Structure and Function of Plasma Membranes
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Phospholipids
Main fabric of cell membranes, amphipathic molecules.
Hydrophilic Head
Polar part of phospholipid, attracts water.
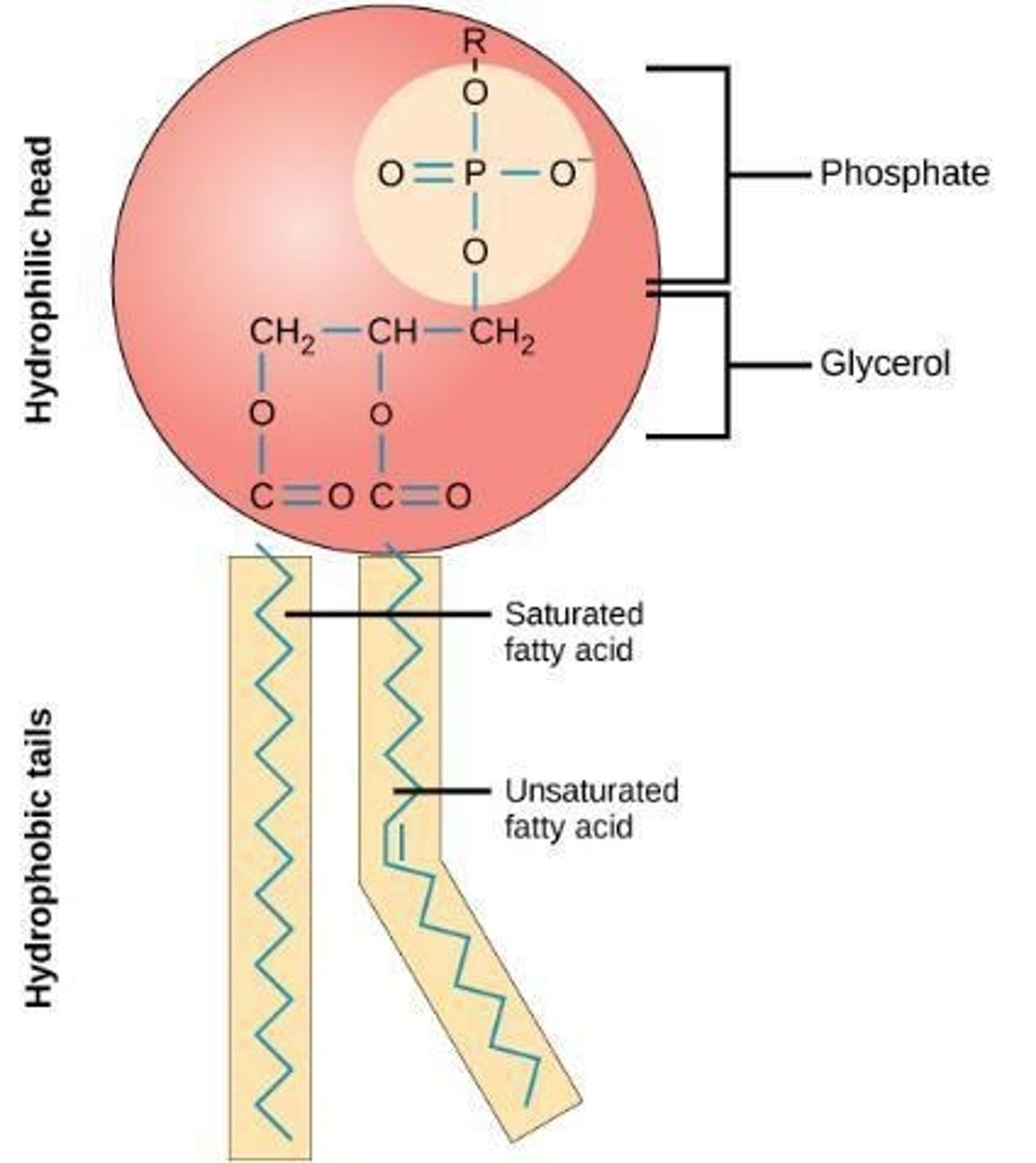
Hydrophobic Tails
Nonpolar fatty acid chains, repel water.
Saturated Fatty Acids
Carbons fully bonded to hydrogen, no double bonds.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
At least one double bond between carbons.
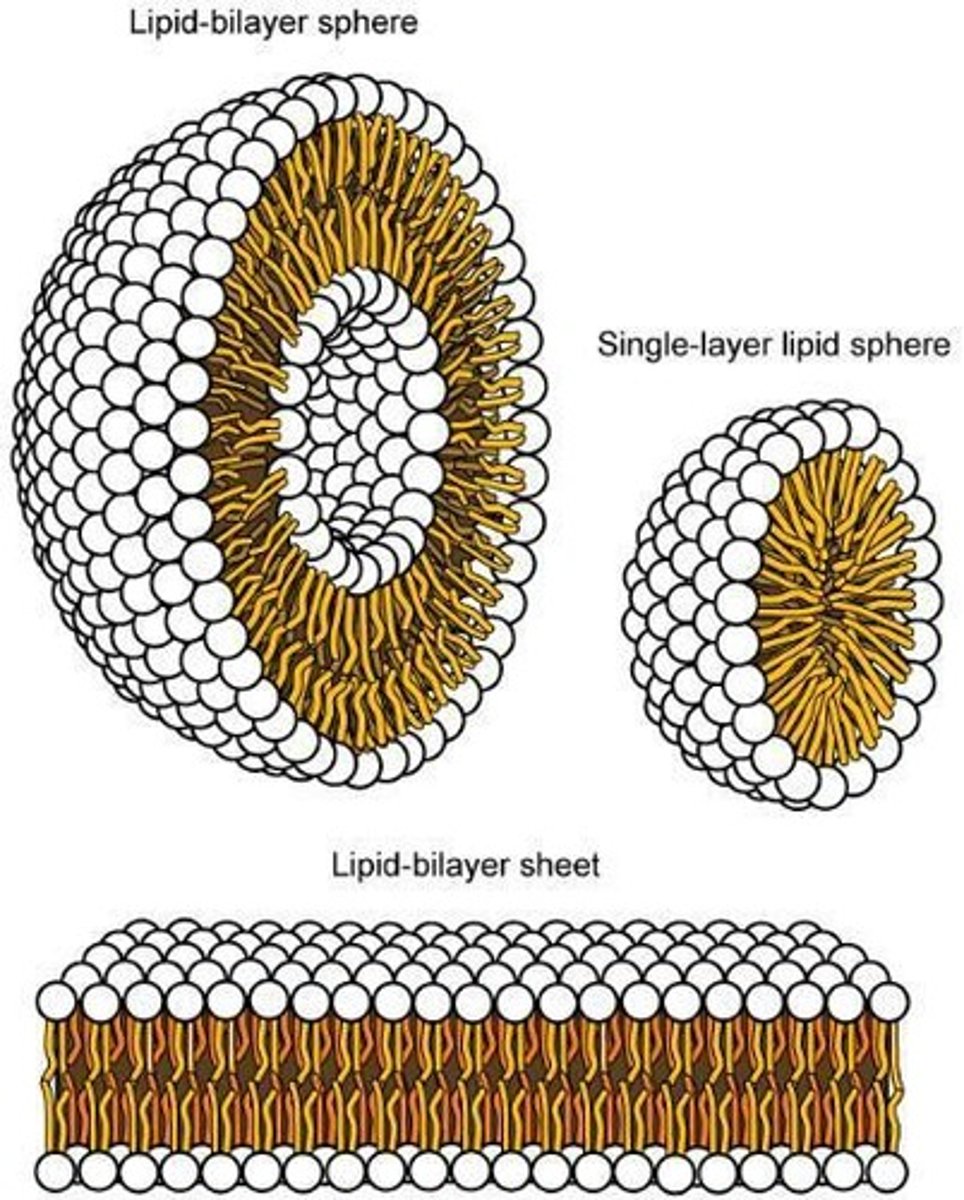
Phospholipid Bilayer
Arrangement with heads outward, tails inward.
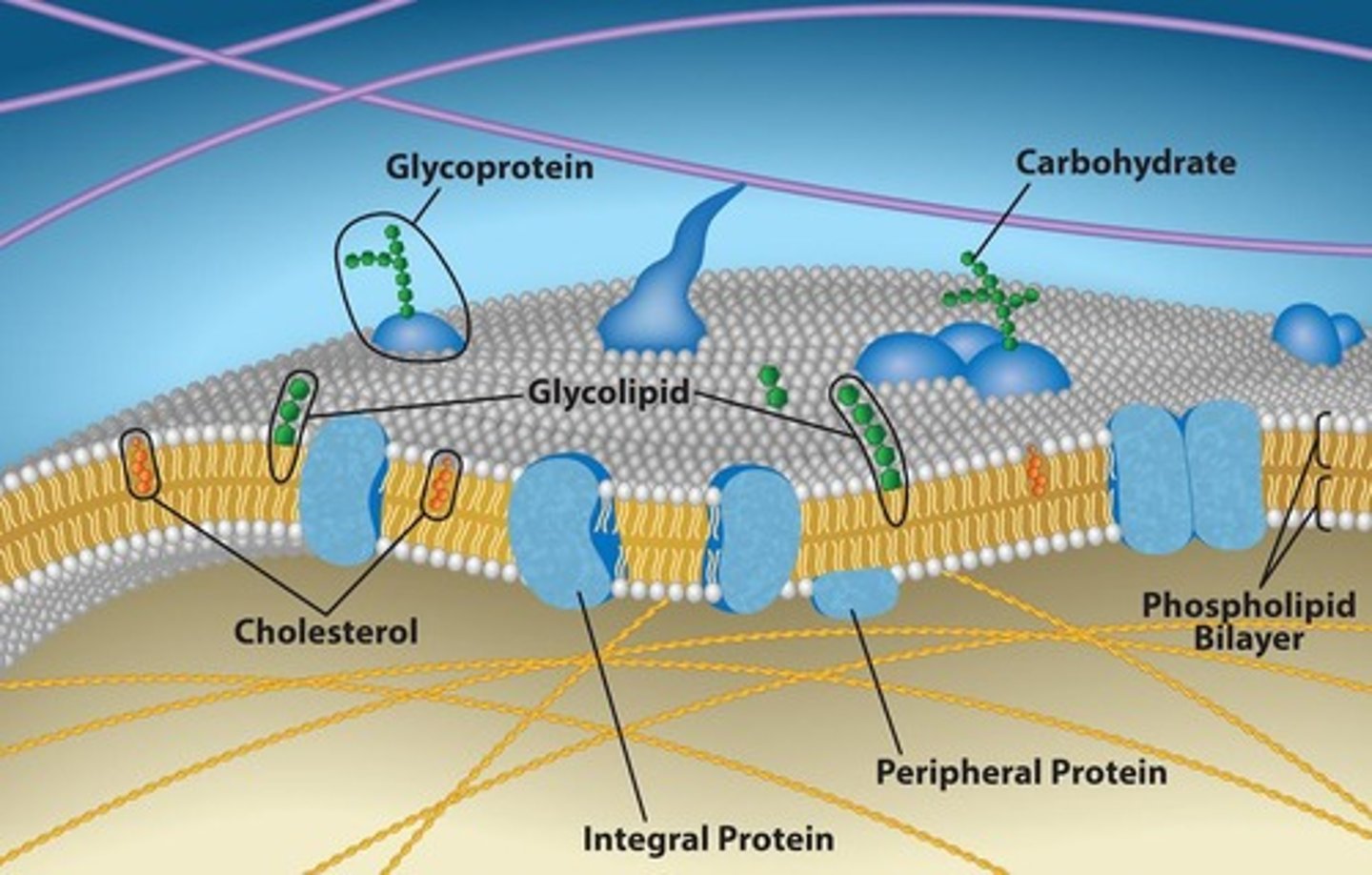
Fluid Mosaic Model
Membrane structure with diverse components, fluid nature.

Integral Proteins
Proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer.
Transmembrane Proteins
Integral proteins spanning the entire membrane.
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins located on membrane surfaces only.
Glycoproteins
Carbohydrates attached to proteins for recognition.
Glycolipids
Carbohydrates attached to lipids, aiding cell recognition.
Membrane Fluidity
Flexibility of membrane, influenced by temperature and composition.
Cholesterol
Regulates membrane fluidity, stabilizes structure.
Cell-Cell Recognition
Function of carbohydrates in identifying cells.
Membrane Asymmetry
Different inner and outer membrane surfaces.
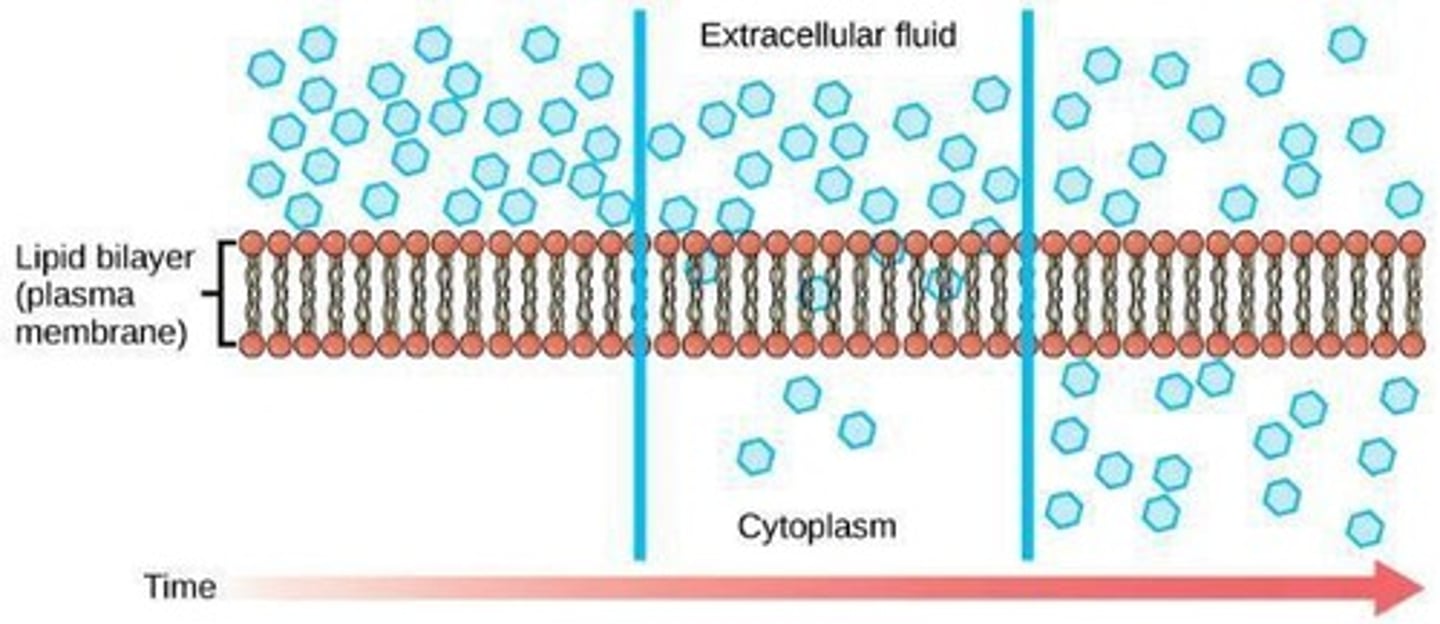
Passive Transport
Movement across membrane without energy input.
Active Transport
Energy-requiring movement against concentration gradient.
Bulk Transport
Transport of large molecules via vesicles.
Cellular Responses
Reactions initiated by external signals received by membranes.
Adhesion
Binding of cells to neighboring cells.
Membrane Functions
Regulates entry/exit, signal reception, and adhesion.
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes cell membrane structure as dynamic and flexible.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Basic structure of cell membranes, hydrophilic heads, hydrophobic tails.
Membrane Proteins
Proteins embedded in membranes, serve various functions.
Glycoproteins
Proteins with carbohydrates, aid in cell recognition.
Passive Transport
Movement of substances without energy input.
Diffusion
Movement from high to low concentration.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
Tonicity
Relative concentration of solutes in solutions.
Permeant Molecules
Molecules that can cross the phospholipid bilayer.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in concentration across a membrane.
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport using membrane proteins for assistance.
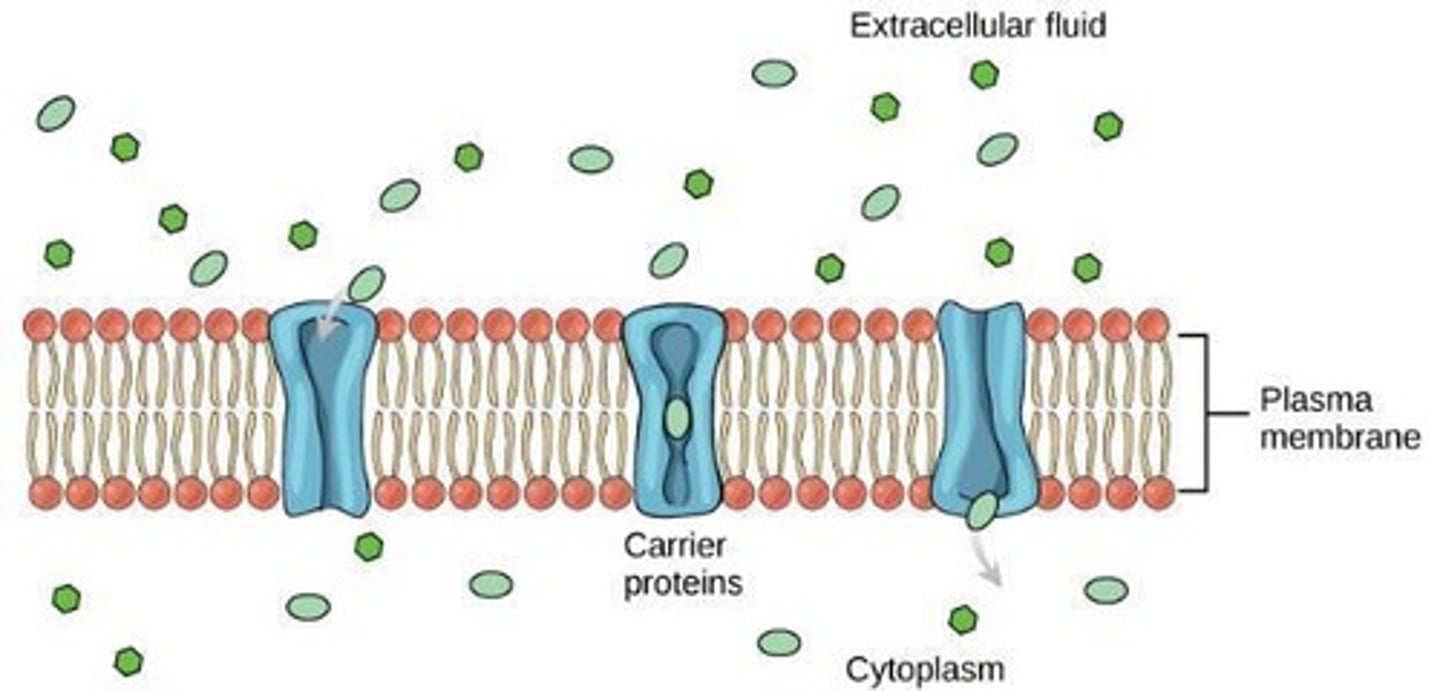
Channel Proteins
Proteins that form pores for ion/polar molecule passage.
Carrier Proteins
Proteins that bind and transport specific substances.
Equilibrium
State where concentrations are equal across a membrane.
Hydrophobic Molecules
Nonpolar molecules that easily pass through membranes.
Small Polar Molecules
Molecules like water that can cross membranes.
Large Polar Molecules
Molecules like glucose that cannot pass through membranes.
Ions
Charged particles that cannot cross membranes freely.
Factors Affecting Diffusion
Concentration, mass, temperature, surface area, pressure.
Active Transport
Movement of substances requiring energy input.
Selectively Permeable
Property of membranes allowing selective molecule passage.
Extracellular Matrix
Network outside cells providing structural and biochemical support.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in solute concentration across a membrane.
GLUTS
Glucose transport proteins facilitating glucose movement.
Tonicity
Relative concentration of solute and water across membranes.
Hypertonic Solution
Lower solute concentration than cytosol; water exits cell.
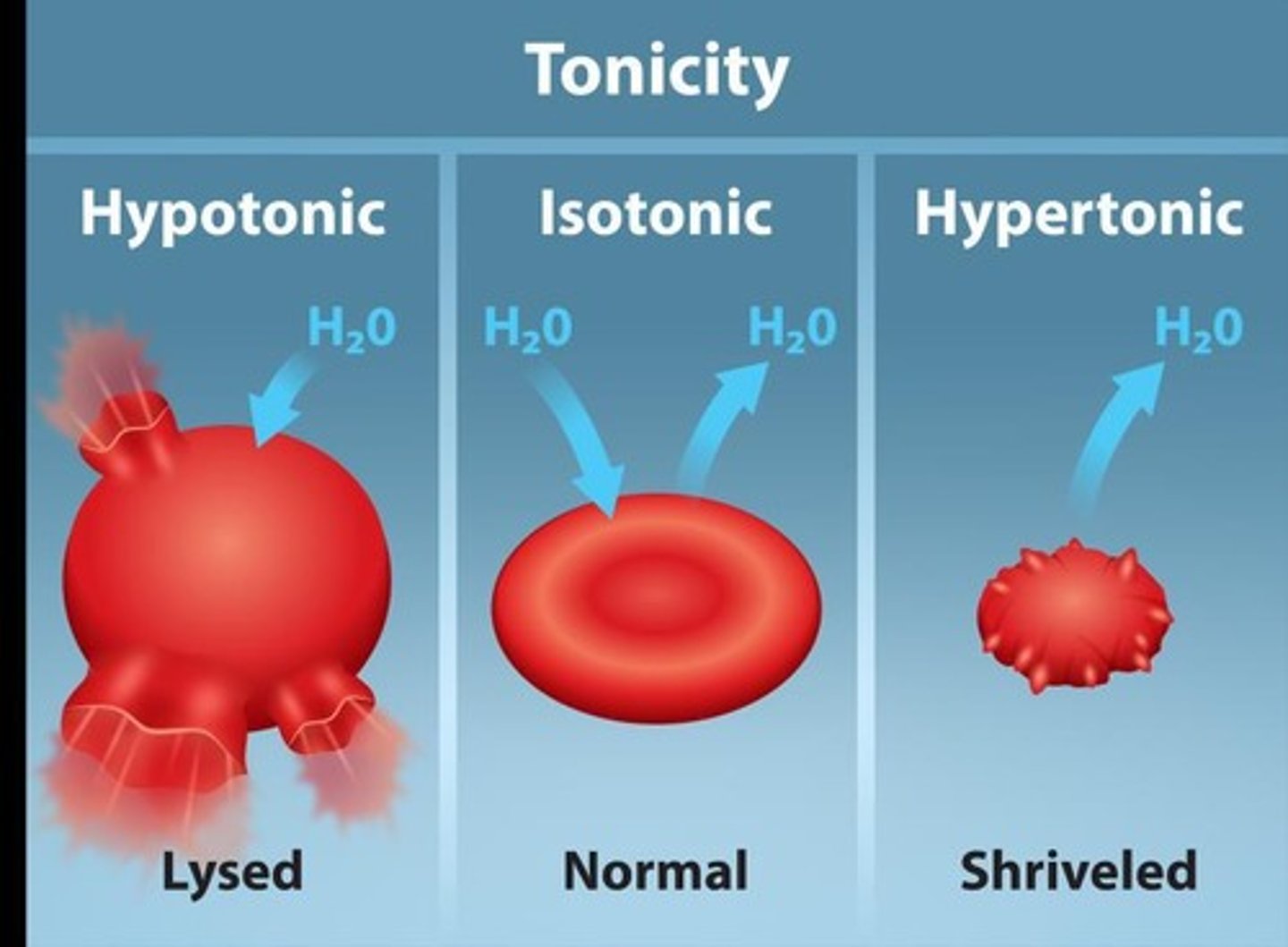
Isotonic Solution
Equal solute concentration to cytosol; no net water movement.
Hypotonic Solution
Higher solute concentration than cytosol; water enters cell.
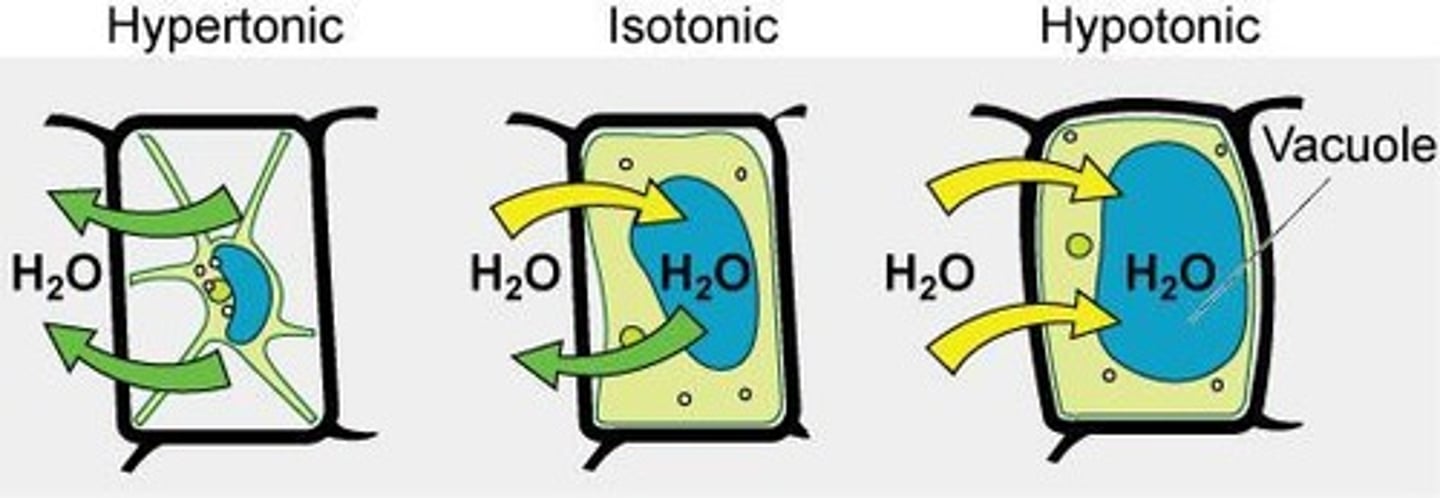
Extracellular Fluid
Fluid outside cells affecting cell volume via osmosis.
Turgor Pressure
Pressure from plasma membrane against cell wall in plants.
Plasmolysis
Detachment of plasma membrane from cell wall in hypertonic solutions.
In Vivo
Processes occurring in a living organism.
In Vitro
Experiments conducted outside a living organism.
Contractile Vacuoles
Organelles in protists that expel excess water.
Osmoregulation
Regulation of water and solute balance in organisms.
Solute
Substance dissolved in a solvent, affecting concentration.
Selectively Permeable Membrane
Membrane allowing certain substances to pass through.
Water Concentration
Amount of water in a solution, influencing osmosis.
Cytosol
Liquid component of the cytoplasm where cellular processes occur.
Net Movement of Water
Overall direction of water movement across a membrane.
Marine Invertebrates
Organisms matching internal salt concentration to environment.
Freshwater Protists
Organisms using vacuoles to manage water influx.
Cell Wall
Rigid outer layer in plant cells providing structure.
Passive Transport
Movement across membranes without energy use.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
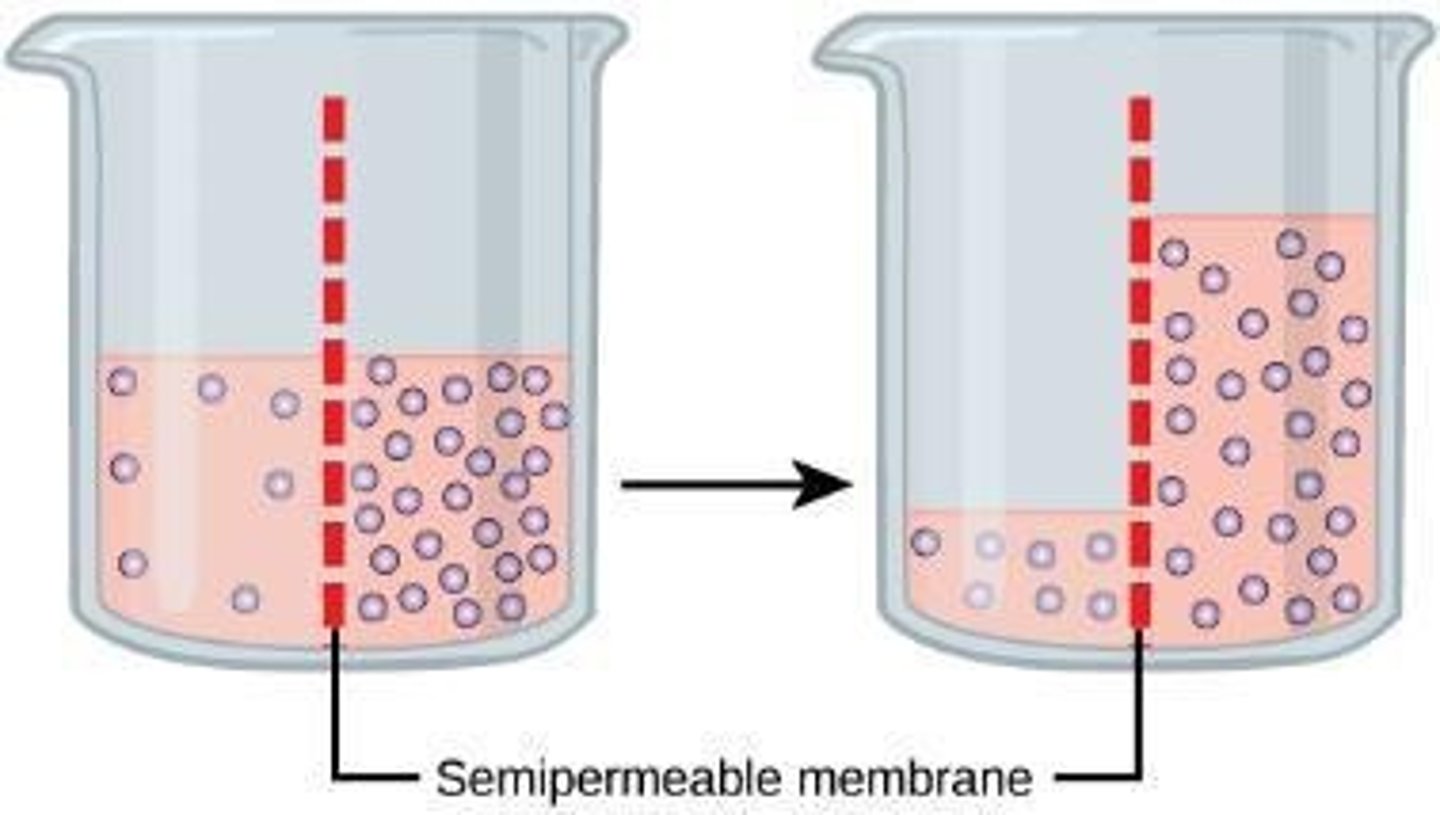
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
Active Transport
Movement against concentration gradient requiring energy.
Electrochemical Gradient
Combined concentration and electrical gradients affecting ions.
Primary Active Transport
Uses ATP to move substances against gradients.
Secondary Active Transport
Uses existing gradients to move different substances.
Uniporter
Transports one molecule or ion across a membrane.
Symporter
Transports two different molecules in the same direction.
Antiporter
Transports two different molecules in opposite directions.
Na+-K+ Pump
Moves 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in using ATP.

Electrogenic Pump
Creates a charge difference across the membrane.
Endocytosis
Process of importing large molecules into cells.
Exocytosis
Process of exporting substances from cells.
Phagocytosis
Cellular eating; engulfs large particles.
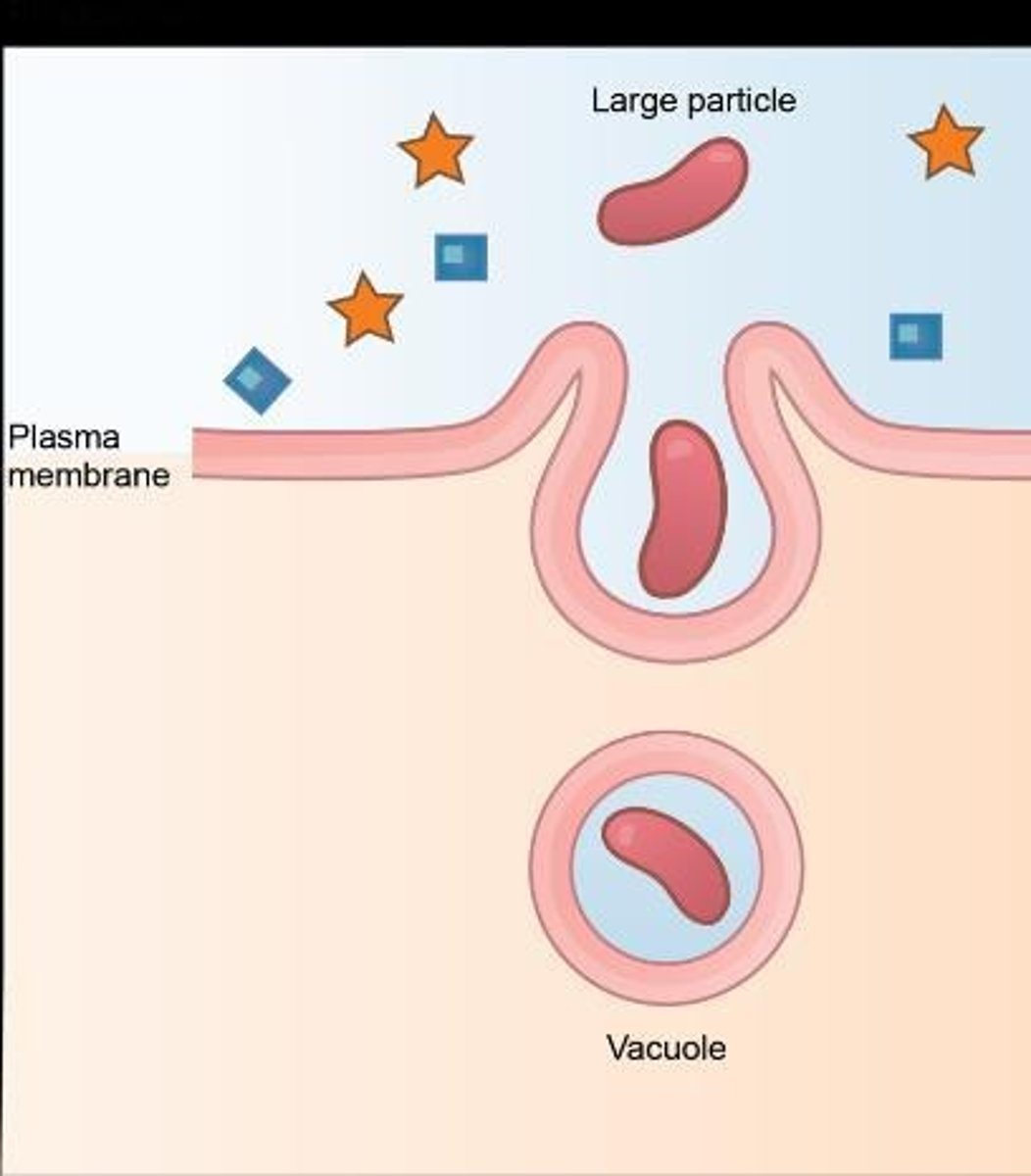
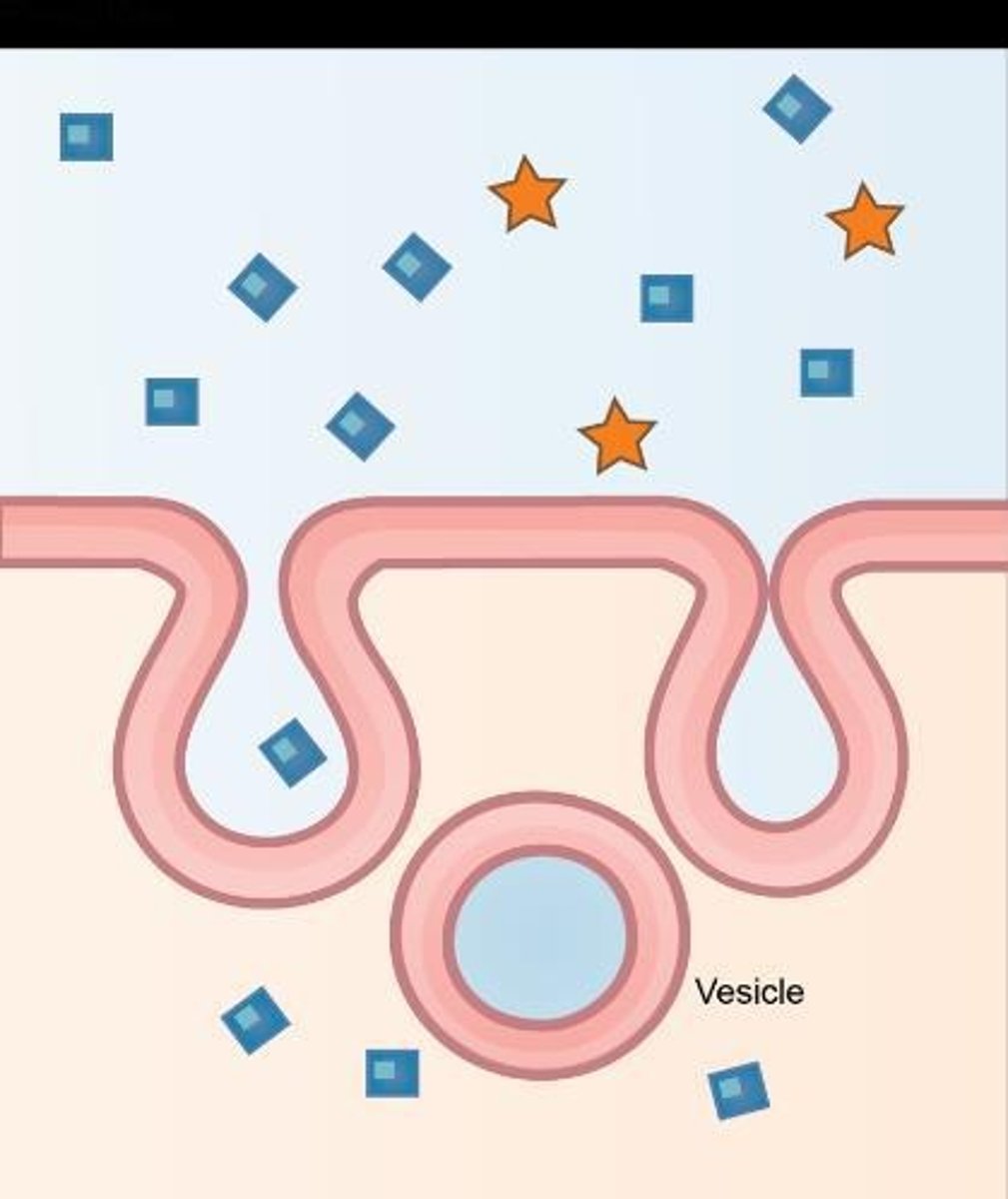
Pinocytosis
Cellular drinking; engulfs small volumes of fluid.
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Targets specific substances via receptor binding.
Carrier Proteins
Integral proteins facilitating transport across membranes.
Vesicles
Membrane-bound sacs transporting materials in cells.
Hydrolysis of ATP
Process releasing energy for active transport.
Integral Membrane Proteins
Proteins embedded in cell membranes for transport.