Cardiovascular System
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Function
Circulate blood which delivers O2 & Nutrients to Tissues; Remove CO2 & Wastes
3 Components
Heart
Blood Vessels
Blood
2 Circulatory Pathways:
Pulmonary Circuit: The Movement of Oxygen - Poor (AKA Deoxygenated) Blood From Right Side of Heart to Lungs & Oxygen - Rich Blood Back to Heart
Systemic Circuit: Movement of Blood From Left Side of Heart to Body Tissues And Back
The Heart - Overview
It is Mostly a Muscle: Made of Cardiac Muscle Cells
Location: Thorax, In the Pericardial Cavity of Inferior Mediastinum
Regions:
a. APEX- The Pointed Bottom; Points Towards Left Hip
b. BASE- The Top; Points Towards Right Shoulder
The Heart - Coverings
Fibrous Pericardium: Tough, Dense CT
Serous Pericardium
a. Parietal Pericardium: Outermost Layer
b. Visceral Pericardium: (AKA Epicardium) - Lies Right On the Heart
c. Serous Fluid: In Between the 2
The Heart - WALLS of the Heart
Epicardium: Same as the Visceral Pericardium
Myocardium: Middle & Thickest Layer, Mostly Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Endocardium: Smooth Inner Layer, Made of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Anatomy Of The Heart - Quick Notes (Before Anatomy Diagram)
Mammals have a 4 Chambered Heart
2 Atria=Receives Blood
2 Ventricles=Pump Blood Out
The Chambers are Separated by 4 Valves
2 Atrioventricular Valves
2 Semilunar Valves
Anatomy Of The Heart & The Pathway Of Blood Diagram


Superior Vena Cava
Large Vein Carrying Deoxygenated Blood (Blood Low In O2 And High In CO2) From Upper Body
( Delivers To: Head, Neck, Arms, Chest )

Inferior Vena Cava
Large Vein Carrying Deoxygenated Blood From Lower Body
( Delivers To: Abdomen, Pelvis, Legs )

Right Atrium
Chamber That Receives Deoxygenated Blood From The Vena Cava

Tricuspid Valve (AKA Right A/V Valve)
Has 3 Cusps (Flaps)
Chordae Tendinae - Fibers That Anchor Cusps To Heart Wall (At The Papillary Muscle)
Hold Valve Flaps In Closed Position

Right Ventricle
Pumps Blood Into Pulmonary Circuit Via Pulmonary Arteries

Pulmonary Valve
A Semilunar Valve; Ensures Blood Goes To Lungs

Pulmonary Trunk

Pulmonary Arteries (Left & Right)
Takes Deoxygenated Blood To Lungs

Pulmonary Veins (Left & Right)
Brings Oxygenated Blood To Left Atrium
2 Pairs

Left Atrium
Chamber That Receives Oxygenated Blood From The 4 Pulmonary Veins

Mitral AKA Bicuspid Valve
AKA Left A/V Valve
Has 2 Cusps And Chordae Tendinae

Left Ventricle
Pumps Blood To Systemic Circuit
Walls Are Substantially Thicker

Aortic Valve
A Semilunar Valve Between Left Ventricle And Aorta

Aorta
Largest Artery In The Body
U Shaped
Descends Posteriorly To Heart

Interventricular Septum
Wall That Separates The Two Ventricles
4 Valves In Order Of How Blood Flows
Tricuspid Valve
Pulmonary Valve
Mitral Valve
Aortic Valve
Types of Blood Vessels - Arteries
Arteries - Blood Vessel that Carry Blood AWAY from Heart (Usually Oxygenated)
Adapted for HIGH Pressure Blood Flow:
Walls are Thicker With Muscle & Elastic Fibers (Recoil)
NARROWER Diameter Lumen
Smooth Muscles can DECREASE the Size of the Lumen to INCREASE Blood Pressure
Lacks Valves - Which ALLOWS for Constant Flow
Types of Blood Vessels - Arterioles
Arterioles-
Are Smaller Arteries
Takes Oxygenated Blood To Capillaries
Types of Blood Vessels - Capillaries
Capillaries - Bridge Between Arteries & Veins
Smallest Blood Vessels Where Gas Exchange Takes Place
Adapted For Rapid Diffusion of Exchange of Materials
Wall Is One Cell Thick = Short Diffusion Distance = Fast Diffusion of Substances
Lumen Diameter is About The Size of One red Blood Cell = The Cell is Touching the Walls of the Capillary
Blood Travels SLOWLY Under LOW Pressure
The Walls can Contain Pores to Further Aid the Diffusion of Substances
Capillary Bed - A Network Of Capillaries That Supplies A Whole Organ
Types of Blood Vessels - Venules & Veins
Veins - Any Blood Vessel that RETURNS Blood to the Heart
Usually Carrying Deoxygenated Blood
Venule - A Small Vein That Drains The Capillary Bed
Veins
Adapted For LOW Pressure Flow:
Thinner - Walled
Wider Diameter Lumen
Have Valves - To Prevent Back Flow Of Blood = Ensures Blood Moves To Heart
Skeletal Muscles Help Move Blood BACK to Heart
Blood Vessel Pathway
Arteries (Oxy. Blood) To Arterioles (Oxy. Blood) To Capillaries (Mix) To Venules (Deoxy. Blood) To Veins (Deoxy. Blood)
Compare & Contrast: Artery vs Vein vs Capillary
An Artery:
Thick Outer Wall
Small Lumen
Thick Layer of Muscles & Elastic Fibers
A Vein:
Fairly Thin Outer Wall
Large Lumen
Thin Layer Of Muscle & Elastic Fibers
A Capillary:
Very Small Lumen
Wall Made Of A Single Layer Of Cell

Major Arteries of the Human Body
External Carotid (R) - Supplies Most of Face
Internal Carotid (L) - Supplies Most of Brain
Common Carotid (R)
Common Carotid (L) - Take Pulse
Right Bracheocephalic
(L) Subclavian
Axillary
Brachial - Used For BP
Renal Artery
Abdominal Artery
Radial - Used For Pulse
Ulna
Common Ilias
External Ilias
Femoral
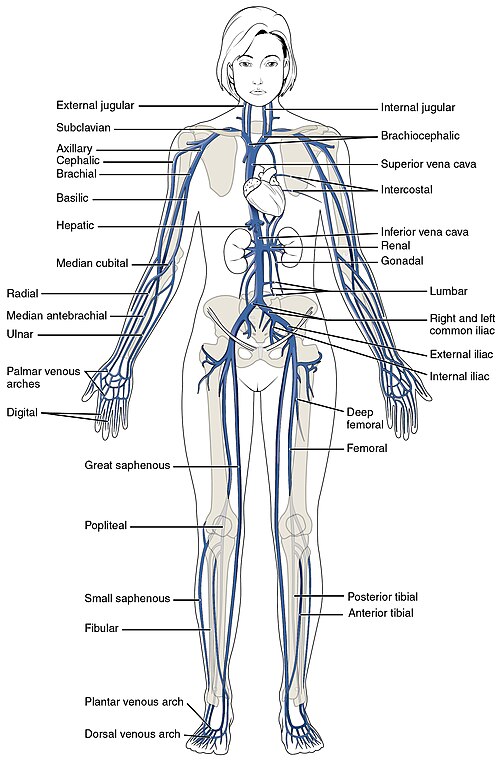
Major Veins of the Human Body
Jugular
Bracheocephalic
Subclavian
Superior Vena Cava
Inferior Vena Cava
Renal
Median Cubital - Typical Venipuncture Site
Great Saphenous - Largest Vein In The Human Body
Popliteal
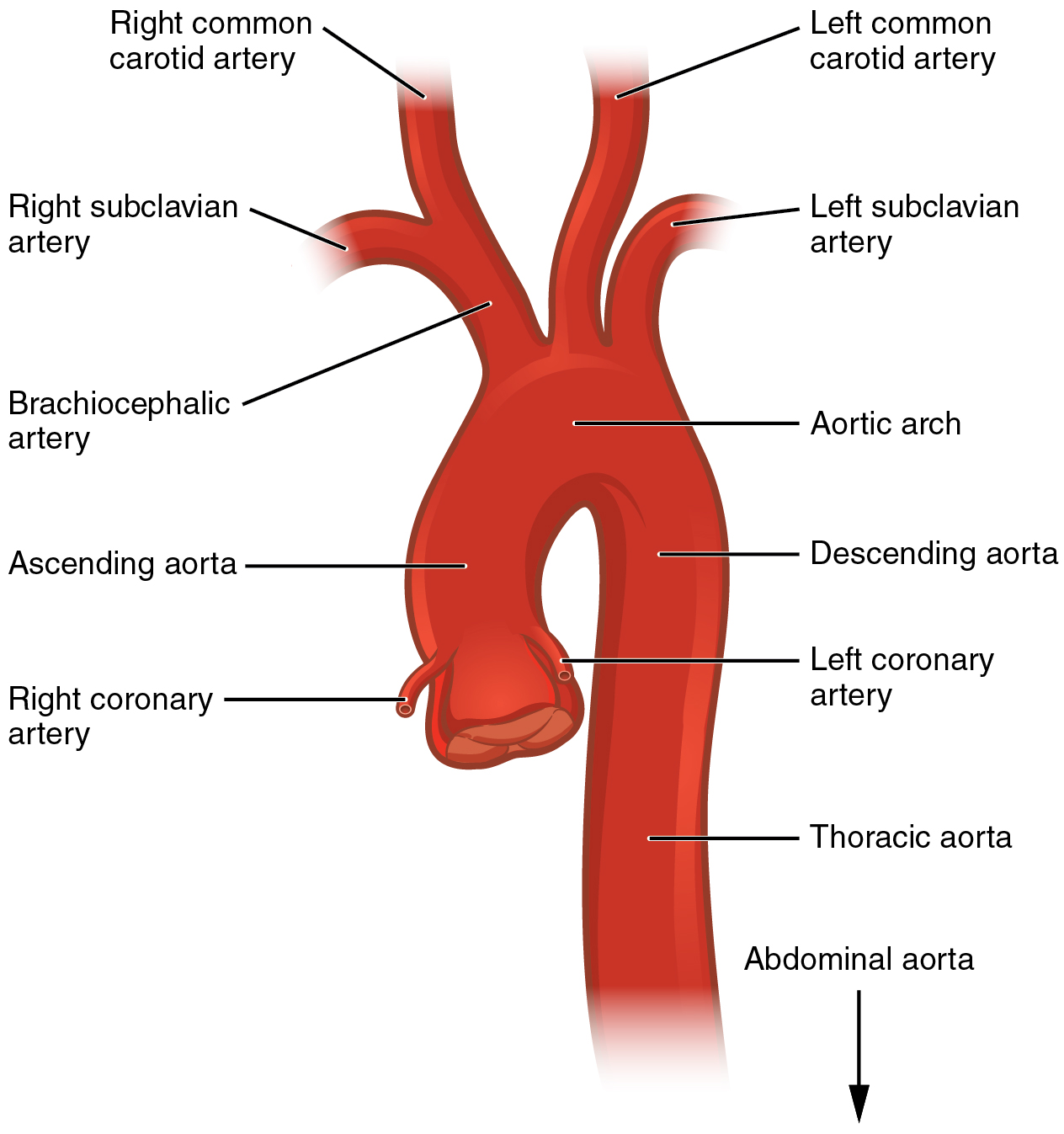
The Aorta
Aortic Arch
Ascending Aorta
R & L Coronary Arteries - These Supply Blood To The Heart Itself
Descending Aorta - Goes Behind The Heart
Branched From L to R:
Brachiocephalic Trunk
Left Common Carotid Artery
Left Subclavian Artery
Cardiac Conduction System - A. Background
Myogenic - The Heart Generates Its Own Electrical Impulses (No Stimulation From Brain)
Myocardial Conduction Cells - Cells That Generate Or Conduct An Electrical Impulse AKA An Action Potential (AP)
Cardiac Conduction System - B. Steps To The Electrical Conduction System:
The Sinoatrial (SA) Node, AKA The Pacemaker, Initiates The Action Potential (Right Atrium)
The AP Spreads Through The Atria And Causes Them To Contract
The AP Goes To The Atrioventricular (AV) Node
After .1 Second Delay, AV Node Sends Its Own Impulses To The Bundle Of His
The AP Travels Down The Septum Via The L & R Bundle Branch
AP Goes To Apex (Bottom Of Heart) And Stimulates The Purkinje Fibers Which Causes The Ventricles To Contract
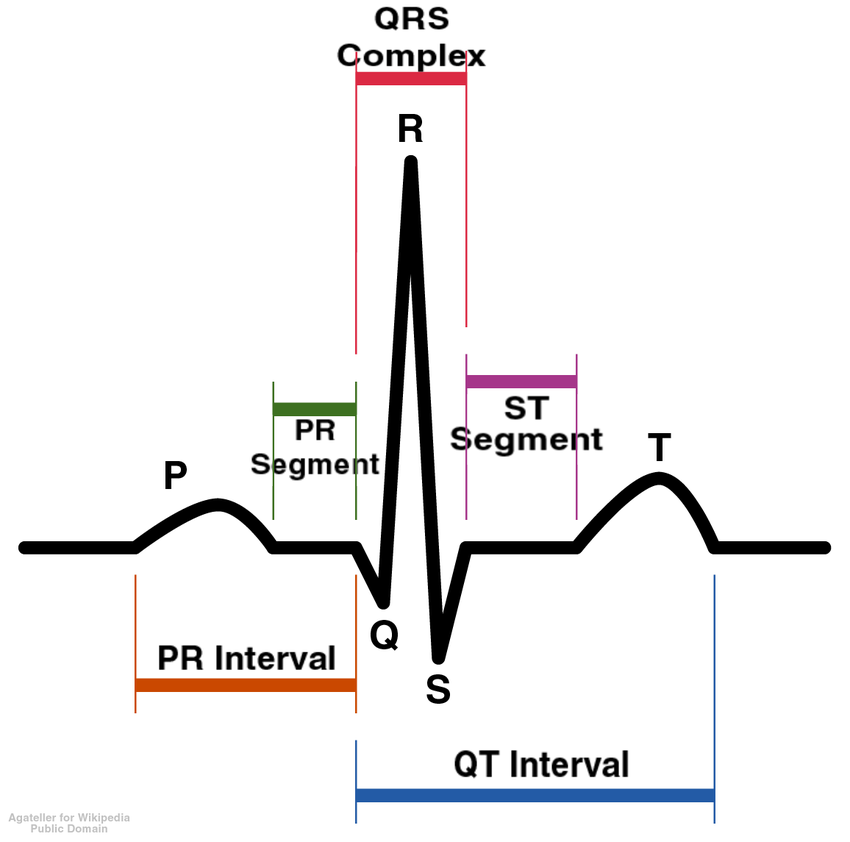
ECG Stands For Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
A Record Of The Electrical Activity Of The Heart
Can Show The Heart’s:
Speed
Strength
Rhythm
Timing
Base Of P - The SA Node Fires
P- P-Wave - Atrial Contraction
R- QRS Complex - Ventricles Receives AP And Contract - Atria Relaxes
T- T-wave - Ventricles Relax, Heart “Resets” For Next impulse
Common Problems With Electrical System:
Arrythmia - Any Problem With Heart Rate Or Rhythm (AKA Normal Sinus Rhythm)
a. Tachycardia - Resting Heart Rate Over 100 bpm
b. Bradycardia - Resting Heart Rate <60 bpm
c. Fibrillations - Unsynchronized Contractions Of Either Atria Or Ventricles Leading To Dangerous Spasmodic Heart Activity
The Cardiac Cycle
The Cardiac Cycle - The Sequence Of Events In One Heatbeart.
Clinical Significance:
Electrical Events
Mechanical Events (Contractions / Valves)
Sounds (Valves)
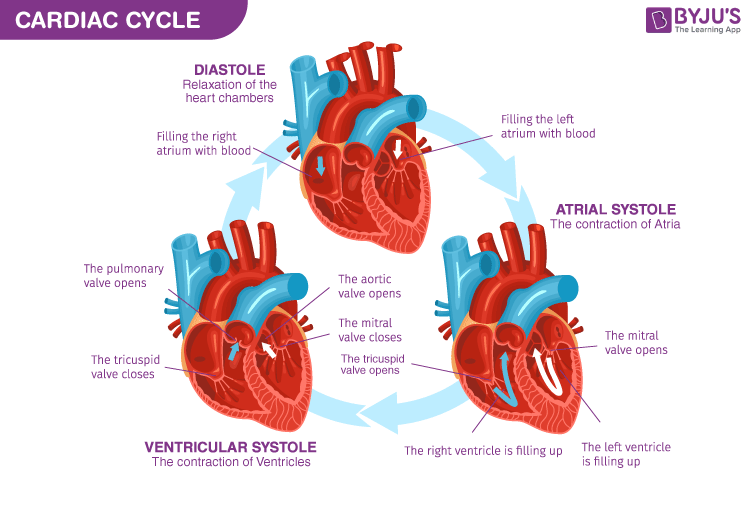
Phases - 1. Diastole
Diastole - Term To Describe A Relaxed Heart
Atria & Ventricles Relaxed
Blood Flows Into Heart Passively
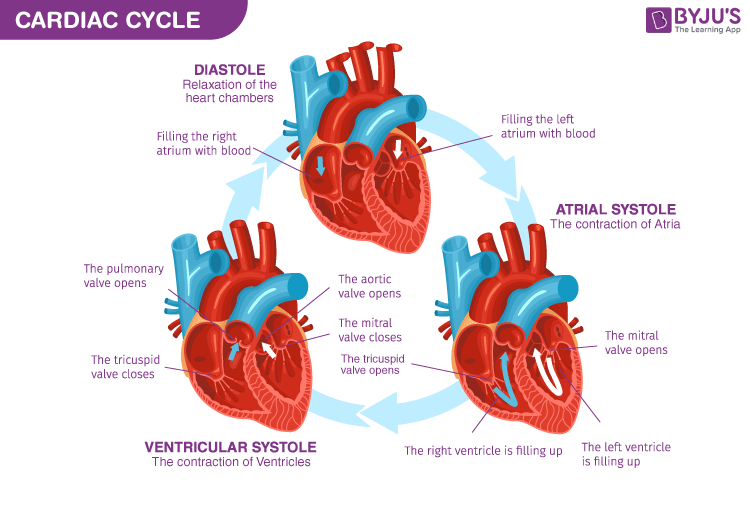
Phases - 2. Atrial Systole
Atrial Systole - Atria Contraction
Blood Pushed Into Ventricles
AV Valves Are Open
Semilunar Valves Closed
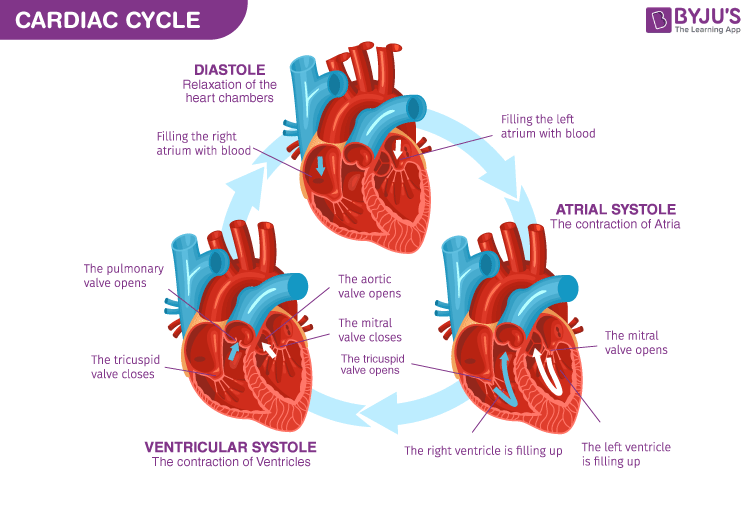
Phases - 3. Ventricular Systole
Ventricular Systole - Ventricle Contracting
Atria Relax
AV Valves Close (Heart Sounds 1 “LUB”) & SL Valves Open
Blood Pushed Out Of Ventricles Into Arteries
SL Valves Then Close (Heart Sounds 2 “DUB”)
Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure - The Amount Of Force The Blood Is Exerting Against Your Artery Walls When The Ventricles Contract
Normal: 120/80
a. Hypertension - Consistently High BP: 140/90 Or Higher
b. Hypotension - Consistently Low BP: Less Than 90/60
The Pressure Of Blood In The Vessels When The Heart Beats: Systolic Pressure: Top # In BP
The Pressure Between Beats When The Heart Relaxes: Diastolic Pressure: Bottom # In BP