AICE Environmental Management ultimate study guide
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
LIC
Low income country; GNI<1036
MIC
Middle income country; GNI = 1036
HIC
High income country; GNI>12535
sustainability
meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
condensation
gas to liquid
precipitation
any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface
interception
Water being prevented from reaching the surface by trees or grass
infiltration
the process of water soaking into the soil
surface run-off
water that does not infiltrate, runs on the surface
through-flow
movement of water laterally through soil
ground water flow
movement of water within an aquifer
transpiration
evaporative loss of water through stomata
evaporation
liquid to gas
biome
large area categorized by a distinct climate and biomass(plants and animals in a given area)
ecosystem
a community of living things interacting with each other and abiotic factors
population
a group of organisms of the same species populating a given area
community
assemblage of different populations that live together in a defined area
habitat
a natural region where a specific organism can be found
niche
an organism's role in an ecosystem
biotic
Describes living factors in the environment.
abiotic
describes nonliving factors in the enviorment
chlorophyll
a green pigment that is used by a plant to capture photon energy
aerobic respiration
A form of cellular respiration that requires oxygen in order to generate energy. Equation: c6h1206 + 6o2 > 6h20 + 6co2 + ATP energy
producer
An organism that can make its own food (autotroph)
primary consumer
an organism in the energy pyramid that obtains it's energy by consuming a producer
secondary consumer
an organism in the energy pyramid that obtains it's energy by consuming a primary consumer
tertiary consumer
an organism in the energy pyramid that obtains it's energy by consuming a secondary consumer
decomposer
An organism in the energy pyramid that breaks down wastes and dead organisms
trophic level
each step in an energy pyramid
reliability
the ability to obtain the same result each time a measurement method is carried out
bias
systematic deviation between data interpretation and accurate description
geospatial systems
models showing information in relation to the Earth
satellite sensors
obtain data from orbit: infrared images, storm wind speed, and chemical composition
radio tracking
allows data to be collected from an animal by placing VHF radio on or within the animal
computer modeling
allows data to be collected by using simulations. Allow multiple scenarios to be studied with smaller expense
crowd sourcing
gathering information through surveys and focus groups
sweep nets
the researcher swings a net side to side to collect arthropods from grassy/bushy areas.
beating trays
researcher collects a sample by beating a tree branch and holding a tray under to collect falling insects
light traps
used to collect nocturnal arthropods like moths. Light attracts the insect and causes them to get trapped on a sheet. Effective in dark areas
kick sampling
researcher disturbs the bottom of a body of water using their hands or feet. invertebrates may be released and captured in a net. inexpensive
pitfall traps
placed in the ground by the researcher to collect crawling animals to assess species abundance and biodiversity. Simple and inexpensive
anti-natalist
anti-brith. Concerned with limiting population growth
pronatalist
pro-birth. Concerned with increasing population size
dependency ratio
non-working population:working. Equation = non-working / working x 100
simpson's index
a method to estimate biodiversity.
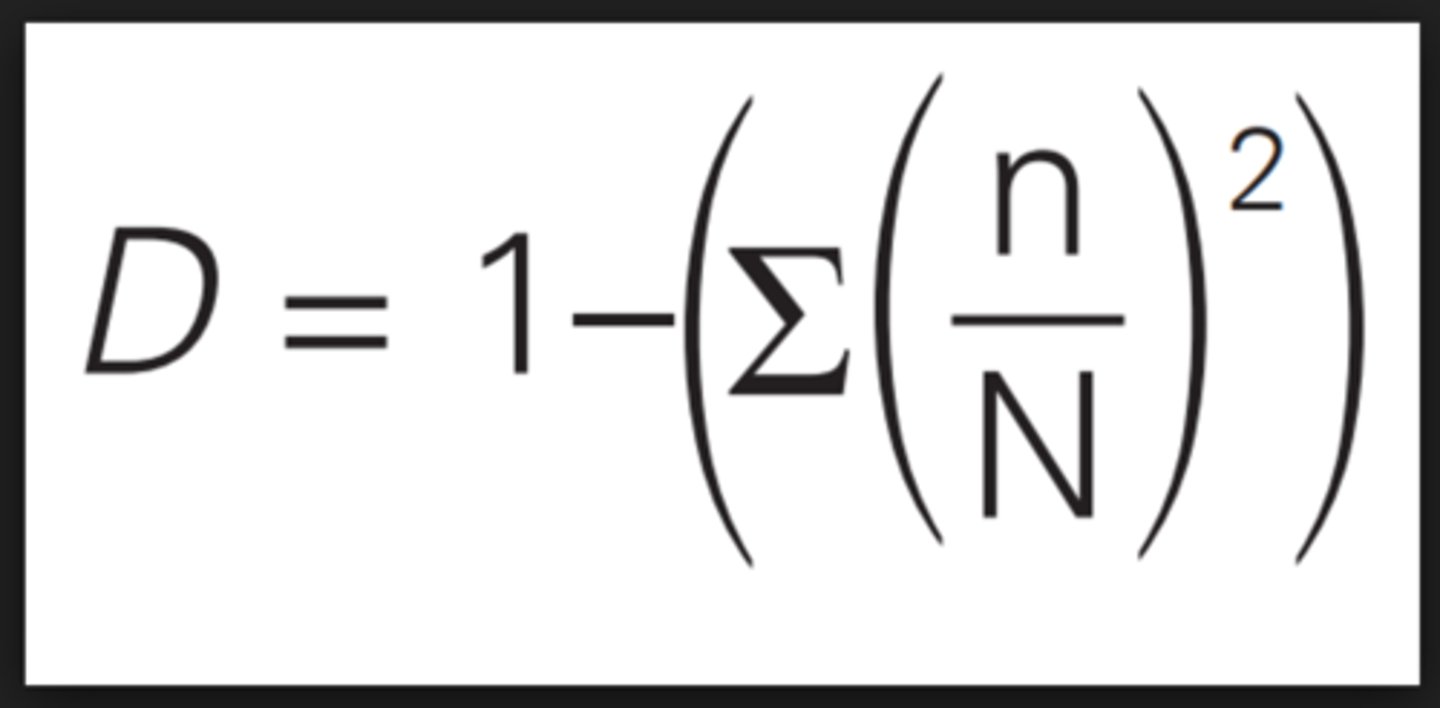
lincoln index
a method to estimate population size of a given sample.
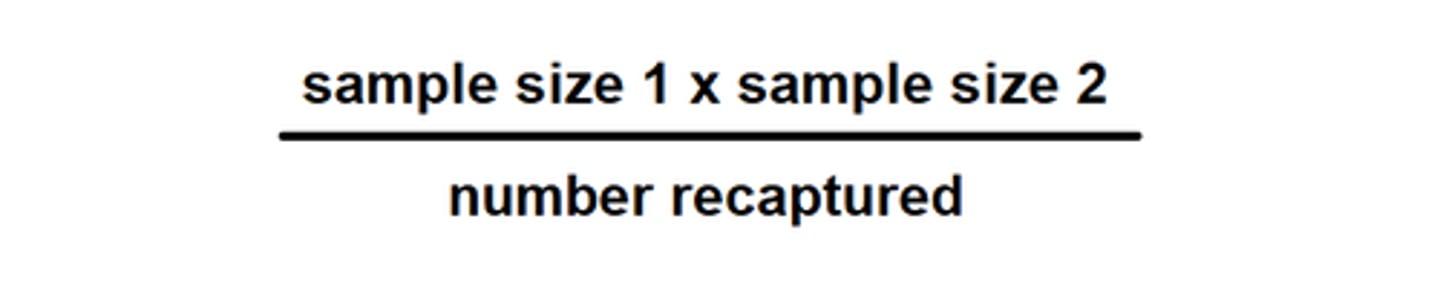
total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
Productivity
rate of biomass production in an ecosystem
Biomass
amount of living material (kg/km²)
Tundra
Biome that is cold, low precipitation, large quantities of ice, thin soil layer, little plant growth
Primary succession
establishment of an ecosystem where there was none before
Pioneer species
First species to colonize an area, don't require much water
Ecological Climax
Ecosystem stabilizes and growth stops
secondary succession
reestablishment of a damaged ecosystem in an area where the soil was left intact
climax community
A community that no longer goes through succession
Plagio climax
a community that climaxed due to human influence
Rule of 10%
Only 10% of energy is available to above trophic levels
The International Whaling Commission (IWC)
Conserves whale stocks, regulates commercial whaling and scientific research on whales
The European Union Common Fisheries Policy
establishes sustainable fish practices to preserve fish stocks
The International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO)
establishes sustainable and legal harvesting of tropical timber and manages its trade
Reduced Impact Logging (RIL)
implementation of harvesting operations to minimize impacts on forests and soil.
Captive breeding
capturing and organism and having it reproduce under protective conditions until population size is large enough to release
Habitat conservation and creation
a) designate areas as protected ¨wilderness¨
b) rewilding - large scale restoration, reintroducing predators or keystone species
Extracted reserves
public, tropical areas set aside for ecological development by residents
Overexploitation
harvesting a resource quicker than they replenish
National parks
protect ecosystems from humans via conservation zones
Nature reserves
similar to national parks, just smaller
Rain forest deforestation is due to...
agricultural expansion, extraction of precious metals, fuel wood and timber collection
Impacts of rain forest deforestation include...
Disrupts water cycle, decreases co2 sequestration, decreases biodiversity, increases surface temperature
Impacts of precious metal extraction include...
erosion, sink holes, deforestation , soil and water contamination
Tropical Forest Conservation Act of 1998
Allows LICs to relieve debt to US by conserving tropical rainforests
Antarctic Treaty of 1959
Designates Antarctica as a natural reserve. Has 50 countries agreeing to use Antarctica for peaceful purposes only, allow freedom of scientific investigation, freely exchange scientific findings
Impacts of tourism in Antarctica include...
Accidentally bringing invasive species, birds abandoning their nest when tourists approach, tourists trample paths and release of waste in coastal waters
Factors discouraging exploration in Antarctica include...
inhospitable territory, expensive, resistance from conservation orgs, minerals found easier in other places
Antarctic Conservation Act (ACA)
bans removing flora and fauna, discharging waste, entering ASPAS or introducing species into Antarctica.
-applies to all US citizens and vessels leaving the US
International Association Antarctic Tourism Operators (IAATO)
-limits size of ships in waters of Antarctica
-limits number of people landing
-makes tourists clean equipment and clothing before leaving
-prohibit removal of native items
Impacts of research stations in Antarctica include...
-melt ice to provide fresh water
-produce waste water
-use fuels (contribute to air pollution)
-produce magnetic field that affect wildlife
Examples of Renewable Energy Resources include...
1. Biofuels- wood, ethanol, biogas
2. Geothermal Energy- convert underground heat into electricity
3. hydroelectric dams- convert flowing water into electricity
4. Tidal wave Energy- convert ocean waves into electricity
5. Solar- convert sunlight into electricity
6. Wind- convert wind into electricity
Examples of Non-Renewable Energy Resources include...
1. Fossil Fuels- convert ancient organic matter into electricity
2. Coal- convert ancient trees into electricity
3. Natural gas- microorganisms producing CH4
4. Uranium- from nuclear fission power plants
Energy security
the environmentally sustainable energy from reliable sources at affordable prices
Long-term energy
security is providing energy in line with economic developments and environmental needs
Short-term energy
promptly providing energy via systems that react to sudden changes in supply-demand needs
Causes of energy insecurity include...
1. FF depletion- when FF are used more frequently that they are renewed
-oil depletion in 30 years
-natural gas depletion in 40 years
-coal depletion in 70 years
2. Inequality in global energy resources
3. Population Growth- placing a larger demand on finite resources
4. CC influence national policies- warmer climate = higher demand to cool homes
5. Natural Disasters- hurricanes and earthquakes can disrupt supply
ex: hurricane rita and katrina damaged many oil platforms and pipelines
6. Piracy and terrorism- disrupt energy supplies moving through the Gulf of Mexico.
Impacts of Energy Insecurity include...
1. Disrupted supply of energy to population- Which increases cost of both energy and industrial goods
2. Unemployment and economic recession
3. Price Setting-higher prices which can lead to energy poverty (classification given to households using more than 10% of income for energy needs)
4. Increased reliance on imported sources of energy
5. Civil disruption and conflict- ex: Iran and Iraq war (1980). Protests over rising prices
Strategies to manage energy insecurity include...
1. Increasing energy efficiency- use energy efficient lighting, programmable thermostats, blowdown control systems, heat recovery systems
2. Develop alternative energy sources- wave energy, solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy
3. Reduce reliance on fossil fuels- use more renewable energy resources. ex: nuclear power
4. Investing in biofuel
5. Rationing Energy- ex: china has begun limiting electricity use for some factories and homes
Food security
everybody in the population having reliable and long-term physical, social and economic access to food
Causes of food insecurity include...
1. Population growth- more people = more demand on finite resources
2. Unsustainable production
3. Increase in homogeneity of global food sources- genetically similar crops increase risk of disease which can cause shortage
4. Price setting- High prices
5. Agricultural disease
6. Climate change- droughts, hurricanes, storms can harm crops
7. Converting crops directly into biofuels
Impacts of food insecurity include...
1. Nutritional deficiency- ex: malnutrition
2. Poverty
3. Conflict
4. Forced migration
5. Famine
Strategies to manage food insecurity include...
1. Agricultural intensification
2. Improved agricultural techniques- ex: aquaculture and hydroponics
3. Producing genetically modified crops- resistant to drought, pests, and produce a larger yield
4. Reducing crop competition- reduce weeds, fungal, and pests by use of herbicides, fungicides and insectivores
5. reduce food waste
6. Improve food transportation and distribution
7. Protecting pollination insects- ex: honeybees
The UN World Food Program (WFP)
UN agency that delivers food to the hungry poor, help farmers transport surplus food to market, acts in emergencies and supports long-term development.
Methods of waste management include...
1. Landfills-
Pros:
-Inexpensive
-keeps cities clean
-provides jobs.
Cons:
-Electronic wastes contain toxins such as mercury, cadmium and led;
-Leaks toxic material into soil and ground water
-Releases methane; produces foul odor
2. Incineration-
Pros:
-reduces volume of trash
Cons:
-significant air pollution
-mercury pollution
-noisy
3. Dispose of waste by sea- allowed with permit, but if done illegally can cause disease
4. Recycling waste
5. Exporting waste to other nations for processing
Strategies to reduce impacts of waste disposal include...
1. Reduce, reuse, recycle
2. Producing biodegradable plastics- which cant be broken down into microplastics
3. Using food waste for livestock feed
4. composting- reduces amount of solid waste and methane production at landfills
5. using waste as fuel to heat water within steam turbines to produce electricity
What percentage of Earth is covered in water?
71%. 97.5% is saltwater, 2.5% is freshwater. 68% of freshwater is in glaciers, 30% is ground water, <1% is surface water
Water security
the ability to access enough clean water to maintain adequate standards of food and goods production, proper sanitation, and health care
Causes of water insecurity include...
1. Climate change- changes in rainfall
2. Natural disasters- droughts, floods, hurricanes
3. Population growth- more people = higher demand on finite resources
3. Inefficient irrigation methods- ex: flood irrigation
4. Inequality of availability between water-rich regions and water-poor regions
Impacts of water insecurity include...
1. Lower crop yields- due to lack of water
2. live stock deaths-
3. Famine
4. Cholera (diarrheal disease)
5. Crop failure- due to lack of water
6. Conflict- ex: in darfur region of Sudan over scarce water
Strategies to manage water insecurity include...
1. Poverty reduction
2. sustainable water extraction- using gravity fed schemes, reserios, dams, piped water systems
3. Rainwater catchment- convert landscapes into sponges that retain water and relieve demand for aqifer water
4. Dam reservoirs-
Pros:
-provide source of drinking and irrigation water
-allow for flood control
-generate electricity
Cons:
-can change water properties
-block fish from moving down stream
-noisy
-produce dust during construction
-cause local climate change
-increase in CH4
5. Artesian wells- extract water from confined aquifers
6. Recycling and reusing water
7. International agreements- ex: Kenya and Ethiopia regarding lake turkana water use
8. Water related aid from non-governmental organizations- ex: Water Aid and Blood water ensure populations threatened by water insecurity have adequate, safe drinking water.
What is wet acid deposition?
Precipitation with a pH<5.6
How is sulfuric acid formed?
Fossil fuel combustion produces sulfur dioxide (SO2) which then reacts with water (H2O) and oxygen (O2) forming sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
How is nitric acid formed?
Nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) react within high temperatures of vehicle engines forming nitrogen monoxide gas (NO), which then reacts with oxygen (O2) and water (H2O) to form nitric acid (HNO3)