Organic Chemistry Exam 4
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
two aldehydes
dial
2 benzene rings fused together
naphthalene
aromatic ring with aldehyde
carbaldehyde
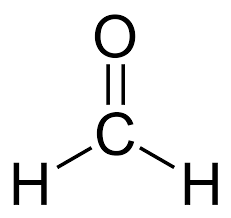
HCHO
Formaldehyde (or methanal)
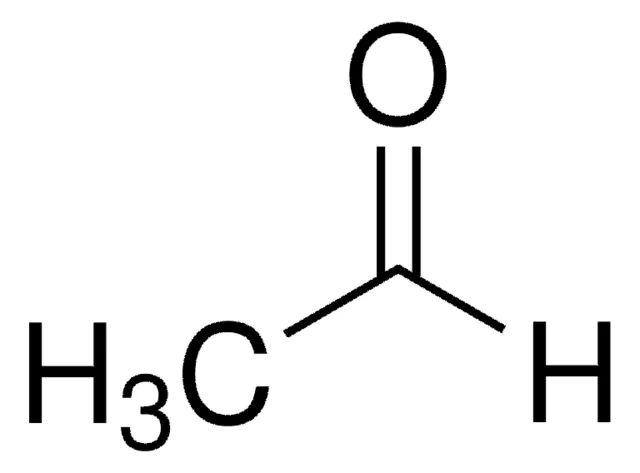
CH3CHO
acetaldehyde (or ethanal)
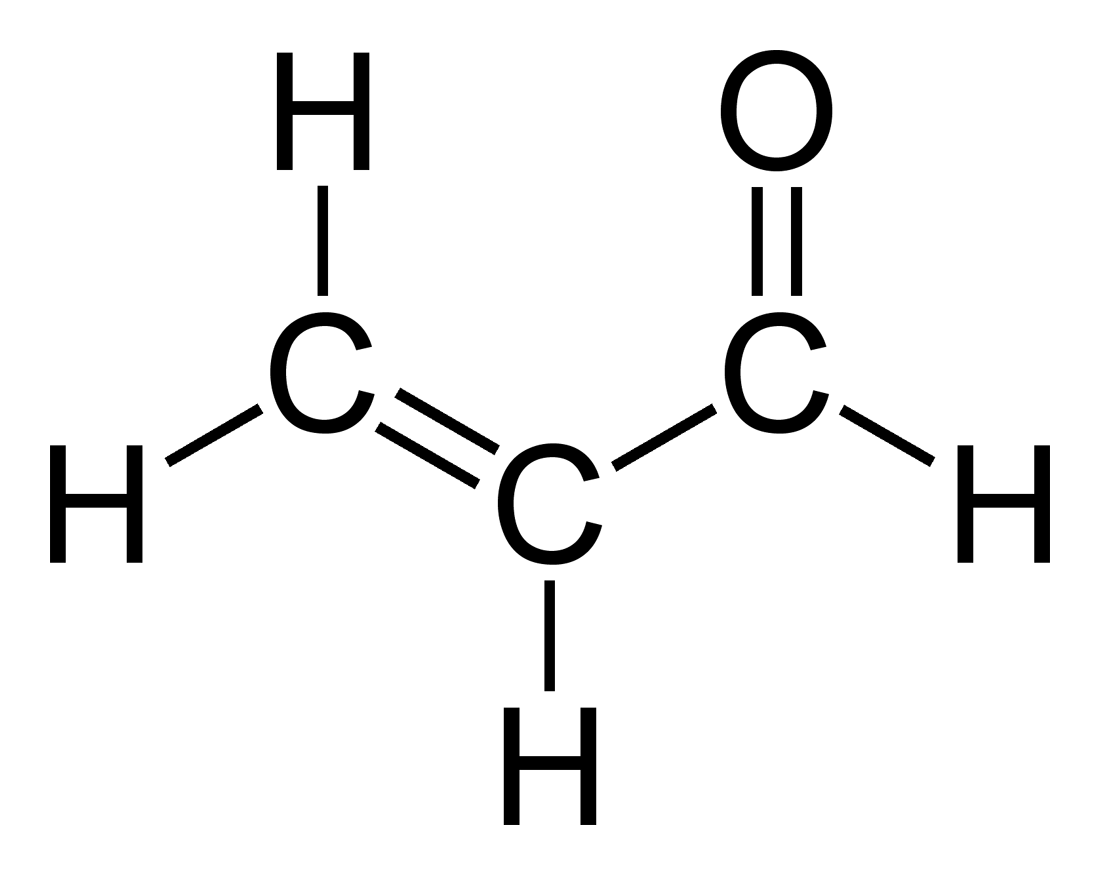
H2C=CHCHO
Acrolein (or propenal)
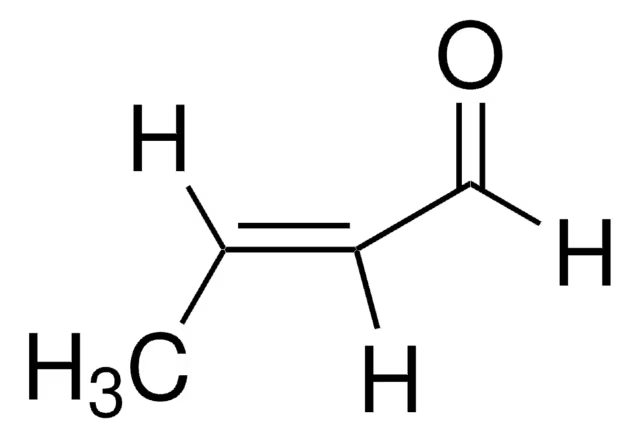
CH3CH=CHCHO
Crotonaldehyde (or 2-Butenal)
benzene ring with aldehyde
Benzaldehyde
two ketones
dione
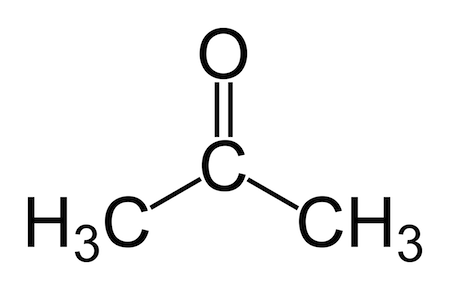
acetone
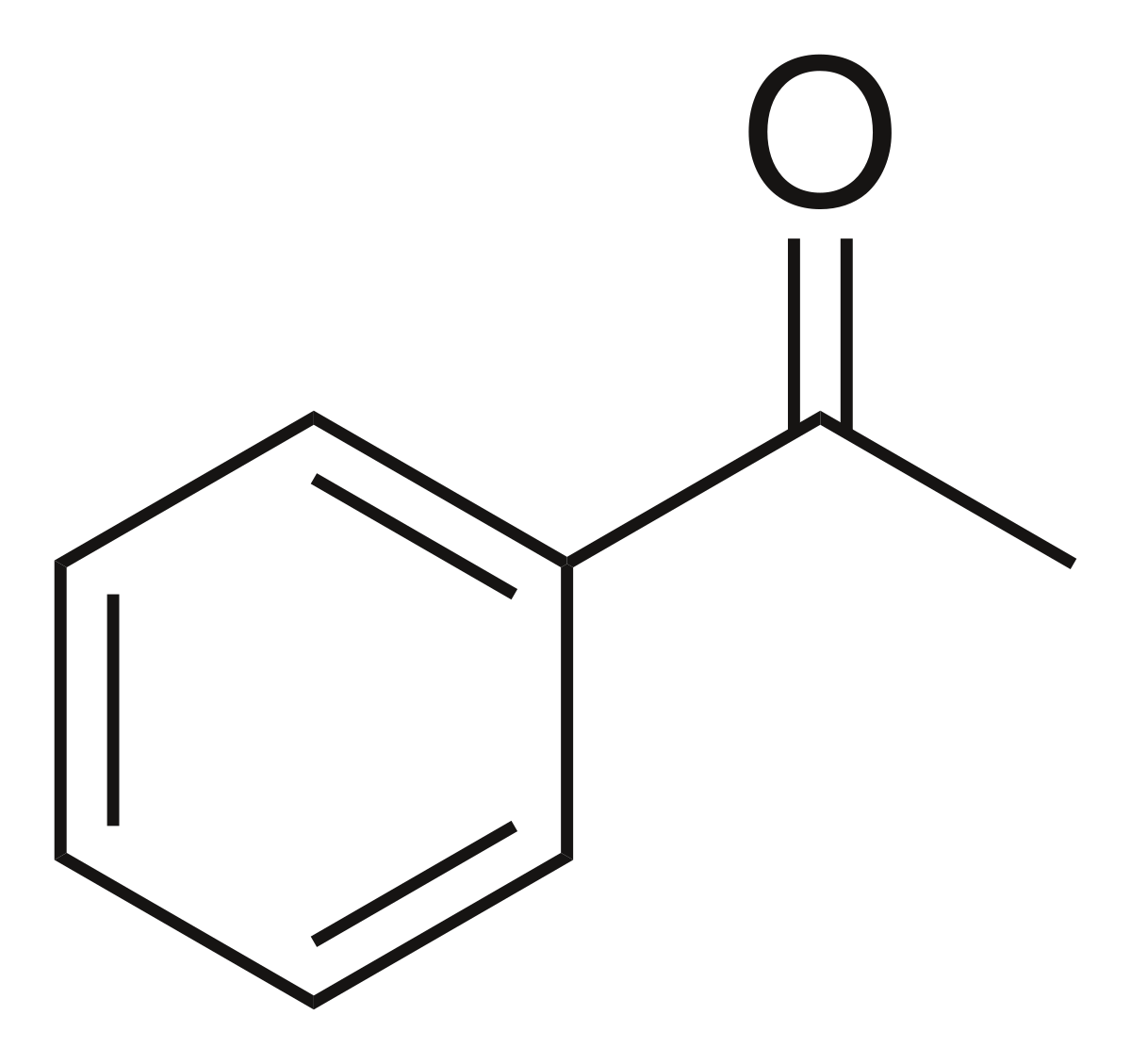
acetophenone
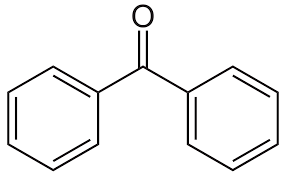
benzophenone
when there is bro an aldehyde and ketone present
name as aldehyde at end
name location of ketone as oxo
ex. 3-Oxohexanal
ketones can’t be ___?
oxidized
unless there are hot conditions
aldehydes will react faster than ketones because
they are less stable due to less hinderance and because they have less electronic support
geminal
both OH on the same carbon
hydration of aldehyde and ketones creates..?
geminal diols
nucleophilic addition of primary amine creates
imine
schiff base
nucleophilic addition of secondary amine creates
enamine
imine
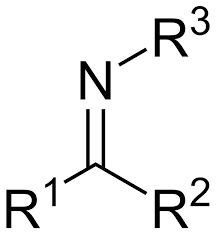
enamine

schiff base
created by the nucleophilic addition of primary amines
carbon nitrogen double bond
N,N-dimethyl amine
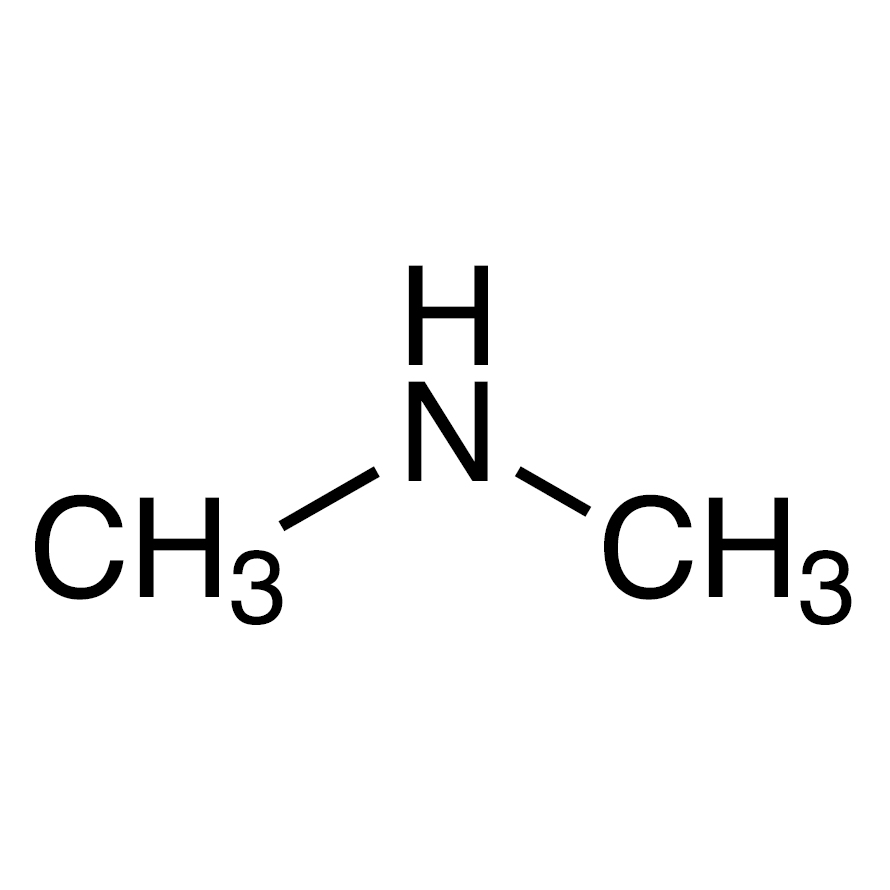
Wolff-Kishner Reaction
reagent is hydrazine
turns C=O to H-C-H
getting rid of carbonyl
Hydrazine
H2NNH2
acetal
2 O-R
used to protect carbonyls
ylide
phosphorus with 3 H
Gilman Reagent
R2CuLi
only uses one R group
2 carboxylic acid groups
dioic acid
carboxylic acid has the ____ naming priority in functional groups
highest
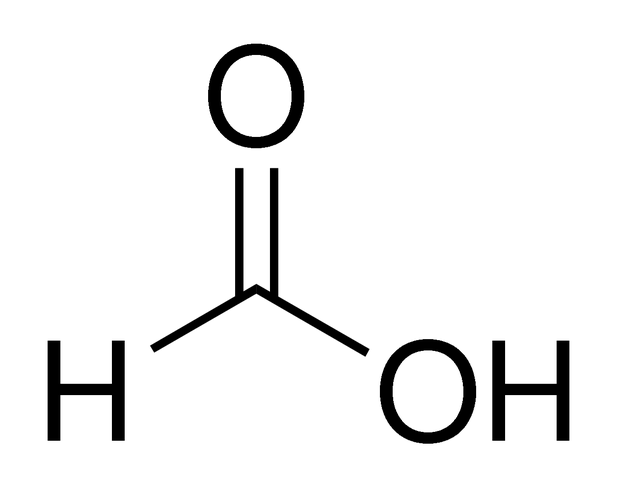
HCO2H
formic acid
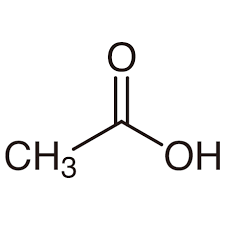
CH3CO2H
acetic acid
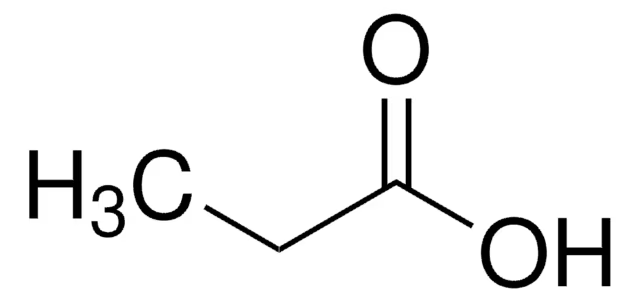
CH3CH2CO2H
propionic acid

HO2CCO2H
Oxalic acid
naming nitriles
leave e in
acetonitrile
acetic acid + nitrile (CH3CN)
benzene ring + nitrile
benzonitrile
aromatic ring + nitrile
carbonitrile
cyano
when there is another carboxylic acid derivate present with nitrile
dimer
2 carboxylic acid molecules together
the acidic strength of ethanol is ____ than carboxylic acid
weaker
why is acetic acid more stable than ethanol
because it is more acidic and because it has resonance
buffers
resist PH change
ex. blood
weak acid with its conjugate base
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
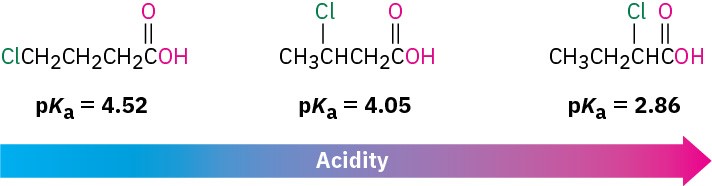
substituent effect on acidity
easier to donate H if you increase electronegativity
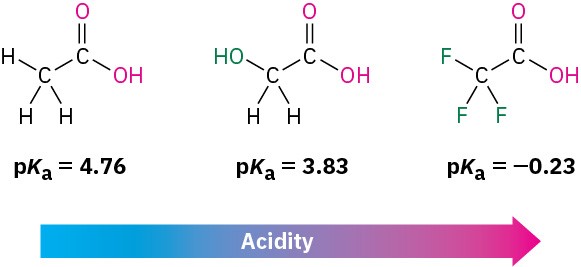
The closer the Electron withdrawing group to carboxylic acid, the ___ the acid because hydrogen will feel it
stronger
What does the reagent PBr3 do
replaces OH with Br
Acid Halides
RCOX
Anhydrides
RCOOCR’
Esters
RCOOR’
Amides
RCONR’2
Thioesters
RCOSR’
naming carboxylic acid derivates
name as carboxylic acid first, then change the end
naming acid halides
-ic acid → -yl chloride
-oic acid → -oyl bromide
cyclohexane carboxylic acid → cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride
Naming Acid Anhydride
an=without, hydride= water
ic acid → -ic anhydride
oic acid → -oic anhydride
naming esters
-ic acid → -ate
-oic acid → -oate
malonate → two esters
naming amides
-ic acid and -oic acid → amide
When R is connected to N, treat N like a number (ex. N-methylpropanamide)
Naming Thioesters
don’t need to know much
what ever is connected to S is the first name + thio bro tbh idek
reactivity of carboxylic acid derivates
more Hydrogens = more reactive/acidic
which carboxylic acid derivate is the least reactive
amides (1) and Esters (2)
which carboxylic acid derivates are the most reactives
Acid Anhydrides (2) and Acid Chloride (1)
hydrolysis
reaction with water to yield a carboxylic acid
Alcoholysis
reaction with an alcohol to yield an ester
Aminolysis
reaction with ammonia or an amine to yield an amide
Reduction
Reaction with a hydride reducing agent to yield an aldehyde or an alcohol
Grignard Reaction
reaction with an organometallic reagent to yield a ketone or an alcohol (with extra carbon)