Medical Terminology - Chapter 9
1/268
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
269 Terms
Mouth (or/o, stomat/o)
Begins preparation of food for digestion
Teeth (odont/i)
Used for biting, tearing, and chewing in mechanical digestion
Pharynx (pharyng/o)
Transports food from the mouth to the esophagus
Esophagus (esopahg/o)
Transports food from the pharynx to the stomach
Stomach (gastr/o)
Breaks down food and mixes it with gastric juices
Small Intestine (enter/o)
Mixes chyme coming from the stomach with digestive juices to complete digestion and absorption of most nutrients
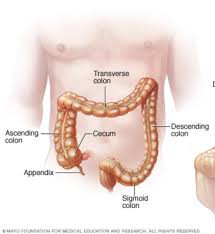
Large Intestine (col/o, colon/o)
Absorbs excess water and prepares solid waste for elimination
Rectum and Anus (an/o, proct/o, rect/o)
Controls the excretion of solid waste
Liver (Hepat/o)
Secretes bile and enzymes to aid in the digestion of fats
Gallbladder (cholecyst/o)
Stores bile and releases it into the small intestine as needed
Pancreas (pancreat/o)
Secretes digestive juices and enzymes into the small intestine as needed
An/o
Anus, ring
Chol/e
Bile, gall
-emesis
Vomiting
-lithiasis
Presence of stones
-pepsia
Digest, digestion
-phagia
Eating, swallowing
Proct/o
Anus and rectum
Rect/o
Rectum, straight
Sigmoid
Sigmoid colon
Aerophagia
Excessive swallowing of air while eating or drinking and is a common cause of gas in the stomach
Anastomosis
Surgical connection between two hollow or tubular structures
Antiemetic
A medication that is administered to prevent or relieve nausea/vomiting
Ascites
Abnormal accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal cavity
Bariatrics
A branch of medicine concerned with the prevention and management of obesity and associated diseases
Borborygmus
The rumbling noise caused by the movement of gas within the intestine
Cachexia
A condition of physical wasting away due to the loss of weight and muscle mass that occurs in patients with diseases like advanced cancer or aids
Canker Sores
Gray-white pits with a red border in the soft tissues lining the mouth
Celiac Disease
Autoimmune disorder characterized by a severe reaction by ingesting gluten
Cheilitis
Also called cheilosis. Inflammation of the lips that has crack-like sores at the corner of the mouth
Cholangiography
Radiographic examination of the bile ducts with the use of a contrast medium
Cholangitis
Acute inflammation of the bile duct characterized by pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, fever, and jaundice
Cholecystectomy
Surgical removal of the gallbladder
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder usually associated with gallstones blocking the flow of the bile
Cholelithiasis
Presence of gallstones in the gallbladder or bile ducts
Cirrhosis
Chronic degenerative disease of the liver characterized by scarring
Colonscopy
Direct visual examination of the inner surface of the entire colon from the rectum to the cecum using a colonscope
Colostomy
Surgical creation of an artificial excretory opening between the colon and the body surface
Crohn’s Disease
Chronic autoimmune disorder that can occur anywhere in the digestive tract. Most commonly found in the ileum and in the colon
Dental Prophylaxis
Professional examining, cleaning, and polishing of the gums and teeth to remove plaque and tartar
Diverticulitis
Inflammation or infection of one or more diverticulum in the colon
Diverticulosis
Chronic presence of an abnormal number of diverticula or sacs. Formed in the weak spots of the colon wall
Dyspepsia
Also called indigestion. Pain or discomfort during the digestive process
Dysphagia
Difficulty in swallowing
Endoscopy
Visual examination of internal structures
Enema
Placement of a solution into the rectum and colon to empty the lower intestine through bowel activity
Enteritis
Inflammation of the small intestine caused by ingesting substances contained with viral or bacterial pathogens, causing diarrhea.
Eructation
Act of belching or raising gas orally from the stomach
Esophageal Varices
Enlarged and swollen veins at the lower end of the esophagus
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Endoscopic procedure that allows the direct visualization of the upper GI Tract
Gastroduodenostomy
The establishment of an anastomosis between the upper portion of the stomach and duodenum
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Also called GERD. The upward flow of acid from the stomach to the esophagus
Gastroparesis
Condition in which gastric motility slows down, causing delayed gastric emptying
Gastrostomy Tube
Surgically placed feeding tube from the exterior of the body on the abdomen, directly on the stomach
Hematemesis
Vomiting of coagulated blood
Hemoccult test
Also called fecal occult blood test. A laboratory test for hidden blood in the stool
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver due to a viral infection
Hiatal Hernia
Anatomical abnormality in which a portion of the stomach protrudes upward into the chest through an opening in the diaphragm
Hyperemesis
Extreme, persistent vomiting that can cause dehydration
Ileus
Partial or complete blockage of the small or large intestine
Inguinal Hernia
Protrusion of a small loop of bowel through a weak place in the lower abdominal wall or groin
Jaundice
Yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes, and eyes
Leukoplakia
Abnormal white, usually benign lesion that develops on the tongue or the inside of the cheek
Malocclusion
Any deviation from the normal positioning of the upper teeth against the lower teeth
Melena
Passage of black, tarry, foul-smelling stools
Nasogastric Intubation
Placement of a nasogastric feeding tube through the nose and into the stomach
Palatoplasty
Surgical repair of a cleft palate, also used to refer to the repair of a cleft lip
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Characterized by sores that affect the mucous membranes of the digestive system
Peristalsis
Series of wave-like contractions of the smooth muscles in a single direction that moves the food into the digestive system
Proctologist
Physician that specializes in the disorders of the colon, rectum, and anus
Regurgitation
Return of swallowed food into the mouth
Salmonellosis
Also called salmonella. Transmitted through feces, through direct contact with animals or eating contaminated raw/undercooked meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, or unpasteurized milk products
Sigmoidoscopy
Endoscopic examination of the interior of the rectum, sigmoid colon, and possibly a portion at the descending colon
Stomatitis
Inflammation of the muccsa of the mouth
Trismus
Also called lockjaw. Any restriction to the opening of the mouth caused by trauma, surgery, or radiation associated with the treatment of oral cancer
Ulcerative Colitis
Chronic condition of unknown cause where repeated episodes of inflammation in the rectum and large intestine cause ulcers and irritation
Volvulus
Twisting of an intestine on itself, causing an obstruction
Xerostomia
Also called dry mouth. The lack of adequate salivia due to diminished secretions by salivary glands
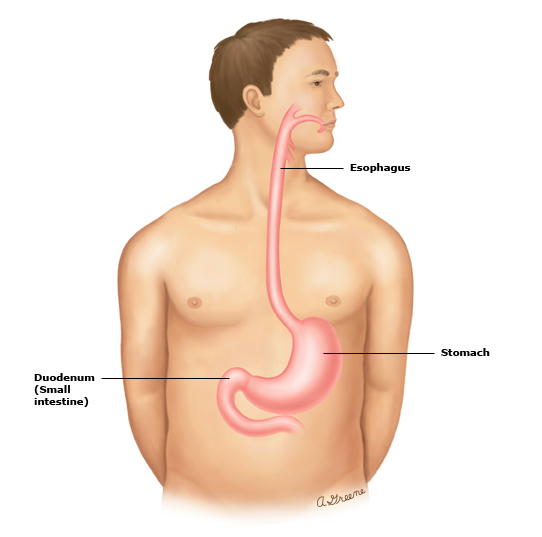
Upper GI Tract
Consists of the mouth. pharynx (throat), esophagus, and stomach. Transports food until digestion begins
Lower GI Tract
Also called the bowels. Made up of the large and small intestine also rectum and anus. Digestion is completed and waste is prepped for expulsion from the body
Accessory Organs
Made up of the liver. gallbladder, and pancreas
Lips
Also called the labia. Surrounds the opening to the oral cavity. While eating, the lips, tongue, and cheeks fold the food into the mouth and are also used for breathing. speaking, and expressing emotions
Palate
Creates the roof of the mouth and consists of three parts
Hard palate
The anterior (front) side and is covered in a specialized mucous membrane
Soft palate
Posterior (back) side and is flexible. It closes the nasal passage to prevent food and liquids from moving up into the nasal cavity while swallowing
Uvula
Hangs off the edge off the soft palate. It moves upward from the soft palate during swallowing and is key in snoring and creation of some speech sounds
Tongue
Extremely flexible and strong. The posterior side is attached to the mouth by the Lingual Frenum, while the anterior side can move freely
Dorsal Tongue
Upper portion of the tongue, which consists of a tough, protective covering and some small bumps called papillae.
Sublingual Surface
The under side of the tongue, The surface and tissues are covered with a delicate, super vascular (lots of blood vessel) tissue.
Periodontium
The structure that surrounds, supports, and is attached to the teeth. Consists of the bone in dental arches and soft tissue around the teeth
Gingiva
Also called the masticatory mucosa or gums. A specialized mucous membrane that covers the bone of the dental arches and surrounds the neck of the teeth
Sulcus
Area between a tooth and surrounding gingiva. Any food debris or bacteria buildup can cause infection
Dental arches
The bony structure of the oral cavity which hold the teeth firmly for speaking and chewing
Maxillary
The upper jaw that consists of bones in the lower surface of the skull
Mandibular
The lower jaw that is a completely separate bone and the only movable one
Temporomandibular
Also called TMJ. Formed at the back of the mouth where the upper and lower jaw meet
Dentition
The natural teeth in the lower and upper jaw. There are 4 kinds of teeth: incisors, canines, and premolars (bicuspids and molars)
Incisors and Canines
The teeth used for biting and tearing. In children, there are 8 incisors and 4 canines. In adults, there are 8 incisors and 4 canines
Premolars
Consists of the bicuspids and molars. In children, there are 8 molars. In adults, there are 8 premolars and 12 molars
Occulsion
Refers to the contact between the chewing surfaces of the upper and lower teeth