Exam 2 Practice
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
Grammar
The analysis of the structure of phrases and sentences
Grammatical categories
Parts of speech/word class: Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, article, and conjunction
The prescriptive approach to grammar
A set of rules for the “proper” use of English
→ Thou shall not split an infinitive (“to” + “verb”)
→ Thou shall not end a sentence with a preposition
Who did you go (with) ?
The descriptive approach to grammar
Describes how the grammar of a language
Structural Analysis
The distribution of forms in language using test-frames: “I saw ___ this morning.”
Constituent (Component) Analysis
Labeled and bracketed sentences
Hierarchical organization
Constituent Analysis
Also known as component analysis.
Labeled and bracketed sentences
Hierarchical organization
What semantic feature must a noun have in order to be used in this sentence?
The __ were eating dinner
[+animate]
Using semantic features, how would you explain the oddness of these sentences?
The television drank my coffee
His lizard paints houses
Verb drink requires a subject with the feature [+animate]
lizards aren’t human or capable of painting houses
Semantic Role: Noun Phrases
Ways to describe words based on the “role” they play in a situation or sentence
Also known as “Thematic Roles”
Agent
The thematic role that is the volitional causer of an event/action (verb).
Ex. The [girl] kicked the soccer ball
Experiencer
The person who has a feeling, perception, or state (copular verb can be a clue)
Ex. [Maurice] is elated; [Angie] heard a plane
Theme
The thematic role that shows that the entity most directly affected by/involved in an event/action.
Ex. Mary took [the candy] from the pantry
Instrument
If an agent uses another entity to perform an action, that entity fills the role of instrument. (preposition like ‘with’ is a clue)
Ex. She painted the picture with [a toothbrush pick]
Identify the roles of the seven noun phrases.
“With her new gold club, Anee Marshall whacked the ball from the woods to the grassy area near the hole and she suddenly felt invincible.”
her new gold club = instrument
Anne Marshall = agent
The ball = theme
the woods = source
the grassy area = goal
she = experiencer
Lexical relations
exploring words in terms of their “relationship” with other words
Synonymy (Synonyms)
Two or more words with very closely related meanings
Could potentially be substituted for one another in a sentence
Can represent regional differences of a word’s meaning [soda/Coke/pop]May be a result of a formal v. informal use (automobile/car)
Antonymy (Antonyms)
Two words with opposite meanings.
Gradable
comparative constructions (small, smaller, smallest)
the negative use of one does not imply the opposite (not old is not the same as new)
Non-gradable
complementary pairs
The negative use of one does imply the opposite (not true = false; not married = single) Direct opposites
Reversives
Words which imply the reverse of the other (dress/undress, enter/exit)
Hyponymy
Words in which the meaning of one is included in the other
Examining word meaning as a hierarchy
Superordinate
A word’s relationship to other words
Synonymy (not total Sameness)
Hyponymy
Which of the following opposite (antonyms) are gradable, non-gradable, or reversive?
absent/present
appear/disappear
fail/pass
fair/unfair
fill it/empty it
high/low
non-gradable
reversive
non-gradable
gradable
reversive
gradable
Prototypes
characteristic instance of a category
A sparrow is a prototypical bird
A carrot is a prototypical vegetable
Homophones
different meanings, sound the same, spelled differently
Two or more different words that sound the same but have different written forms (flour/flower)
Homonyms
different meanings, sound the same, spelled the same
When one word form (spoken or written) has 2 or more different meanings, separate dictionary entries, separate histories
Polysemy
similar meanings, spelled the same
Two or more words with the same form, but have related meaning; one dictionary entry, multiple meanings
Date on a calendar, date as in appointment
run; people do, water does, colors do
Metonymy
close connection between words in everyday experience: may use one to refer to the other; a figure of speech = think “metaphor”
representative symbol: white house/president; king/crown; whole part; car/wheels
Container contents; bottle/water; bag/chips
Collocation
words that frequently occur together
What is the basic lexical relation between each pair of words?
assemble/disassemble
damp/moist
deep/shallow
dog/labrador
furniture/table
married/single
exercise/run
peace/piece
pen/pen
antonymy (reversives)
synonymy
antonymy (gradable)
hyponymy
hyponymy
antonymy (non-gradable)
hyponymy
homophony (homophones)
homonymy (homonyms)
The original word game
demonstration of relationship between comprehension and production
The original word game: demonstration of relationship between comprehension and production
Adult labels object “ball” → Child forms hypothesis about its nature (conceptualizes ball) → Child test hypothesis by applying label “ball” to other objects → Adult monitors child’s accuracy between adult and child version of “ball” → Adult improves child’s accuracy for providing evaluative feedback → Child’s comprehension and production are fine tune
Word-Learning
Auditory cure → Phonological Representation → Word Representation
Joint Attention
is triadic and involves:
Self-referenced information processing
Other referenced information processing
Object or Event information processing
Semantic Development
1 to 1 ½: Toddlers develop around a 20 word vocabulary during this time
2: By the time a child is 2 years old, he/she will have a 200-300 word vocabulary
3: Vocabulary grows to be about 900-1,000 words by the time a child is 3 years old
4: The typical 4 year old child will have about a 1,5000-1,600 word vocabulary
5: By the time a child reaches school age and heads to kindergarten, he/she will have between a 2,100 and 2,300 word vocabulary
Yule Grammar and Syntax
Yule Chapter 7 pp. 92-101
Antonyms (Gradable or Non-Gradable)
Hot/Cold
Loud/Quiet
Happy/Sad
Innocent/Guilty
True/False
Unique/Ordinary
Wet/Dry
Gradable: Hot/Cold, Loud/Quiet, Happy/Sad, Wet/Dry
Not gradable: Innocent/Guilty, True/False, Unique/Ordinary
What is grammar?
It is the analysis of the structure of phrases and sentences.
Yule language typology
pg 106 Table 7.3
something important yule
page 21
What are grammatical categories?
grammatical categories are parts of speech/word class. This includes Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, articles and conjunctions
What is the difference between prescriptive and descriptive approach grammar?
The prescriptive approach to grammar is a set of rules for the “proper” use of English such as “Thou shalt not split an infinitive (“to” + “verb”) “ and “thou shalt not end a sentence with a preposition (Who did you go (with) )?”
On the other hand, the descriptive approach to grammar describes how the grammar of a language is actually used. Examples of this include structural analysis (The distribution of forms in a language using test-frames: “I saw __ this morning”) and constituent (component) analysis (labeled and bracketed sentences and hierarchical organization).
Which of the following words are co-hyponyms?
A. Ant
B. Cabbage
C. Insect
D. Plant
E. Turnip
F. Vegetable
E. Turnip and B. Cabbage
Module 5.3 Video
Chomsky and the Lad
What are Parts of Speech?
Parts of speech are lexical categories. This includes nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, conjunctions, prepositions. and interjections
What is grammar comprised of?
Grammar is comprised of parts of speech (lexical categories)
Nouns refers to
a person, object, place, qualities, phenomena, and abstract idea
Verbs refer to
actions and states of being
Adverbs modify
a verb, adjective, and adverb
Conjunctions are
words used to make connections
Pronouns are
words used in place of noun phrases
Adjectives describe
a noun or pronoun
prepositions are used with
nouns to give information about time, place or other connections
Determiners/articles are used with
nouns to form noun phrases
Schoolhouse rock adverb video
Lolly Lolly Lolly Get Your Adverbs Here
Adverbs modify
Verbs
Can end in -ly: I ate my ice cream slowly
Can tell where: I will run there
Can tell when: I will run tonight
Can tell how: I will run fast
Can tell all three: Tonight, I will run there quickly
Adjectives (how much)
The really small cat climbed the tree
Other adverbs (how much)
The cat almost never climbed the tree
How do adverbs modify adjectives?
They describe how much there is. (Ex. The (really) small cat climbed the tree)
How do adverbs modify other adverbs?
They describe (how much) (Ex. The cat almost never climbed the tree)
What are nouns?
subjects/objects. person, place, thing or an abstract
Pronouns serve as
a subject or object and takes the place of a noun
Verbs include
action words, state words (have, do, and be family copulas)
Adjectives include
words preceding and modifying nouns
Adverbs include
words that describe a verb, an adjective or another adverb. Where? When? How?
What do prepositions express?
It expresses a relation to another word or element in the clause. it can tell us where or when something is in relation to something else.
Prepositions are used with
nouns or pronouns in phrases to provide information about time, place, connections involving actions and things
What do conjunctions do?
Conjunctions male connections and demonstrate links between events. They connect two clauses or phrases.
When are determiners used?
Determiners are used prior to a noun to form the noun phrase
What do determiners include?
It includes articles (A, An, The), demonstratives (This, These, That, Those) and possessive pronouns (his, her, their)
What does a definitive article tell us?
It tells us something is specific. (Ex. “the pirate” is a specific pirate. The writer and readers know about him)
What does the indefinitive article?
It tells us something is non-specific. (Ex. “A pirate” refers to any pirate. He’s not known to the writer or the readers)
What are direct objects?
They answer the questions “what” or “who” the action happened to. They can be nouns, pronouns, phrases or clauses.
Direct objects can be
nouns, pronouns. phrases or clauses
What is the direct object in the following sentence? : “Brian baked a cake for Simone".”
a cake
What is the direct object in the following sentence? : “Sylina locked her keys in her car.”
her keys
What is the direct object in the following sentence? “Jerome kicked Mr.Smith in the chin.”
Mr.Smith
What is the direct object in the following sentence? : “The girl liked Davis after he brought her a rose.”
Davis
The direct object is the
recipient of an action in a clause or sentence. It is the thing being acted upon (i.e., the receiver of the action)
How can you find the direct object?
You can find the direct object by finding the verb and asking “what?” or “whom?”
What is the direct object in the following sentence? : “Tommy hit the ball.”
the ball
What is the indirect object?
The recipient of the direct object
How can you find the indirect object?
By finding the direct object and then asking who or what received it
Noun agreement
aingular= is, plural= are
What is the noun number agreement in the following sentence? : “The owls are colorful.”
owls are
Point of view
first person, second person, third person
First person
I, me, my, mine, we, us, our (narrator)
Second person
you, your, yours (listener)
Third person
he, she, it
Tense Agreement
Verbs, Present, Past
What is the tense in the following sentence? : "I want cake.”
Present
What is the tense in the following sentence?: “I wanted cake.”
Past tense
Voice agreement
active and passive voice
Active voice
The subject is doing the action.
Passive voice
The target of the action goes to the subject position
Which voice is present in the following sentence? : “She loves cake.”
Active voice
Which voice is present in the following sentence? : “The cake is loved by her.”
Passive voice
Gender agreement
male, female, masculine, feminine
What is the syntax breakdown for the following sentence? “Colorless green ideas sleep furiously.”
Noun phrase: “Colorless green ideas”
Noun phrase: “green ideas”
Verb phrase: “sleep furiously”
Adjective: Colorless
Adjective: green
Noun: ideas
Verb: sleep
Adverb: furiously
The Ling Space Syntax
General: Word Crimes and Misdemeanors
Yule Chapter 8
pp. 112-119
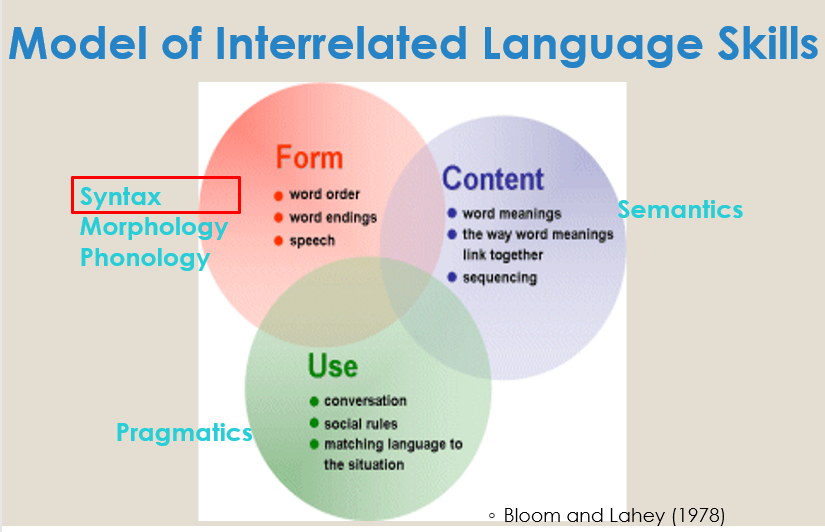
Where does syntax fall on the Bloom and Lahey (1978) Model of Interrelated Language Skills?
It falls under form, which deals with word order, word endings and speech
The “All” and “Only” criterion
Analysis must account for ALL the grammatically correct possibilities an only those in a given language. The rules must apply to all possible creations.
Generative Grammar
The small and finite set of rules in a language that allow for “infinite” creations of well-formed structures (e.g., phrases, sentences)
Break down the syntactic structure of the following sentence: “A fat man saw the timid dog.”
Noun Phrase: “A fat man”
Verb: “saw”
Noun Phrase: “the timid dog.”
Article: A
Adjective: fat
Noun: man
Article: the
Adjective: timid
Noun: dog
Constituent Analysis
Noun Phrases, Verbs, Verb Phrases, Prepositional Phrases