Carbohydrates
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
carbohydrates function
provides fast, short term energy for the body
build and provide structural support in cells to help them stay intact and function properly
carbohydrates structure
consist of C, H, and O atoms in 1:2:1 ratio, CH2O
form ring structures in aq solutions (cell fluids)
forms of carbohydrates
monosaccharide
disaccharide
polysaccharide
monosaccharide
simplest form/ monomer of carbohydrates
simple sugars that can directly release energy
what functional group belongs to monosaccharides
hydroxyl (OH-)
glucose, galactose, and fructose relation
types of monosaccharides
isomers of each other (same formula, different structure)
disaccharides
two monosaccharides covalently bonded by a glycosidic linkage (made of two OH- bonding)
formed by condensation (dehydration synthesis) rxn
water is removed
polysaccharides structure
many monosaccharides bonded together
polysaccharides function
energy storage because it is unable to release energy without being broke down to the simplest form
structural support (depending on the polysaccharide)
types of polysaccharides
glycogen, starch, cellulose, chitin
all made from glucose, differs with how they are linked and structurally arranged
glycogen function
short term energy storage in animals
used up in one day unless storage is replenished by food consumption
glycogen structure
chains of a-glucose molecules, OH points down
many side branches
starch function + structure
short term energy storage in plants
long chains of a- glucose molecules
could be branched (side groups) or unbranched (straight chain)
where is chitin found
exoskeleton of insects and crustaceans (shellfish)
cell wall of fungi
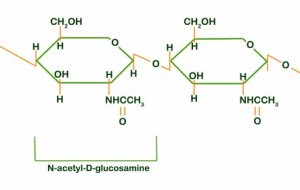
chitin structure
b- glucose monomers that contain an amine group (NH2)
amine group provides additional hydrogen bonding, makes structure stronger and more resistant to decay
cellulose function + structure
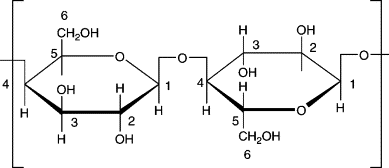
major component of cell wells in plants
cannot be digested by humans, lack the enzyme
b-glucose polymers bonded by glycosidic linkages
how does glycogen respond to dropping of blood sugar
it is hydrolyzed (breaks into glucose monomers)
uses that energy to raise back up
two types of starch chains
amylose and amylopectin
amylose
simple starch that is unbranched
starch has 20-30% of amylose
hard to digest
insoluble in water
amylopectin
complex starch that is branched
makes up 70% of starch
easy to digest, many attachment points for enzymes to break it down
soluble