magnets and magnetic field
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapter 26 and 27
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a magnetic field
any region of space where magnetic forces can be felt
what are magnetic poles
the regions at each end of a magnet where the magnetic forces are greatest. magentic poles are always found in pairs
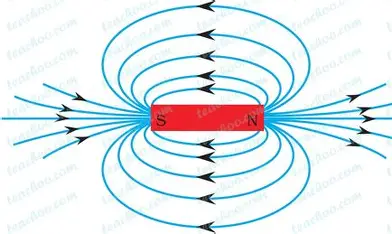
draw the magnetic field around a bar magnet
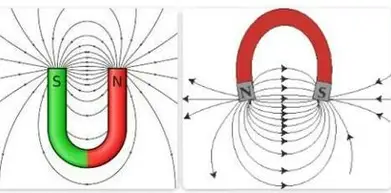
draw the magnetic field around a u-shaped magnet
give one use of earth’s magnetic field
a magnetic compass shows direction, it is used in each navigation
why does a magnet that is free to rotate point towards the north
because the earth has a magnetic field that exerts a force on the magnet
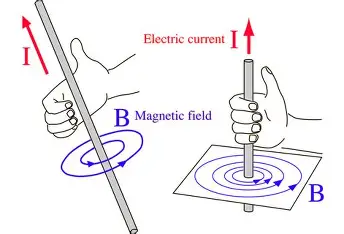
Describe an experiment to demonstrate the magnetic effect of an electric current
Apparatus- compass, battery(dc power source) wires and switch
procedure- 1.set up equipment with the wire lined up north-south. the plotting compass also lines up North-South 2. close the switch,sending direct current through the wire.the compass needle will deflect. 3.reverse the direction of the current and the needle deflects in the opposite direction. 4. open the switch no current flows, the magnetic field disaoppears and the ompass again lines up N-S
Conclusion- every current carrying conductor has a magnetic field around it caused by the current
draw a sketch of the magnetic field due to a long straight current-carrying conductor
give one use of an electromagnet
Scrapyard cranes; electric motors; electric bell; doorbell
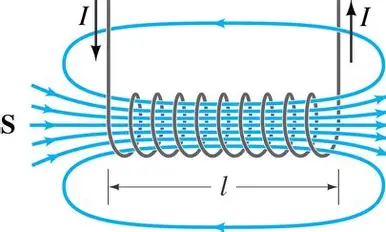
sketch the magnetic field due to a current in a solenoid
describe an experiment to show that a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field experiences a force
Apparatus- aluminum foil, strong magnet, d.c power source,wire
procedure-switch on current
observation- the foil will be seen to move forwards and backwards depending on which direction the current is flowing
conclusion- a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field experiences a force
list two devices based on the fact that a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field experiences a force
an electric motor, a moving coil meter, a loudspeaker
list three factors that affect the force on the current carrying conductor in the magnetic field.
the size of the current
the length of the wire
the magnetic flux density
the sine of the angle between the conductor and the magnetic field
what happens if the conductor is placed parallel to the magnetic field
there will be no force on the conductor
define magnetic flux density
At a point in a magnetic field the magnetic flux density is a vector whose: direction is the direction of the force on a north pole placed at that point and whose magnitude is the value of B from the equation F=IlB, where F is the force on the conductor of length l carrying a current I perpindicular to the magnetic field
Describe an experiment to show the forces on a current carrying coil in a magnetic field.
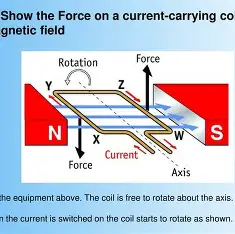
Set up the equipment as shown above. the coil is free to rotate about the axis shown. When the current is switched on, the coil begins to rotate in an anti-clockwise direction due to the forces acting on it
what is the direction of the forxeoon a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field
the force is always perpendicular to the current and perpendicular to the magnetic field
si unit of magnetic flux density
the tesla T
give two ways of deflecting a beam of electrons
it can be deflected in an electric field or in a magnetic field
what is electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge
deine the ampere . what is the si unit
the ampere is that current which, if maintained in two infinitely long parallel conductors of negligable cross-section placed 1 metre apart in a vacuum,would produce a force on each wire of 2×10-7 newtons per meter length
state the principle on which the ampere is based
two current carrying conductors exert a force on each other due to their magnetic fields
define the coulomb
the amount of charge that passes any point in a circuit when a current of 1 ampere flows for 1 second
describe the experiment to demonstrate the principle on which the definition of the ampere is based
apparatus - parallel strips of alluminium foil connect to a wire circuit, ampere d.c power supply
procedure-1. send a current through the parallel strips of aluminium foil
observation the foil strips will be seen to move away from eachother
conclusion-there is a force between current-carrying conductors due to their magnetic fields