RAD 205: Chapter 5 GI System
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
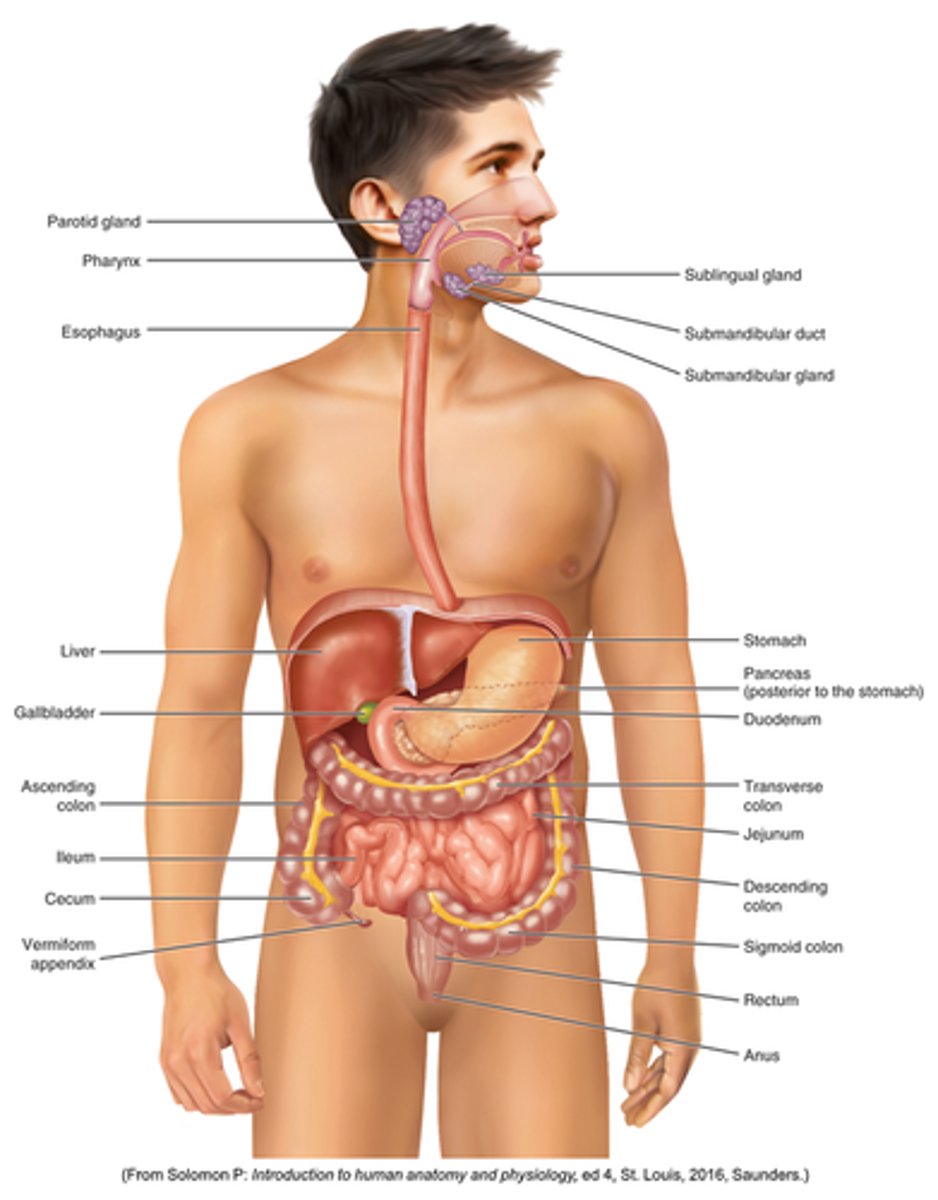
Know anatomy:
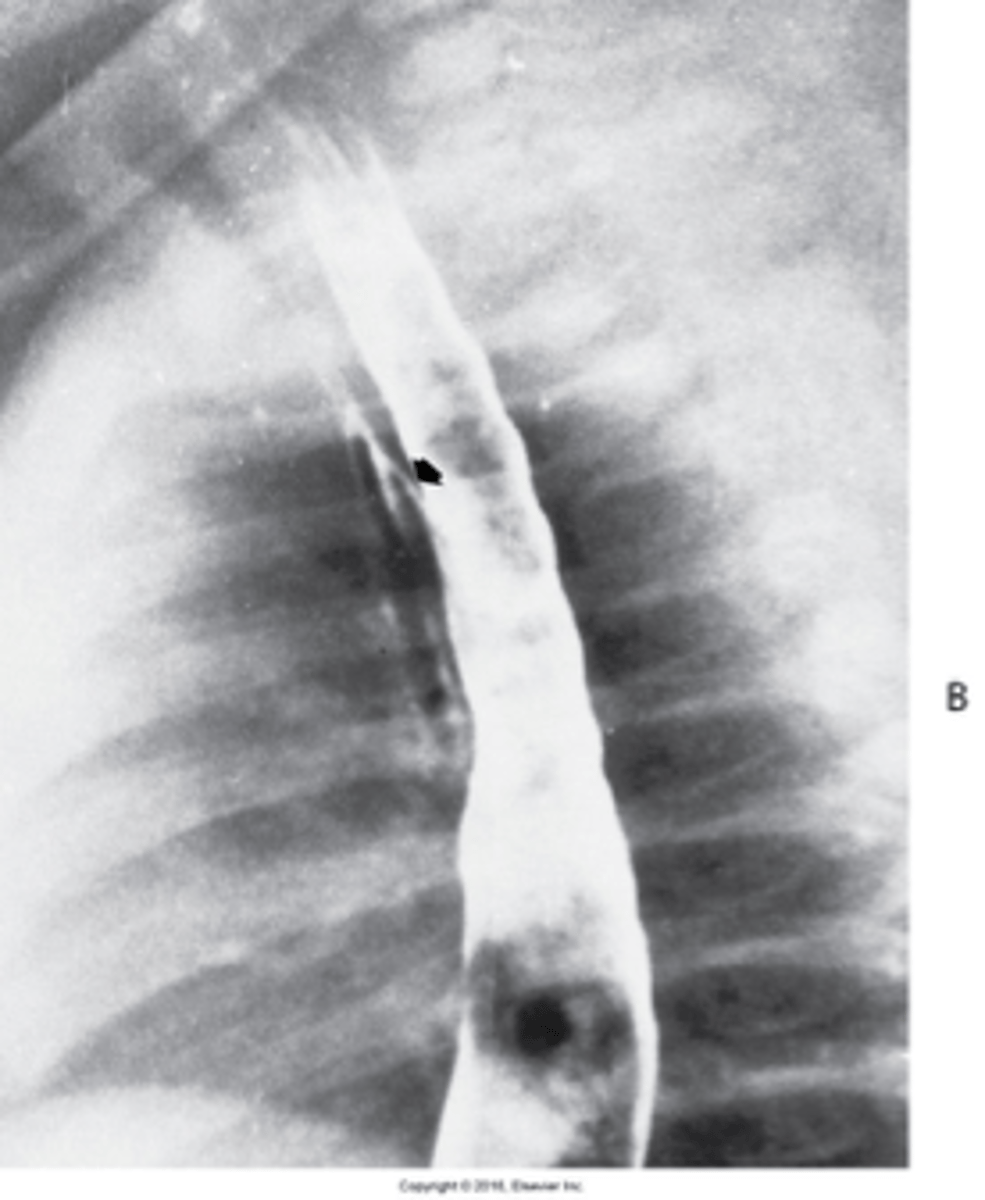
results from the failure of the esophageal lumen to develop completely separate from the trachea
What is the Tracheoesophageal Fistula congenital form?
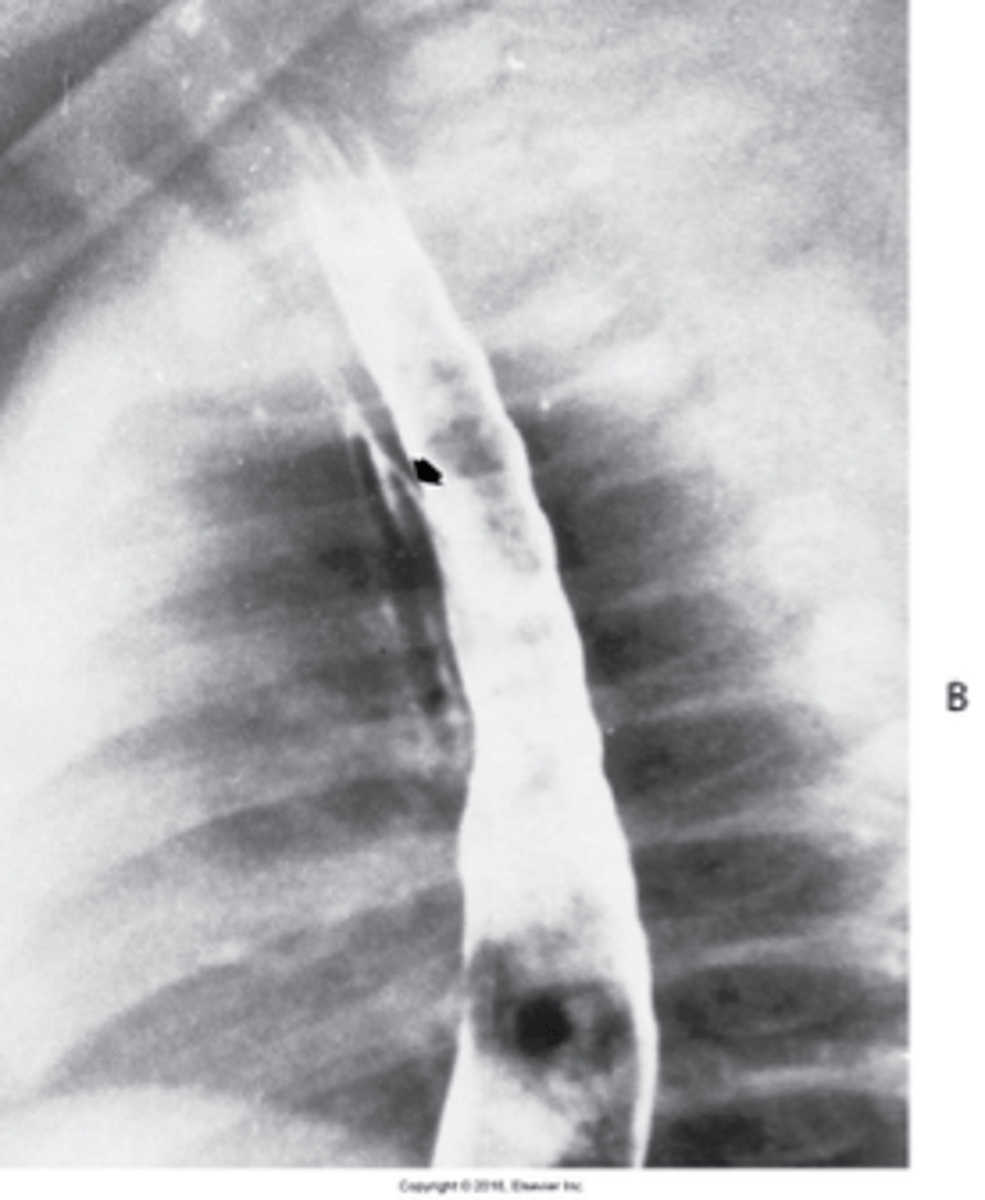
caused by cancer, infection, trauma, instrumentation perforation
What is Tracheoesophageal Fistula congenita Acquired type ?
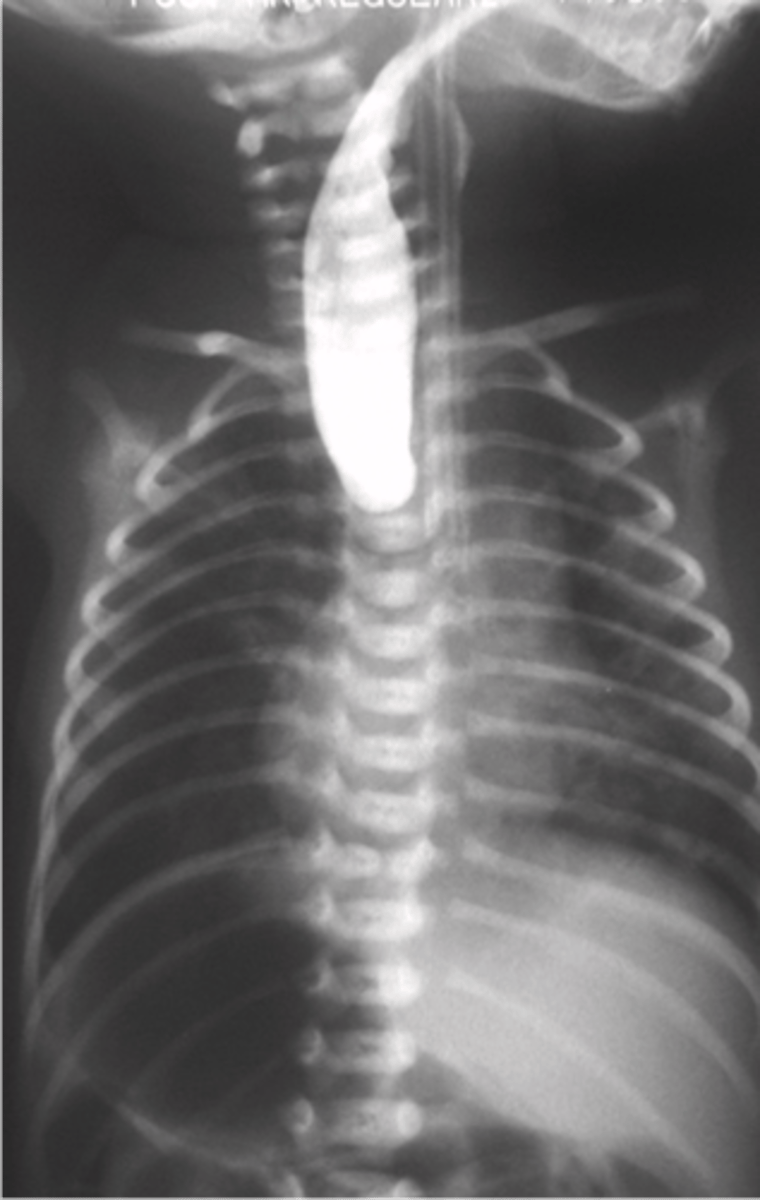
The lack of the development of the esophageal lumen resulting in a blind pouch
What is Esophageal Atresia
Acute form of esophagitis is most commonly the result of reflux of stomach contents into distal esophagus
What is esophagitis "GERD - gastroesophageal reflux disease"?
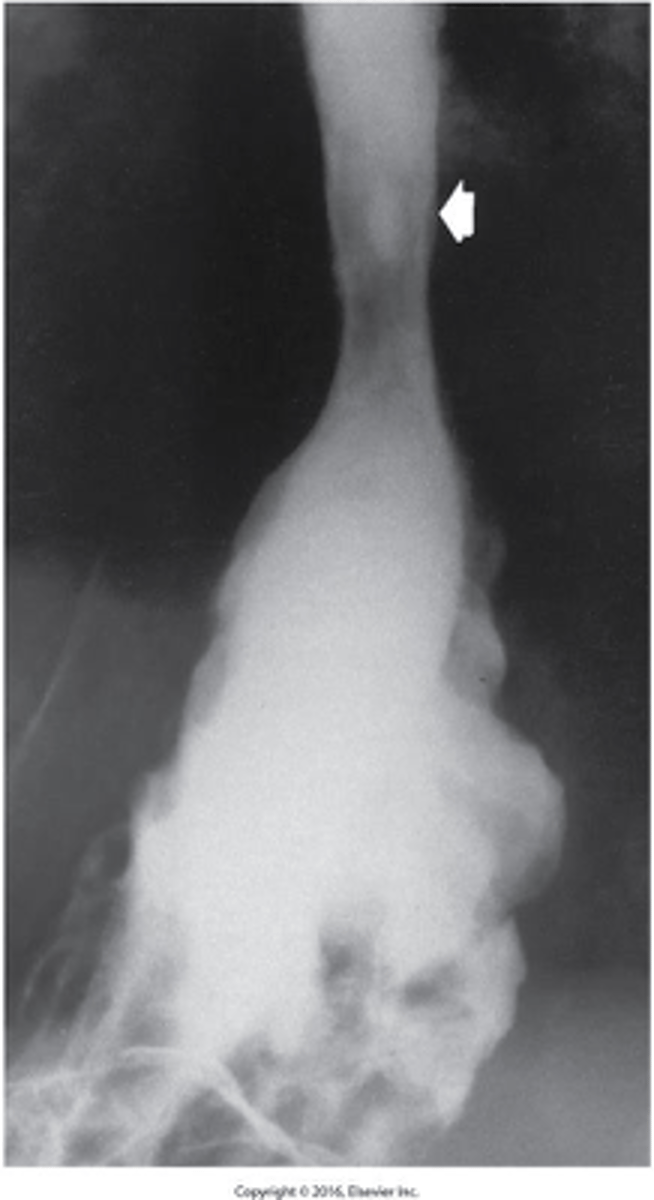
Shaggy esophagus (due to infection)
What is esophagitis due to infection called?
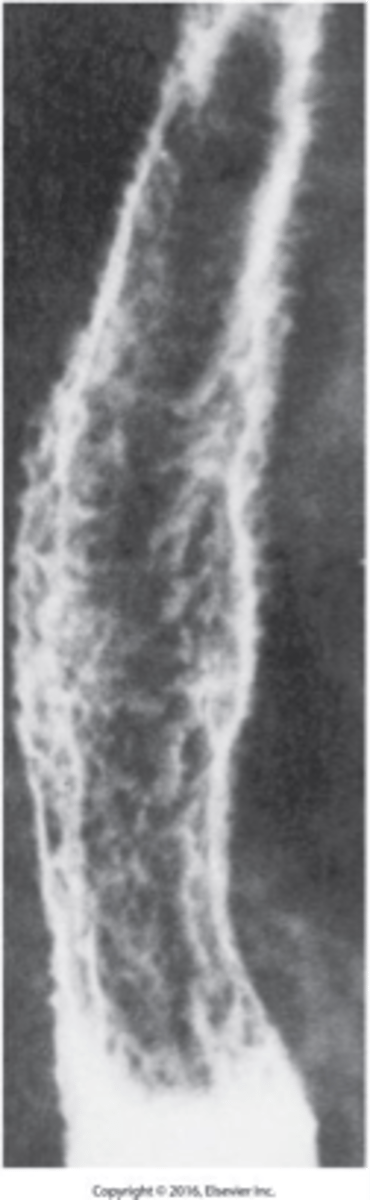
- condition related to GERD in which the squamous lining is destroyed and replaced by columnar
- adenocarcinomas
- hital hernia commonly demonstrated
What is Barrett Esophagus
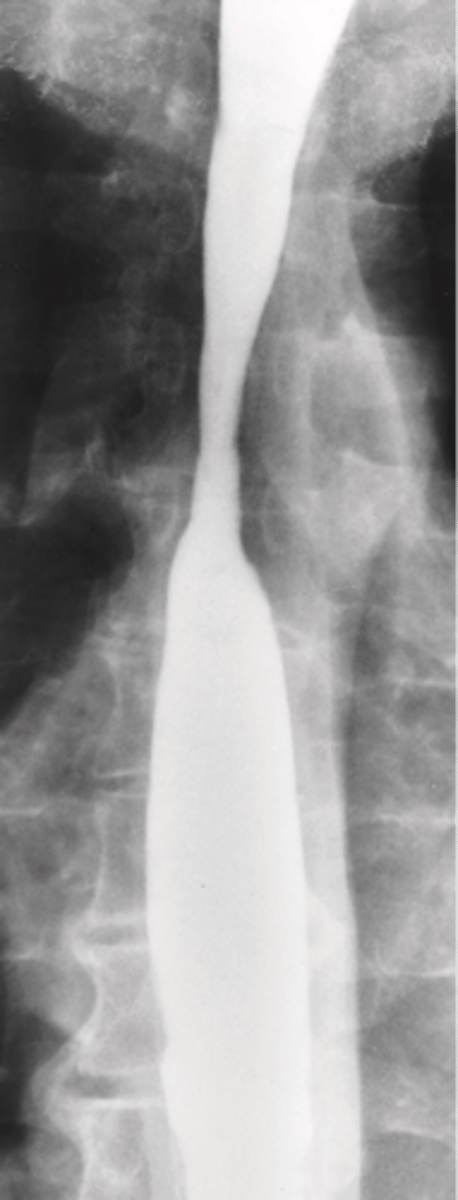
- Produces acute inflammatory changes in the esophagus
- long lesions with tapered ends
What is Ingestion of Corrosive Agents?
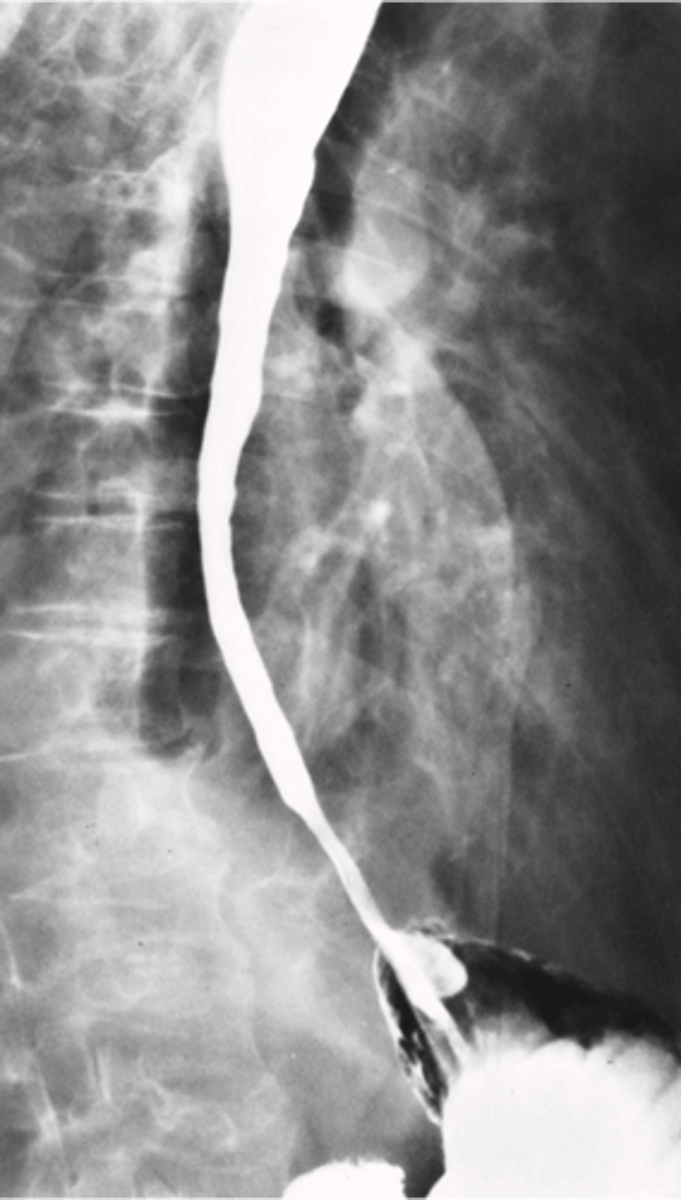
- Most are squamous cell type.
- common site is esophagogastric junction.
- Associated with excessive alcohol intake and smoking.
- Dysphagia occurs
- Advanced stages appear as irregular narrowing on Esophagram
What is esophageal Cancer ?
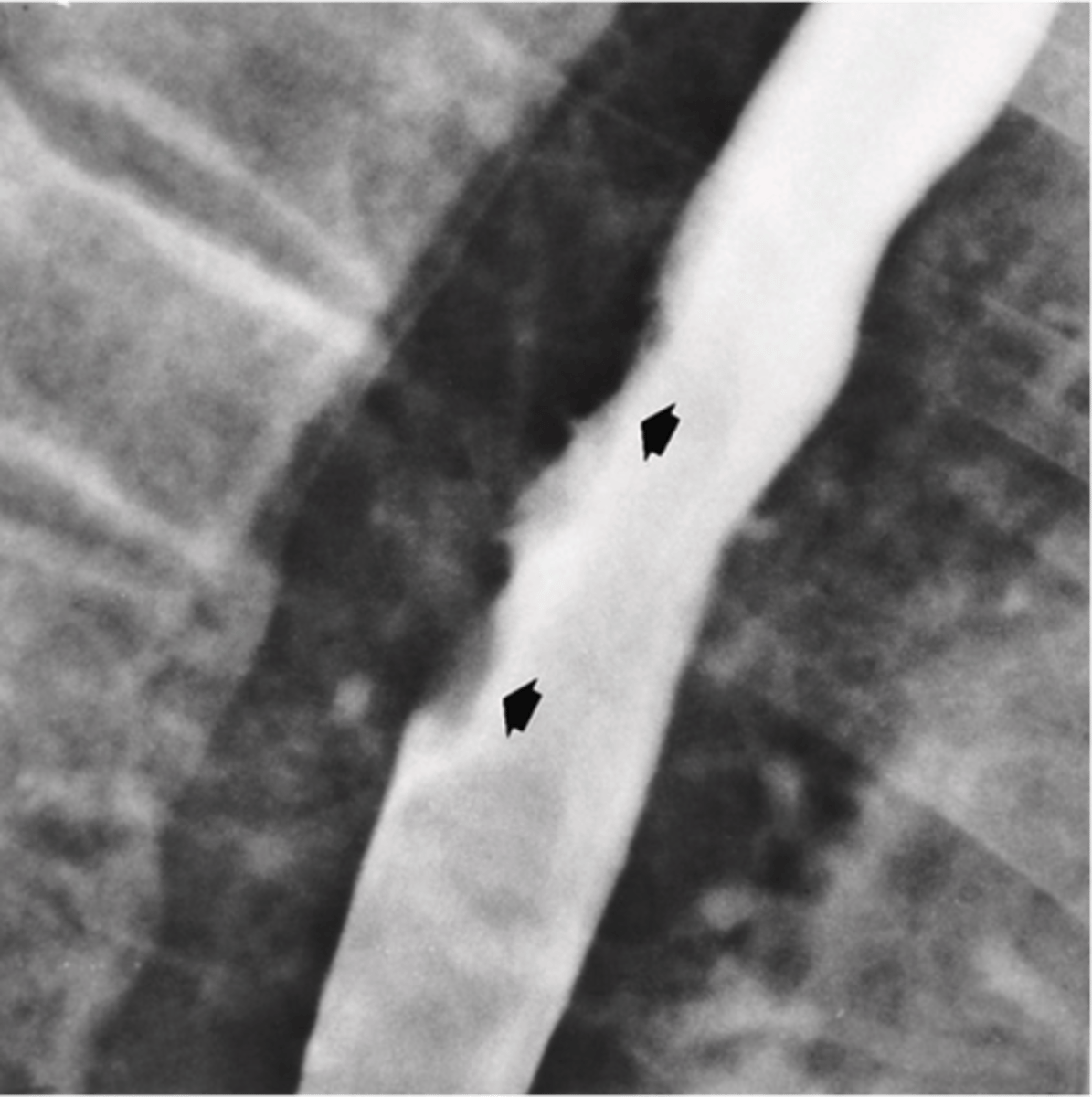
- Outpouchings of the esophageal wall, typically in weak areas
- two types
What is esophageal Diverticula?
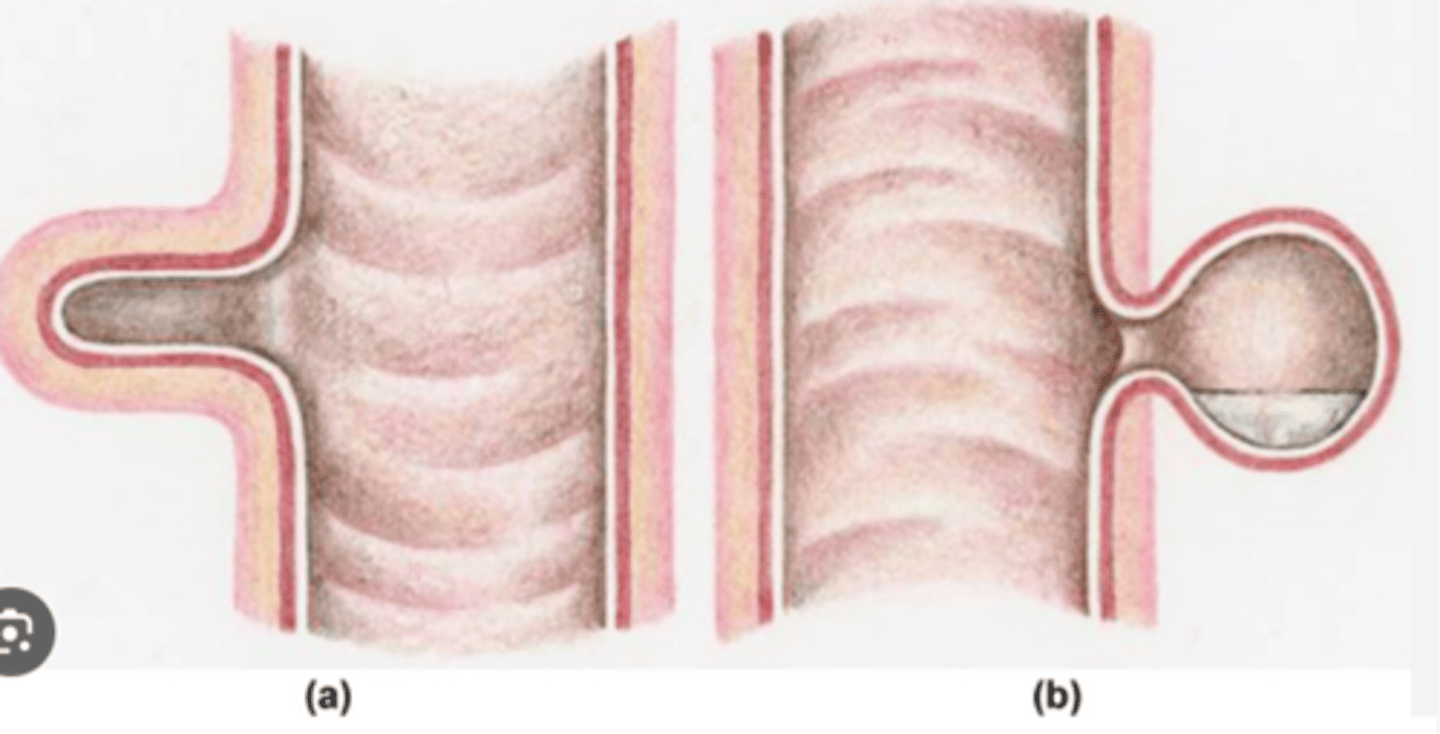
- True or traction= Involve all layers of the wall
- False or pulsion = uComposed of only mucosa and submucosa herniating through the muscular layer
What are the two types of diverticula?
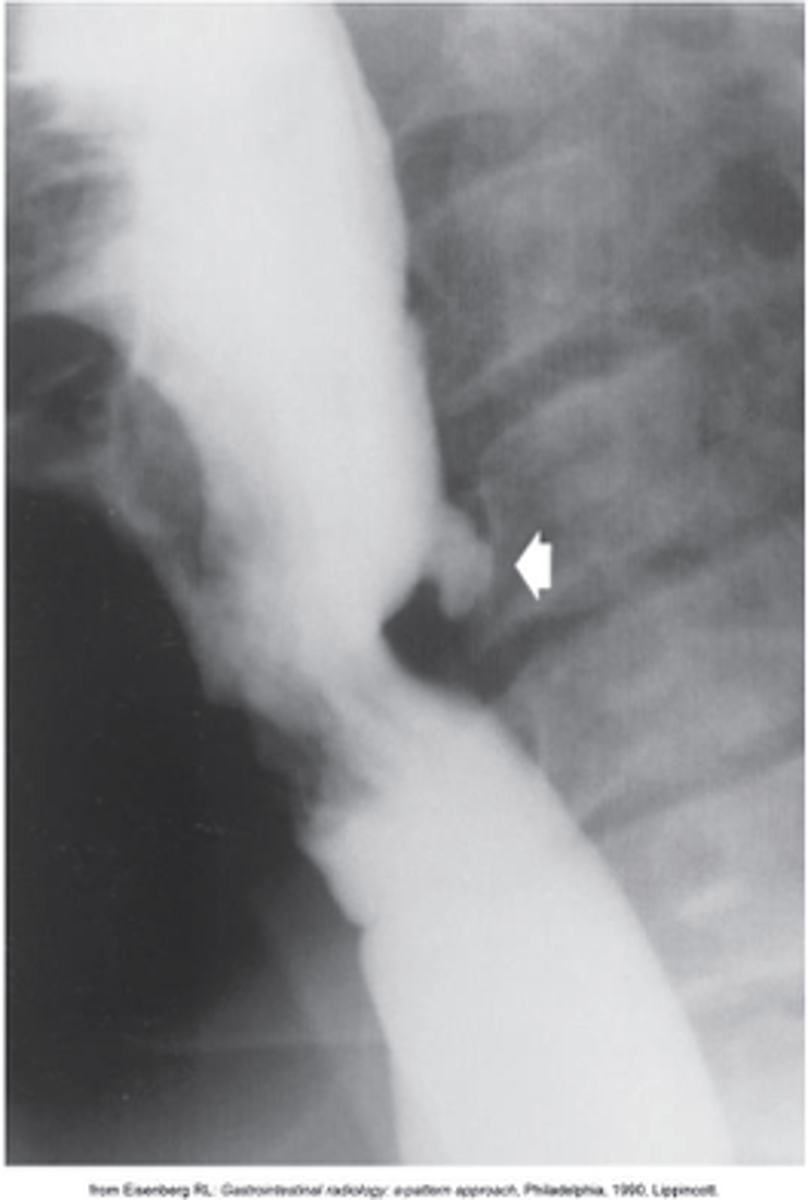
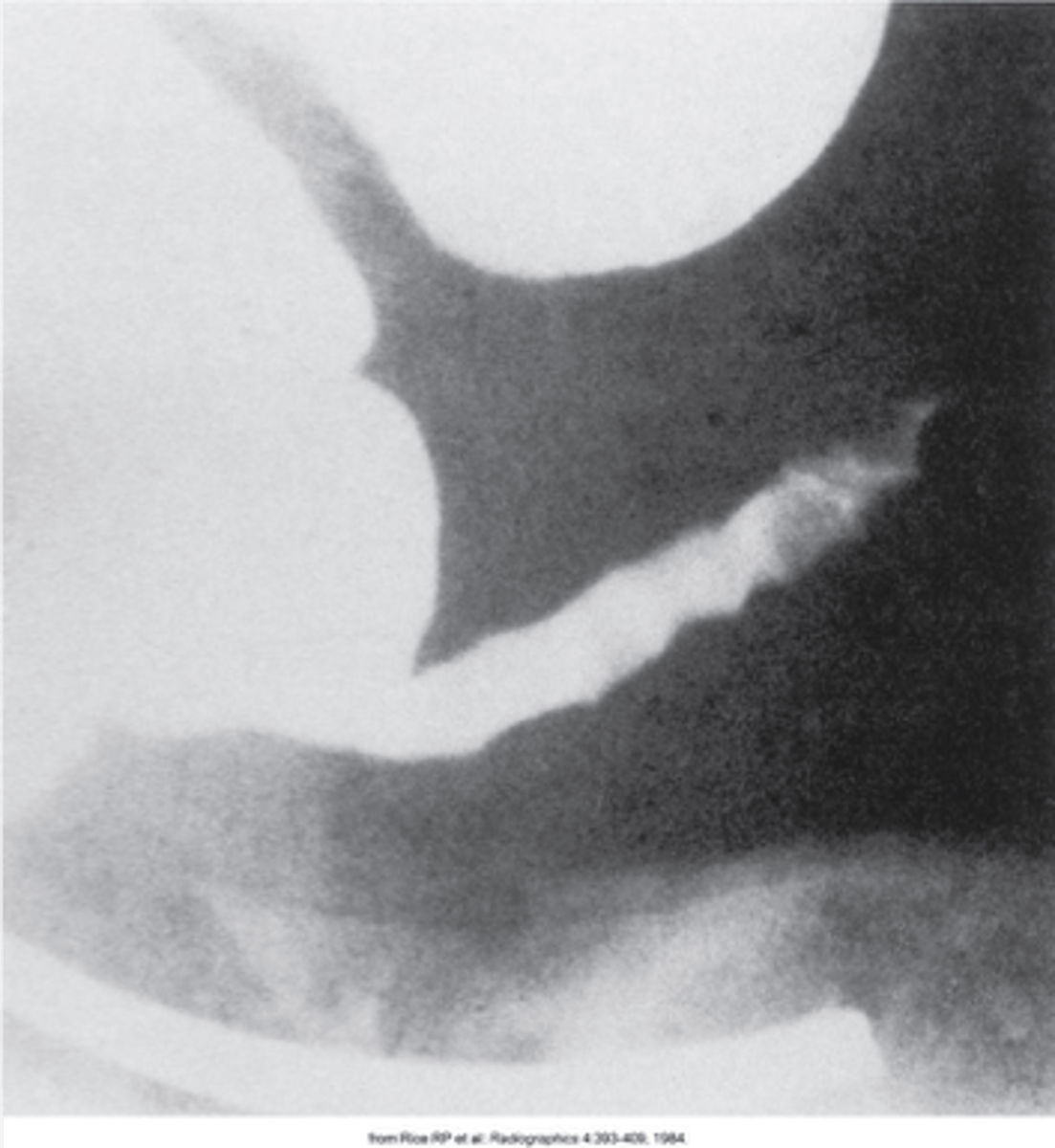
type of esophageal diverticula that arise from the posterior wasll \
What is Zenkers Diverticula?
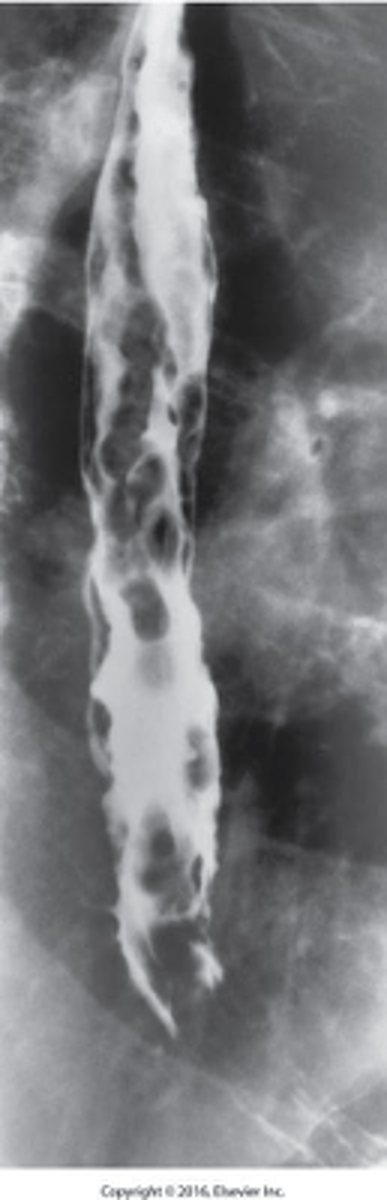
- “Rosary Beads”
- Dilated veins in the distal esophagus
- Caused by portal hypertension (caused by cirrhosis.)
- May hemorrhage
What is Esophageal Varices ?
- Protrusion of a portion of the stomach into the thoracic cavity through the esophageal hiatus in the diaphragm
- Commonly causes GERD
What is a hiatal hernia?
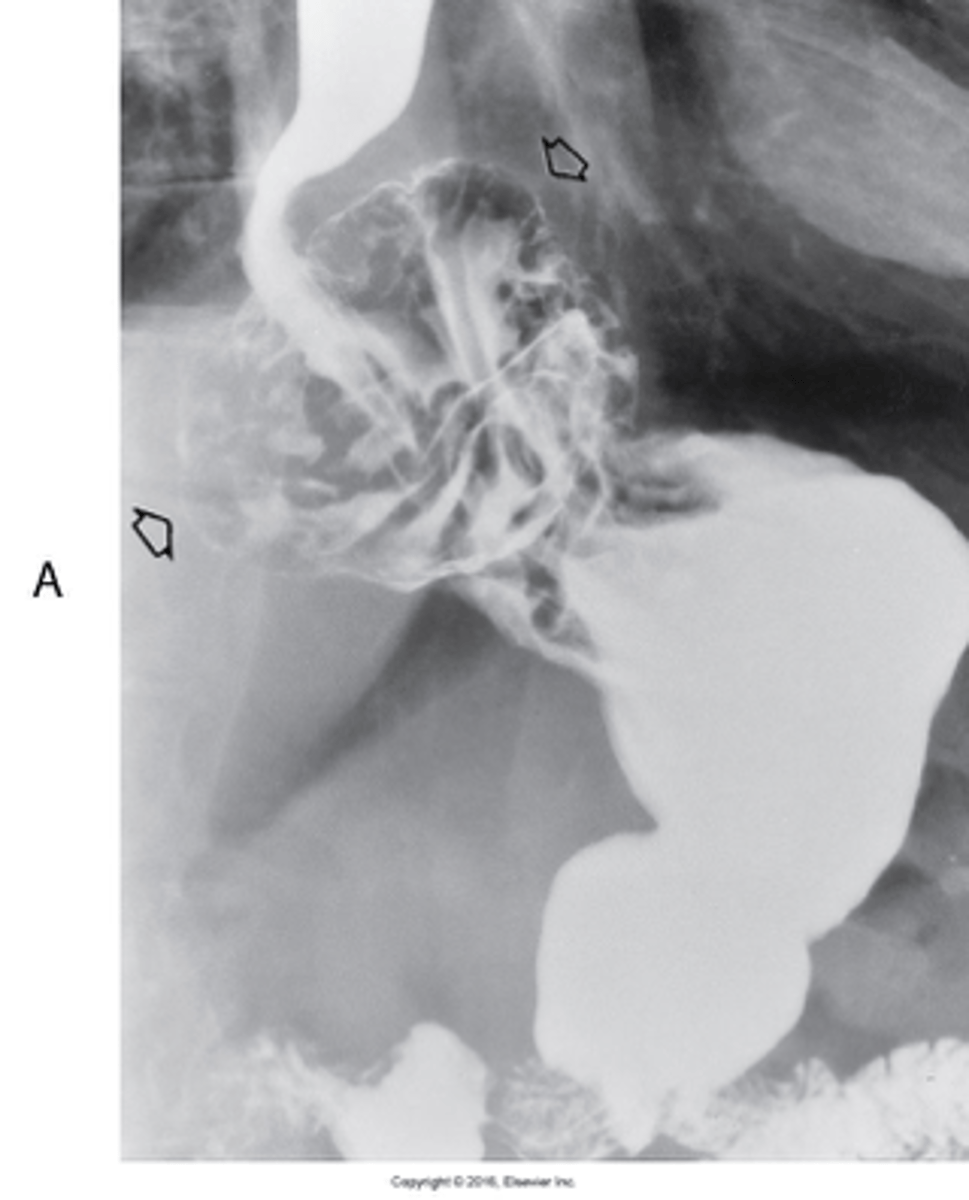
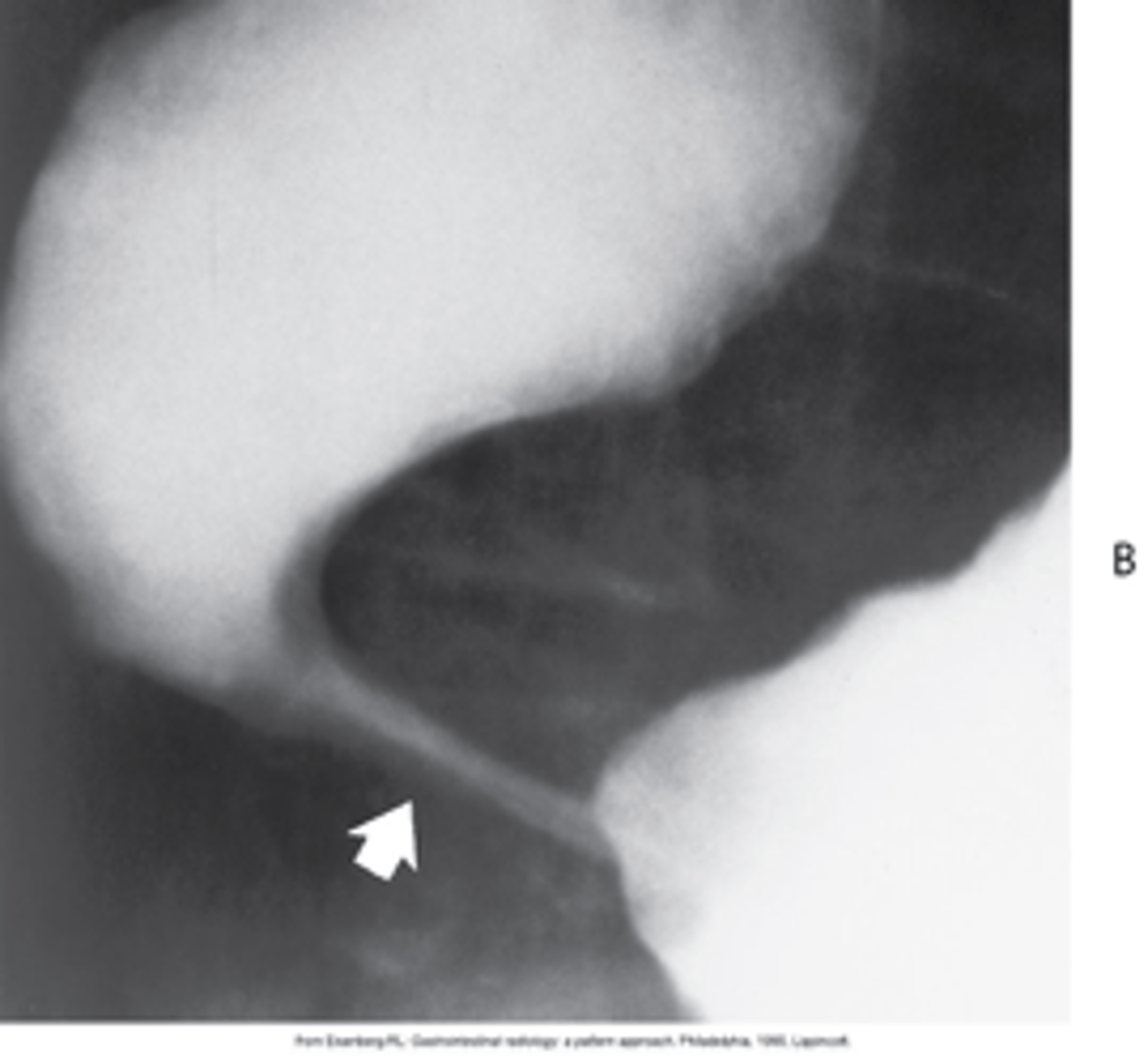
“rat tail” or “jet effect”
- Functional obstruction of the distal esophagus with proximal dilation
- Caused by incomplete relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter
What is Achalasi
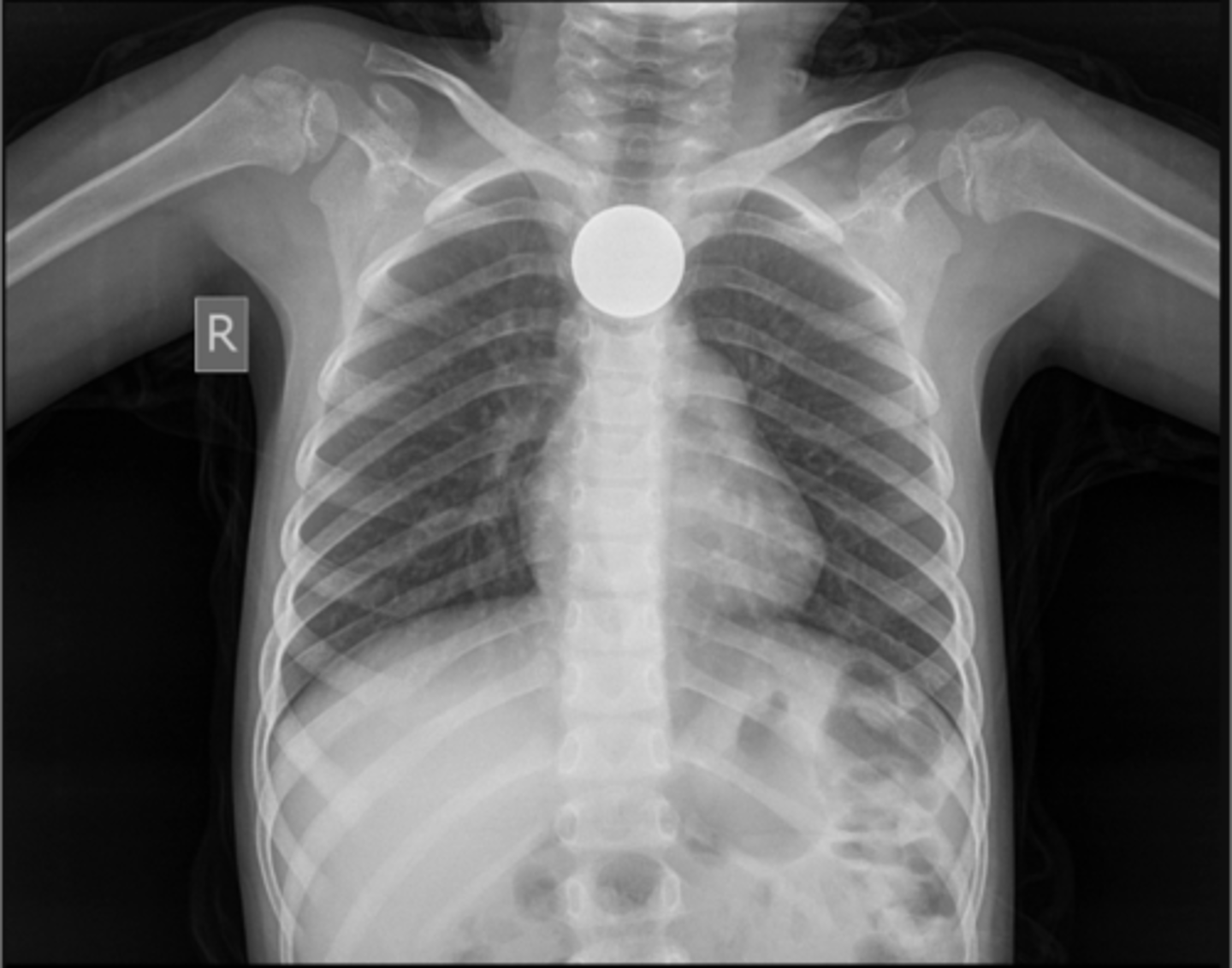
object often seen without the aid of contrast
Define radiopaque foreign objects?
best seen with the aid of barium swallow
Define radiolucent foreign objects ?
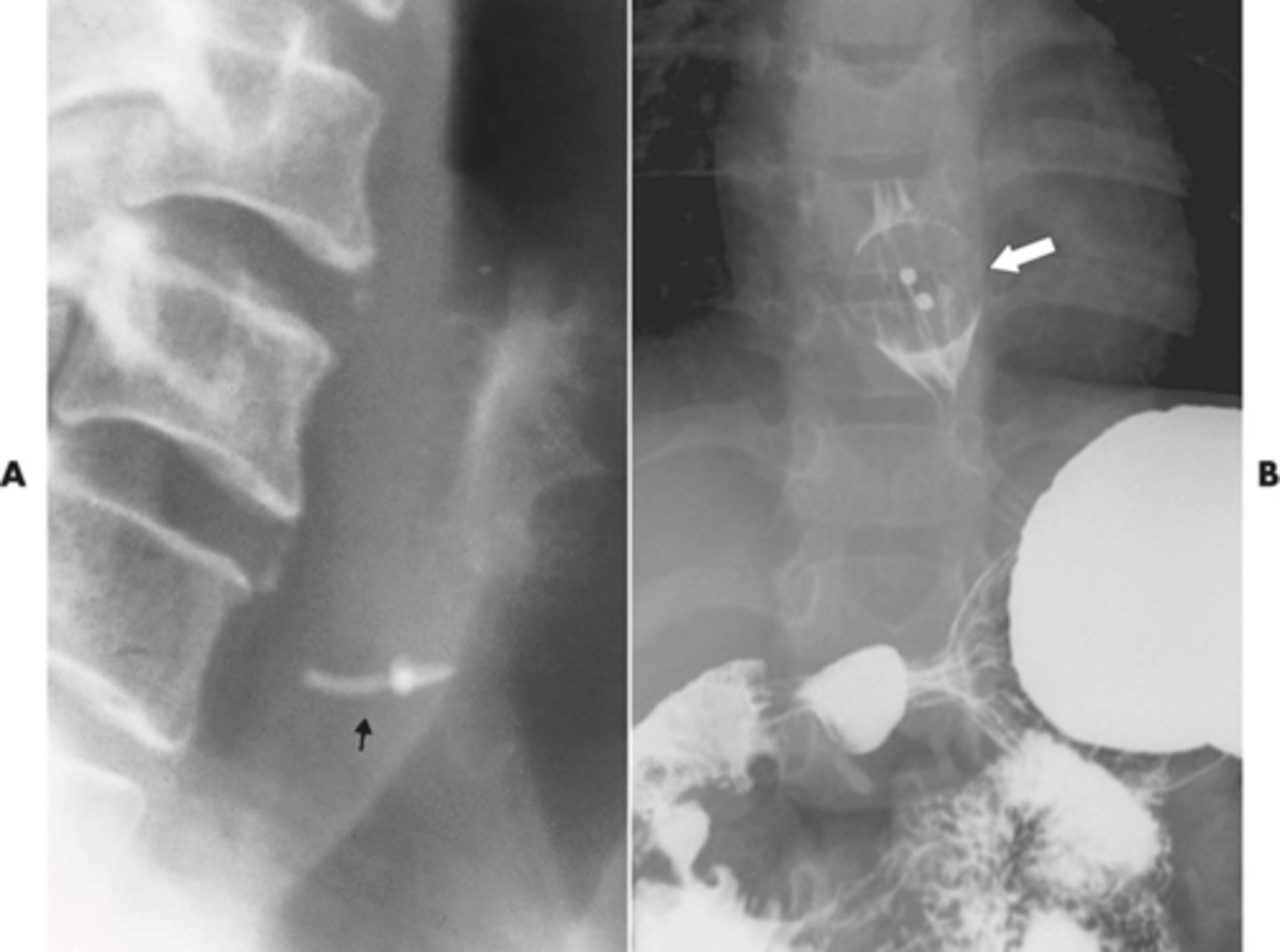
Two projections 90 degrees from each other required to truly determine object is lodged in esophagus
How should you radiograph foreign bodies?
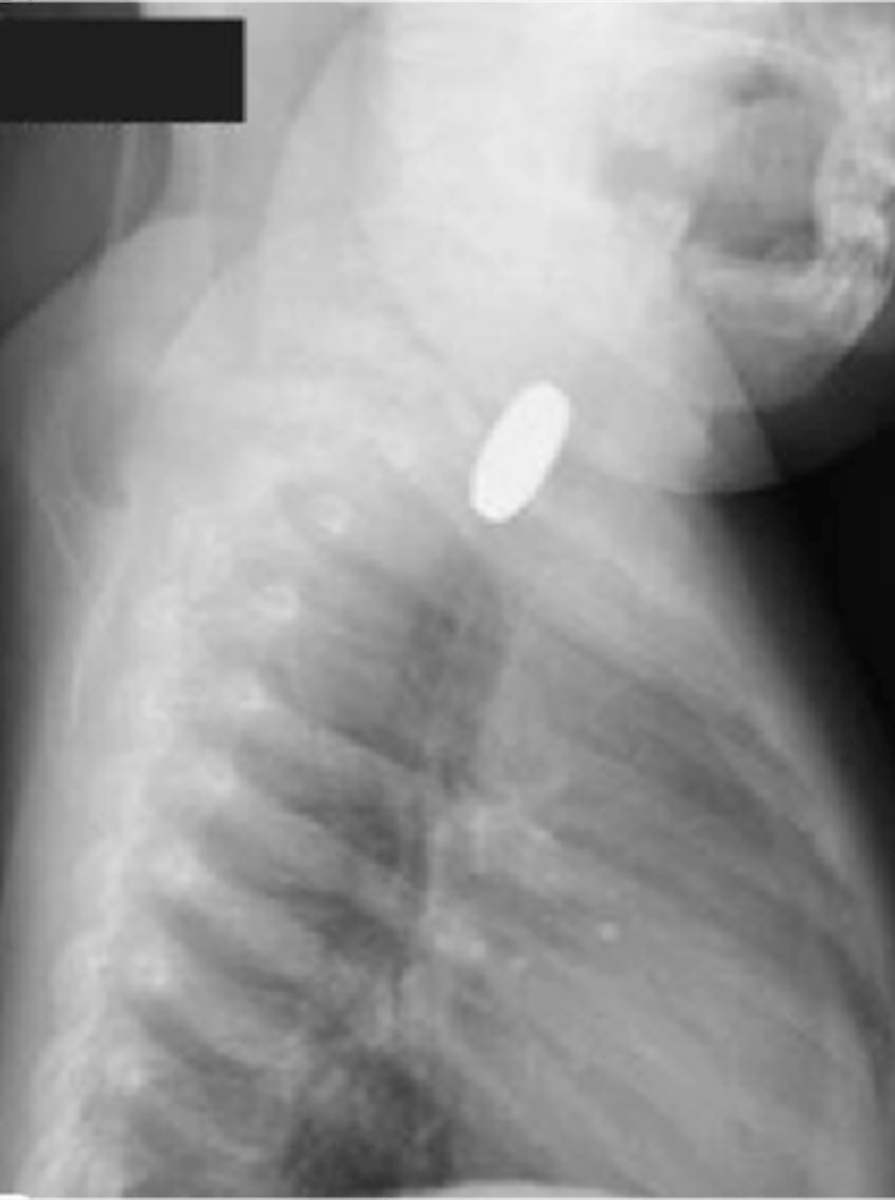
- Esophagitis
- Peptic ulcer
- Neoplasm
- External trauma
- Instrumentation
What are complications of Perforation of the Esophagus?
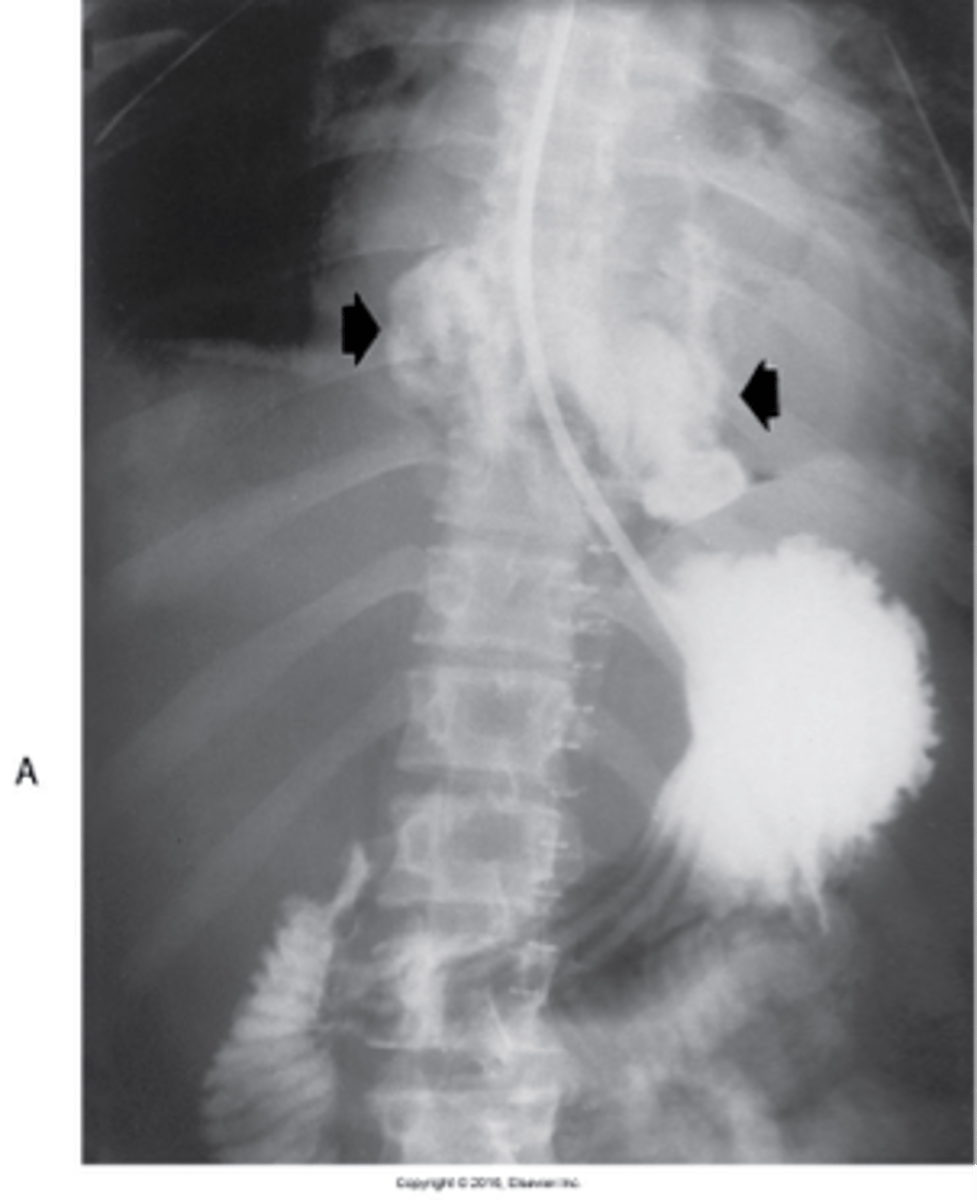
- inflammation of the stomach mucosa.
Caused by irritants including:
- Alcohol, Caffeine, Acidic foods, Medications
- Corrosive agents
- Infection, (Helicobacter pylori (H. Pylori) can cause chronic gastritis that may lead to peptic ulcer disease.)
What is gastritis ?
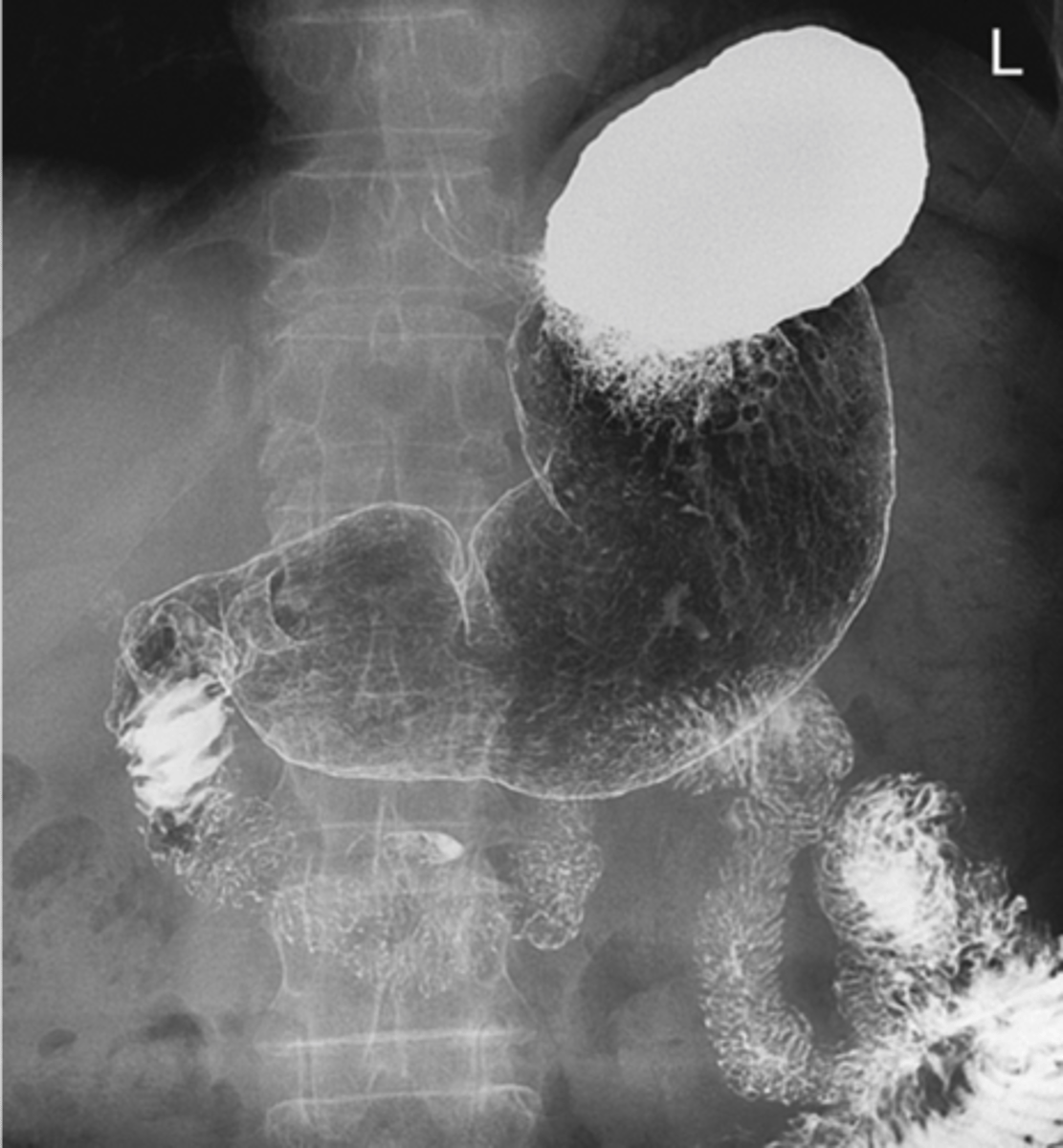
appears as thickening of the stomach rugal folds
What does gastritis appear as?
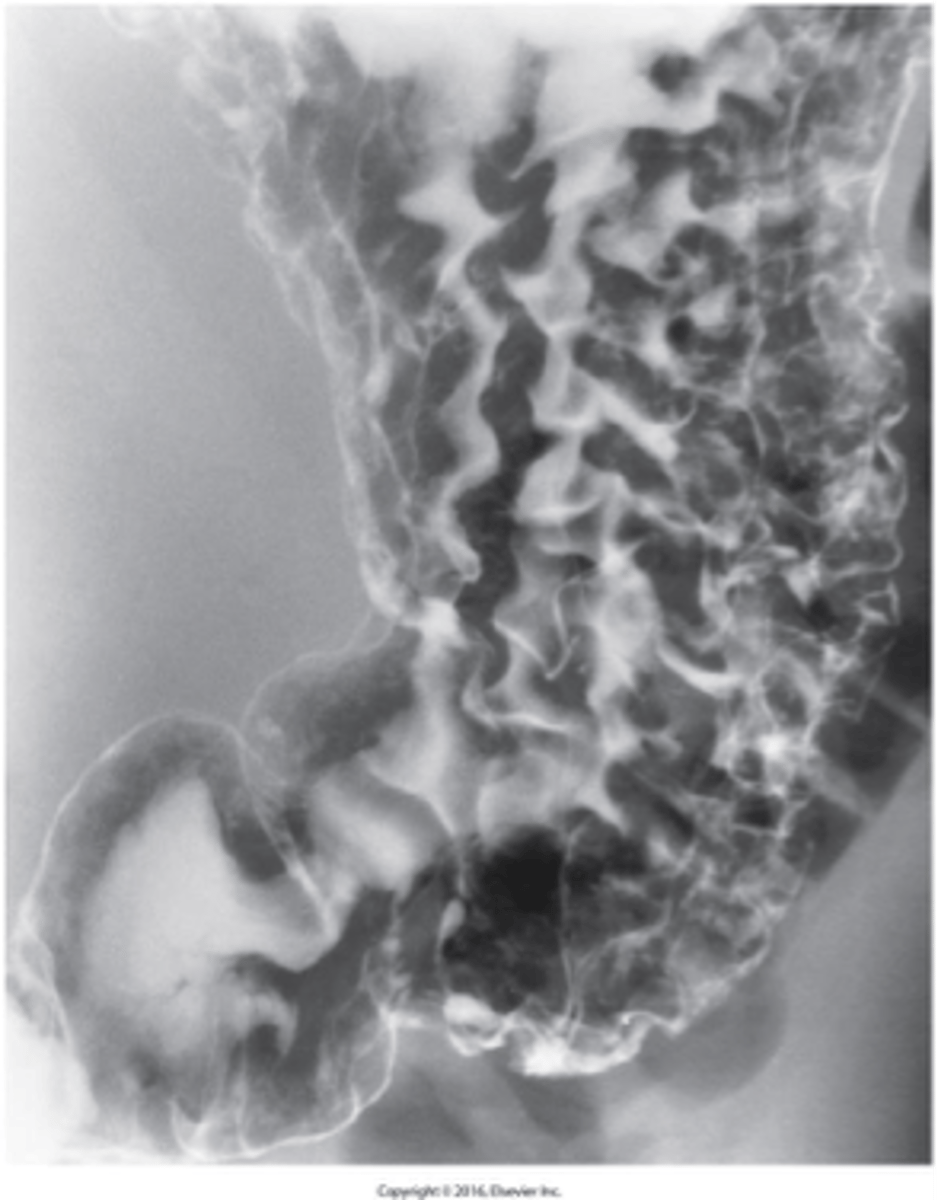
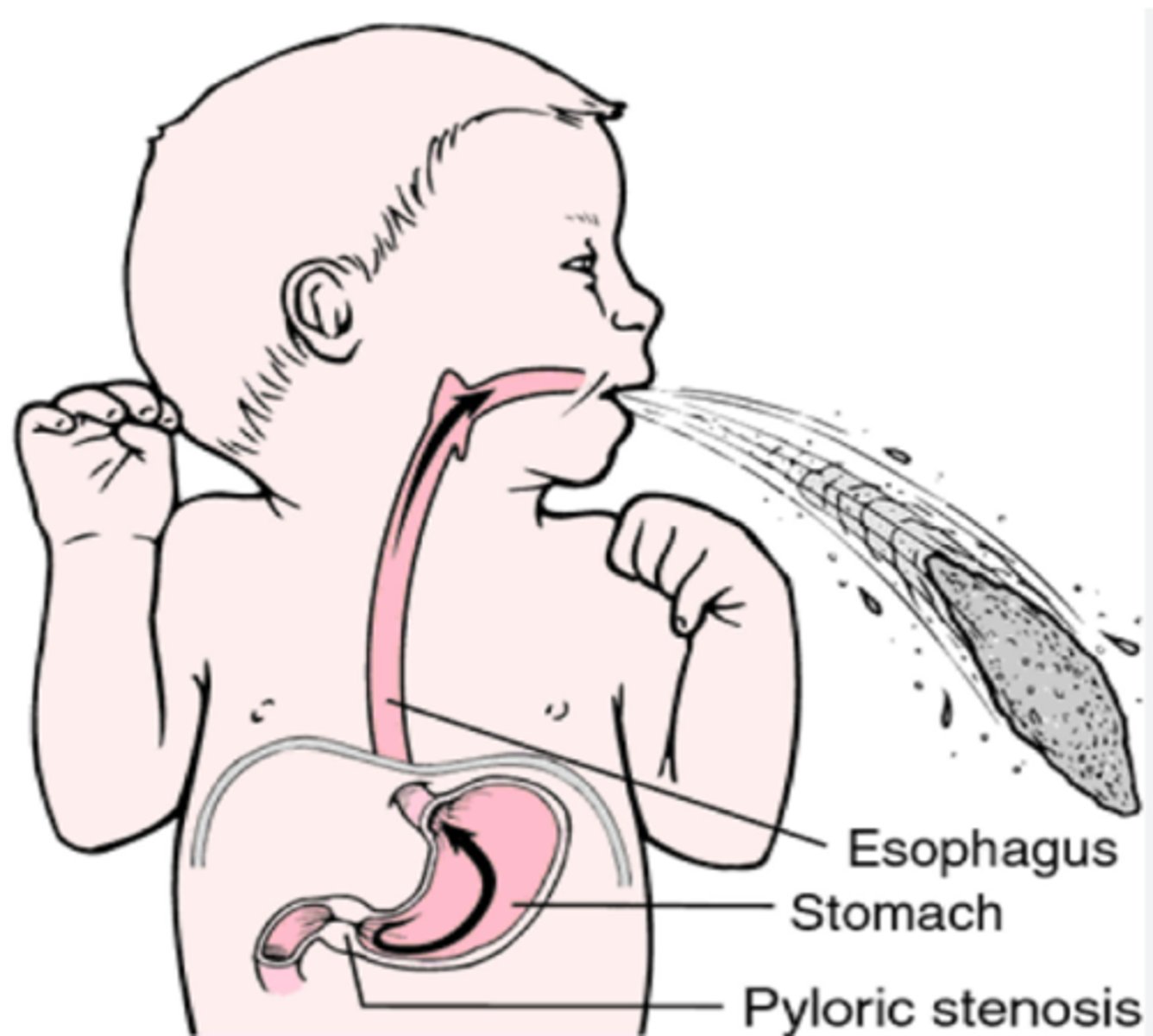
- caused by enlarged pylorus
-Two muscular layers of the pylorus become hyperplastic and hypertrophic.
- Causes are thought to be a combination of environmental and hereditary factors
Why is pyloric Stenosis "as infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (IHPS)" ?
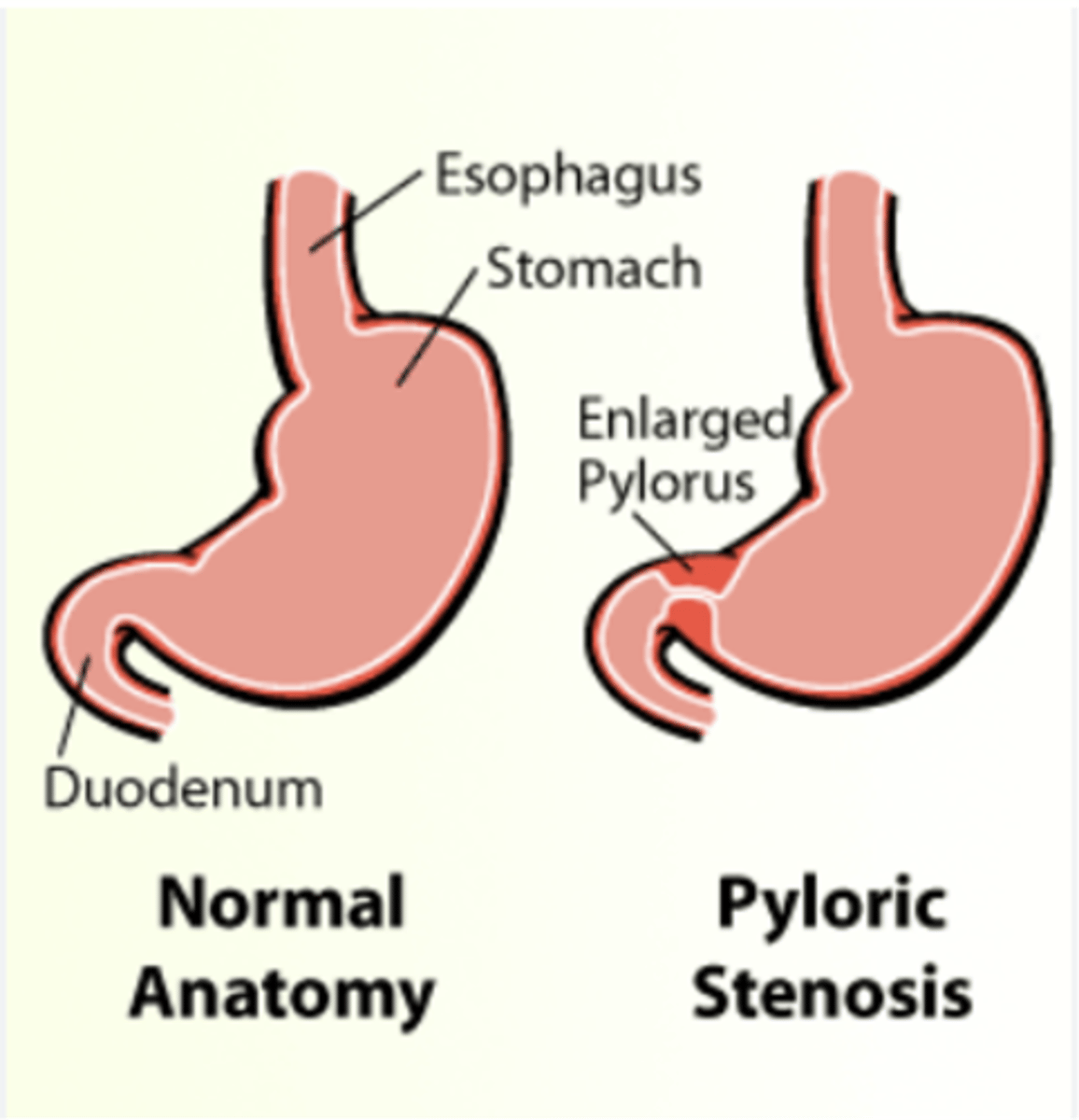
- causes obstruction (incomplete or complete), preventing food from entering into the duodenum.
- Can be palpated and often described as a mobile, hard "olive."
What does pyloric Stenosis cause?
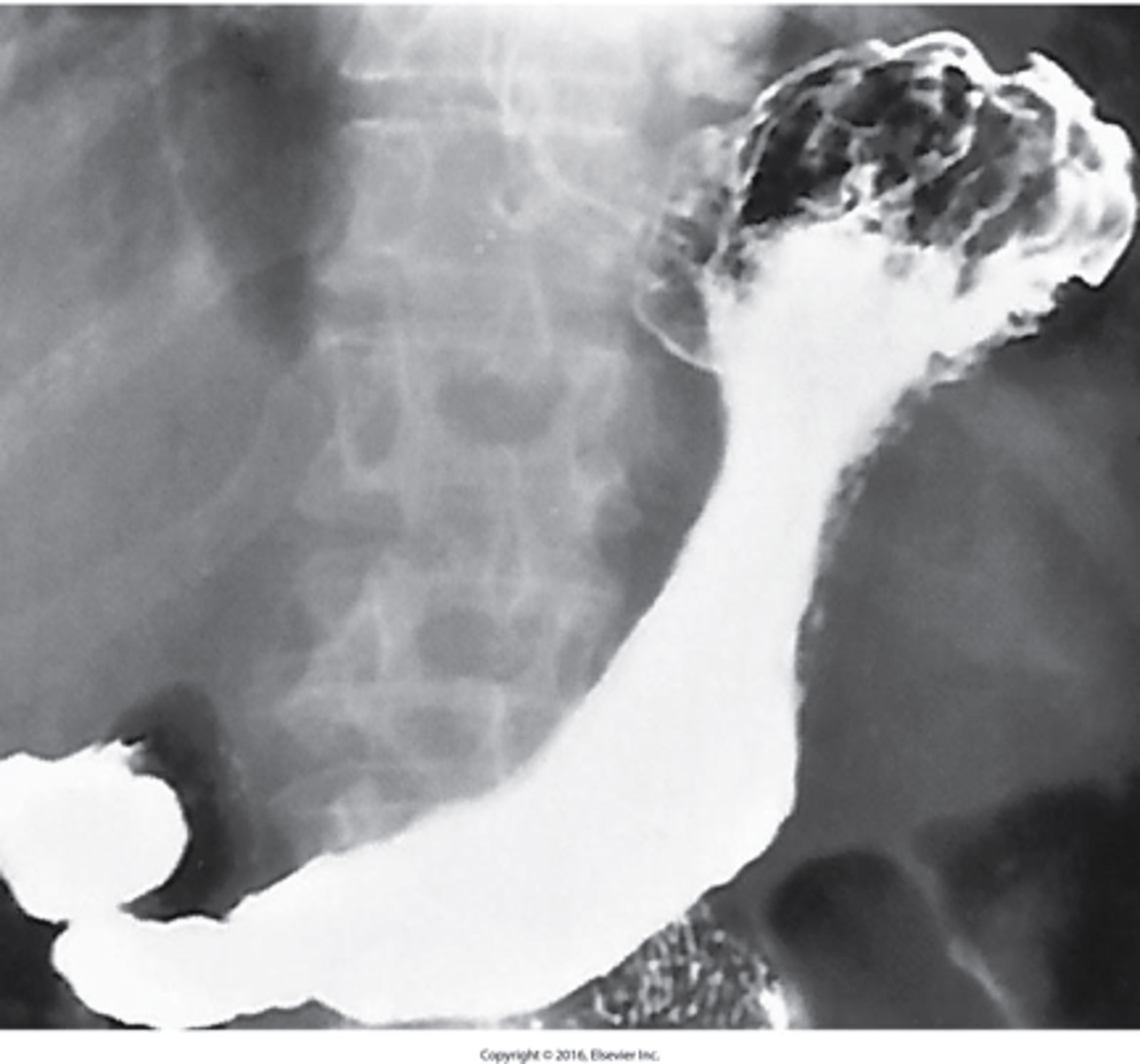
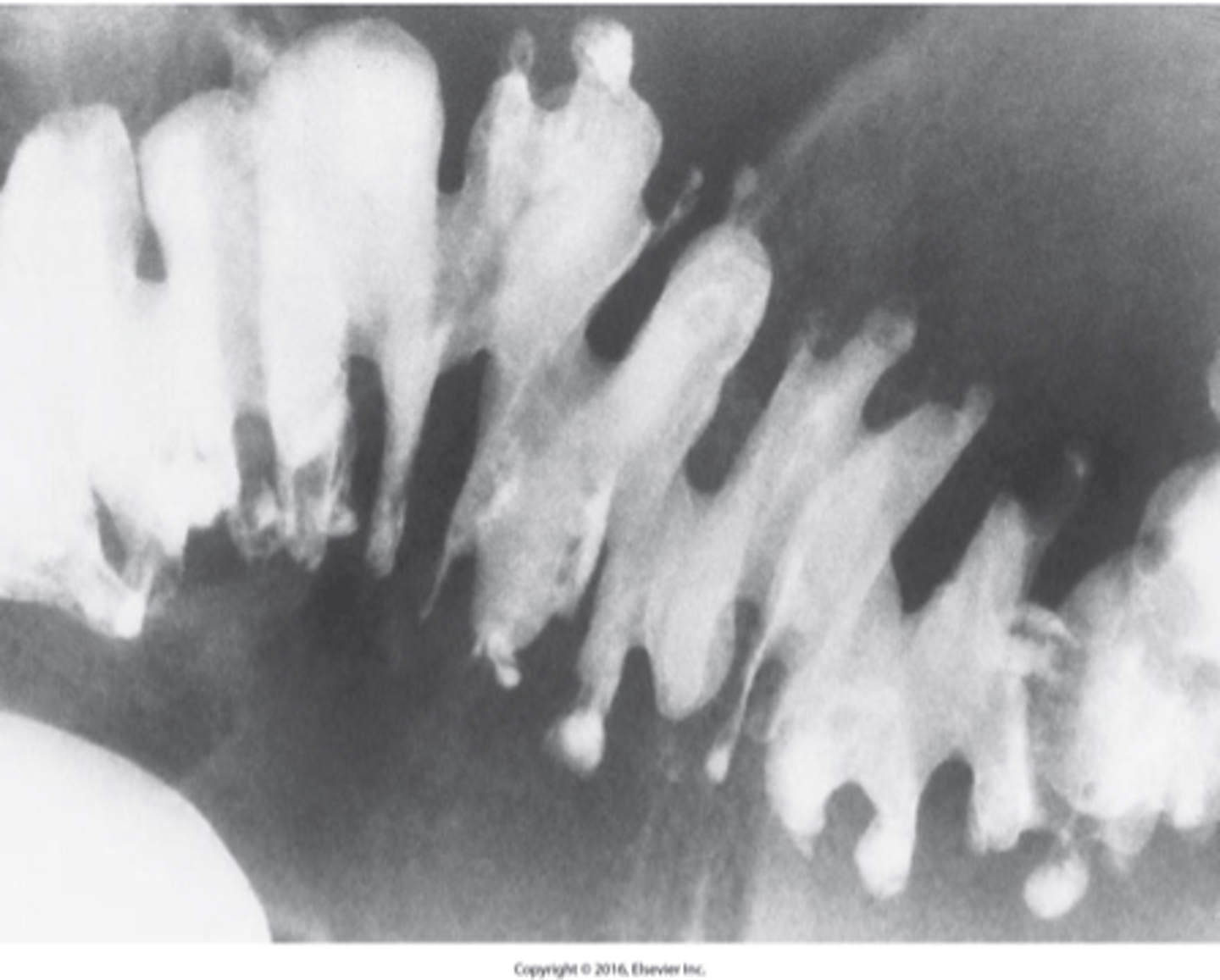
- group of inflammatory processes involving the stomach and duodenum
- Most common location is the lesser curvature
- 5% are malignant, appears as small collection of Ba projecting from lumen
What is peptic Ulcer disease?
- Hemorrhage
- Gastric outlet obstruction
- Perforation
What are the major complications of peptic ulcer disease?
Peptic Ulcer Disease
What is the most common case of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding?
- Duodenal ulcer is the most common manifestation.
- Majority occur in the duodenal bulb.
Peptic Ulcer Disease most common in? Manifest as?
- rare in the United States
- pain is not an early symptom
- gastric carcinoma = linitis plastica pattern
Describe Cancer of the Stomach:
an idiopathic, chronic, inflammatory disorder that most often involves the terminal area of the ileum and most common in young adults
What is Crohn's Disease (Regional Enteritis) ?
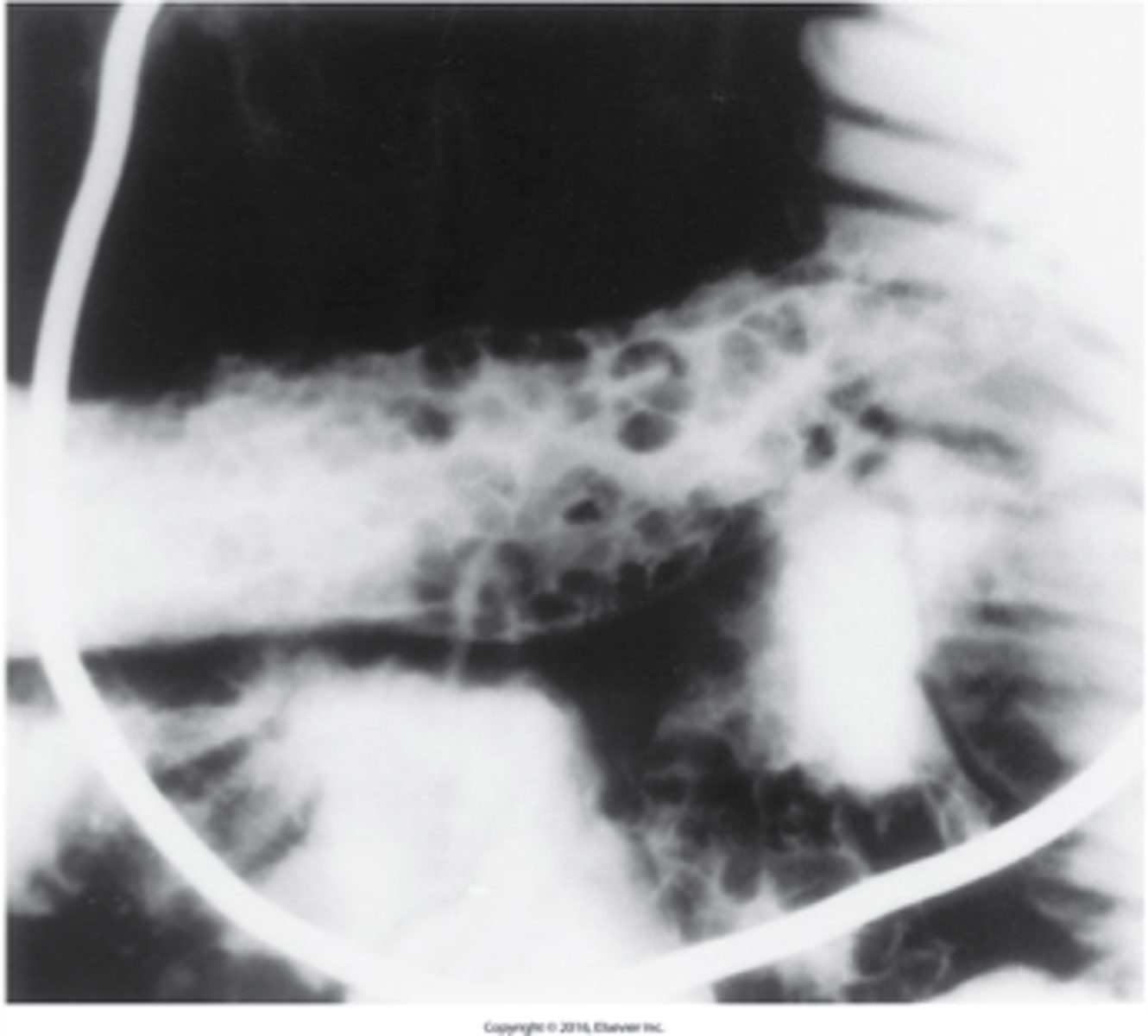
displays skip lesions or cobblestone appearance
What is the imaging appearance of Crohn's Disease (Regional Enteritis)?
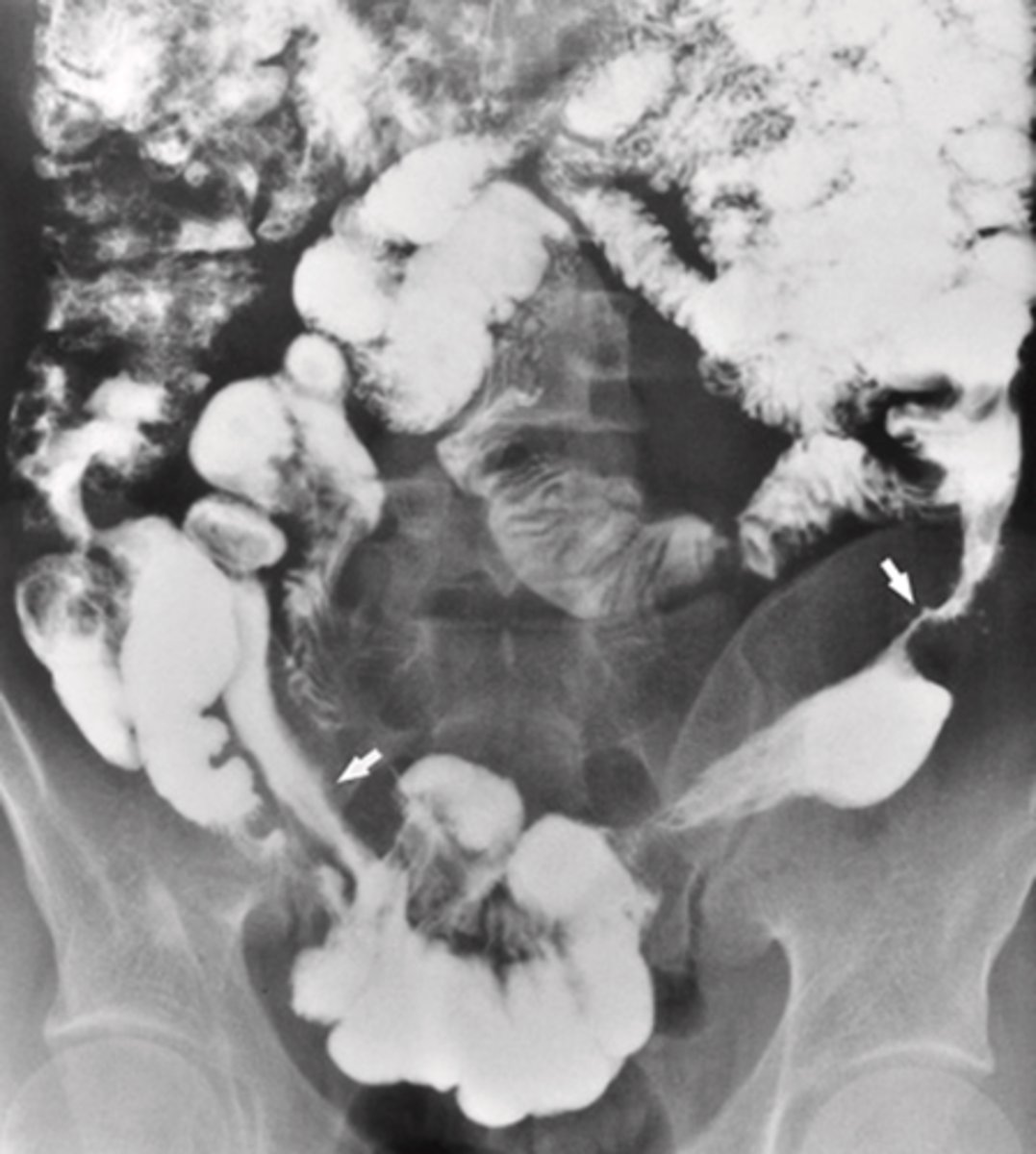
- Most often caused by fibrous adhesions from previous surgery
- Second most common cause is hernias
Other causes:
- Luminal occlusion (gallstone, intussusception)
- Intrinsic lesions (neoplastic or inflammatory strictures, vascular insufficiency
What is a small bowel obstruction?
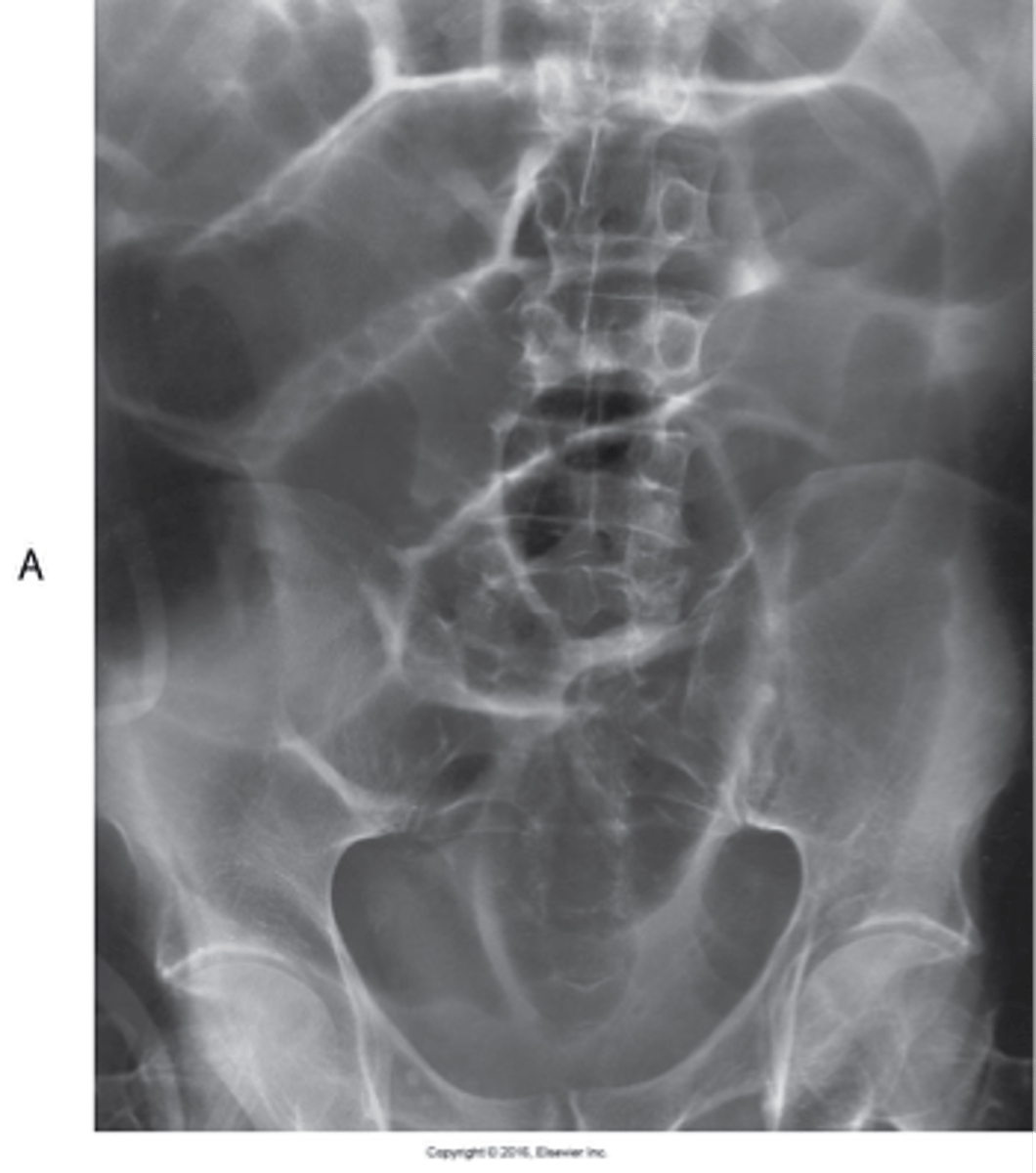
paralytic ileus common disorder of intestinal motor activity
- Fluid and gas do not progress normally through a non-obstructed small and large bowel.
- occurs more often than other obstructions ( normally from surgery)
What is adynamic ileus ?
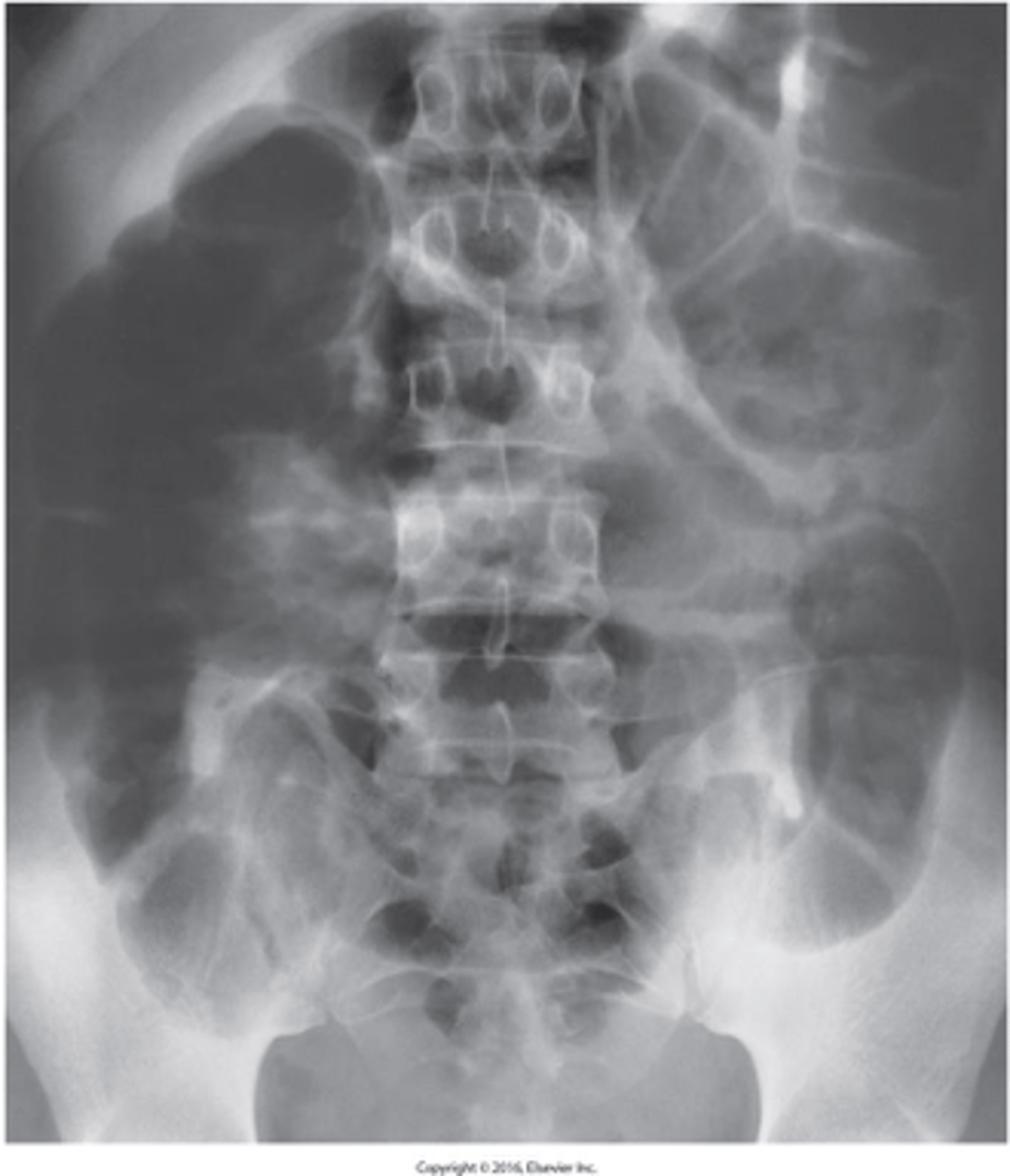
- telescoping of one part of the intestinal tract into another because of peristalsis
- major cause of obstruction in children
What is intussusception?
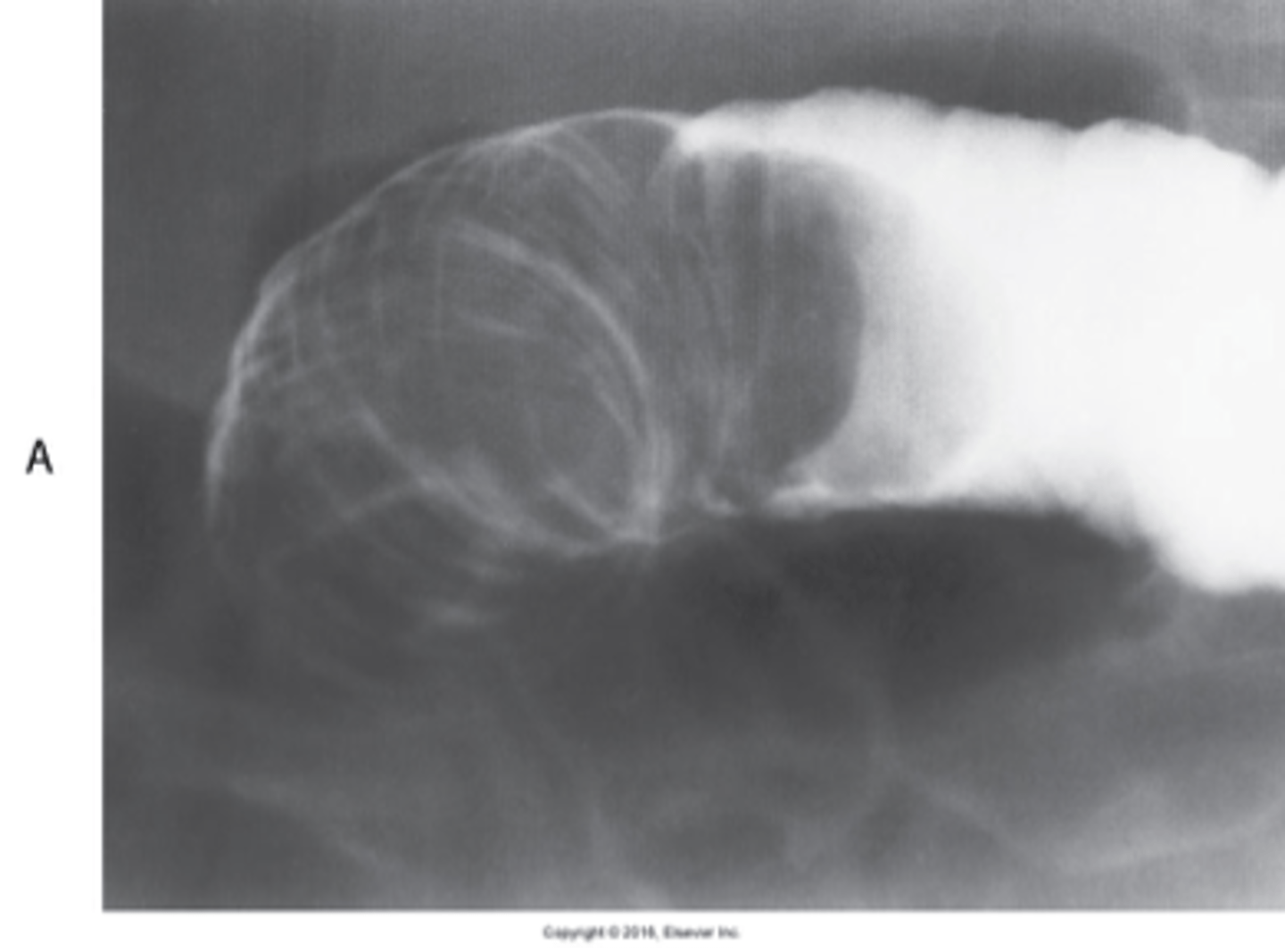
- refers to a multitude of conditions in which there is defective absorption of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats from the small bowel
- results in steatorrhea
What is a Malabsorption Disorders?
the passage of bulky, foul-smelling, high-fat-content stools that float
What is steatorrhea?
a syndrome characterized by acute or chronic diarrhea, weight loss, and malabsorption of nutrients
What spure?
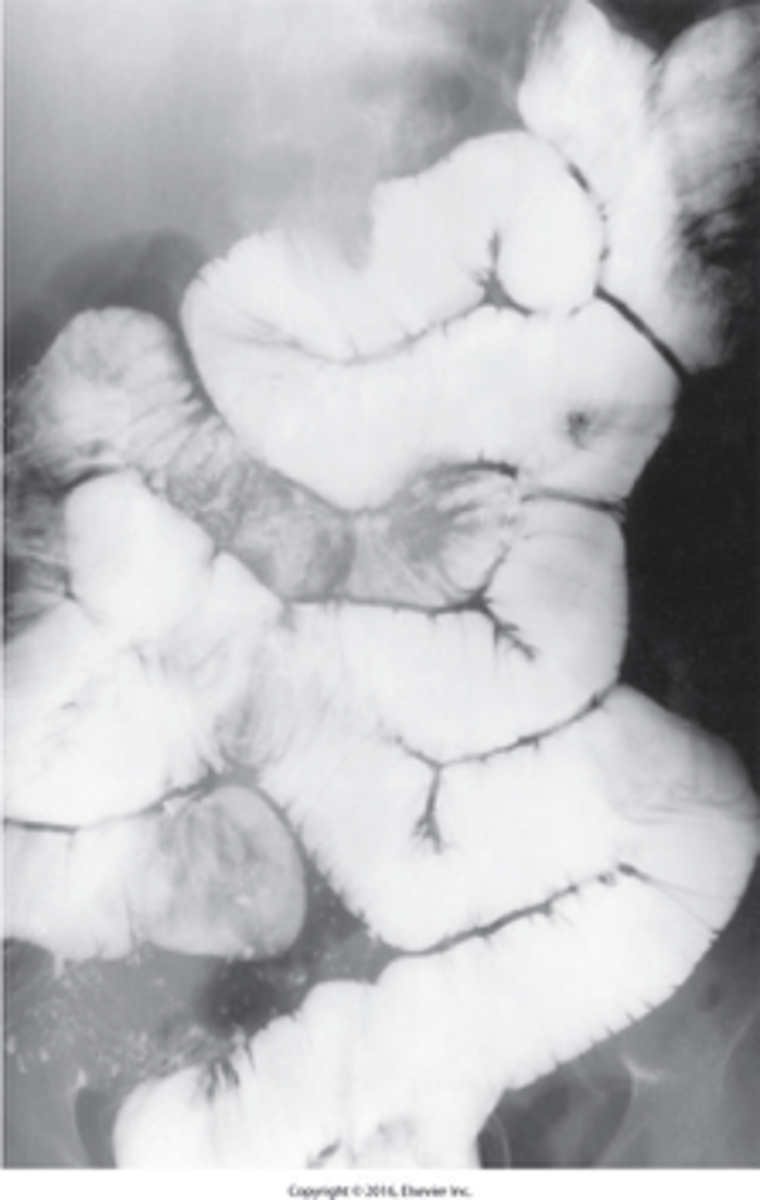
a rare bacterial infection that interferes with normal digestion by impairing the breakdown of foods and the body's ability to absorb nutrients.
What is Whipple disease?
- inflammation of the appendix
- causes: Obstruction of fluid flow by fecalith or scarring
Complications: Gangrene, Abscess, Perforation
What is appendicitis?
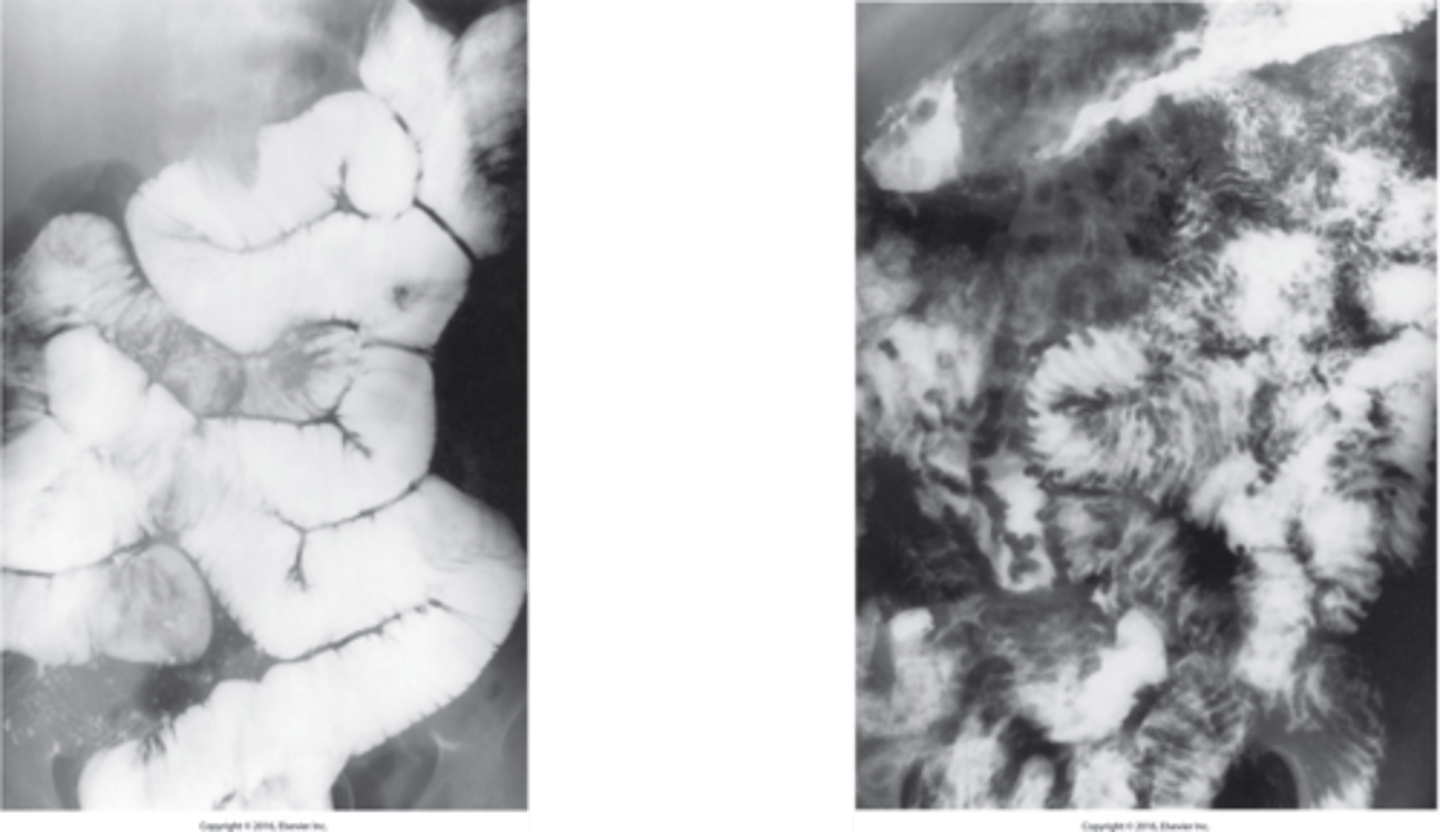
- outpouchings that are acquired herniations of mucosa and submucosa through the muscular layers at points of weakness in the bowel wall
- most commonly in the sigmoid portion
- increases with age
What is diverticulosis "sawtooth"?
is necrosing inflammation in the diverticula.
- Diverticulitis is a complication of diverticulosis
- Complications: Perforation, Abscess, Fistulas to adjacent organs
What is diverticulitis?
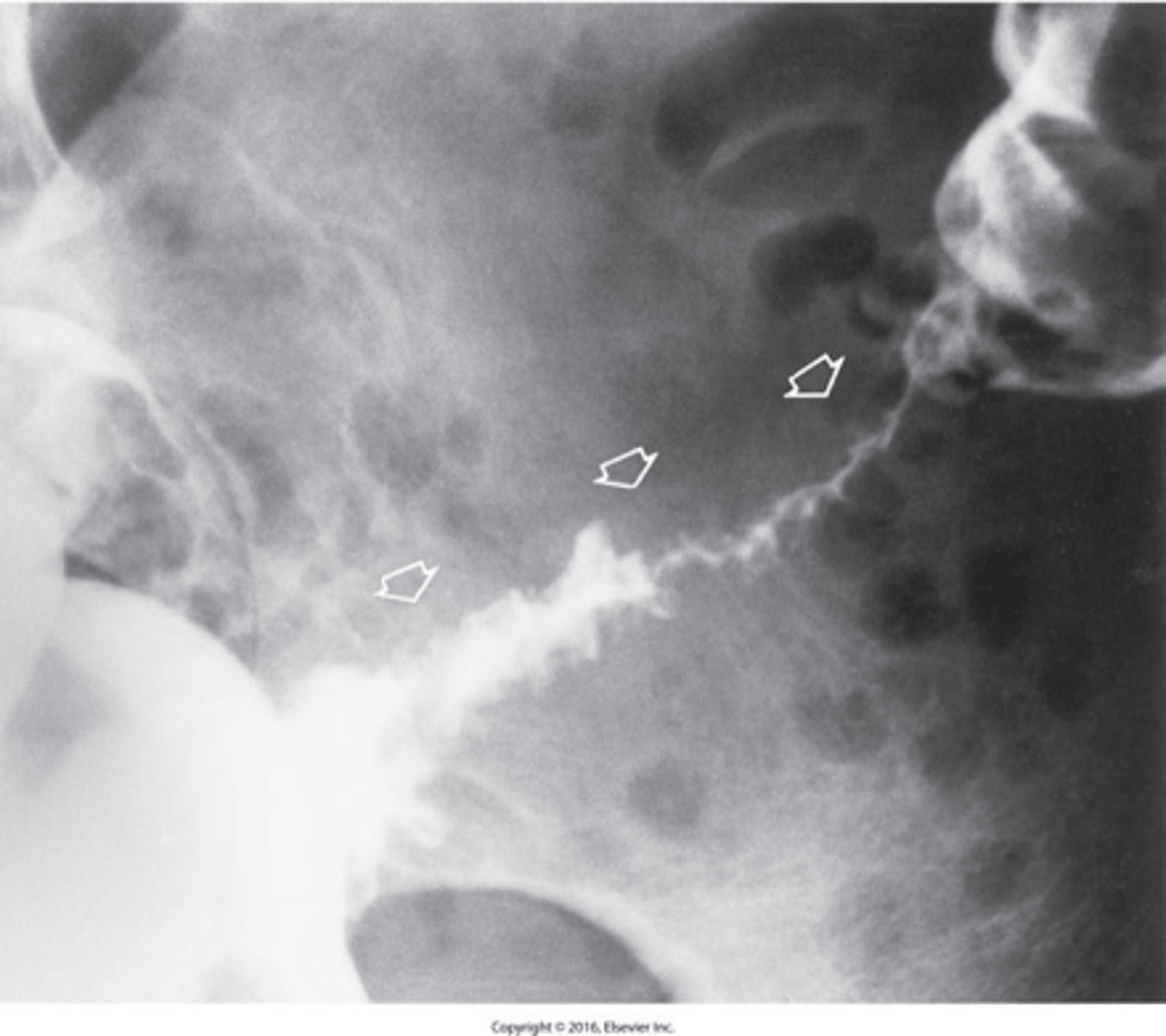
- an idiopathic inflammatory disease of the bowel.
- characteristic feature is alternating periods of remission and relapse.
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
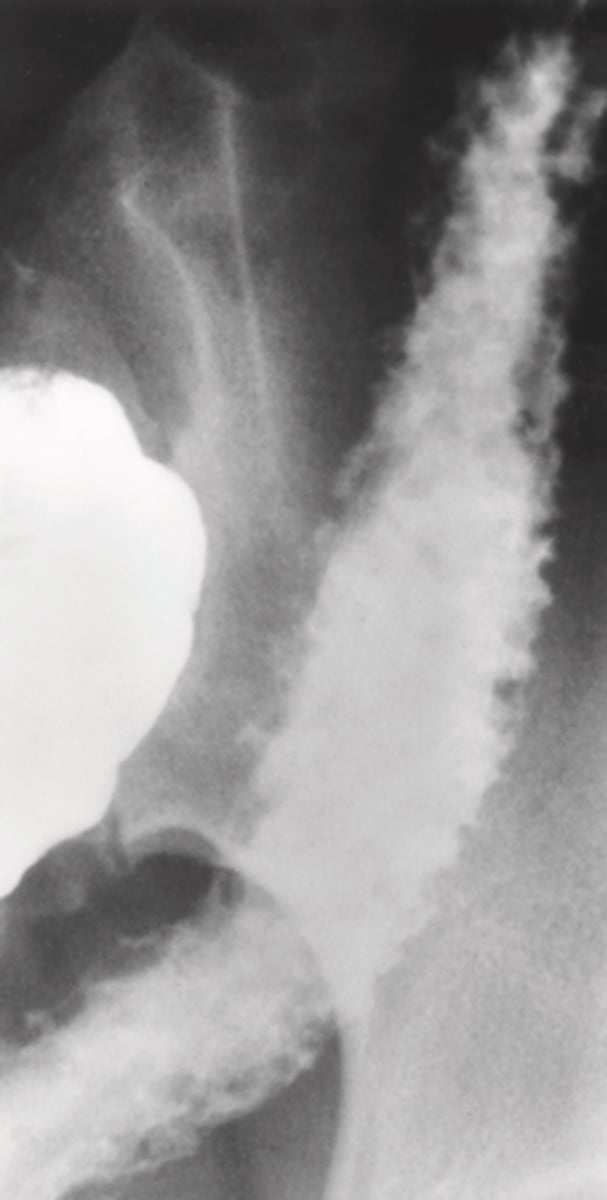
lead pipe
What can Ulcerative colitis be described as not an X-ray ?
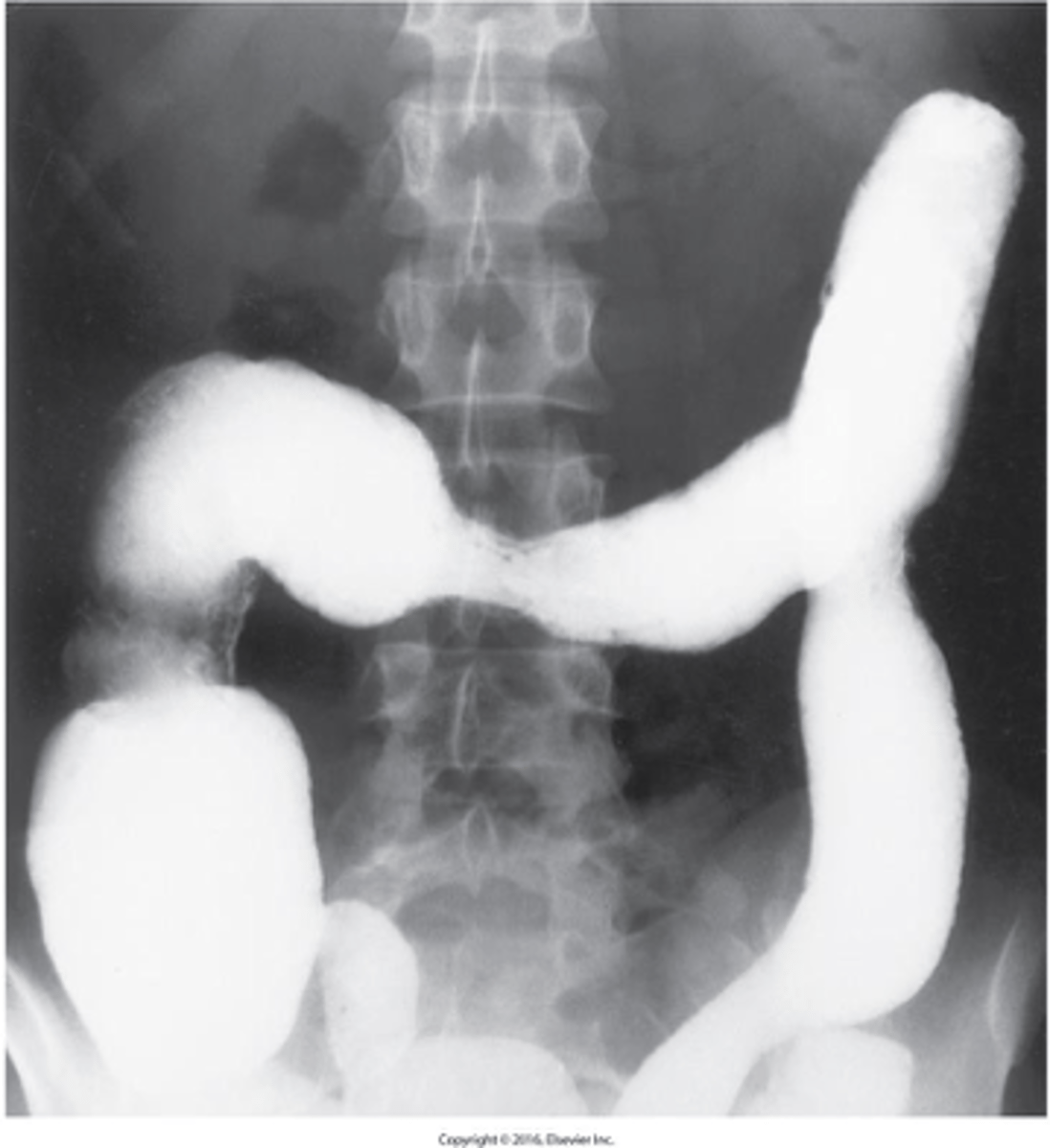
- second major cause of inflammatory bowel disease.
- It most commonly affects the proximal colon
Different from ulcerative colitis
What is Crohn's Colitis?
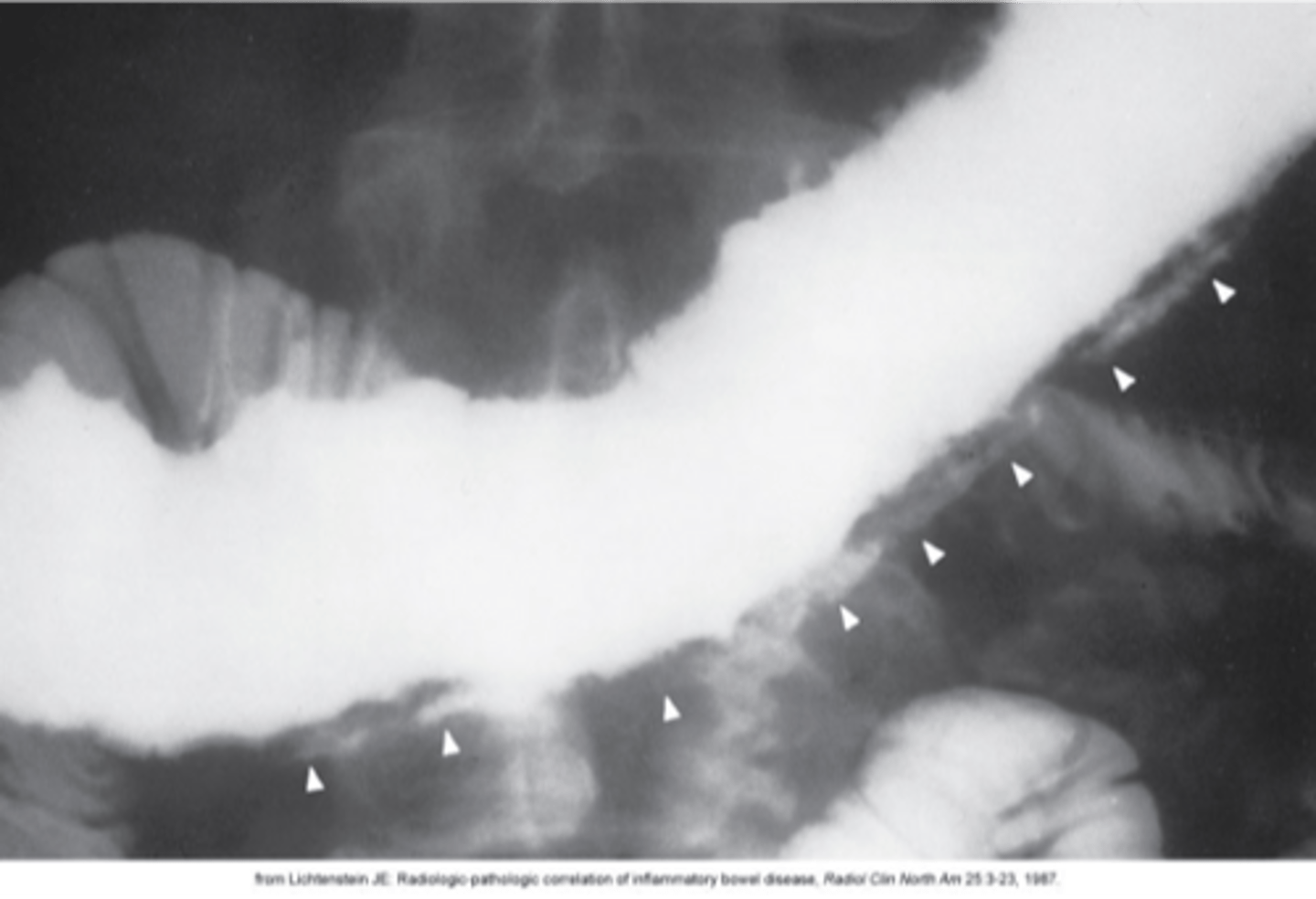
- the abrupt onset of lower abdominal pain and rectal bleeding
- Diarrhea is common
- a history of cardiovascular disease
What is Ischemic colitis?
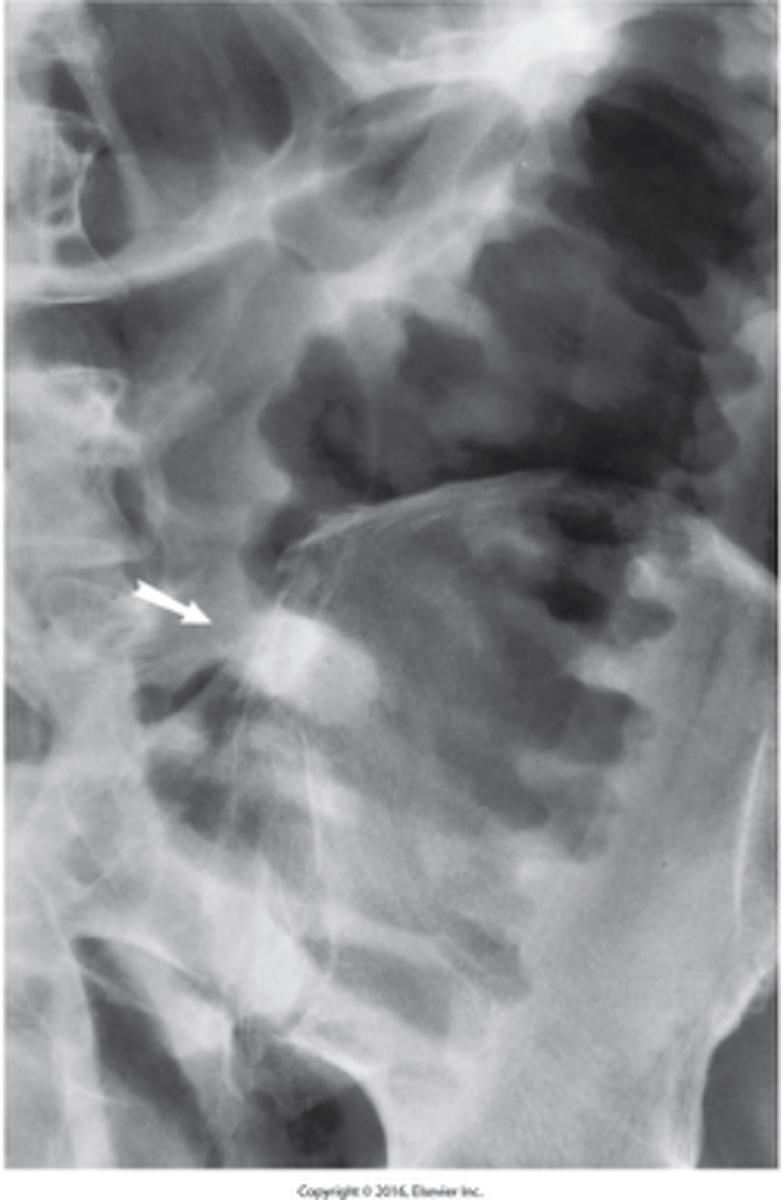
- several conditions that have an alteration in intestinal motility as the underlying pathophysiologic abnormality.
- Most common symptoms are alternating periods of constipation and diarrhea
What is IBS?
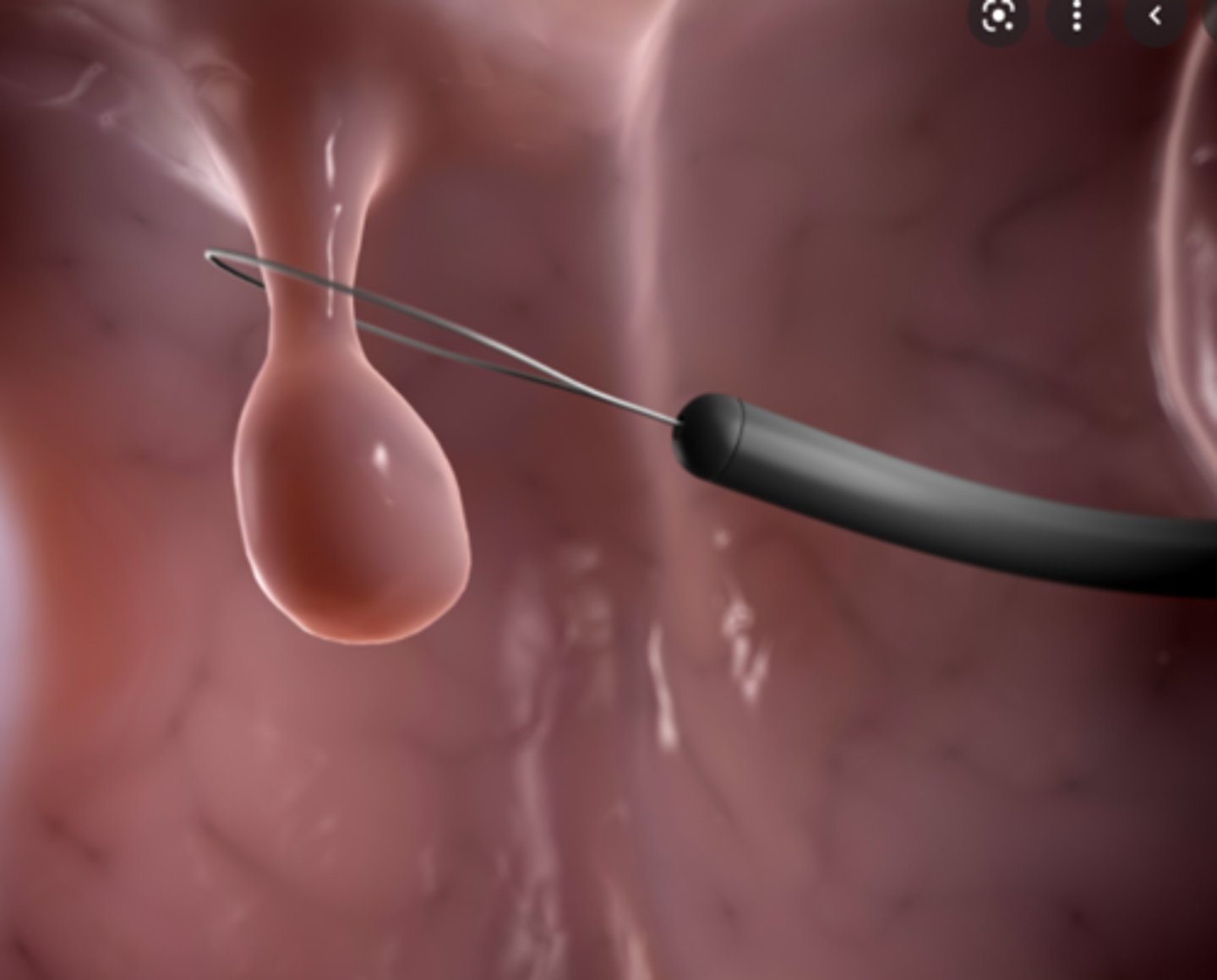
- third leading cause of cancer death in the United States
- Peak age incidence is 50 to 70 years old.
- It is twice as common in men
- Predisposing factors (Long-term ulcerative colitis and Family history of polyps in colon)
What is cancer of the colon?
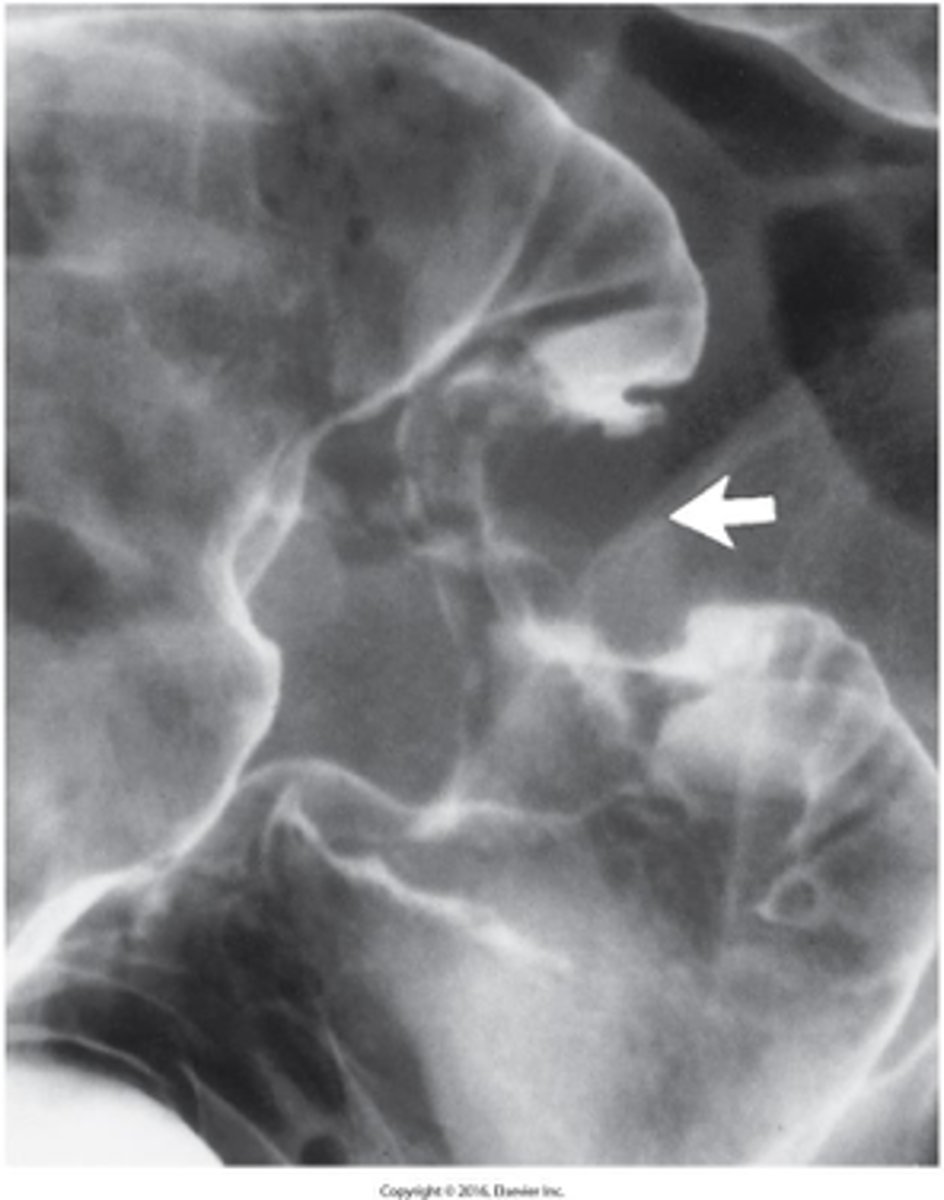
Bulky lesion in the rectum or "apple core / napkin ring"
What is the imaging appearance of colon cancer
- About 70% of large bowel obstructions result from primary colonic carcinoma
- It is usually less acute than small bowel obstructions
- Fewer fluid and electrolyte disturbances are produced
What is a large bowel obstruction?
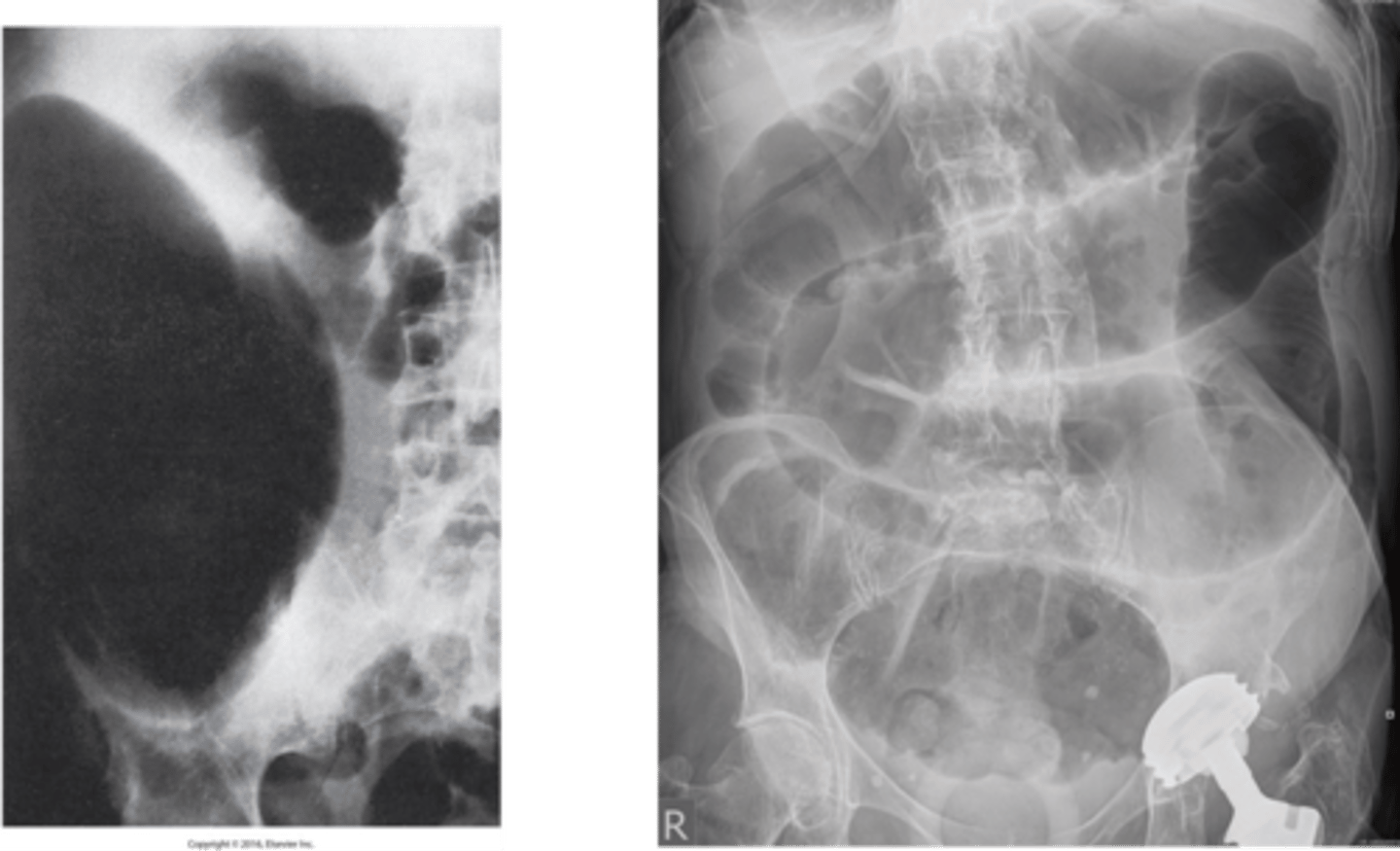
- a twisting of the bowel on itself
Most common sites: Cecum and Sigmoid
Appears as "birds beak"
What is Volvulus of the Colon ?
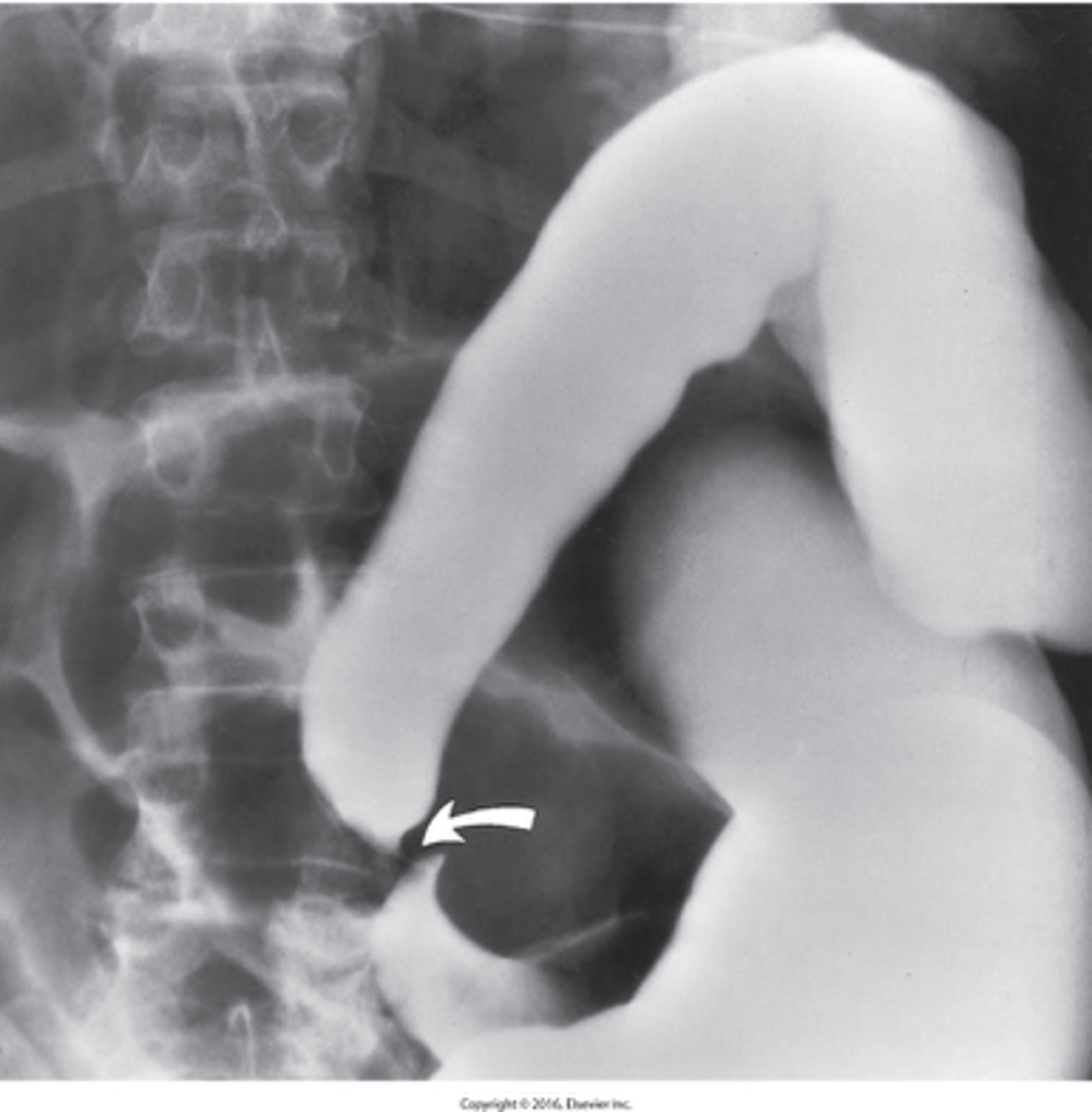
- varicose veins of the distal rectum
- Caused by increased venous pressure, such as with: Constipation, Pelvic tumor, and Pregnancy
What are hemorrhoids?
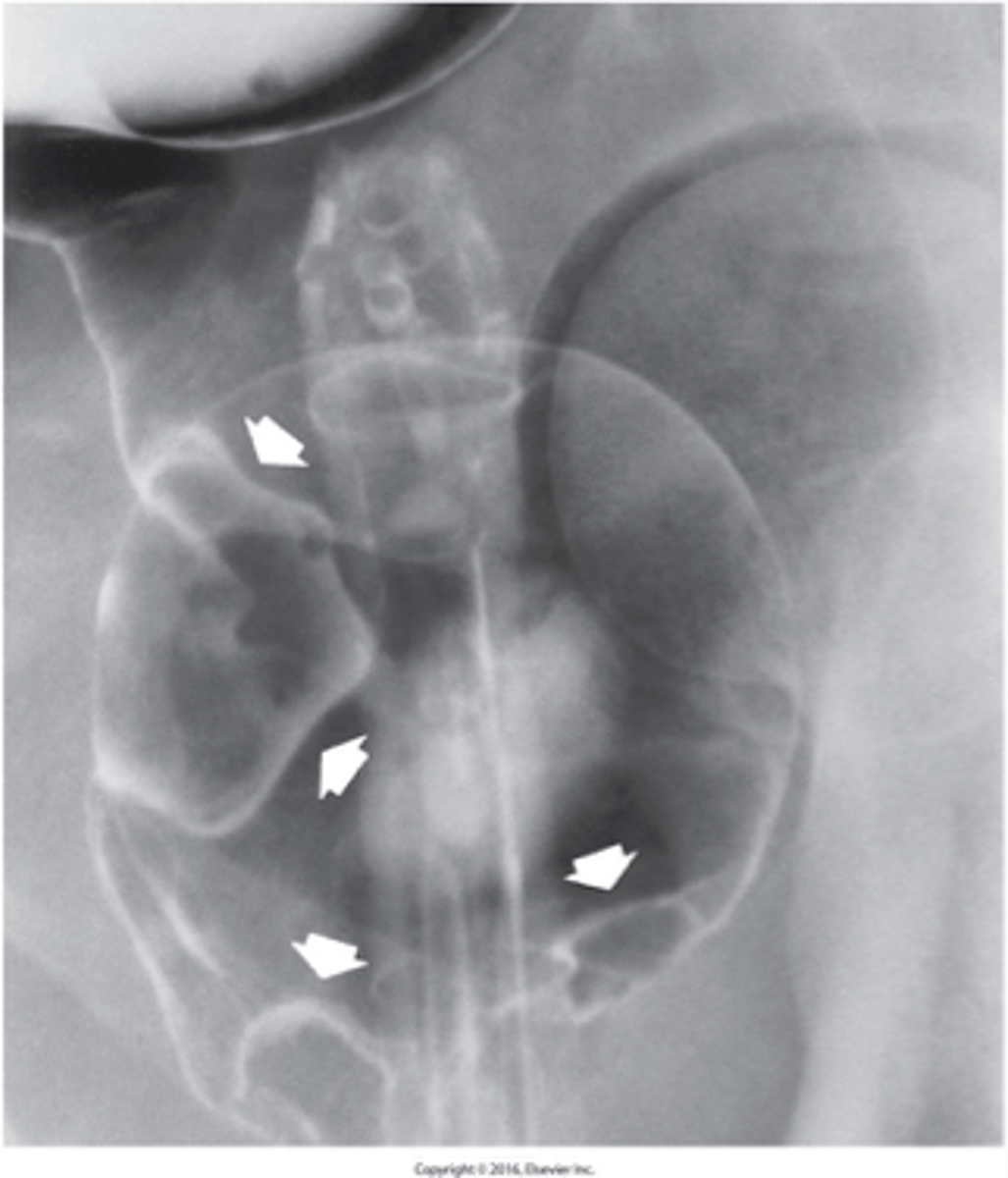
- Cholesterol - predominant type in the United States
- Pigment
What are the two major types of Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) ?
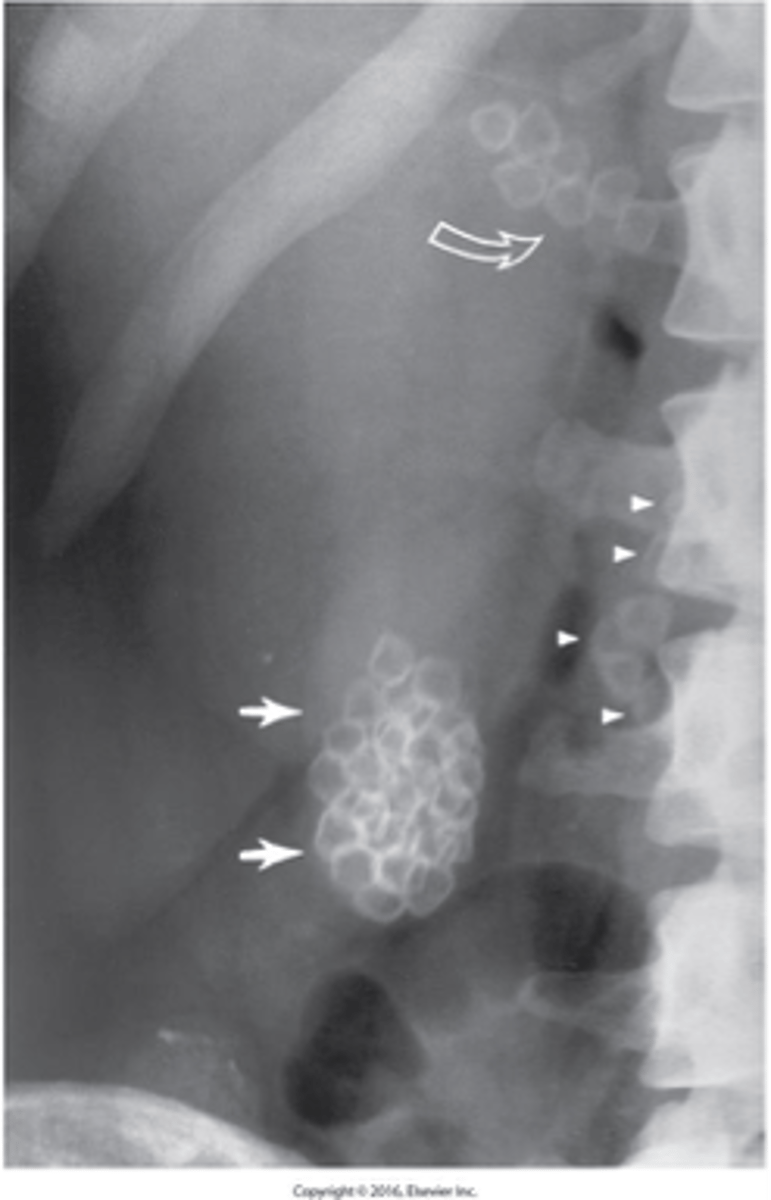
Predispositions:
- Family history - Over age 40 - Overweight - Female
- Ultrasound is the imaging modality of choice to diagnosis.
Describe Gallstones (Cholelithiasis):
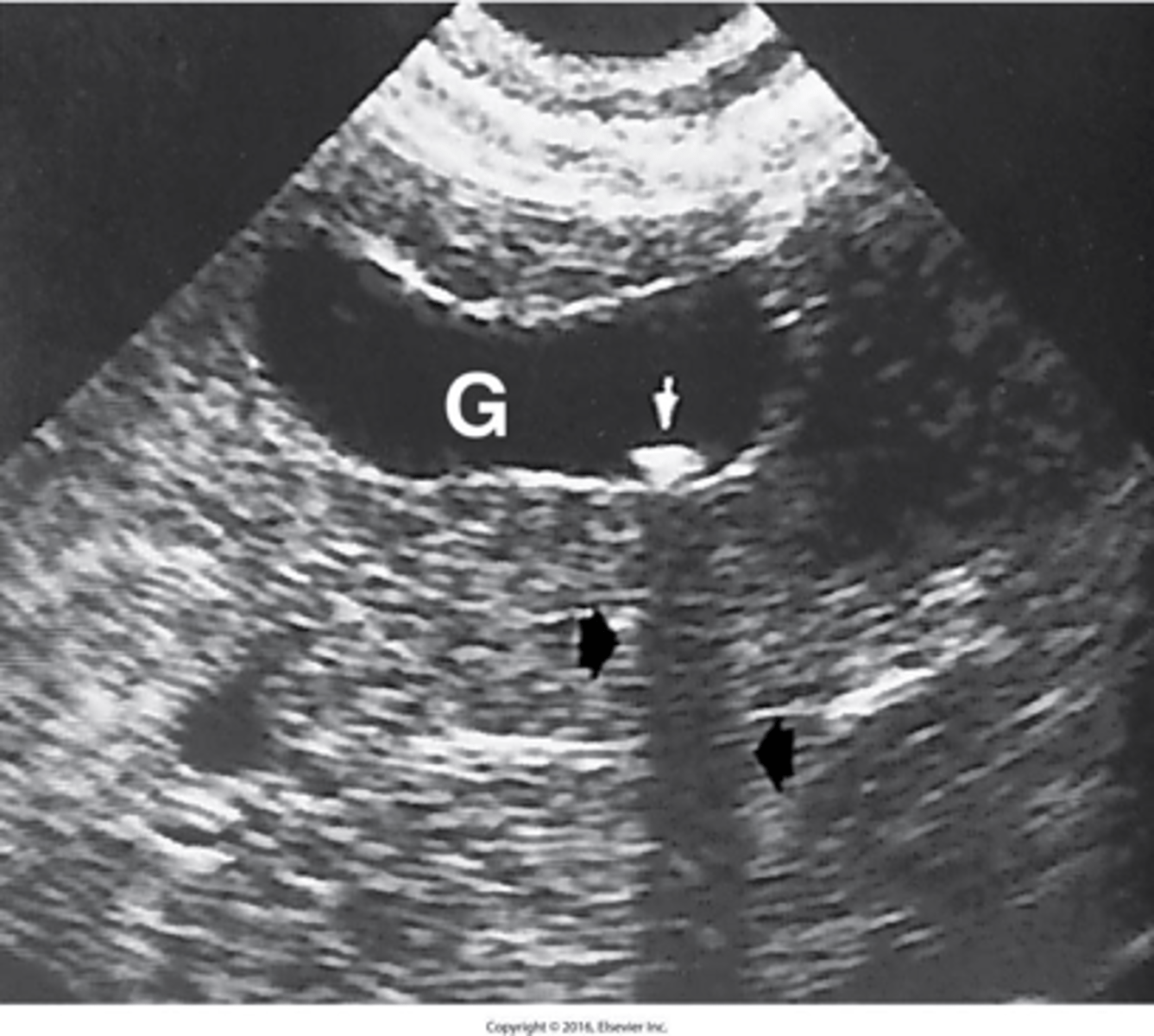
- is acute inflammation of the gallbladder.
- It is usually caused by cystic duct obstruction by a gallstone.
What is acute cholecystitis?
growth of gas-forming organisms in the gallbladder.
What is Emphysematous Cholecystitis?
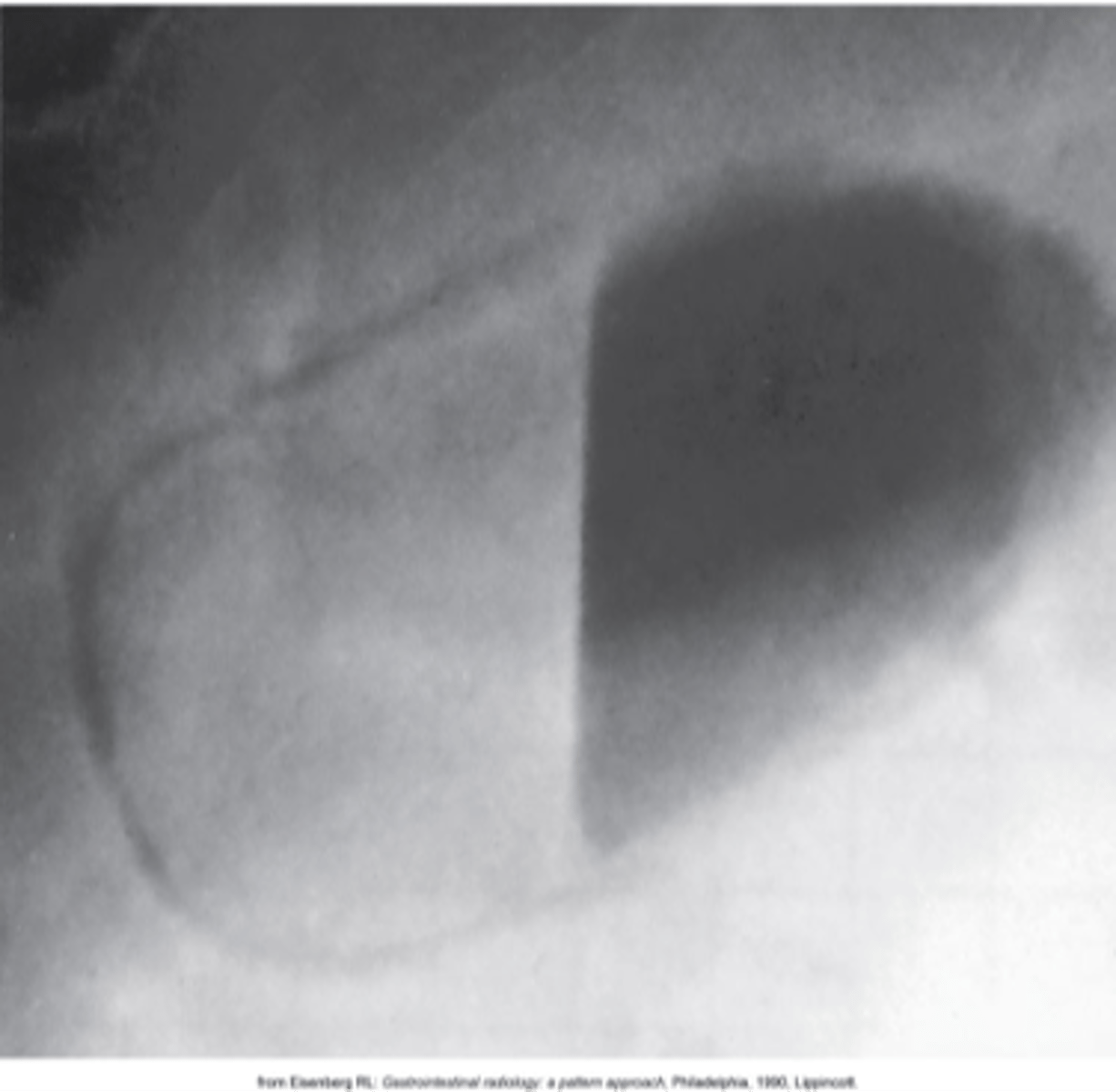
- calcification of the gallbladder walls.
- is caused by chronic cholecystitis.
(Walls become fibrous, then calcified)
- additive
What is porcelain gallbladder?
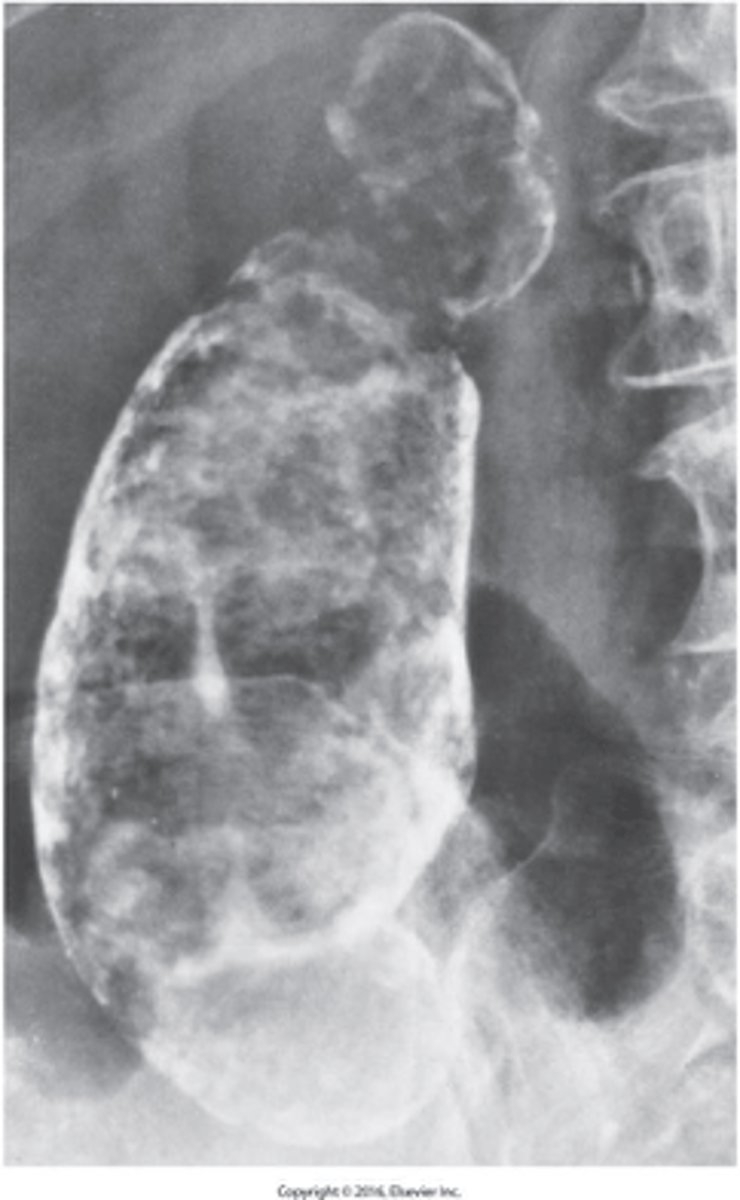
- most prevalent inflammatory disease of the liver.
- Common causes: Viral infection and Reaction to drugs and toxins
What is hepatitis?
HAV, infectious hepatitis, spread via digestive tract from oral or fecal contact.
What is Hepatitis A virus
HBV, serum hepatitis, contracted by exposure to contaminated blood or blood products or sexual contact.
(Healthcare workers are at risk and vaccine is available)
What is Hepatitis B virus (HBV)?
common cause of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, & hepatocellular carcinoma, contracted by blood transfusion or sexual contact
What is Hepatitis C virus (HCV)?
acquired by ingesting food or water that has been contaminated with fecal material.
What is Hepatitis E virus (HEV)?
- the chronic destruction of liver cells and structure, with nodular regeneration of liver parenchyma and fibrosis.
- end-stage liver disease.
- The fibrous connective tissue replaces the destroyed liver cells with cells that have no liver cell function.
- Most characteristic symptom – ascites
What is cirrhosis?
- fluid in the peritoneal cavity or abd.
- aditive
What is ascites ?
- inflammatory process in which protein- and lipid-digesting enzymes become activated within the pancreas and begin to digest the organ itself.
- Most common cause (Excessive alcohol consumption)
- other causes (Gallstones entering the common bile duct, obstructing the ampulla, , and causing bile to reflux into the pancreas which causes an inflammatory reaction)
What is Acute Pancreatitis?
- results when frequent injury to the pancreas causes scar tissue.
- It causes the gland to lose its ability to produce digestive enzymes, insulin, and glucagon
Three symptoms: Pain, Malabsorption causing weight loss, Diabetes
What is Chronic Pancreatitis?
adenocarcinoma.
What is the most common type of cancer of the pancreas is?
head of the pancreas
What is the most common site of cancer of the pancreas?
free air in the peritoneal cavity.
What is Pneumoperitoneum?
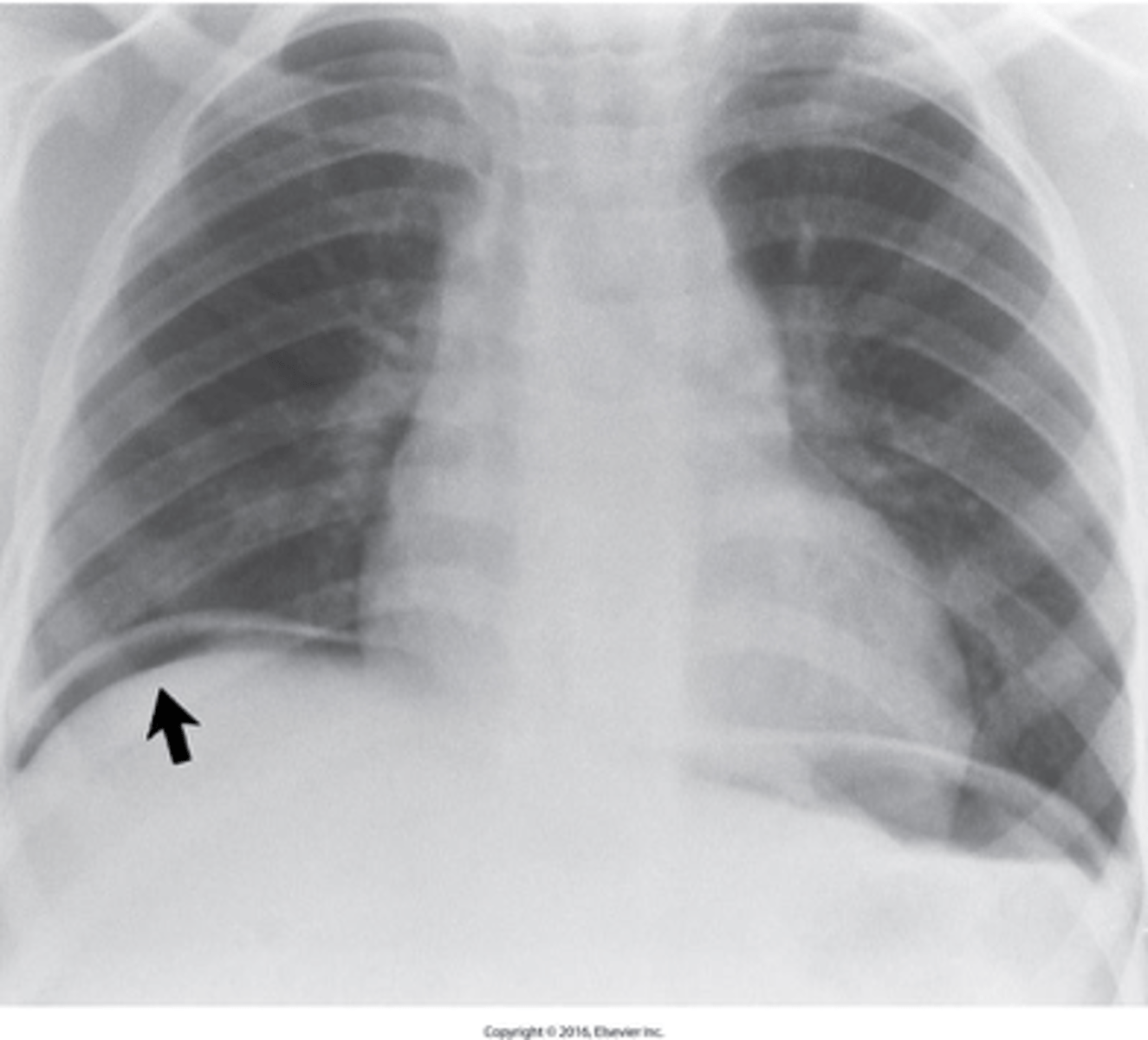
left lat decub
What position is performed to show Pneumoperitoneum?
enlargement of the spleen
What is Splenomegaly?
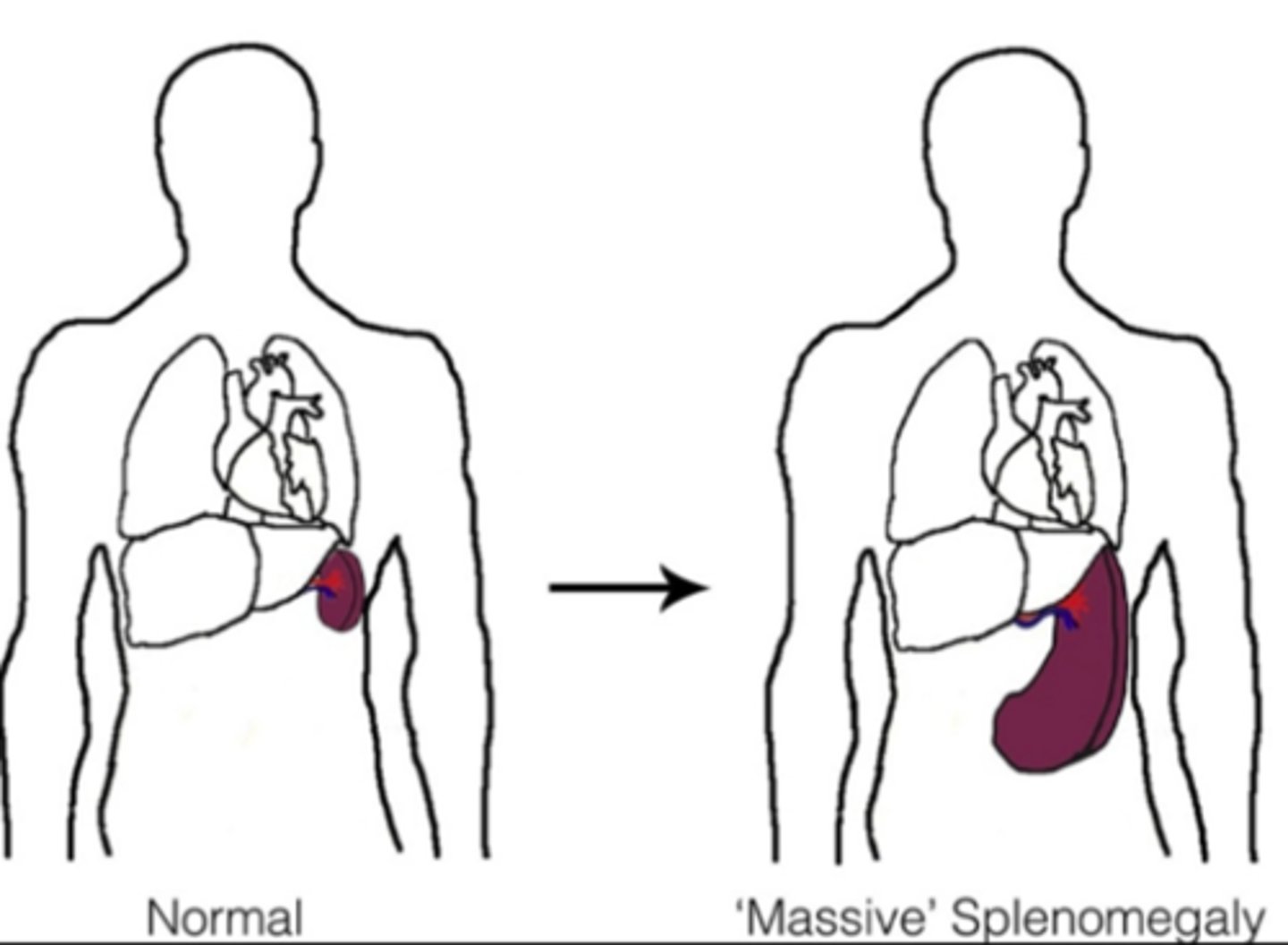
Most common cause of splenic rupture is trauma
What is a splenic rupture?
What is Chronic atrophic gastritis?
Long-term stomach lining damage that causes thinning and less acid production.
What is Chyme?
The thick, soupy food mixture in your stomach after digestion starts.
What is colonic ileus?
It is a distention of the large bowel without signs of obstruction
-Usually accompanies or follows an acute abdominal inflammatory process or abdominal surgery.
What is degluttion?
swallowing
What is Emulsifier?
substance that helps mix fat and water in food or digestion.
What is Epiphrenic diverticula?
Pouches that form near the lower end of the esophagus.
What is Gastrinomas?
Tumors that release too much stomach acid, causing ulcers.
What glycogen?
A stored form of sugar in the liver and muscles, used for energy.
What is insulinoma?
A tumor in the pancreas that makes too much insulin.
What is Localized ileus?
A small section of the intestine that temporarily stops moving food.
What is Mallory-Weiss syndrome?
Tears in the lower esophagus usually caused by severe vomiting.
What is a Polypoid?
Something shaped like a polyp (a small growth, often in the colon).
What is Ulcerogenic islet cell tumors (gastrinomas)?
Tumors that produce too much acid, causing ulcers
What is Villi?
Tiny finger-like structures in the small intestine that help absorb nutrients