11.1 - changing allele frequencies
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
* all dem alleles
* natural selection
* gene flow
* genetic drift
\
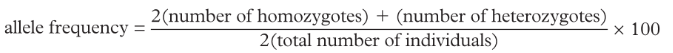
heterozygotes will have ___ copy
* heterozygotes → 1 copy of allele
* can have a beneficial or harmful effect, or no effect at all
* change to DNA composition of a cell or organism that generally results in changed phenotype
* chromosome mutation/abnormality
* silent - affected codon still codes for same amino acid
* missense - codes for different amino acid
* nonsense - changes to stop codon, truncating protein
* frameshift
* insertion
* deletion
chromomal/block mutations
affects structure of chromosomes
result of errors in meiosis
leads to sgnificant changes in genes
types of block mutations
duplication: gene sequence repeated
inversion: chromosome segment breaks off, flips around backwards and reattaches
deletion: due to breakage, piece of chromsome lost
translocation: involves 2 chromosomes that aren’t homologous where part of 1 chromosome is transferred to another chromosome
\
* different forms of radiation → UV radiation can cause mutations in skin cells that results in skin cancer
* may bring new allele in gene pool, potentially influencing allele frequencies
what is natural selection
applies when selective agent removes unsuited individuals from the population. suitable phenotypes survive and then breed and have offspring, increasing those alleles in each generation
genetic diversity between individuals in a populations results from different phenotypes (traits) having varying advantages for survival and reproduction
individuals well suited to their environment are more likely to survive & reproduce
* artificial pressures brought about by humans through selective breeding
* competition for resources → food & water, competition for shelter
* mate availability
* predator abundance
* individual is more likely to survive to reproduce & pass alleles to next generation
* individuals from different populations interbreed
* individuals enter (immigration) or leave (emmigration) a population
* results in new alleles being introduced or lost, increasing or decreasing genetic diversity of population
why is a reduced genetic diversity bad?
inbreeding: keeps harmful genes in gene pool
lower adaptive potential - populations become vulnerable to new selection pressures that could challenge or wip out entire population due to absence of advantageous alleles
* founder effect
* ex) natural disaster, human activities (hunting, land clearance)
* inbreeding results in reduced genetic diversity in population & increase in numbers of homozygous individuals
* vulnerable to environmental change & dying out
* low level of genetic diversity → species or populations go through genetic bottleneck, increasing risk of extinction
* increased inbreeding & loss of alleles due to genetic drift
1. born with pre-existing genetic variation
2. selection pressure
3. selective disadvantage
1. won’t survive until reproduction - alleles won’t be passed down to next gen
2. allele frequency decreases - no reproduction
4. selective advantage
1. can access food & survive until reproduction
2. can produce viable, fertile offspring
3. allele frequency increases