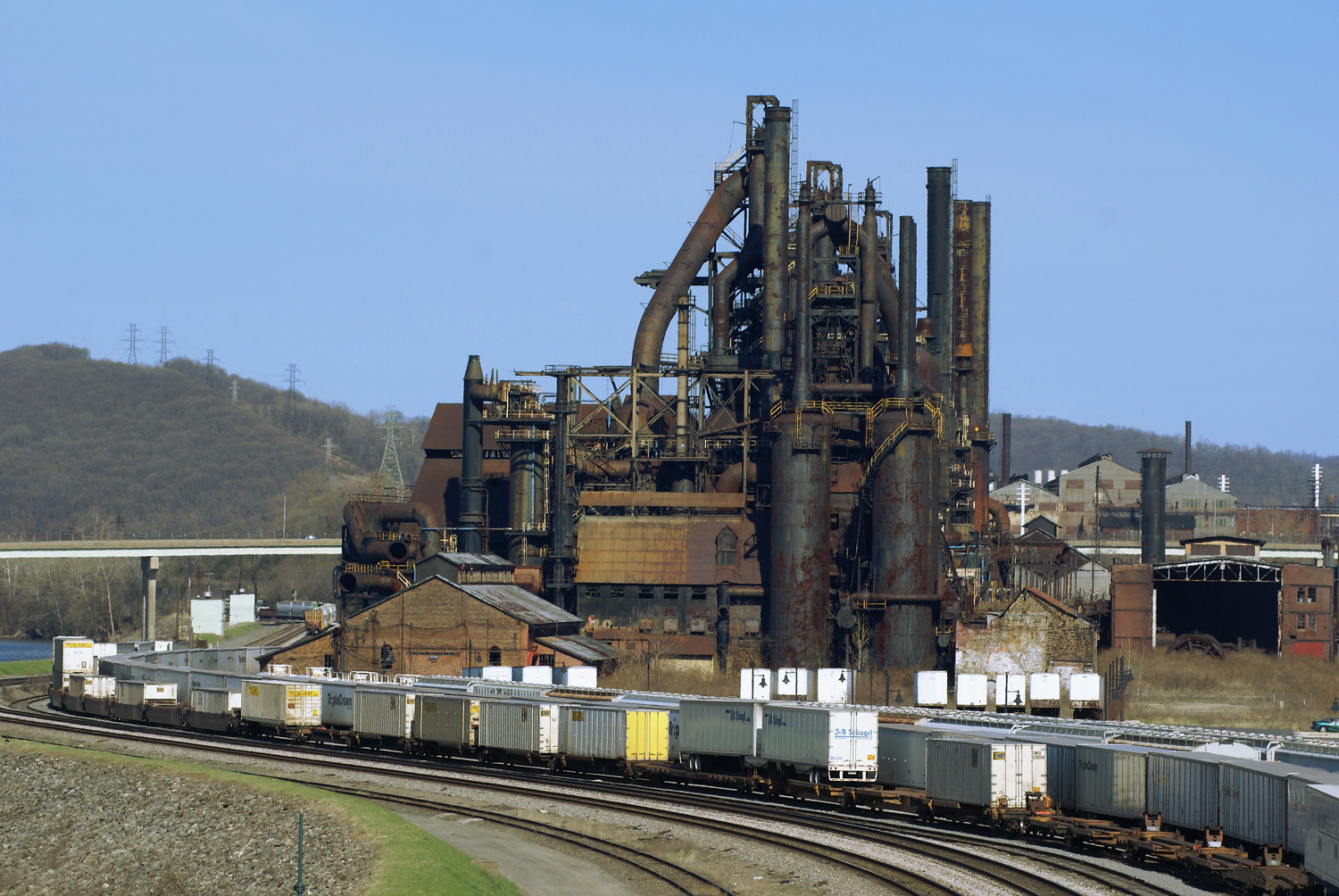
Deindustrialization
Moving industrial jobs to other regions (Great Lakes Manufacturing Belt to Rust Belt)

3
New cards
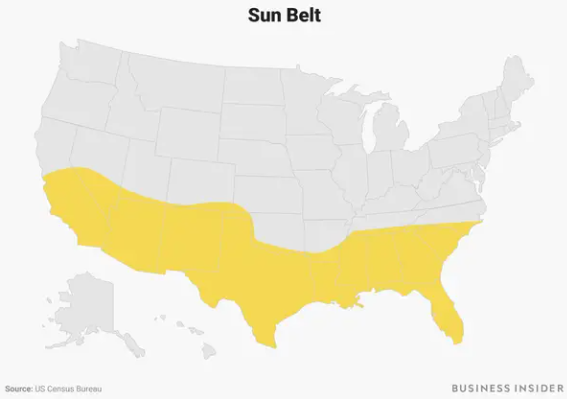
Sunbelt
Area of Southern United states that experienced population growth after the deindustrialization of the Great Lakes region
4
New cards
New international division of labor
Transfer of some types of jobs (especially those requiring low-paid less skilled workers) from MDCs to LDCs; the whole world is a labor pool (leads to outsourcing)
5
New cards
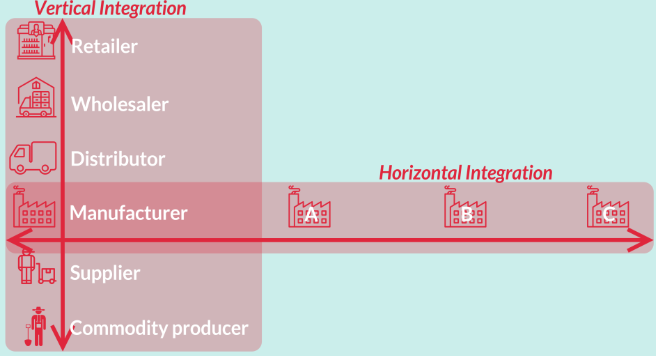
Vertical integration
When one company controls all aspects of its production process
6
New cards
Offshore
The practice of outsourcing operations overseas, usually by companies from industrialized countries to less-developed countries, with the intention of reducing the cost of doing business
7
New cards
Outsourcing
Moving labor and secondary economic activity to a different country (Nike)
8
New cards
Maquiladora
Factories built by the U.S. companies in Mexico near the U.S. border, to take advantage of much lower labor costs in Mexico
9
New cards
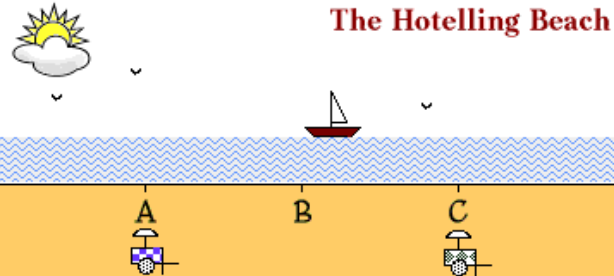
Locational interdependence
Competitors will seek to constrain each other's territory as much as possible which will therefore lead them to locate adjacent to one another in the middle of their collective customer base (Hotelling’s Model)
10
New cards
Agglomeration
The clustering of like-minded industries, activities, and people for mutual advantage (cooperative use of infrastructure and sharing of labor resources) (Hotelling’s Model)
11
New cards
Technopole (Also known as High Tech Corridors or Growth Poles)
Area where tech and computer industries agglomerate (brain gain)
12
New cards
Deglomeration
Separation of agglomerated industries due to negative effects and high costs
13
New cards
Least Cost Theory
States that the optimum location of a manufacturing firm is explained in terms of cost minimization
14
New cards
Break-of-bulk point
A location where transfer is possible from one mode of transportation to another
15
New cards
Bulk-gaining industry
An industry in which the final product weighs more or comprises a greater volume than the inputs (beer) (Least Cost Theory)
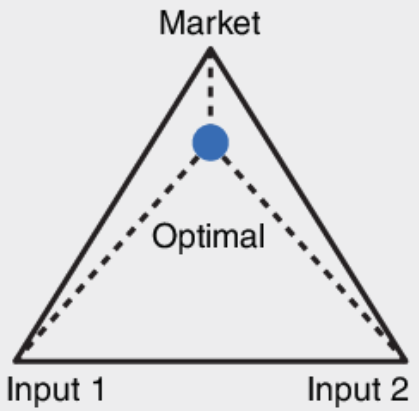
16
New cards
Bulk-reducing industry
An industry in which the final product weighs less or comprises a lower volume than the inputs (copper, paper) (Least Cost Theory)
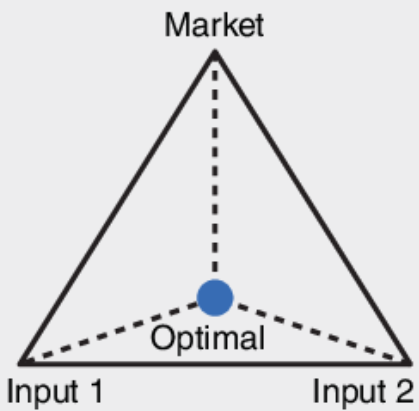
17
New cards
Distance decay
As the distance between two places increases, the interaction between those two places decreases
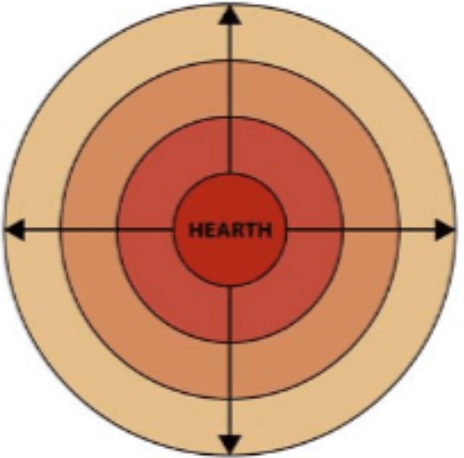
18
New cards
Friction of distance
Movement incurs some form of cost, in the form of physical effort, energy, time, and/or the expenditure of other resources, and these costs are proportional to the distance traveled
19
New cards
Fordist production
Form of mass production in which each worker is assigned one specific task to perform repeatedly; the production of consumer goods at a single site
20
New cards
Post-Fordist production
Goods are not mass-produced at a single site (companies outsourcing production)
21
New cards
Site factors
A part of locational criteria related to the costs of business production (land, labor, capital - i.e. rivers, port cities, coal)
22
New cards
Situation factors
A part of locational criteria related to the features of a location’s surrounding area and the costs of transportation (relation to other places, regional/global trade)
23
New cards
Variable costs
A part of locational criteria related to costs that changes based on the level of output that a business produces (energy, transportation, resources, friction of distance)
24
New cards
Demand
The quantity of something that consumers are willing and able to buy
25
New cards
Supply
quantity of something that producers have available for sale
26
New cards
Recycling
To convert waste into a reusable material (use again)
27
New cards
Remanufacturing
The rebuilding of a product to the specifications of the original manufactured product using a combination of reused, repaired, and new parts
28
New cards
Sanitary landfill
A place to deposit solid waste, where a layer of earth is bulldozed over garbage each day to reduce emissions of gasses and odors from the decaying trash, minimize fires, and discourage vermin
29
New cards
Pollution
Contamination of the air, water, or land
30
New cards
Point-source pollution
Any single identifiable source of pollution from which pollutants are discharged, such as a pipe, ditch, ship or factory smokestack
31
New cards
Air pollution
concentration of trace substances and solid particles at a greater than normal level
32
New cards
Ozone
A gas that absorbs ultraviolet solar radiation
33
New cards
Fission
The splitting of an atomic nucleus to release energy
34
New cards
Fusion
Creation of energy by joining the nuclei of two hydrogen atoms to form helium
35
New cards
Active Solar Energy
Solar radiation captured with photovoltaic cells that convert light energy to electrical energy
36
New cards
Geothermal energy
Energy from steam or hot water produced from hot or molten underground rocks
37
New cards
Fossil fuel
A natural fuel such as coal or gas, formed in the geological past from the remains of living organisms
38
New cards
Renewable energy
Energy sources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale (sunlight, wind, water, geothermal heat)
39
New cards
Nonrenewable energy
A source of energy that is a finite supply capable of being exhausted
40
New cards
Potential reserve
A supply of energy that is undiscovered but thought to exist
41
New cards
Proven reserve
A supply of energy remaining in deposits that have been discovered
42
New cards
Cottage industry
Manufacturing based in homes rather than in a factory, commonly found before the Industrial Revolution
43
New cards
Just-in-time delivery
Keeping on hand just what you need; new deliveries every few days
44
New cards
Labor-intensive industry
An industry for which labor costs comprise a high percentage of total expenses
45
New cards
Primary industrial regions
Areas with the largest agglomeration of industries (Europe, N America, E Asia, Russia and Ukraine)
46
New cards
Right-to-work law
A law preventing a union and company from negotiating a contract that requires workers to join a union as a condition of employment