UCONN Biology 1108 Lab Practical 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Scientific Method
1. Ask a question
2. Background research
3. Formulate a hypothesis
4. Test hypothesis
5. Analyze results and draw conclusions
6. Publish results
Hypothesis
Educated guesses, can be tested, data can support or not support the hypothesis
Independent variable
Variable tested/manipulated
Dependent variable
Measurable outcome/responding variable
Lines of evidence for macroevolution
1. Fossil record
2. Molecular sequence data
3. Structure homology
4. Developmental similarities
5. Vestigial structures
6. Convergent evolution
7. Patterns of distribution
Fossil types
1. Impression (no organic matter preserved)
2. Compression (some organic matter preserved)
3. Petrification (plant tissue replaced with minerals)
4. Amber (preservation with fossilize plant sap)
Three domains of life
Eukarya, bacteria, archaea
Where are fossils located?
Sedimentary rocks
How old is Earth?
4.6 billion years old
Synapomorphy
Shared-derived-shape
How is the time scale broken down?
Eons, Eras, Periods, and Epochs
What causes a new Era to start?
A major extinction event
What era are we currently in?
The Cenozoic Era
What epoch are we in?
The Holocene epoch
What happened during the Permian Period?
A major extinction event 251 MYA
What happened during the Cretaceous Period?
All the dinosaurs died 65.5 MYA
What era did the dinosaurs live in?
Mesozoic
What are the eras in order of time?
Haden, Archaen, Proterozoic, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic
What is the new epoch humans are considered to be in?
Anthropocene
When did cyanobacteria appear on Earth?
3.5 billion years ago
When did earthworms appear on Earth?
200 million - 145 million years ago
When did coral appear on Earth?
488 million years ago
When did trees appear on Earth?
416 - 354 million years ago
When did the switch from gymnosperms to angiosperms occur?
135 million years ago
Cladogram/Phylogenic Tree
Depicts evolutionary relationships among different taxa, evolutionary hypothesis
Taxa
A group of one or more populations of an organism, species, genus, order, etc.
Synapomorphies
Shared derived characteristics present in ancestral species, shared exclusively
Character matrix
Chart to show different taxa and different synapomorphies (characters), use information to build a cladogram
Parsimony
Simplest scientific explanation that fits data is the BEST explanation
Monophyletic group
Common ancestor and ALL descendants
Paraphyletic group
Common ancestor and SOME descendants; not evolutionary meaningful
What does a branch on a cladogram signify?
It signifies each taxon as they branch off from the node
What does a node signify?
A common ancestor
Hierarchical classification system?
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
When did Homo Sapiens first appear?
0.16 mya
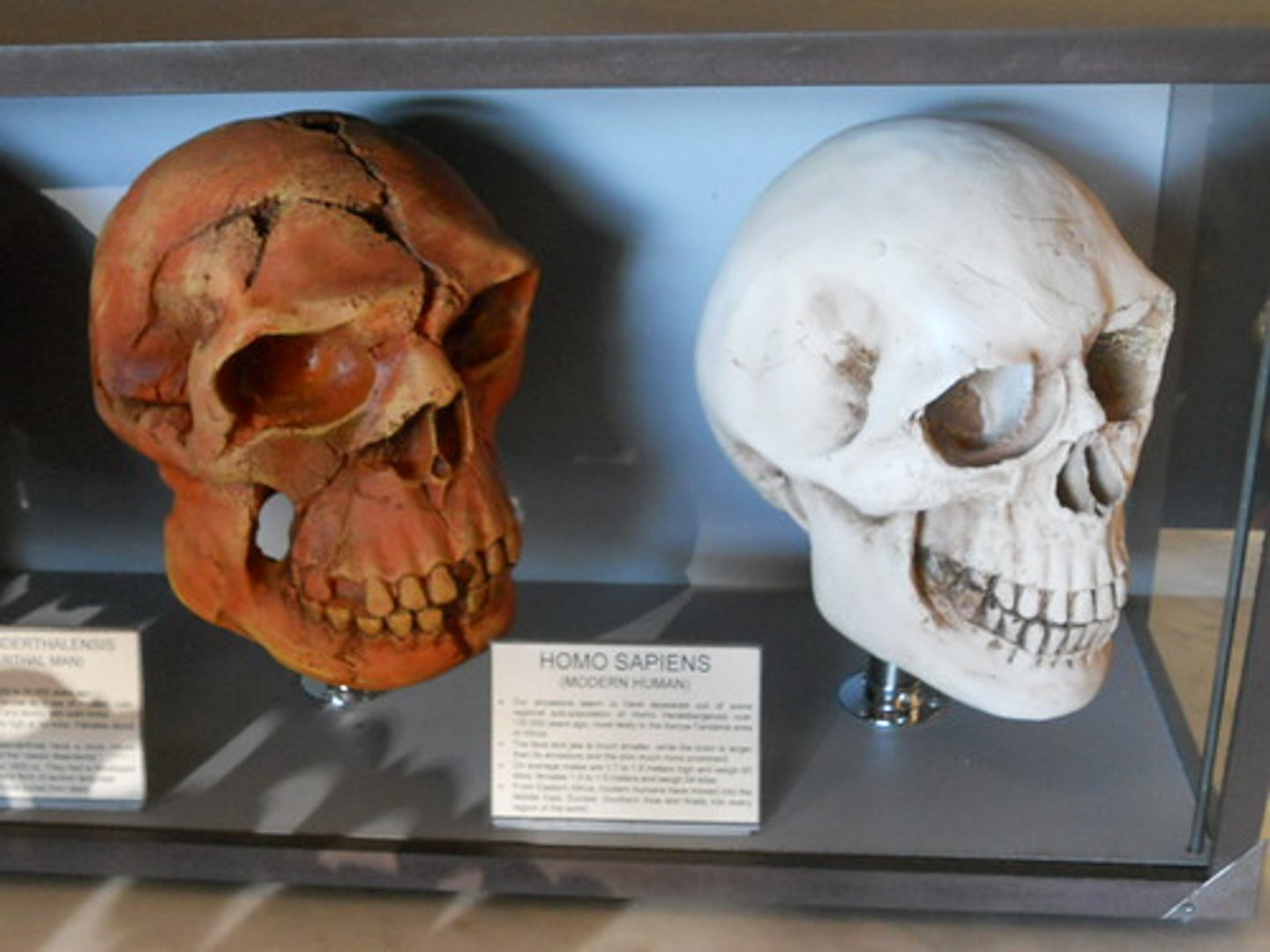

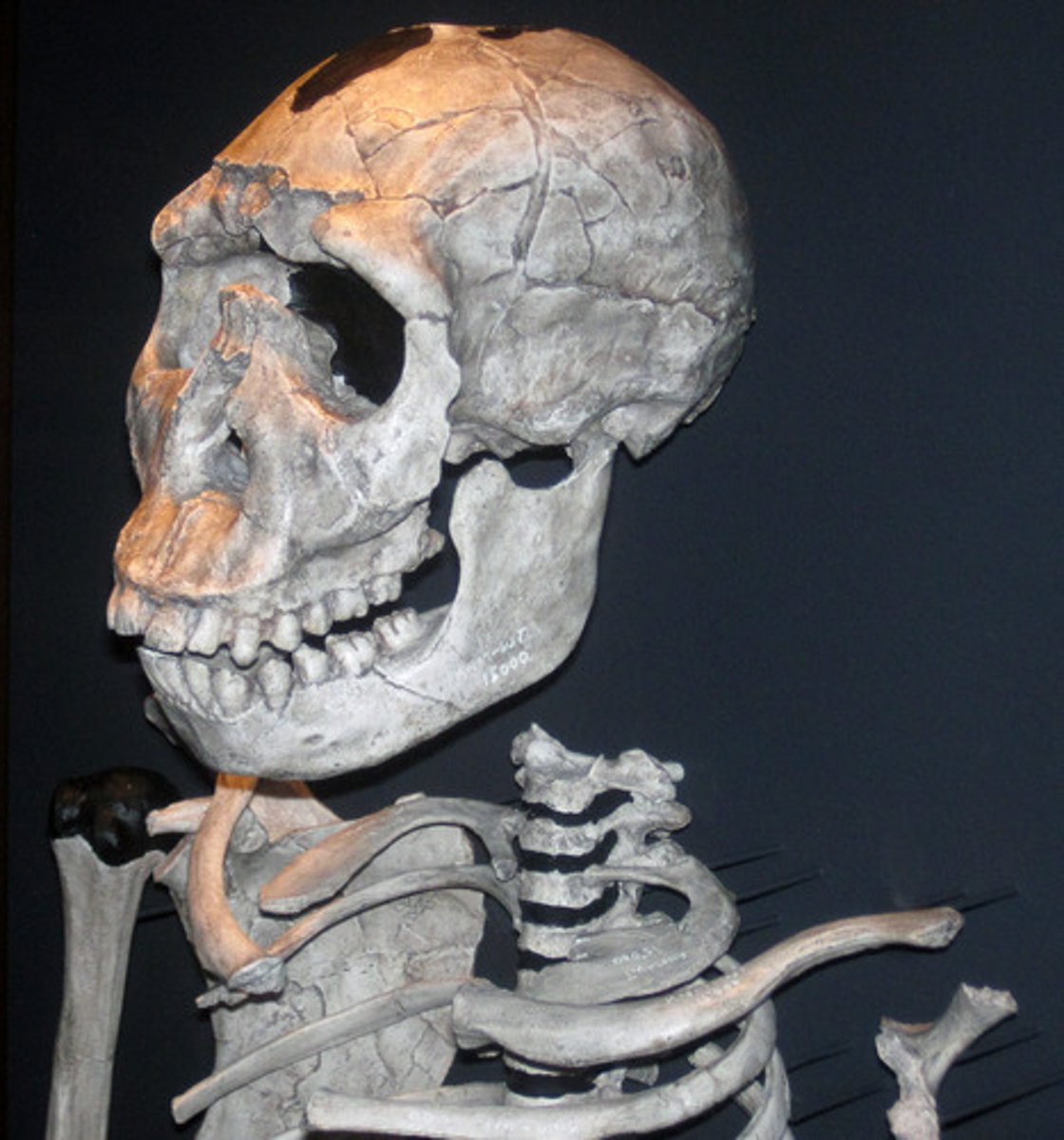
When did Homo Neanderthalensis first appear?
600,000 years ago
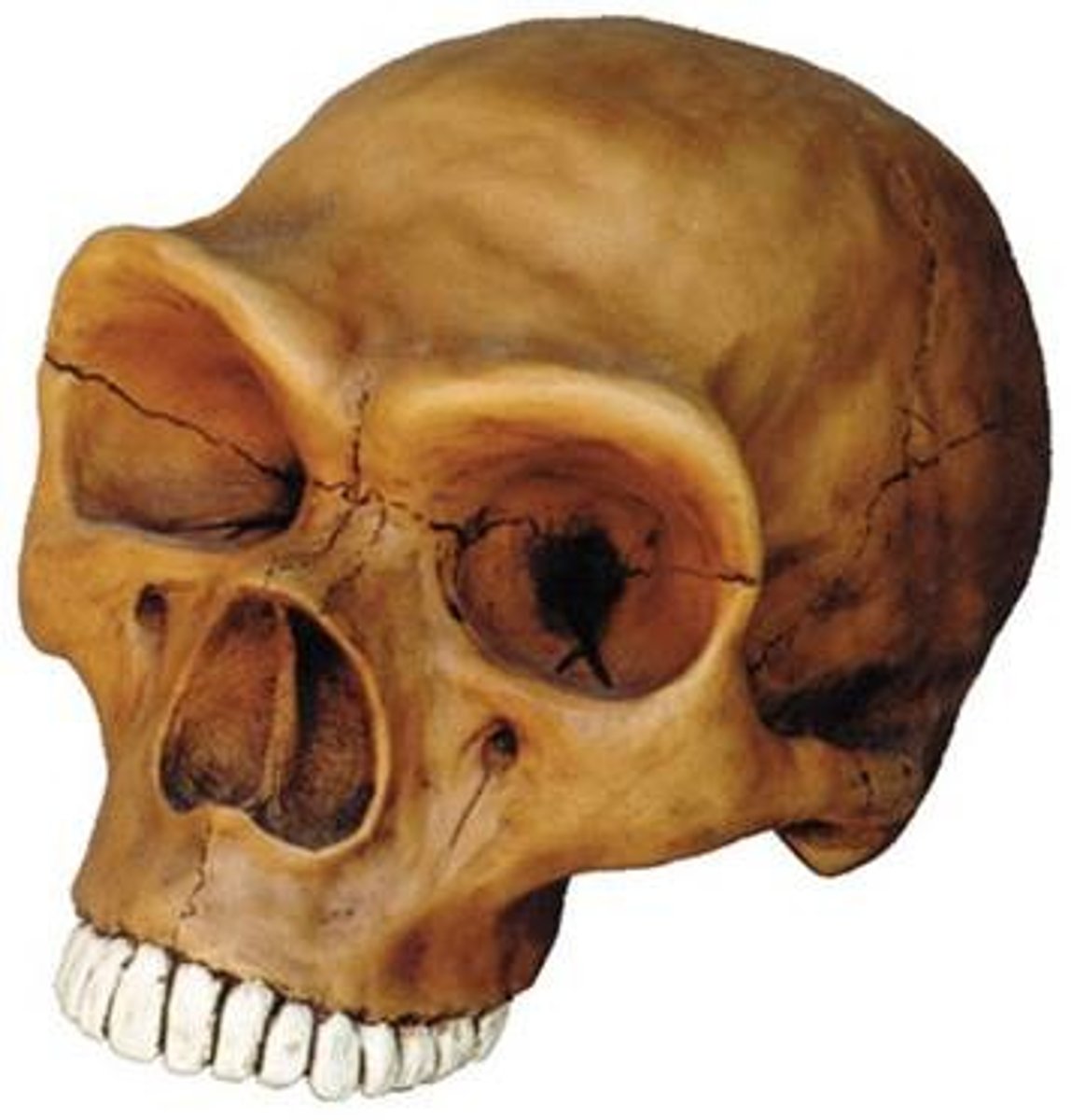
When did Homo Ergaster/Erectus first appear?
2 mya
When did Lucy first appear?
3.2 mya
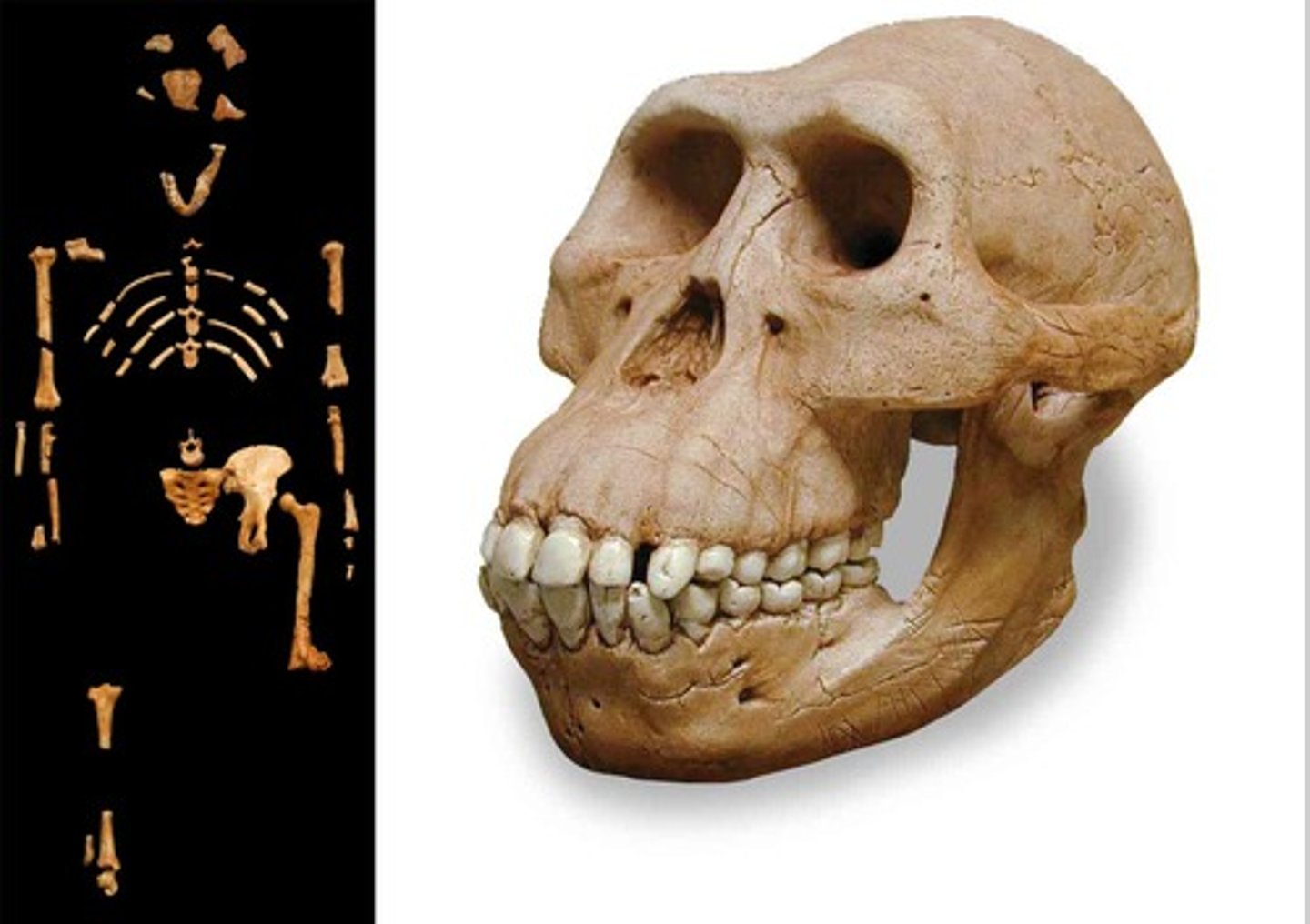
Early evolving homonid traits
Had features such as prominent brow ridge, sagittal crest, forehead slopes back, facial prognathism (facial bones project forward), foramen magnum in rear of skull, small cranial capacity
Modern hominid traits
No brow ridge, no sagittal crest, vertical forehead, no prognathism, central foramen magnum, large cranial capacity
Gene
Structural unit of hereditary information in the form of DNA nucleotide sequences
Allele
Alternative forms of a gene
Locus
Specific place along a chromosome where a given gene is located
Autosomal allele
Allele located on a non-sex chromosome
Genotype
An individual's inheritable genetic makeup
Heterozygous
Possessing two different alleles for a given biallelic gene
Homozygous
Possessing two of the same alleles for a given biallelic gene
Phenotype
The observed characteristics and traits, influenced by the genotype and the environment
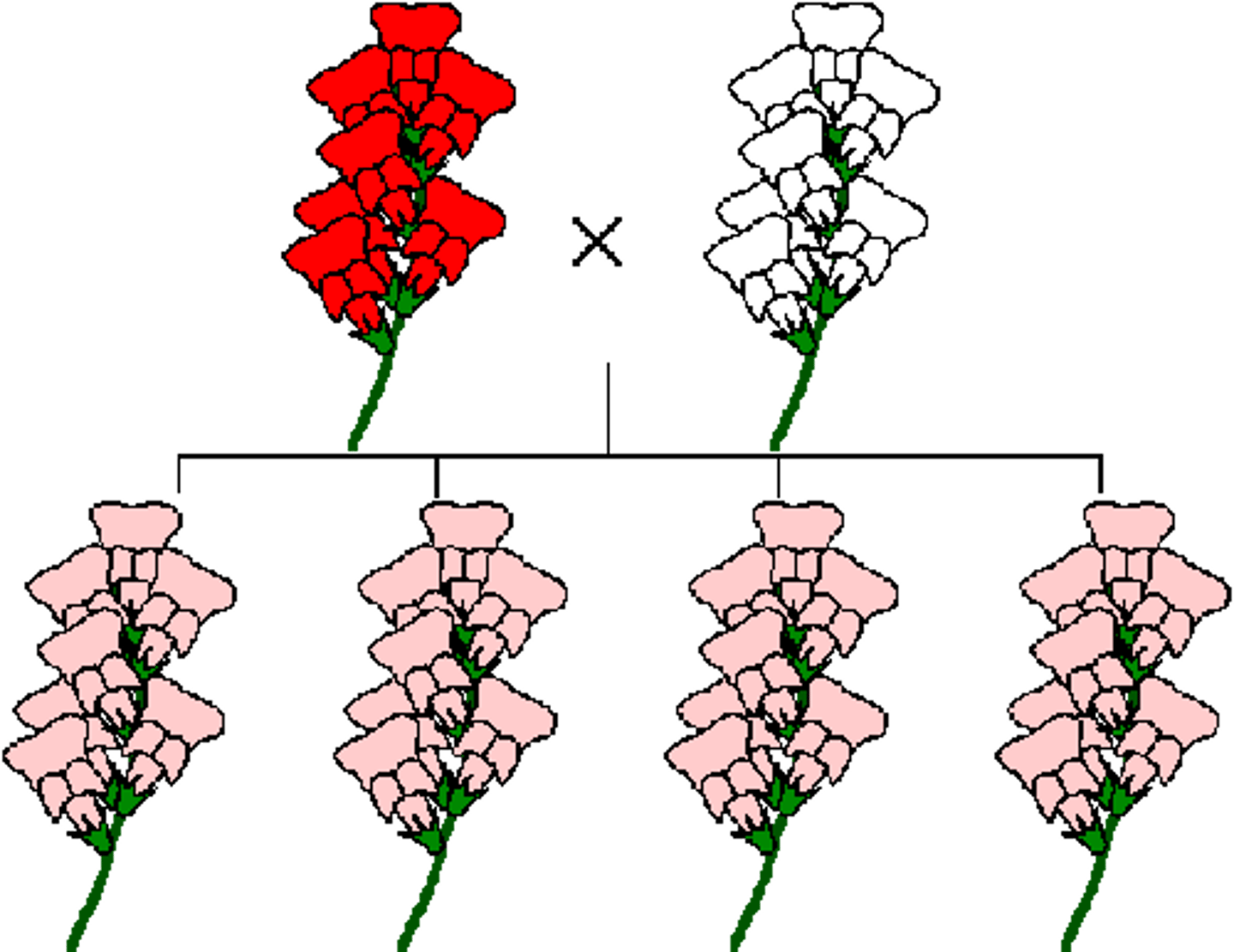
Incomplete Dominance
When the phenotype of the heterozygous is an intermediate between the homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive (AA = red, aa = white, Aa = pink)
Complete dominance
When the homozygous dominant and heterozygous genotype produce the same phenotype; from complete dominance from dominant allele (AA = red, aa = white, Aa = red)
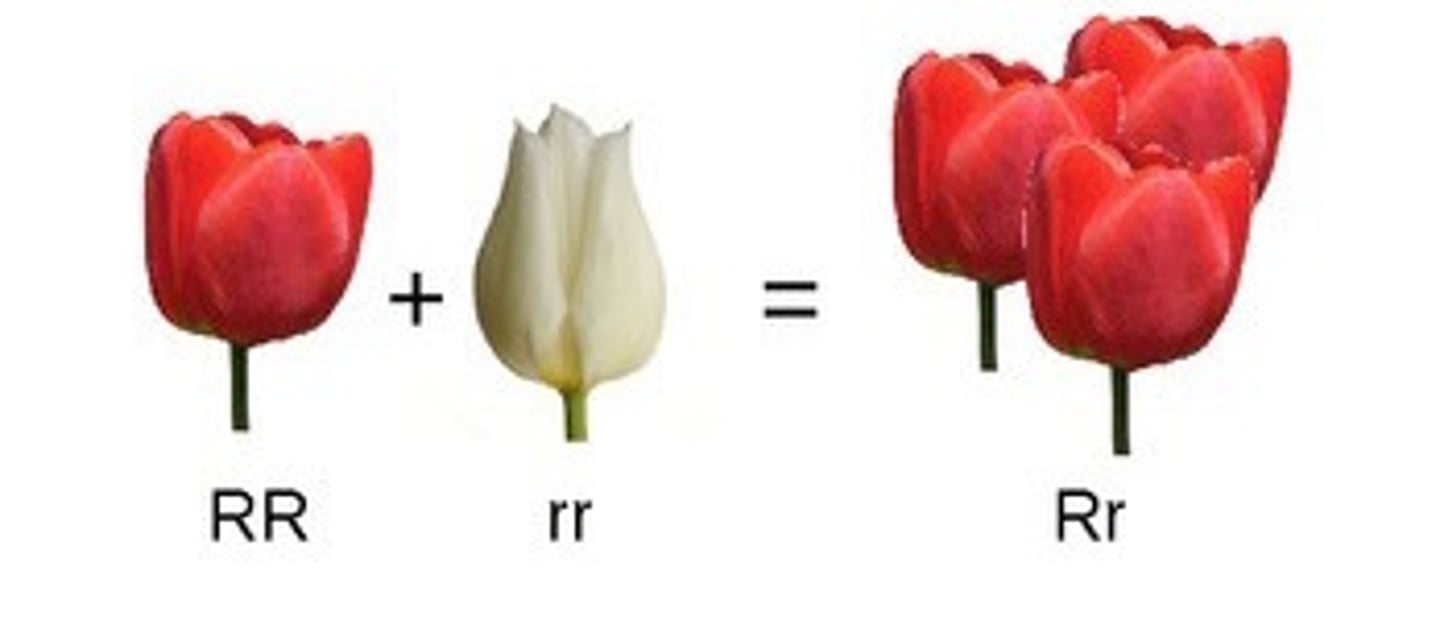
19th Century Evolution Scientist
Charles Darwin
Evolution
Changes in relative frequencies of alleles in a population's gene pool over time
Gene pool
Collection in relative frequencies of alleles in a population's gene pool over time
What is the Hardy-Weinberg Principle?
Makes 5 assumptions when NO evolution occurs in a population; NO evolution means genotype and allele frequencies are maintained in a population over time
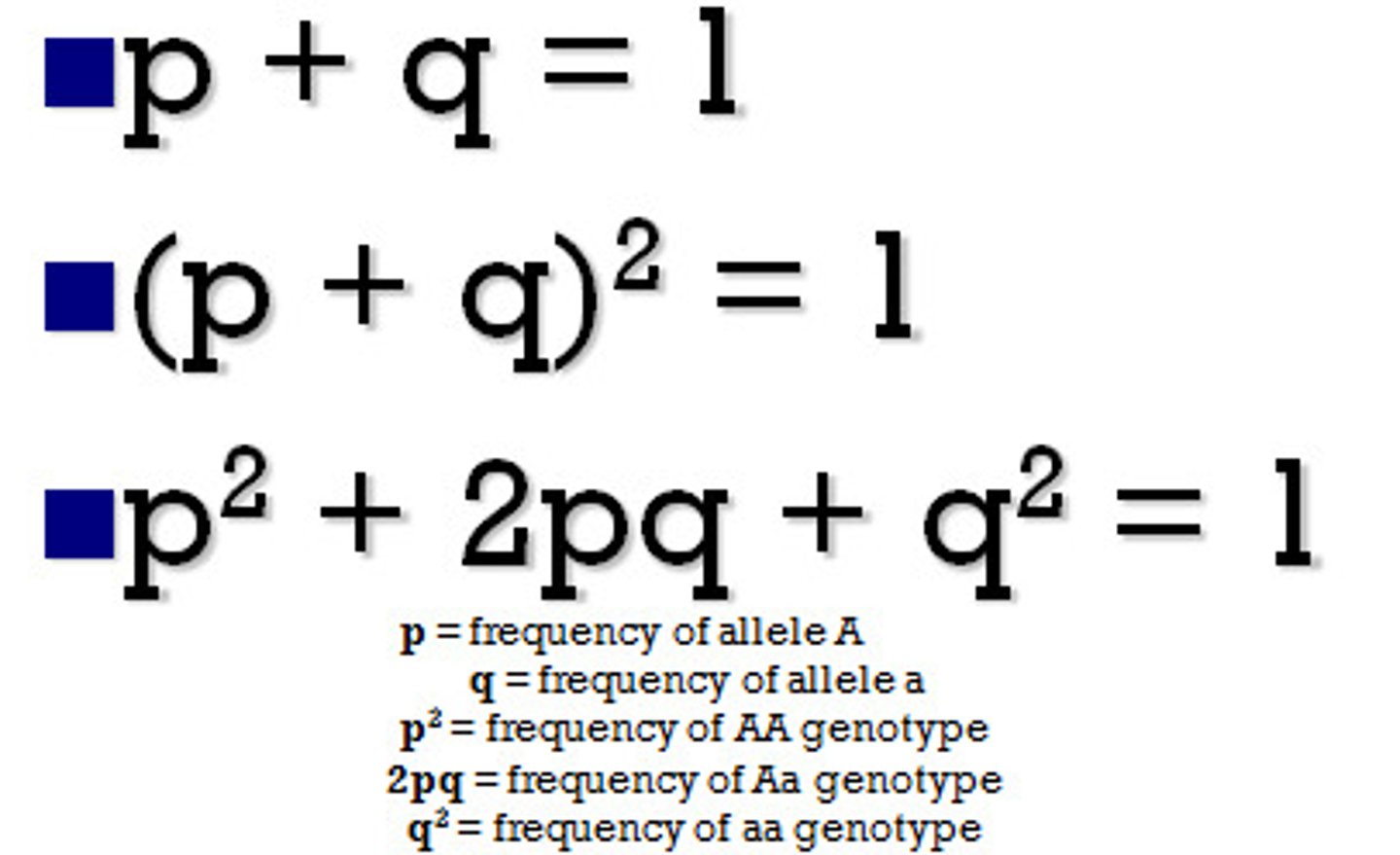
Hardy-Weinberg assumptions?
1. No mutation
2. No migration
3. No natural selection
4. No impact from genetic drift (large population size)
5. Random mating
**Under these conditions, allele and genotype frequencies will remain constant across generations aka maintaining an equilibrium
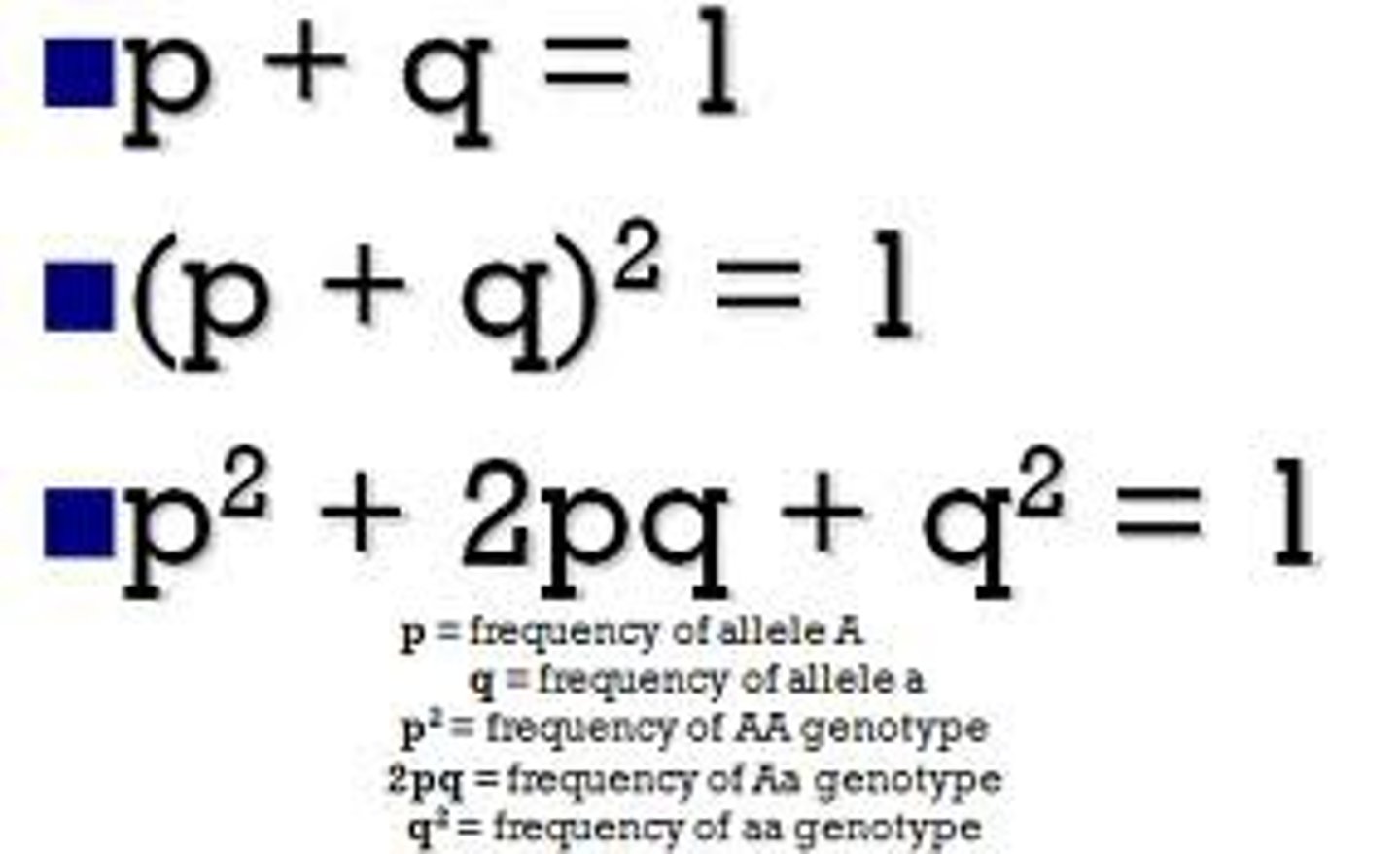
Why is Hardy-Weinberg important?
It is how we detect change
What happens when the conditions of the HW Principle are not met?
Evolution has occurred
Allele frequency calculations
Frequency of A (dominant) allele = p
Frequency of a (recessive) allele = q
p + q = 1
Genotype frequency calculations
use p and q (allele frequencies)
Frequency of AA genotype = p^2
Frequency of Aa genotype = 2pq
Frequency of aa genotype = q^2
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
If population is in HW equilibrium, no evolution is occurring, so you can calculate the _________
expected genotype for the next generation
Mutations
Biochemical changes in the genetic material of the organism
Gene flow
The emigration or immigration of genes out of or into the population
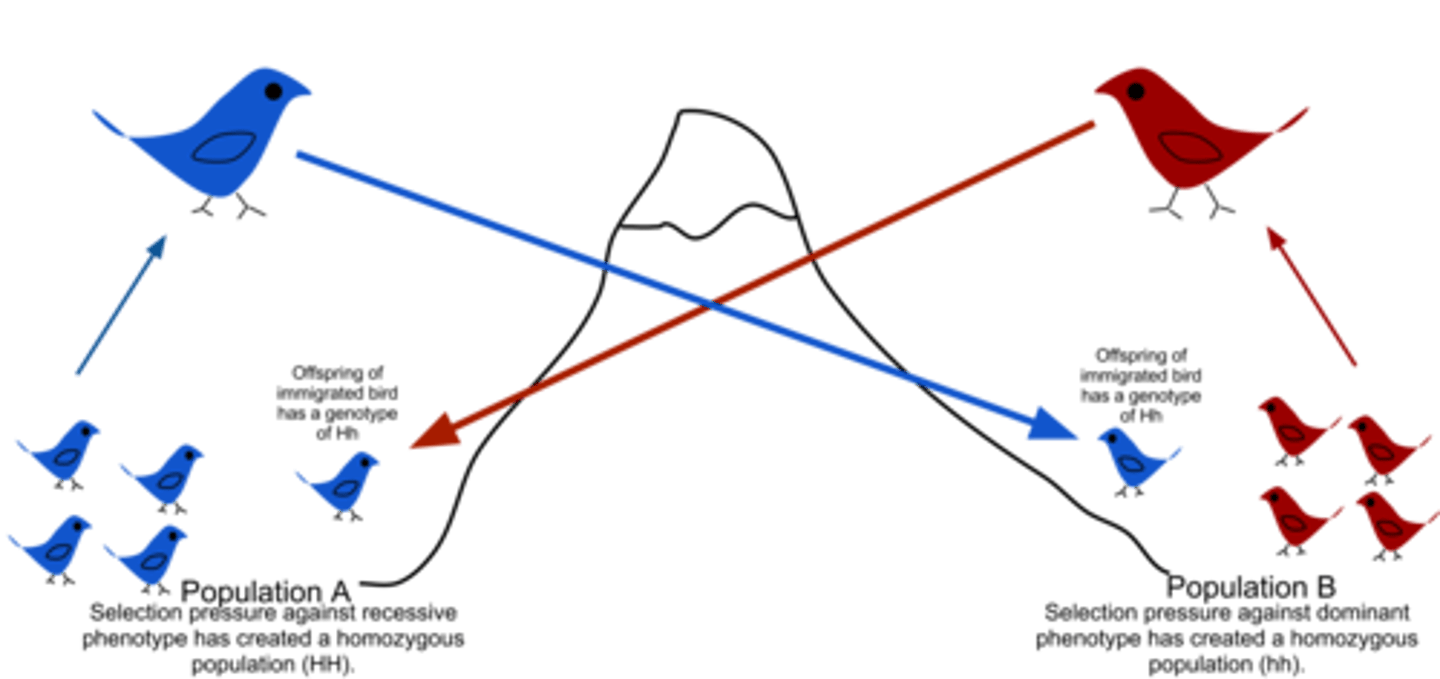
Genetic drift
When unpredictable variations change the structure of the gene pool

Natural selection
When a particular phenotype has a greater (or lesser) reproductive success than an alternative phenotype.
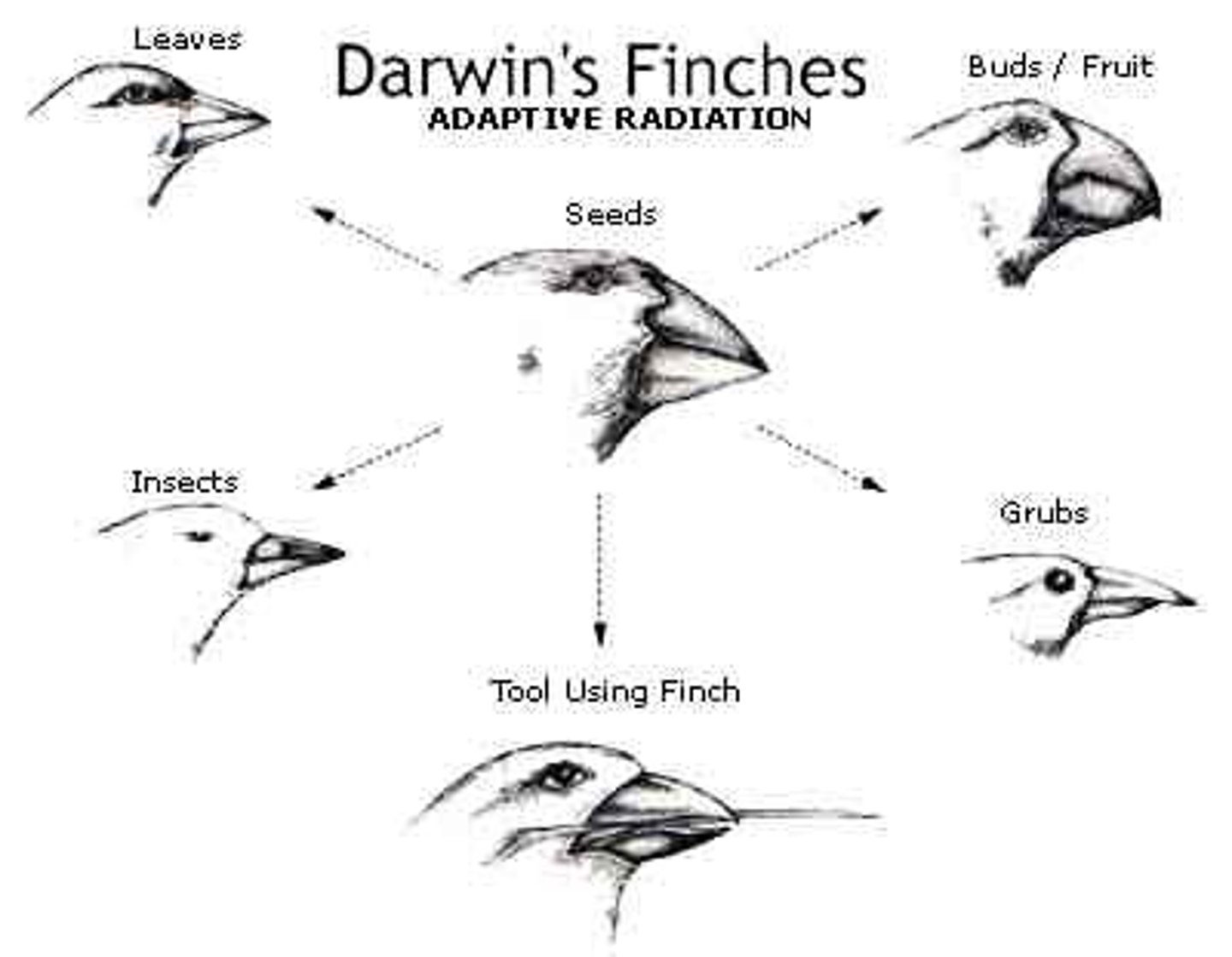
Allelic frequencies are impacted by _____, ______, and _______
Natural selection, genetic drift, and migration
If a population is in HW equilibrium, genotype frequencies depend on _____________
Allele frequencies
Populations that are endangered should be worried about ____________
Genetic drift (due to small pop. size)
On an island, a new predator is introduced. Prey on the island should be worried about ____________
Natural selection
How to calculate total magnification
Ocular (10x) x Objective Lens
(Objective lenses are either 4x, 10x or 400x)
Field diameter
Diameter of the microscope's field of view
(Mag1)(FD1)=(Mag2)(FD2)
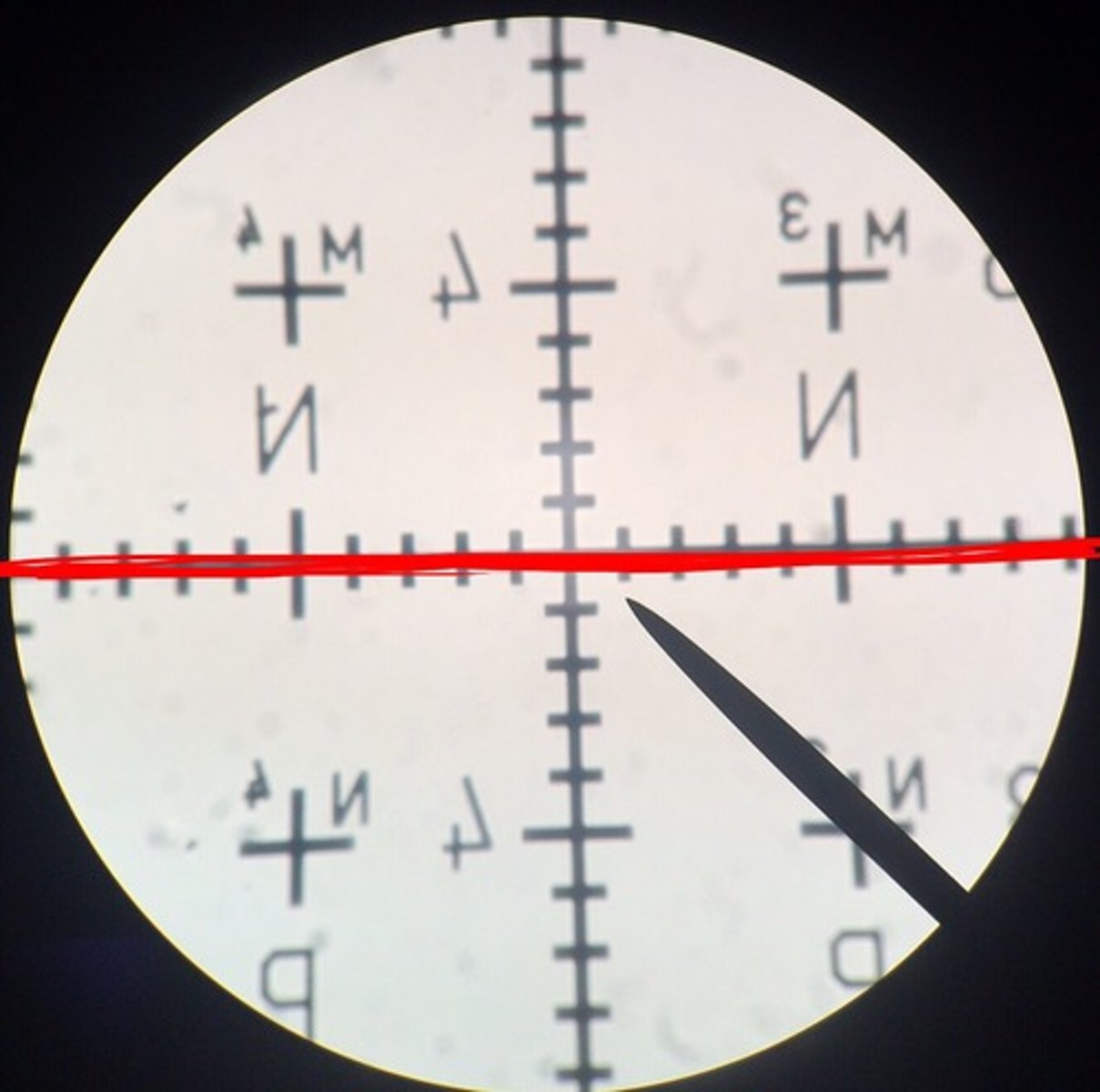

What units is field diameter usually measured in?
mm or μm
1000 μm = 1 mm
Working distance
Distance between a lens and in focus object
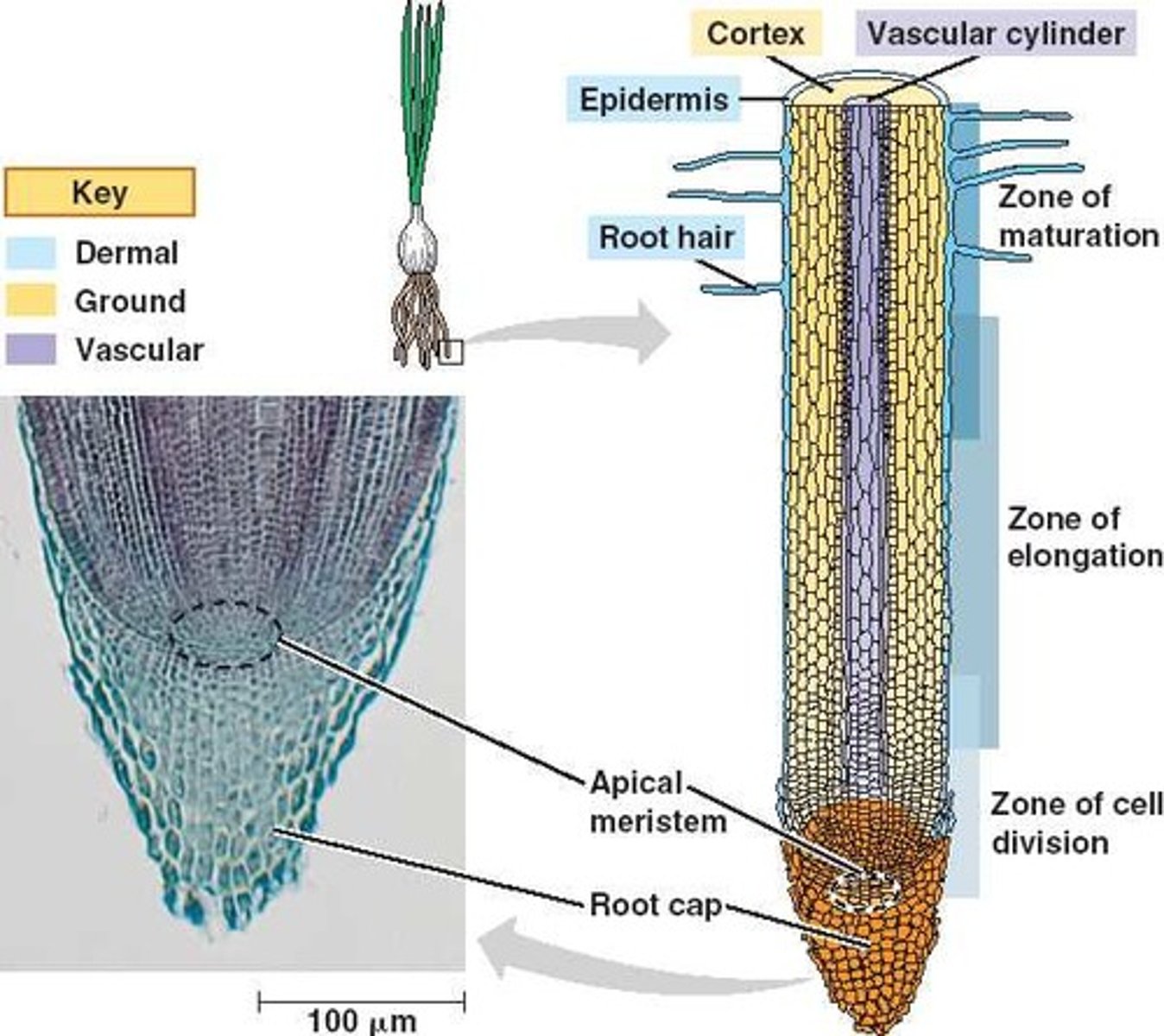
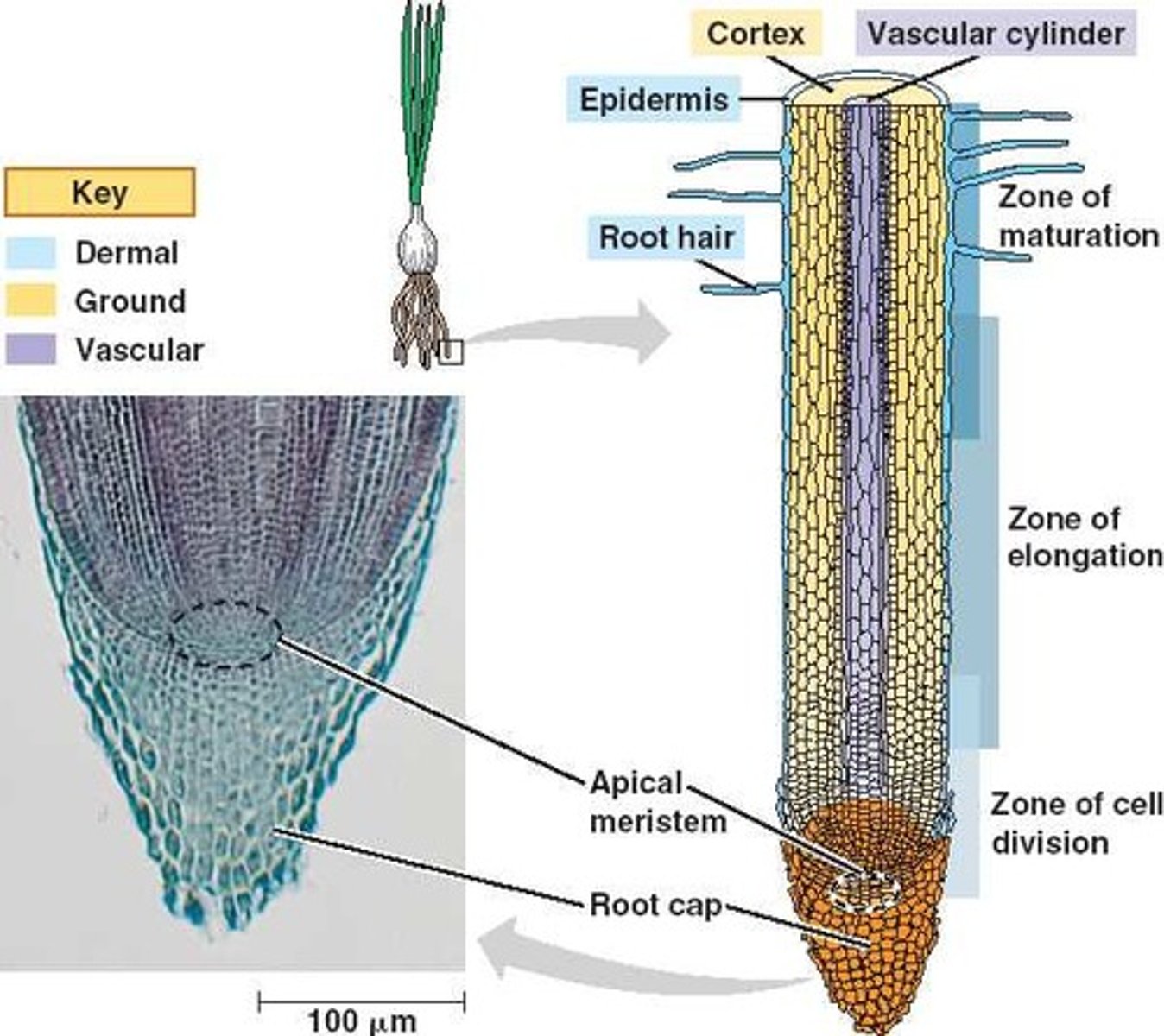
Meristem
Plant tissue that remains embryonic for intermediate growth
Plastid
Family of plant organelles; includes chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and amyloplast
Chloroplast
Absorb sunlight, produce energy for plant via photosynthetic electron transport chain
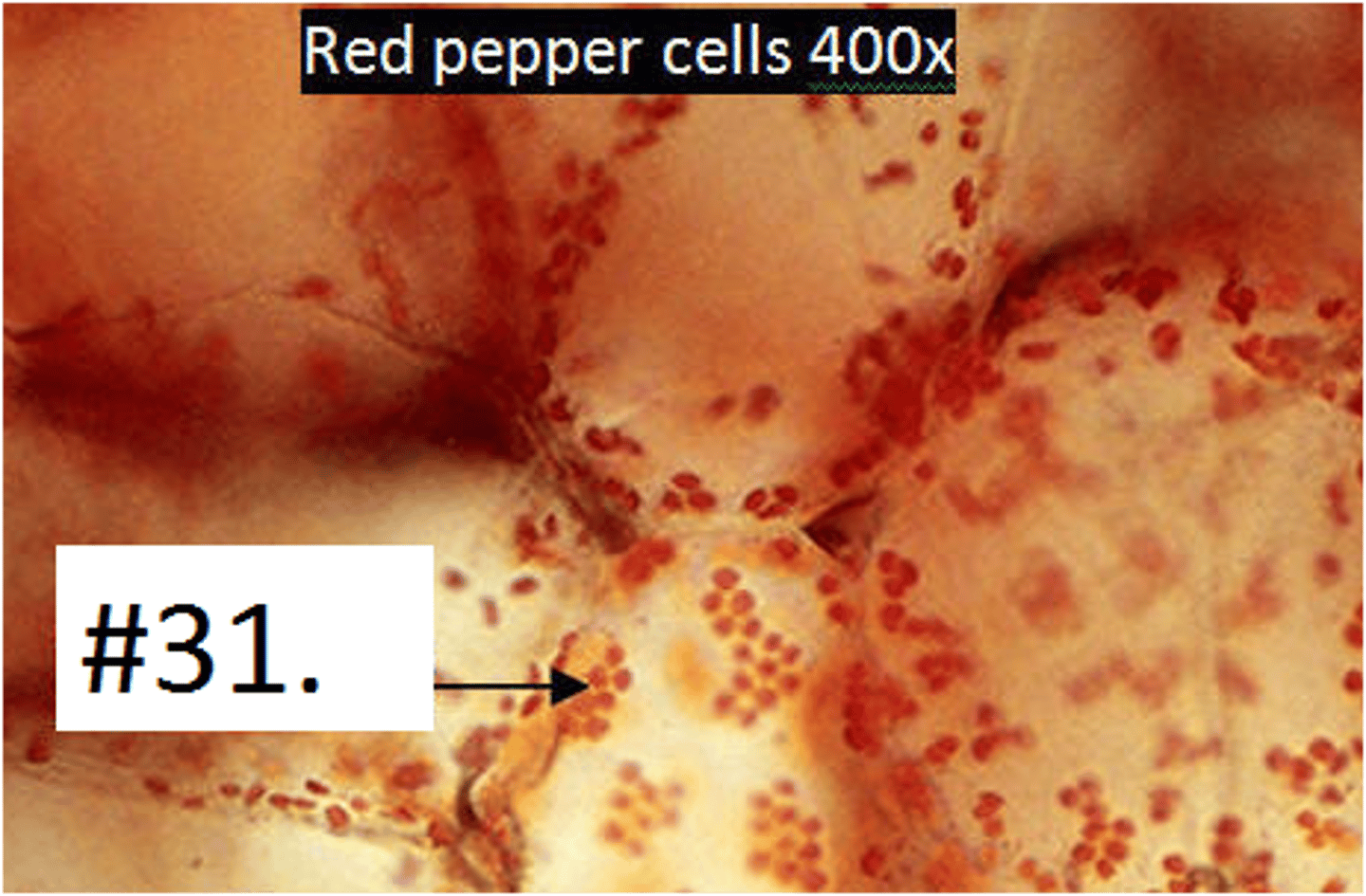
Chromoplast
contain carotenoids (red, orange, yellow pigments), attracts birds to eat plant and disperse the seeds
Leucoplast
Contain no pigment, storage for starch and oils
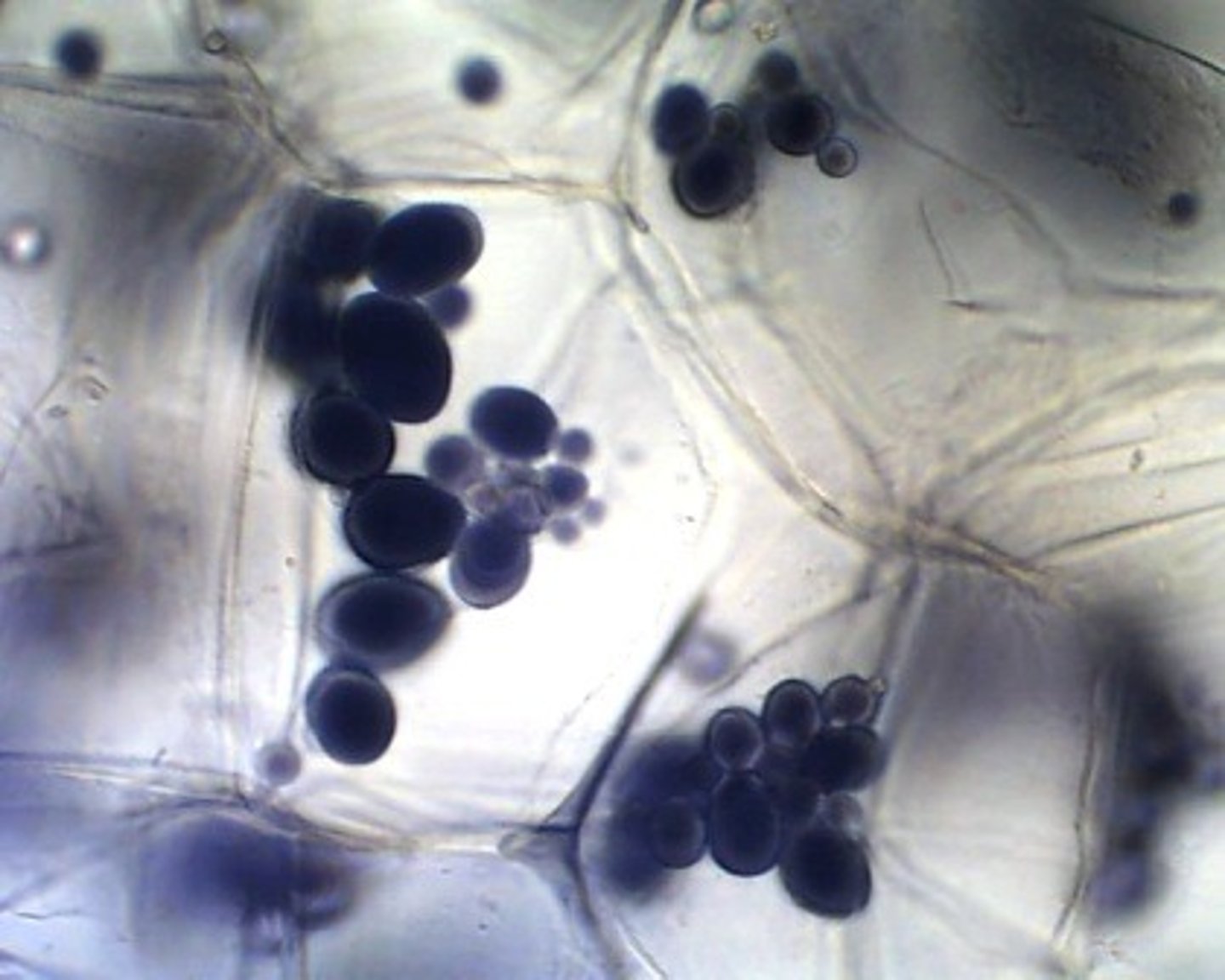
Starch
Storage form of carbohydrates in plants
Crystals
Calcium ovulate, found in various tissue for protection and defense, stored in vacuoles or parenchyma cells
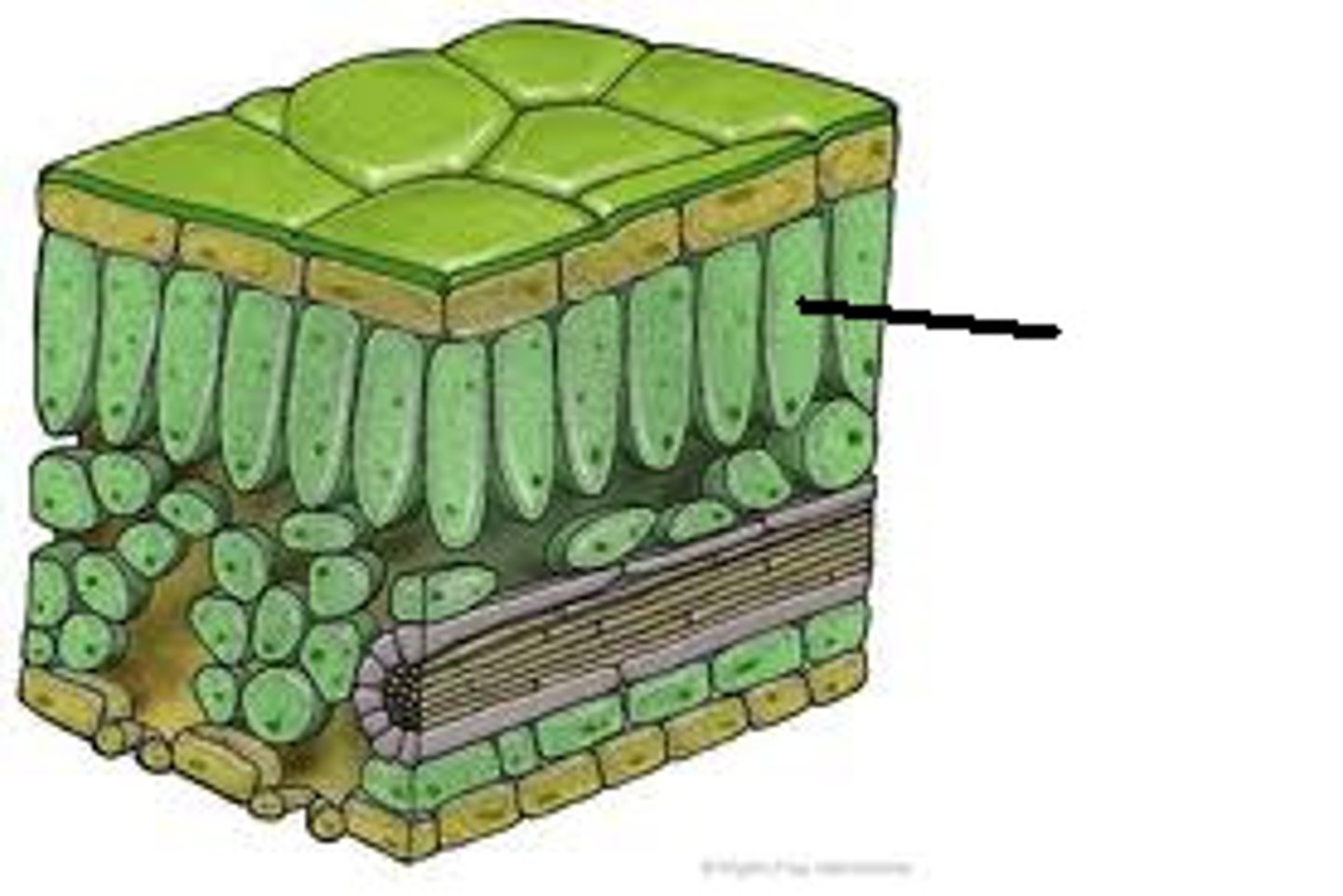
Dermal Tissue
Epidermis and periderm
Ground Tissue
Parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma fibers
Vascular Tissue
Xylem and phloem, continuous veins of plant from roots to leaves
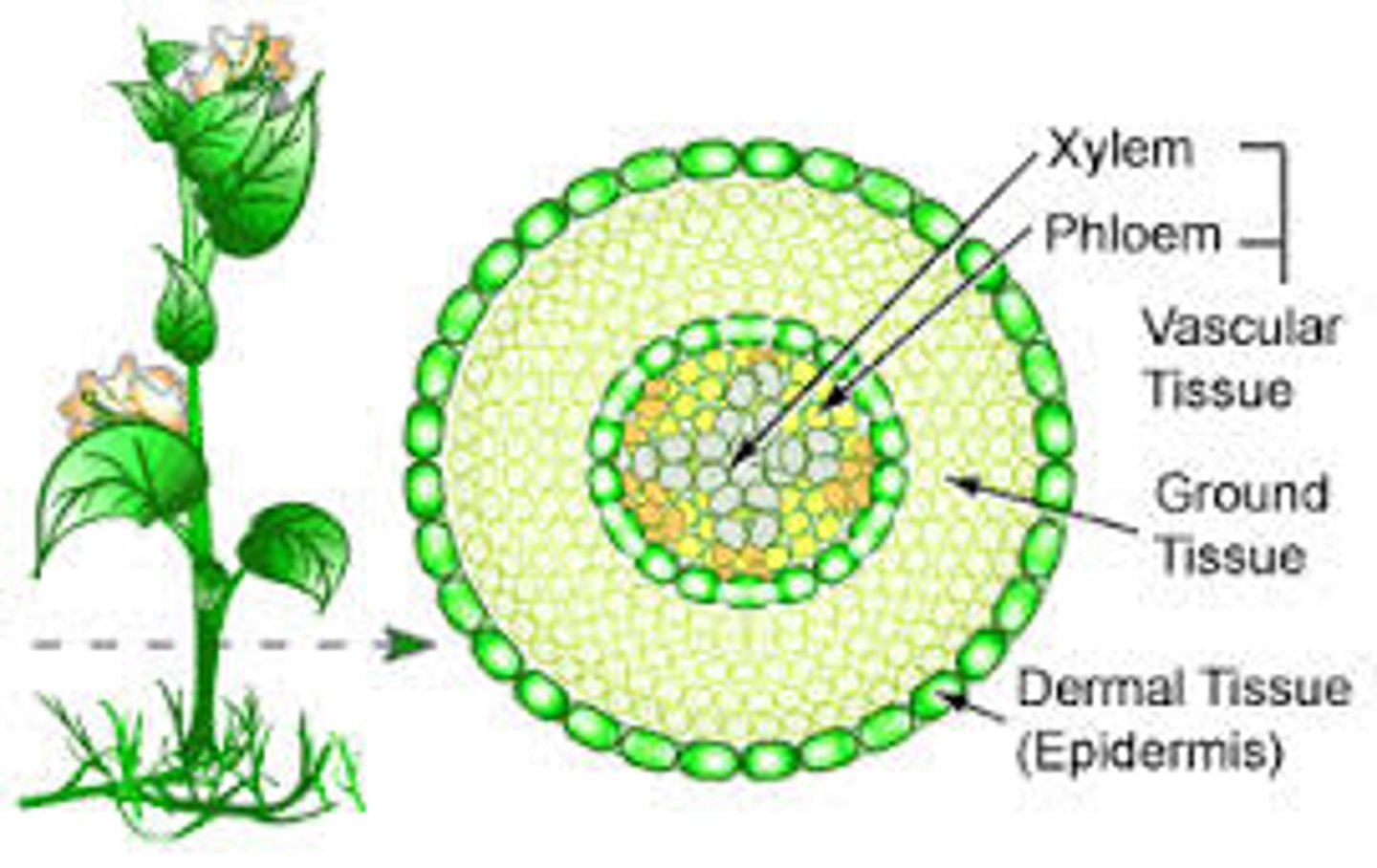
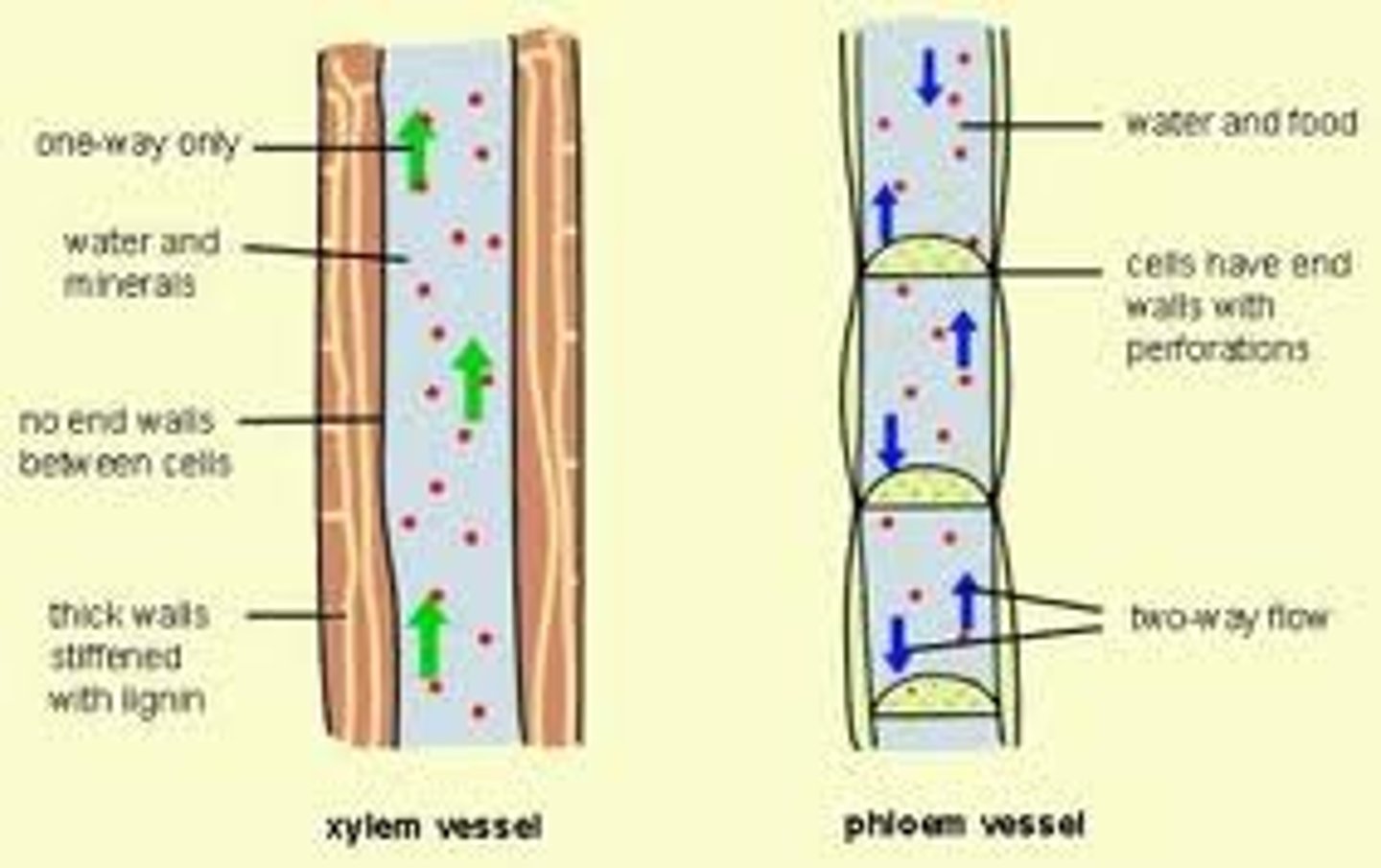
Xylem
Dead tissue, transports water and minerals
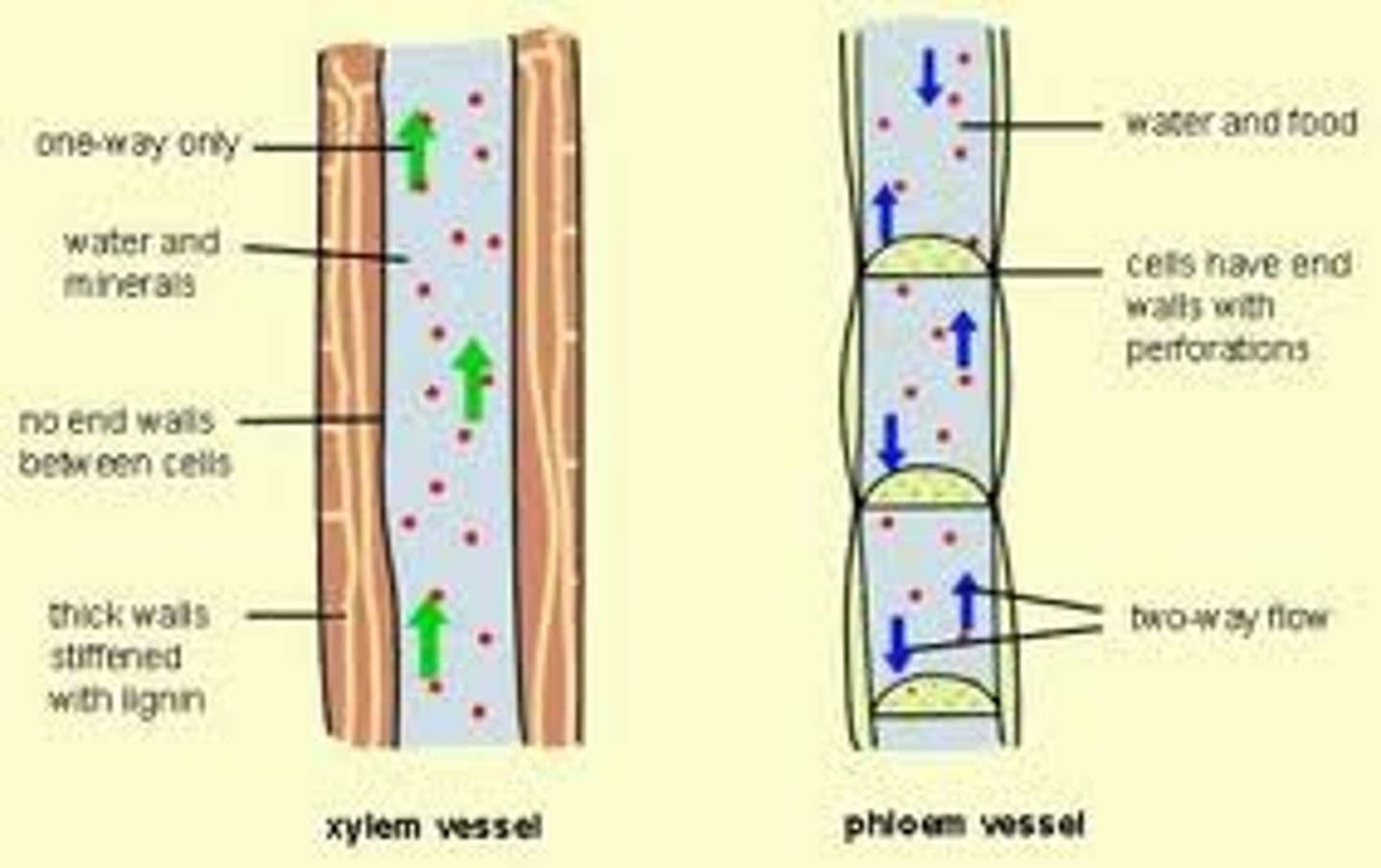
Phloem
Alive tissue, transports sugars
Meristematic cell types
Apical and lateral meristems, for primary and secondary cell growth, in shoots and roots
Undifferentiated cells that give rise to new cell types
General cell types
Parenchyma cells; storage molecules, may contain chloroplasts
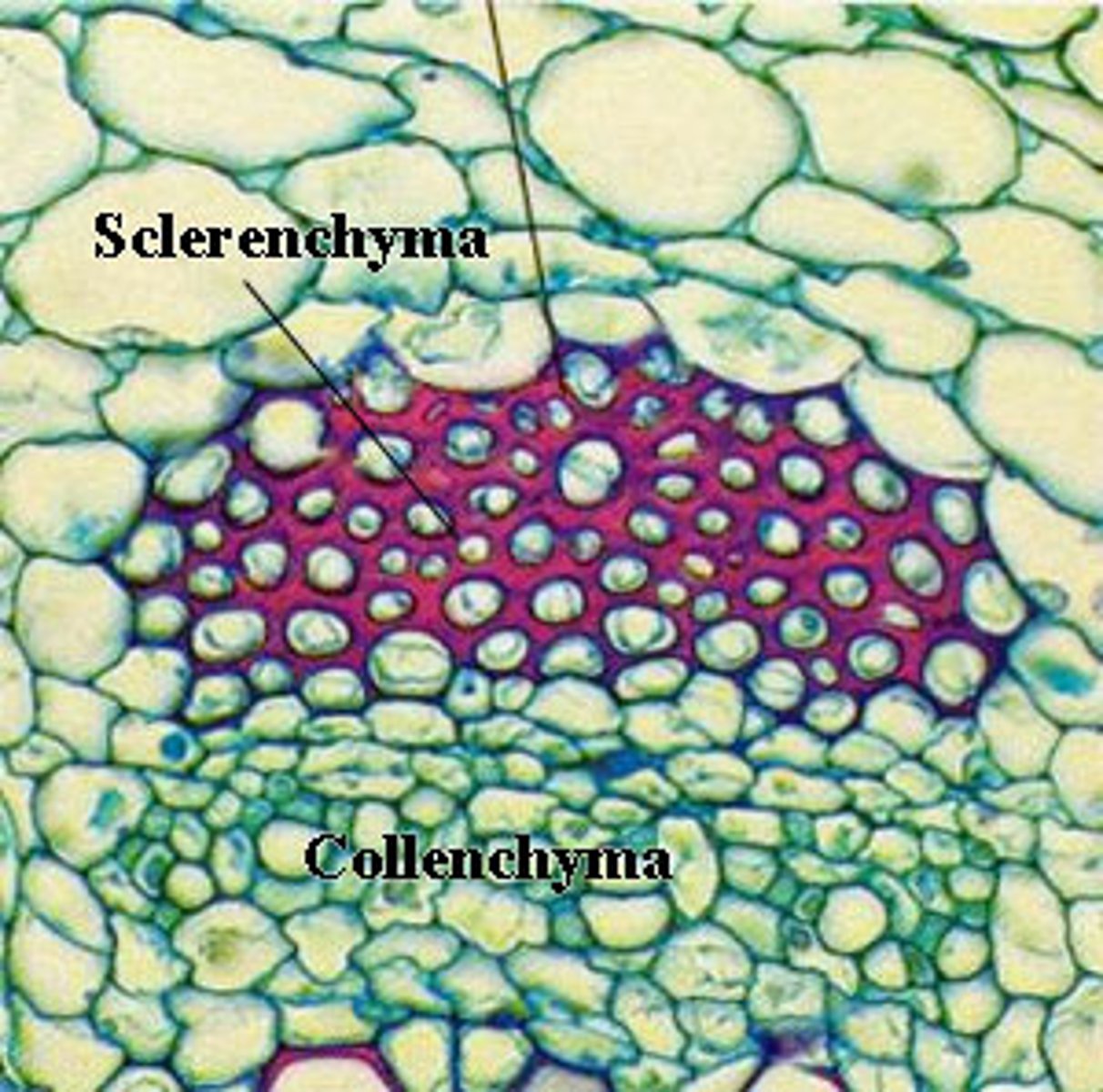
Supportive cell types
Collenchyma
- Alive when functional; provide support in young plants
Sclerenchyma
-Dead when functional; lignified fibers
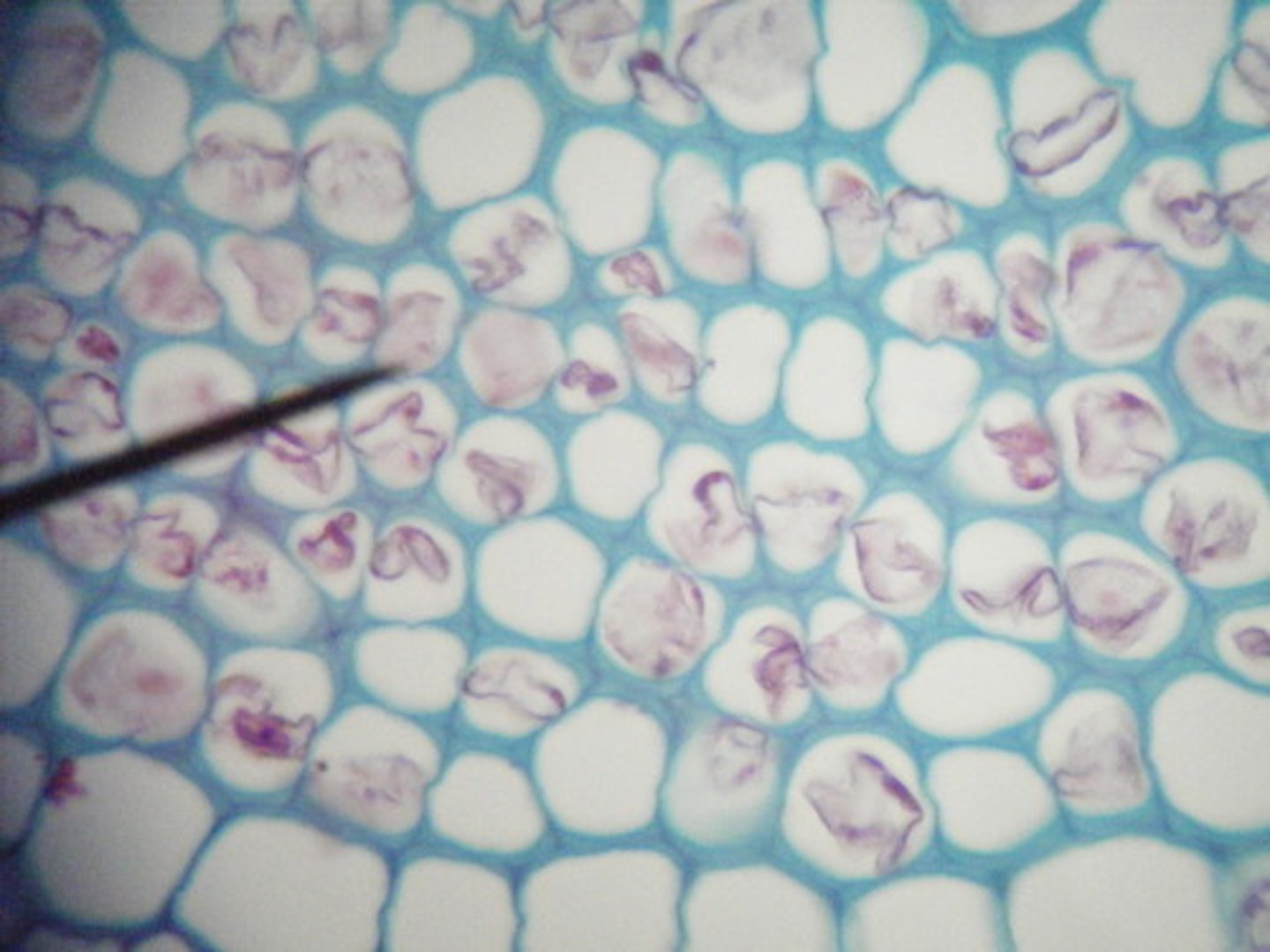
Vascular cell types
Phloem tissue
- Sieve cells, sieve tube elements; conduct sugars
Xylem tissues
- Tracheids (long, thin, tapered ends), Vessel elements (short, wide, with perforation plates at the end); conduct water and minerals
Protection cell types
Epidermis and periderm
Parenchyma
Unspecialized cells that carry out metabolism, stores products, develops into differentiated cell types, contain vacuoles, thin cell
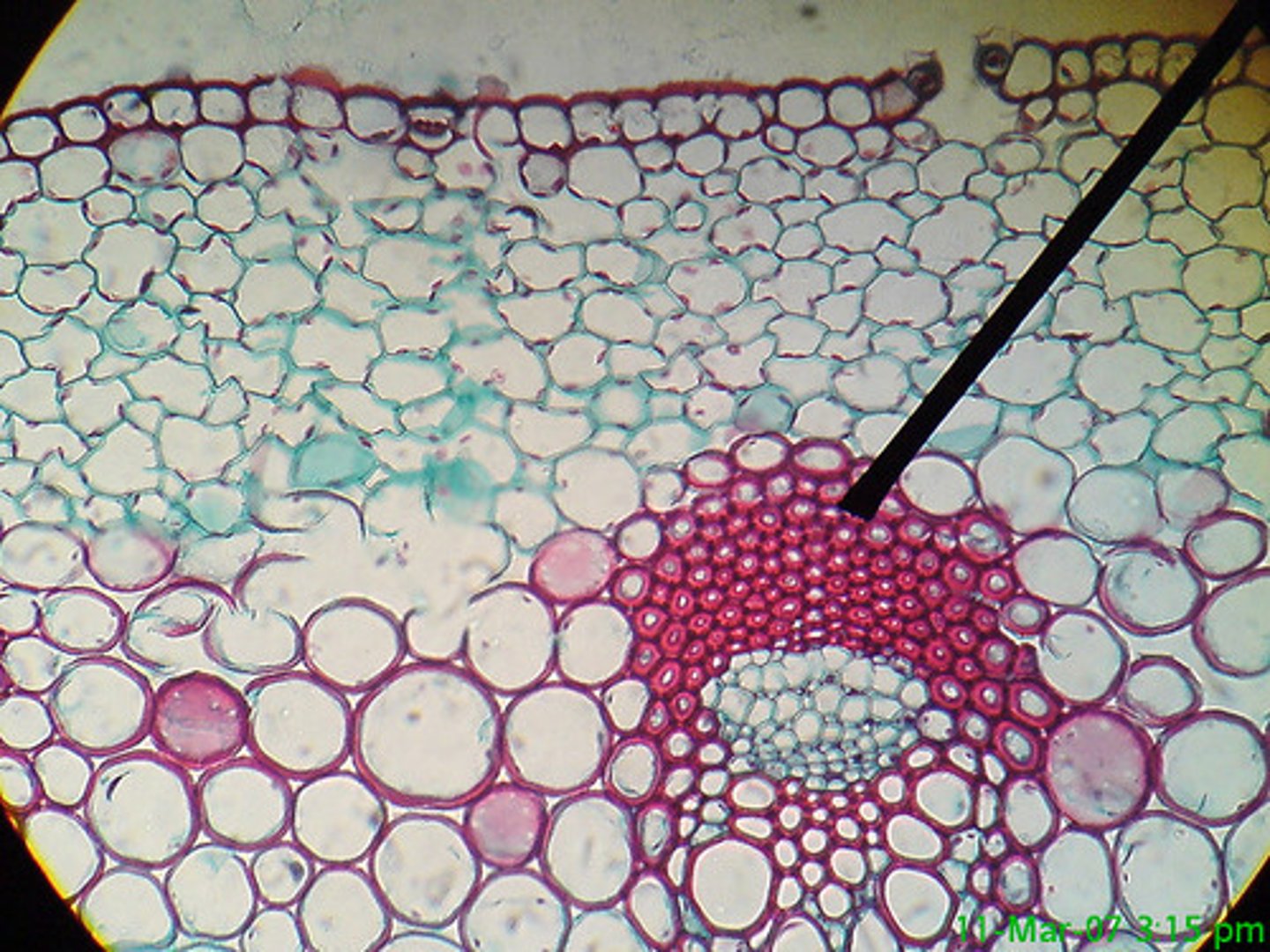
Collenchyma
Flexible plant cell, support young plant without restraining growth, thickened with pectin and cellulose
Sclerenchyma
Rigid supportive fiber cell, thick secondary cell walls, strengthened by lignin at maturity
What is the primary source of food and energy for all plants?
Photosynthesis
What does the PSN ETC require?
Light energy, takes place on thylakoid membrane
the calvin cycle
It is the process of converting CO2 into sugar, and it requires energy from NADPH and ATP but NOT LIGHT
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
The stoma
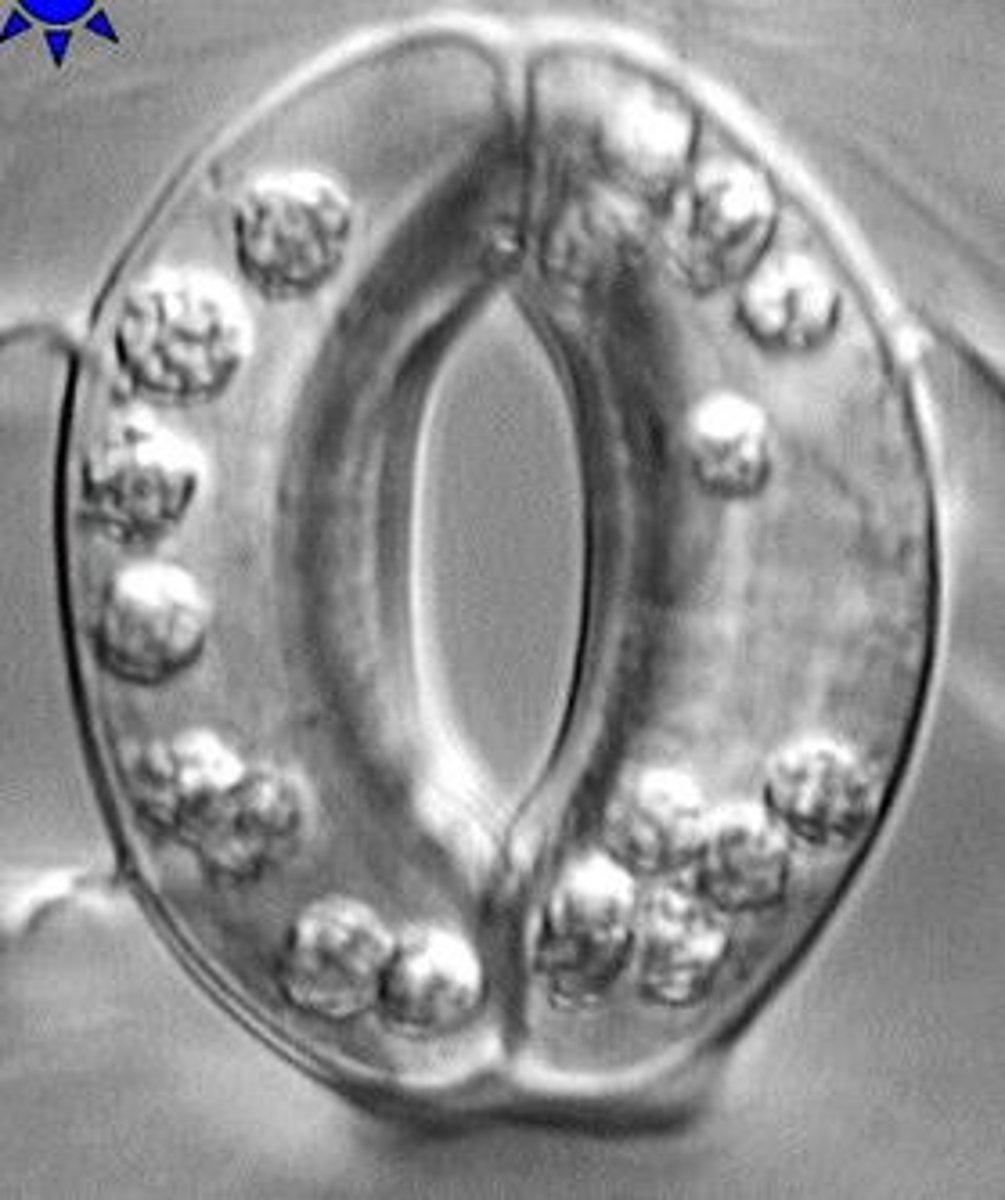
PSN uses ____ and releases ______
CO2 and O2
What is the oxidizing agent in PSN
H2O, its the source of O2
Cuticle
Waxy substance, water impermeable
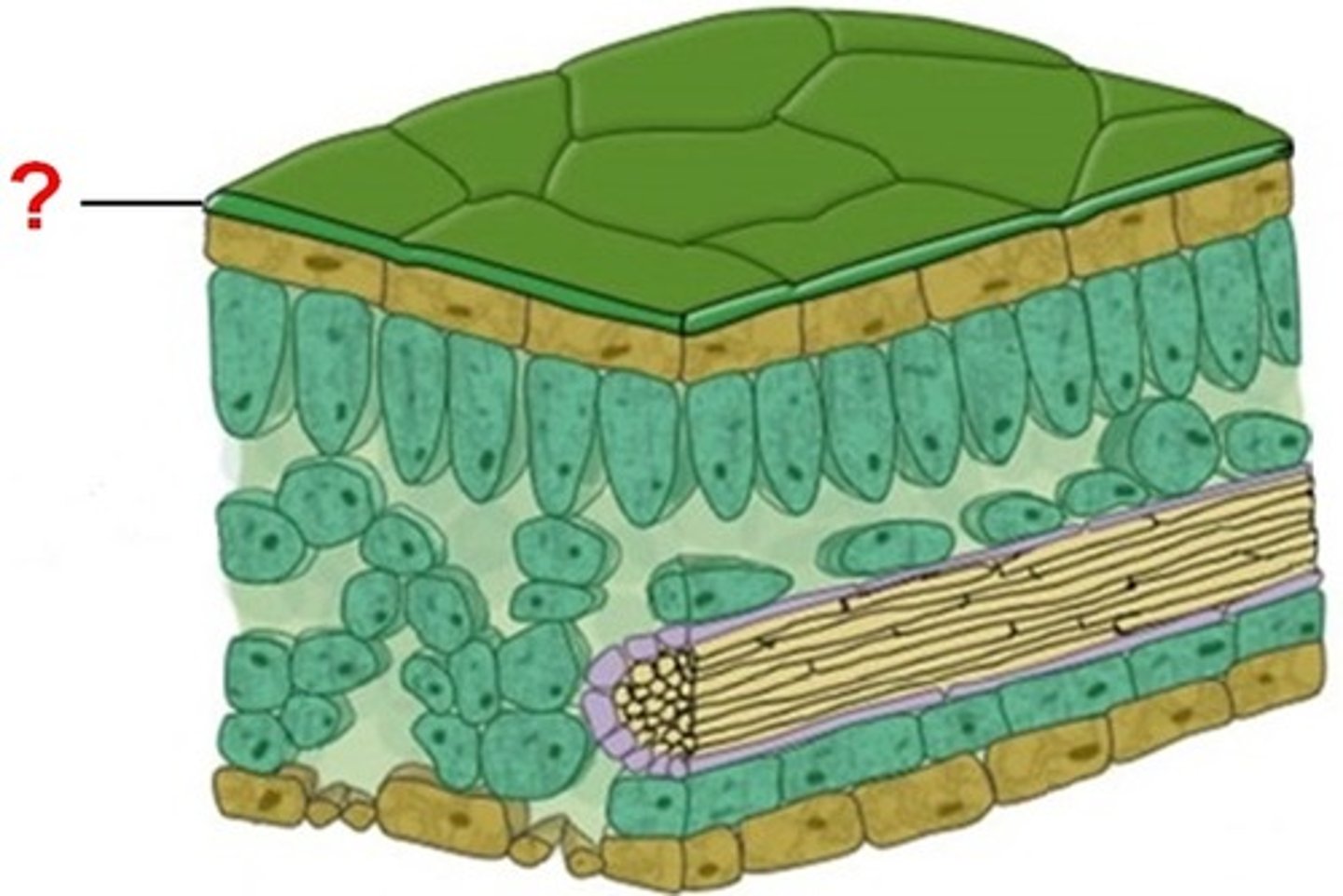
Palisade mesohyll
light absorption occurs here, high concentration of chloroplasts