Biology Honors Unit 1: Biochemistry Test
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Organic Molecules
Contain carbon and all living things have it.
Carbon
Forms up to 4 bonds. Forms chains or rings with single, double, or triple bonds.
What is the primary molecule? Why?
Carbon because of it’s ability to bond (covalent)
Strong bond to other molecules
Shares negative electrons
Monomer
Individual molecules that hook together to make a polymer.
Polymer
Large molecules made up of monomers.
What are the four macromolecules/biological molecules
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
Short term energy (releases quickly & burns quickly)
Structural support (in the cell wall of plants and fungi)
Four calories per gram
What do Carbohydrates usually end in?
-ose
What is the chemical formula for glucose?
C6H12O6
What are the elements of carbohydrates?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What do carbs need to be paired with to release properly?
Fats and proteins
What is the monomer of a carb?
Monosaccharide: Glucose (plants), galactose (milk), fructose (fruit).
What is the polymer of a carb?
Polysaccharide - many sugars bonded together to form one long polymer.
Dehydration Synthesis [formation (aka the marriage of complex carbs)]
Combining single/simple compounds into a complex one by removing water.
Hydrolysis (divorce of complex carbs)
Breaking apart of complex carbs by adding water.
What are the functions of lipids?
Long term energy storage
Protection to organs
Insulation
Waxy covering
Water loss protection for plants
Qualities of lipids
Nonpolar
Repels
Does not dissolve
What do lipids do in plants?
Store oil
Monomer and polymer of a lipid
Monomer: 2 parts - glycerol and fatty acid
Polymer: triglyceride - 3 monomers
What are saturated fats?
Solid and straight structure, referred to as bad, and are single bond carbon.
What are unsaturated fats?
Not solid, bent, referred to as good, liquid at room temperature, double bond of carbon.
What are the elements of lipids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen - mostly CH
What are the elements of proteins?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
What is the monomer of a protein?
Amino acid - joined together by peptide bonds to form primary structures.
What is the polymer of a protein?
Polypeptide - many amino acids held by peptide bonds (aka protein).
How many amino acids are there?
20
What are the functions of proteins?
Enzymes
Antibodies
Hemoglobin
Muscle movement
Builds hair and nails for structure/protection
Some hormones, like insulin, for regulating body processes.
What are the elements of nucleic acids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
Nucleotide
Phosphate group
Sugar
Nitrogenous base
What is the polymer of nucleic acids?
DNA - inheritance of traits (genetic info/code)
RNA - Used to make proteins
Ribosome - organelle that makes protein
What is a chemical reaction?
A process in which one or more substances is either combined or broken down.
Enzyme
proteins which are heterogeneous unbranched chains of amino acids.
Biological catalysts
Increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.
Chemical agents that selectively speed up chemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction.
*In simple terms, Enzymes are used by cells to trigger and control chemical reactions.
*They lower the activation energy and increase the rate of reaction.
*One or more substances are converted into one or more different substances.
What would not be possible or useful without enzymes?
Growth
Blood coagulation
Healing diseases
Breathing
Digestion
Reproduction
What do most enzyme names end in?
-ase
Ones that don’t end in -ase are peptin, trypsin, and chrymotrypsin.
Substrates
Fit in a lock and key fashion.
One enzyme can break down one substrate.
A substrate is an enzyme bound to a molecule.
They are the reactants that are catalyzed by the enzyme.
What is the lock and key hypothesis?
Enzymes bind to substrates based on shape because each protein has a specific shape.
Active site
Where substrates bind on an enzyme
Enzymes are NOT
Changed by the reactions they catalyze, therefore they are reusable.
What does catalyze mean?
To accelerate a reaction by lowering activation energy.
What do enzymes do?
They either break a substance into smaller ones, or combine substrates into one larger one.
What is the induce fit hypothesis?
Enzymes can change shape slightly to fit the substrate a little better.
Activation energy
Energy needed to start a reaction.
What are enzymes affected by?
Temperature and pH.
Temperatures outside correct range can cause enzymes to break or change shape. (Denaturing)
Enzymes denature when pH is too acidic or alkalotic, but they can restore to their original shapes.
What are denatured enzymes and what do they mean?
Denatured = messed up
Enzymes denature when temp. or pH is too high or too low.
pH scale
0 = acidic
7 = neutral
14 = alkaline
What is the first step of an enzymatic reaction?
The substrate(s) bind to the active site.
What do most cells contain that allows them to turn enzymes on or off during critical stages of development?
Proteins
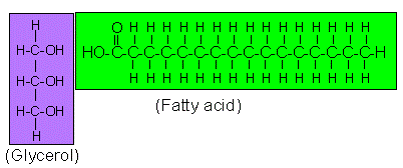
Which macromolecule is represented below?
Lipid
Main source of energy for living things
Carbohydrate
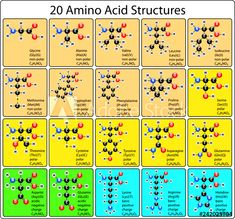
Which macromolecule is represented below?
Protein
Helps us to regulate cell processes by the use of hormones such as insulin
Protein
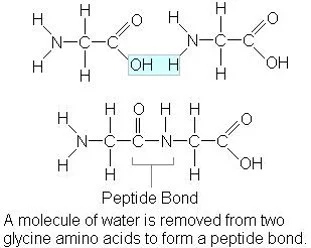
Which macromolecule is represented below?
Protein
Starch is the main form of stored energy in plants
Carbohydrate
Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy
Protein
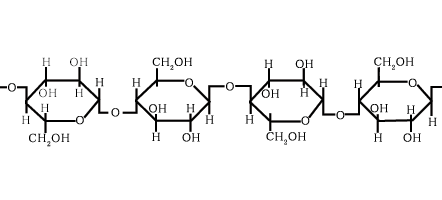
Which macromolecule is represented below?
Carbohydrate
The monomer of a polysaccharide is a monosaccharide
Carbohydrate
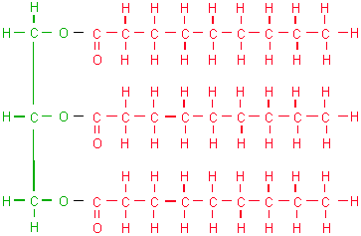
Which macromolecule is represented below?
Lipid
The monomer of DNA is a nucleotide
Nucleic Acid

Which biomolecule is this?
Lipid
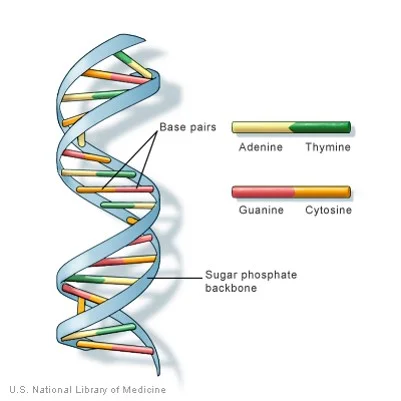
Which macromolecule is represented below?
Nucleic Acid
Contains the code to make proteins
Nucleic Acid
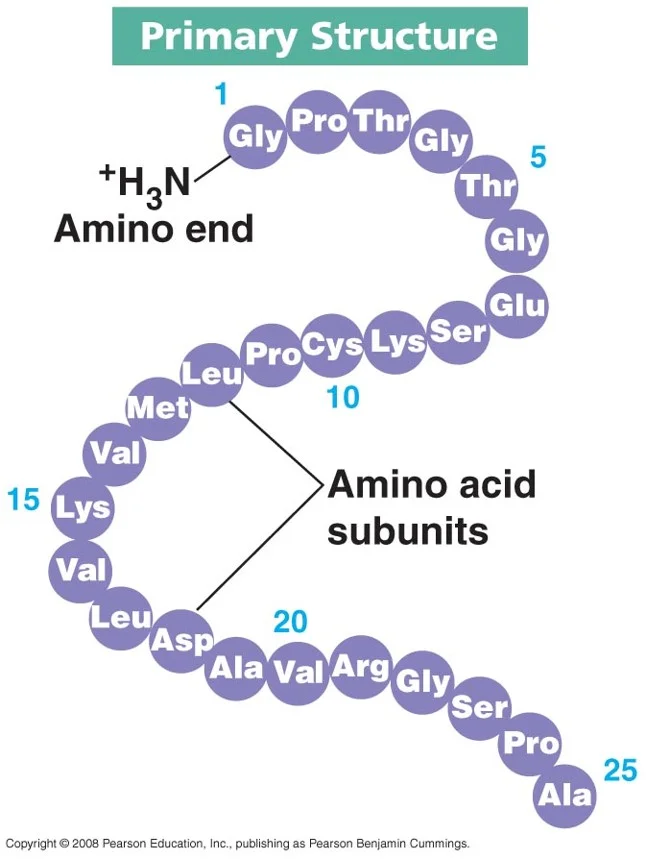
Which macromolecule is represented below?
Protein
The monomer of this biomolecule is an amino acid
Protein
Most of these biomolecules in the suffix -ose
Carbohydrate
Glycogen is the main form of stored energy for animals
Carbohydrate
This biomolecule includes fats, oils, & waxes
Lipid
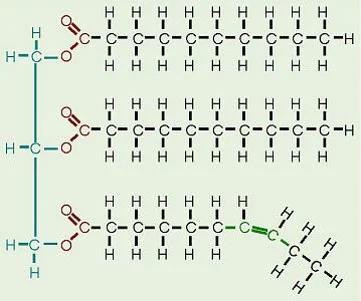
Which macromolecule is represented below?
Unsaturated Lipid
Cellulose provides support and structure for plants
Carbohydrate
Antibodies help defend against disease and fight infections
Protein
An important part of cell membranes
Lipid
Transports substances in and out of cells through channels in the cell membrane
Protein
Used to store energy that is released slowly
Lipid
Forms bones, muscles, hair, and nails
Protein

Which biomolecule is this?
Protein
What are examples of polysaccharides?
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
Chitin
What is the second step of an enzymatic reaction?
The enzyme-substrate complex is formed.
What is the third step of an enzymatic reaction?
Bonds are formed or broken in the substrate.
What is the fourth step of an enzymatic reaction?
The products are released.
What is the last step of an enzymatic reaction?
Enzymes can be reused over and over again.
What is starch?
Energy storage for plants
What is glycogen?
Storage excess of glucose in an animal’s live
What is cellulose?
Makes up cell walls in plants (Humans cannot digest this and animals barely can)
What is chitin?
Exoskeleton of insects and arthropods. (In the cell walls of fungi)
What are antibodies?
Protection from diseases
What is hemoglobin?
Transports oxygen in the blood
What are the aspects of muscle movement as a function of proteins?
Titin is the biggest protein
Has over 27,000 amino acids
What do lipids do in animals?
Fat energy storage, protection, and insulation
What is an example of lipids?
Waxes: waterproof coverings
What are phospholids? (aka lipids)
Make up cell membranes
What are hormones? (aka lipids)
Messengers for body
Cholesterol, estrogen, testosterone, steroids