Intrapartum Exam
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CU NSG 3010
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Stage 1 of labor
from the onset of labor contractions to complete dilation
Assessment of contractions (3 things)
frequency
duration
intensity
timing from the beginning of one contractions to the beginning of the next contraction
frequency
from the beginning of one contraction to the end of the same contraction
duration
palpate fundus with fingers to determine strength of contractions: mild, moderate, strong, or use IUPC to calculate Montevideo units
intensity
Vaginal exam (three things)
dilation
effacement
station
the gradual opening of the cervix (closed to 10cm dilated)
dilation
the gradual thinning of the cervix (thick to 100% effaced)
effacement
the location of the baby’s presenting part (hopefully the head) in comparison to mom’s ischial spines
station
phases of stage one of labor (2 phases)
latent phase
active phase
latent phase measurements
0-5 cm
active phase measurements
6-10 cm
Stage 2 of labor and delivery
from complete dilation to pushing/delivery/birth of the baby
stage three of labor and delivery
from birth of baby to delivery of placenta
Stage four of labor and delivery
recovery-the first 2 hours (minimum) after delivery or until patient is stable, assess pt every 15 minutes
4th stage: every 15 minutes, what are you assessing?
VS
fundus
perineum
locia
etc.
cervical dilation of 10cm and 100% effacement
Goals for 1st stage of labor
birth of baby
Goals for 2nd stage of labor
delivery of placenta
Goals for 3rd stage of labor
Uncomplicated recovery
Goals for 4th stage of labor
Five Essential Factors of labor and delivery
passenger
passageway
powers
positions
psyche
passenger
fetus and placenta
passageway
maternal bony pelvis and soft tissues
powers
uterine contractions and maternal pushing efforts
position
of laboring woman
psyche
laboring woman
passenger: fetal size (especially head)
fetal skull bones
fetal sutures and fontanels
fetal skull diameter
fetal skull bones
frontal
temporal
parietal
occipital
fetal sutures and fontanels
frontal
coronal
sagittal
lambdoidal
fetal fontanels
anterior fontanel - is diamond shape (much easier to palpate)
posterior fontanel - is triangle shape (more difficult to palpate, very small and closes early)
Fetal skull diameter
widest transverse measurement = biparietal diameter (9.5 cm)
anterior-posterior measurement (smallest = suboccipito = 9.5 cm)
First fetal part to enter the pelvic inlet. First part felt on vaginal exam.
fetal presentation
Types of fetal presentations
cephalic (head down) - 96% = occiput
breech - 3% = sacrum
shoulder - 1% = scapula (baby’s CANNOT deliver vaginally this way!!!!)
Cephalic positions: head flexed, occiput presents (most ideal)
vertex
Cephalic positions: neck straight, bregma presents
military
Cephalic positions: head partially extended, sinciput presents (most of the time cannot deliver vaginally)
brow
Cephalic positions: head fully extended, mentum presents (difficult to deliver vaginally)
face
breech positions: both knees and hips flexed
complete
breech positions: hips flexed but knees extended (at risk for hip dysplasia)
Frank
breech positions: single or double with both knees and hips extended
footling
Shoulder position: baby’s cannot deliver vaginally this way!!!
scapula
relation of the long axis (spine) of fetus in relation to long axis (spine) of mother
Fetal lie
Types of fetal lie (2 types)
longitudinal (may be either cephalic of breech)
transverse (impossible to deliver vaginally)
the relationship of the fetal body parts to one another
Fetal attitude
Types (in relationship to cephalic presentation) - 3 types
flexed (“vertex'“)
extended (“brow/face”)
neutral (“military”)
the relationship of the presenting part to the four quadrants of the maternal pelvis
fetal positions
Types of fetal positions: denoted by a 3-letter abbreviation
1st letter: R or L
2nd letter: O (occiput) - could be m/chin or s/sacrum)
3rd letter: A or P or T (transverse)
Most common fetal position
OA (R or IOA)
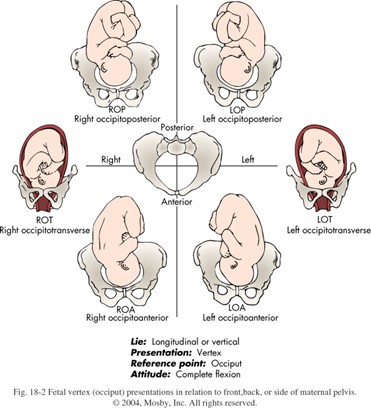
Fetal positions
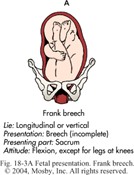
frank breech
Obstetric abdominal examination
Leopold’s maneuvers
First maneuver
curve fingers of both hands at top of fundus
Second maneuver
place both hands on sides of uterus
Third maneuver
with thumb and middle finger of one hand, press gently but deeply into the mother’s abdomen immediately above the symphysis pubis and grasp the presenting part
fourth maneuver
place both hands on sides of lower uterus, press deeply and move fingertips towards pelvic inlet
Bony Pelvis: bones
ilium
pubis
ischium
sacrum
coccyx
true pelvis is where?
below the linea terminalis, and the false pelvis is above it
three divisions of true pelvis: (3 things)
inlet
midpelvis
outlet
upper pelvic opening (top of pubis and sacrum)
inlet
pelvic cavity (ischial spines project into this space)
midpelvis
lower pelvic opening
outlet
pelvic measurements: measured from bottom of pubic bone to top of sacrum
diagonal conjugate
four pelvic types (most people are combinations of the 4)
gynecoid (50%)
anthropoid (25%)
android (20%)
platypelloid (5%)
female type pelvis, most favorable and most common for vaginal delivery; round inlet adequate for vaginal delivery
gynecoid
fairly common, usually favorable for vaginal delivery; more oval inet
anthropoid
male pelvic type; babies get hung up at the inlet; a heart-shaped pelvis, unfavorable for vaginal delivery unless forceps/vacuum is used
android
flat pelvis where pubic arch is wide, very unfavorable for vaginal delivery
platypelloid
soft tissues: lower uterine segment
cervix
pelvic floor muscles
vagina
bladder (most common soft tissues dystocia, mom should be emptying her bladder every 2 hours)
powers (2 types)
uterine contractions
maternal pushing efforts
involuntary power (primary), frequency, duration, intensity, resting tone (if effective, cause cervical changes (dilation and effacement), and fetal descent)
uterine contractions
voluntary power (secondary)
maternal pushing efforts
general principle of position of mother (5 things)
frequent position changes enhance the labor process
the position most beneficial for the baby may be critically important
position most comfortable for the mom
certain positions help solve specific problems
options: upright, gravity assistance (walking, sitting, squatting), lateral, on hands and knees, etc.
personality/psyche of mother; depends on various factors (6 listed)
mom’s physical, intellectual, emotional, social, and spiritual preparation for labor
previous childbirth experience
personal attitude and readiness
involvement and input from significant people/the support system in her life
expectation
culture
theories of labor onset (37-42 weeks gest) > labor initiation is caused by increased _______ and decreased __________
estrogen, progesterone
a placental hormone that relaxes uterine smooth muscle, levels decrease as placenta ages near term
progesterone
increases uterine sensitivity to oxytocin, increase at 34-35 weeks gestation
estrogen
stimulates contractions (which hormone)
oxytocin
cervical ripening agent
prostaglandin
Known to stimulate sooth muscle, levels increase just before labor begins
prostaglandin
stimulates uterine smooth muscle contractions, released from maternal posterior pituitary, fetal _______release (silences brain which is helpful for labor and helps to stimulate fetal contractions), receptors on the uterus increase as labor begins
oxytocin
increase production by fetus nearing term
fetal cortisol
two possible effects of fetal cortisol
slows production of progesterone
stimulates prostaglandin precursors
most smooth muscle contracts when it is stretched (the hormones keep this from happening), and also stimulates prostaglandin production
uterine distention (mechanical stimulation)
divides into two portions above and below the physiologic retraction ring
uterus
2/3 portion is actively contracting (pushes baby down)
upper uterus
1/3 portion is passing (cervix included) (pressure from baby effaces and dilates the cervix)
lower uterus
effaces def
thins
dilates def
opens
_____ effaces and dilates
cervix
stimulates contractions, increases fluid retention (acts like an antidiuretic hormone), and silences fetal brain
oxytocin
contractions stimulate the baby to be pushed down onto the cervix, the stimulates the brain (PP/posterior pituitary) to release oxytocin which stimulates stronger and more contractions > feedback loop
ferguson reflex
S/S of impending labor (may have some or all of these
lightening (when baby “drops”)
weight loss of 1/3 lbs in the last 1-2 wks of pregnancy
GI upset, N/V & diarrhea
Braxton Hicks contractions increased (irregular and not uncomfortable, may do some cervical ripening but not true labor)
energy spurt (“nesting” 24-48 hrs before onset of labor)
rupture of membranes (gush or leaking fluid from vagina: SROM = spontaneous rupture of membranes)
lightening s/s
decreased fundal height
frequent urination
generalized pelvic pressure
easier breathing
backache increased (baby’s head puts on her sacrum)
leg cramps increase
edema in LEs in response to decreased venous return
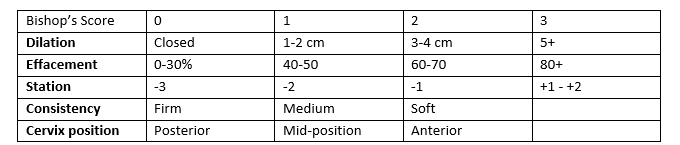
*dilation-effacement-station is the three things documented
cervical changes “ripening” summarized in Bishop’s score
Bishop’s Score of ____ = cervix is favorable for induction
>8 (score up to 13)
Bloody show ___-___ hrs before labor common (the cervical mucous plug that is blood-tinged) - starts to be expelled as cervix is thinning, no integrity to hold the mucous plug in place
24-48
Contractions of True labor
regular UCs
increasing frequency
increasing duration
painful
pain starts in back
walking intensifies true labor
UC’s CONTINUE WITH REST AND WARM BATH
contractions of false labor
irregular or infrequent UCs
no increase in frequency or duration of UCs
abdominal comfort (may be painful but only in the front)
walking does not affect intensity
REST AND WARM BATH DECREASES UCs
bloody show in true labor
present (may also be caused by recent vaginal exam or intercourse)
bloody show of false labor
bloody show not usually present