Cell Signals and Nervous System PMCY 4020
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
In the PNS, neuroglia is made of __. These cells cover the surface of neuron cell bodies, provide support and might control their microenvironment
Satellite cells.
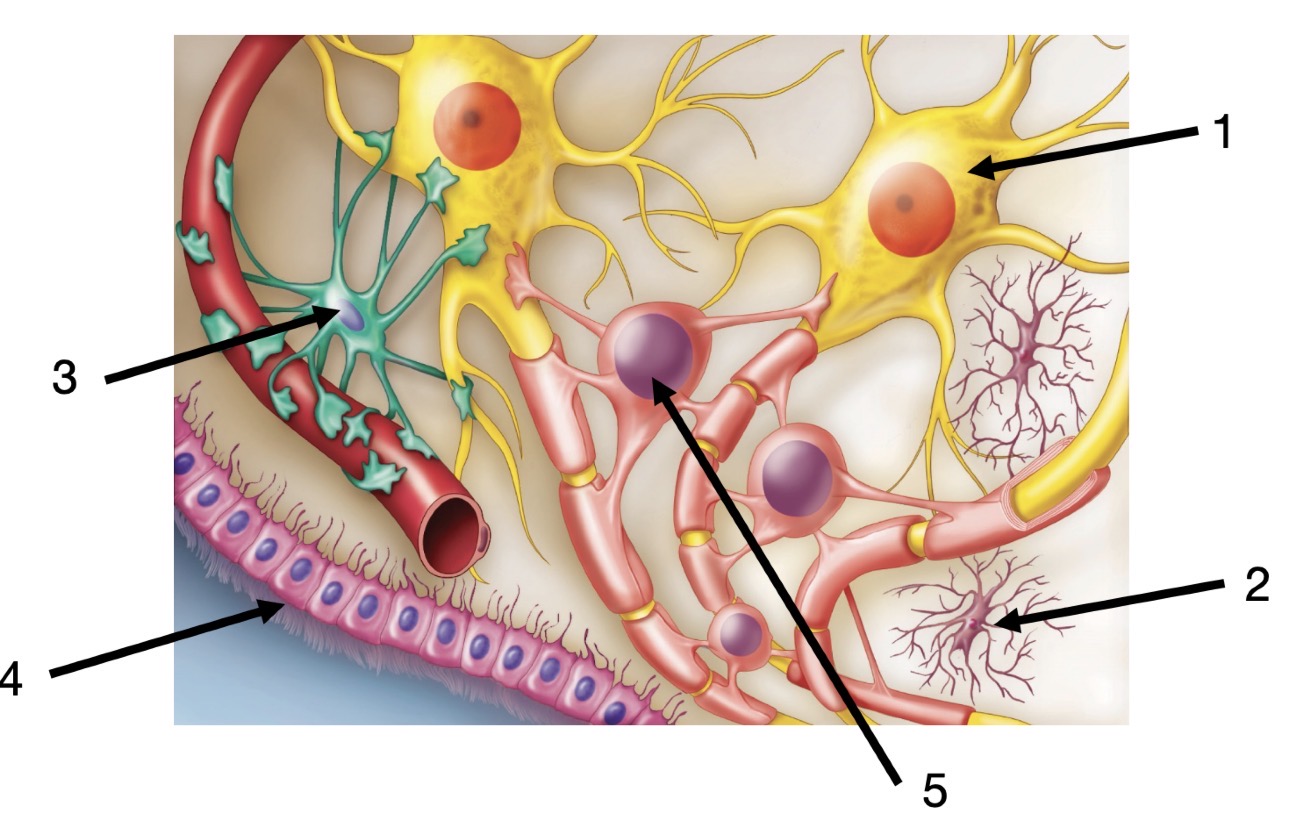
Match.
1.Neuron
Microglia
Astrocyte
Ependymal cell
Ooligodendrocyte
An adult male has difficulty moving his hand after a head injury that resulted in damage to neurons in his brain. The damage is likely permanent because __________.
A. He is an adult, and CNS neurons can only regenerate in childhood
B. Inhibitory proteins in the PNS will prevent axons in his hand from ever regenerating
C. Neurons in the CNS lack Schwann cells, which play a major role in axon regeneration
D. Astrocytes that surround the CNS axons do not have enough myelin for regeneration
C
If astrocytes were damaged or lost, how would this impact CNS function?
A. An individual may experience difficulty initiating movement, or slowness in movement
B. The composition of the CSF would be very similar to blood plasma
C. Production of CSF would be diminished
D. Toxic substances could easily build up in the brain
B. & D.
In the CNS, neuroglia is made of __. Produce myelin sheaths around axons
Oligodendrocytes.
Myelin sheaths give a white color:
White matter
__ __: cell bodies and dendrites of neurons in the CNS
Grey matter
In the PNS, __ cells support nerve degeneration; When an axon is cut, the severed portion degenerates and is phagocytosed by __ cells
Shwann
Schwann cells form a __ __. These structure is a guidance track for the regenerating axon
Regeneration trube
Schwann cells seem to secrete __: promote axon regeneration
Neurotrophins
In the CNS, neurons die upon injury or die later via:
Apoptosis
Regeneration in the CNS is __ by inhibitory proteins at the surface of myelin sheaths (ie. Nogo)
Prevented
A __ __ rapidly forms, further preventing axon repair
Glial scar
In the CNS, neuroglia is made of __. Main form of immune defense in the CNS. Able to detect sites of infection or damage
Microglia.
Microglia are also involved in __ __
Synaptic pruning
An altered state of the extracellular environment can lead to microglial activation:
Cells become ameboid and become phagocytic cells. They can detect ATP released from damaged cells thanks to ATP receptors found on their surface
Microglia have the capacity to realse __ ___, ending ___ responses and contributing to neuroprotection
Anti-inflammatory; inflammatory
In the CNS, neuroglia is made of __, they help to regulate the external environment of neurons
Astrocytes
__ are the most abundant microglia in the CNS
Astrocytes
Astrocytes encircle the endothelial cells of blood capillaries with projections named:
End-feet. They are also adjacent to the space between the axon terminal and another neuron
Astrocytes seem to perform many different functions:
K+ uptake. Astrocytes might soak up the K+ exiting from the neuron during an action potential
Glucose take up from the blood and releasing lactate for neurons to use
Neurotransmitter take up
Synapse maintenance, formation and maturation
GDNF secretion (promotes neuron survival)
Astrocytic dysfunction is linked to __
Neurodevelopmental disorders such as Alexander’s disease (point mutation)
Astrocytes induce the formation of the ___ __
Blood-brain barrier
Astrocytes release signaling molecules that regulate neuron function:
Gliotransmitters
Capillaries across the body are __. They have pores. Non-specific filtering can happen
Fenestrated
All endothelial cells in the blood-brain barrier are joined by tight junctions and surrounded by __.
Astrocytes
Molecules in the blood can only move through the endothelial cells either by __, __, __.
Diffusion, active transport, or endocytosis.
*O2, CO2, and nonpolar molecules can cross
*Ions and polar molecules require channels and carriers
Astrocytes secrete __ to increase the production of transporters and tight junction proteins; Endothelial cells __ promoting astrocyte growth and differentiation
Regulatory molecules; secrete regulators
__ cells are ciliated epithelial cells lining the entire ventricular surface of the CNS and the central canal of the spinal cord
Ependymal
Ependymal cells also produce __ __ . Using their cilia, they ensure that the _ circulates in the ventricles. It transports nutrients signaling molecules and remove waste products
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Transmission in synapses occurs in one direction: from the __ neuron to the _ neuron or effector cell
Presynaptic; postsynaptic
Explain Otto Leowi experiment
Used two frog hearts to demonstrate existence of neurotransmitters
The neurotransmitter discovered was acetylcholine
Can either be chemical or electrical
Stimulate vagus nerve
Heart rate slows
Add fluid to recipient heart
To be electrically coupled, cells must be almost what? Why?
Must be almost the same size and joined by areas of contact with low electrical resistance
Allows the impulses to be regenerated without interruption
Two electrically coupled cells are joined together by:
Gap junctions
Gap junctions are made of proteins called:
Connexins
__ connexins form a _, then two _ from opposing cells come together to form a complete gap junction
six; hemichannel; hemichannels
The _ muscle has gap junctions that allow the whole organ to be contracted as a unit
Cardiac
_ synapses are the most abundant type of synapse. Occurs when the presynaptic axon releases neurotransmitters
Chemical
The axon endings of the presynaptic neuron are called:
Terminal boutons
The space between the presynaptic and the postsynaptic cell is the:
Synaptic cleft
_ _ are located in the terminal bouton. They contain neurotransmitters awaiting to be released
Synaptic vesicles
Describe neurotransmitter release:
Action potentials reach axon terminals
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels respond to the action potentials and open. Ca2+ enters the cell
Ca2+ binds to synaptotagmin, triggering the fusion of the synaptic vesicle to the plasma membrane leading to exocytosis of neurotransmitter.
Once released, the neurotransmitters reach the postsynaptic membrane where they bind to specific receptors
Binding causes the opening of ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane: chemically regulated channels
When chemically regulated channels open, they produce a:
Graded potential
If Na+ and Ca2+ channels open, they produce a postsynaptic membrane becomes less negative: graded depolarization called:
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
If Cl- channels open, the postsynaptic membrane becomes more negative: graded hyperpolarization called
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
EPSPs and IPSPs are produced in the __, and must propagate from the cell body to the _ _ of the axon to influence action potential production
Dendrites; initial segment
The initial segment has a high Na+ and K+ channel density and is where _ _ and the first action potential occurs
Synaptic integration
One neuron can make synapses with many others: there is a ; Many axons can converge into one neuron: __
Divergence of neural pathways; convergence of neural pathways
What is spatial summation? (Add photo)
Release of neurotransmitters from neurons 1 and 2
Temporal summation:
Successive release of neurotransmitters from one neuron only
__and __ hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane: post-synaptic inhibition
Glycine; GABA
What is paracrine signaling?
Happens in cells within an organ. Happens when a cell targets a nearby cell. Local
Cells that are adjacent to each other can communicate through _ junctions
gap
What is synaptic signaling?
happens only between neurons and their target cell. The neuron releases neurotransmitters
What is endocrine signaling?
happens when cells from endocrine glands release hormones into the blood. The hormones can then reach their cells
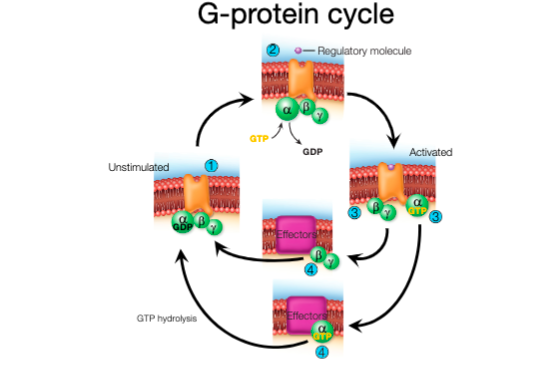
Second messengers are _ _ upon binding of the regulatory molecule to its receptor
indirectly produced
Explain the G-protein cycle
All cells have a membrane potential:
the resting membrane potential
Only a few cells can change their membrane potential upon stimulation:
excitable cells
After stimulation, if positive charges enter the cell →
depolarization
If negative charges inter the cell →
hyperpolarization
Return to the rpm →
repolarization
In neurons, depolarization is __and hyperpolarization is __
excitatory; inhibitory
In general, Na+ channels are all _
voltage gated
2 types of K+ channels:
voltage gated and not voltage gated (leakage channels)
Na+ channels can be also blocked by different molecules:
sodium channel blockers
Describe action potential
The voltage-gated Na+ channels open: Na+ rushes into the cell
The Na+ channels close, then the voltage-gated K+ channels open: K+ rushes out of the cell
The K+ channels close, bringing the membrane potential back to rpm
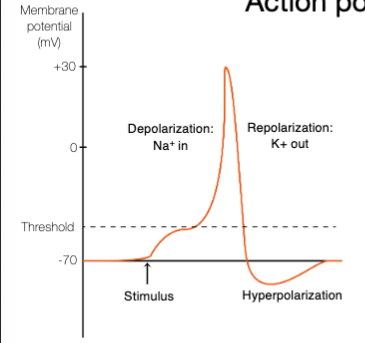
When the gated Na+ channels open, _
a positive feedback loop occurs
When the gated K+ channels open, a _
negative feedback loop
The length of time that the Na+ and K+ channels remains open is _ of the depolarization stimulus
independent
If the threshold is not reached: no action potential is produced. If the threshold is reached: and action potential is reached
all or none
a stronger stimulus does not produce an action potential with greater amplitude
stimulus strength is not amplitude modulated
stronger stimuli on a neuron triggers more action potentials:
strength is frequency modulated
When a neuron generates an action potential, it is incapable to respond to further stimulation
The neuron is refractory to further stimulation
The refractory period is caused by:
the inactivation of the voltage-gated Na+ channels
Explain the absolute refractory period
When a region of the axon is producing an action potential, it is incapable of responding to further stimulation
Explain the relative refractory period
When the membrane is repolarizing, only a very strong depolarization will trigger a new action potential
Action potential conduction is _ due to the refractory period
unidirectional
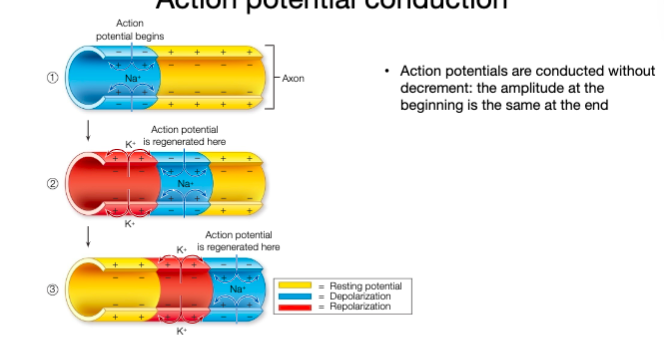
Action potentials are produced along the entire length of the _
axon
What is myelin?
Insulating layer of phospholipids and proteins found wrapped around axons
Myelin prevents …
any ion movements except in zones of the axon where it is not present: nodes of Ranvier
Action potentials are propagated through _ _ A new action potential is produced at every node and not at every region of the axon’s membrane
saltatory conduction
True or false: action potentials are propagated faster in a myelinated axon
true (100m per second!)
The nervous system can be divided into two:
Central nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
Neurons have three principal regions:
Cell body. Contains the nucleus of the neuron
Dendrites.
Axon
A cluster of cell bodies in the CNS:
nucleus
A cluster of cell bodies in the PNS:
ganglion
_ _ conduct impulses out of the CNS to effector organs
Motor (or efferent) neurons
_ _ conduct impulses from sensory receptors into the CNS
sensory (or afferent)
_ relay signals between two other neurons. Located only in the CNS
interneurons
_ _ are the most abundant neurontype, possess several dendrites and one axon
multipolar neurons

_ _ one branch received stimuli, while the other relays the signal into the CNS
pseudounipolar neurons
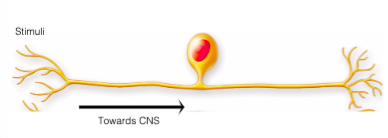
_ _ neurons with two extensions, one at either side of the cell body
bipolar neurons
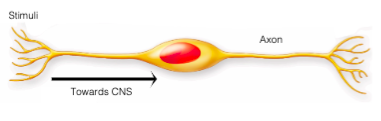
In the PNS, multiple axons together form a . _In the CNS, they form a _
nerve; tract
In the PNS, neuroglia is made of _ cells. Produce myelin sheaths around axons and surround all PNS axons to form the neurilemmal sheath
Schwann
There are two inhibitory neurotransmitters in the CNS:
GABA. 1/3 of the brain uses this
Glycine. Used by the spinal cord, brain stem and retina
GABA and glycine receptors are — gated. Binding to their receptors opens Cl- channels, leading to — and —.
ligand;hyperpolarization;IPSPs
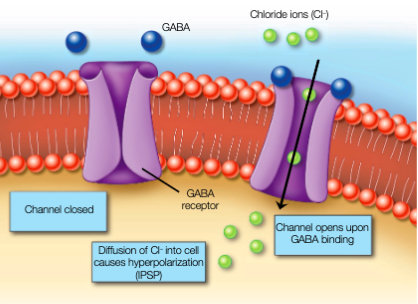
GABA is involved in — control: a deficiency of GABA-releasing neurons is linked to Huntington’s disease
motor
— is used as an excitatory neurotransmitter by somatic motor neurons at the neuromuscular junction.
Acetylcholine
At autonomic nerve endings it can be excitatory or inhibitory due to the presence of different types of Ach receptors:
Nicotinic Ach receptors (nicotine can bind them)
Muscarinic Ach receptors (muscarine (mushroom) can bind to them)