ACCT 2301 All Questions
1/242
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
243 Terms
Ch 1
The accounting equation is:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
True or False
True
Ch 1
Accounts Receivable are an asset.
True or False
True
Receivable = smth (usually cash) will be received in the future.
Ch 1
Accounts Payable are debts owed by the business entity.
True or False
True
Payable = smth (usually cash) will be paid by the corp. in the future
Ch 1
Assets are increased with a
a. Debit
b. Credit
a. Debit
Ch 1
Liabilities are increased with a
a. Debit
b. Credit
b. Credit
Ch 1
The accounting equation can be expressed as
Assets - Liabilities = Shareholder’s Equity
True or False
True
A = L + E
A - L = E
Ch 1
The accounting equation can be expressed as
Assets + Shareholder’s Equity = Liabilities
True or False
False
Should be A - E = L
Ch 1
If Assets total $10,000 & Liabilities are $4000, Equity must be $14,000.
True or False
False
A = L+E
A - L = E
10000 - 4000 = 6000 ✅
Ch 1
Dividends a company pays reduce net income.
True or False
False
Dividends are a distribution of profits paid to the shareholders.
Dividends do not affect net income.
Dividends directly reduce retained earnings.
Ch 1
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is the authoritative body that has primary responsibility for developing accounting principles.
True or False
True
The FASB do not have any enforcement authority.
FASB was given the power to set accounting standards for publicly traded companies by the SEC.
Ch 1
The Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) has regulatory authority over all corporations.
True or False
False
The SEC regulate publicly traded companies.
Ch 1
The primary role of accounting is to provide many different users (stakeholders) with financial information needed to make economic decisions.
True or False
True
Ch 2
The Cash account is increased with a
a. Debit
b. Credit
a. Debit
Ch 2
The Sales Revenue account is increased with a
a. Debit
b. Credit
b. Credit
Ch 2
The Equipment account is increased with a
a. Debit
b. Credit
a. Debit
Ch 2
The Loan Payable account is increased with a
a. Debit
b. Credit
b. Credit
Ch 2
The chart of accounts should be the same for each business.
True or False
False
Ch 2
To determine the balance in an account, always subtract credits from debits.
True or False
False
If the normal sign is a debit, then debits - credits.
If the normal sign is a credit, then credits - debits.
Ch 2
To determine the balance in an account which has a normal credit balance. always subtract debits from credits.
True or False
True
If the normal sign is a credit, then credits - debits.
Ch 2
Both debits & credit entries are posted to accounts like Cash & Inventory.
True or False
True
Ch 2
The Inventory account may have a credit balance.
True or False
False
Inventory is under Assets (Debit)
Ch 2
Revenues - Expenses = Net Income
True or False
True
If Assets total $30,000 & Equity is $21,000, Liabilities must be $9,000.
True or False
True
A = L + E
A - E = L
30000 - 21000 = 9000 ✅
Ch 2
Providing services to a customer increases revenue which increases equity.
True or False
True
Ch 2
The Inventory account is decreased with a credit when a product is delivered to a customer.
True or False
True
Ch 2
The transactions that have been “journalized” are “posted” to the general ledger.
True or False
True
Ch 2
Revenue & Liability accounts are increased with a debit.
True or False
False
They are increased with a credit.
Ch 2
Consuming goods & services in the process of generating revenues results in expenses.
True or False
True
Ch 2
Debiting the asset account “Accounts Receivable” will increase the account.
True or False
True
Ch 2
The expense account “Rent Expense” may have a credit balance.
True or False
False
It has a debit balance.
Ch 2
If inventory is purchased “on account,” the liability is credited to Accounts Receivable.
True or False
False
The liability is credited to Accounts Payable.
Ch 2
Revenue & liability accounts are increased with a debit.
True or False
False
They are increased with a credit & decreased with a debit.
Ch 3
An account in its simplest form has three parts to it: a title, an increase side, & a decrease side.
True or False
True
Ch 3
The Common Stock account appears in which area of the financial statements.
a. Asset
b. Liability
c. Equity
d. Revenue
c. Equity
Ch 3
The Salaries account appears in which area of the financial statements.
a. Asset
b. Liability
c. Revenue
d. Expense
d. Expense
Ch 3
The Sales account appears in which area of the financial statements.
a. Liability
b. Equity
c. Revenue
d. Expense
c. Revenue
Ch 3
The Loan Payable account appears in which area of the financial statements.
a. Asset
b. Liability
c. Equity
d. Revenue
b. Liability
Ch 3
The Inventory account appears in which area of the financial statements.
a. Asset
b. Liability
c. Revenue
d. Expense
a. Asset
Ch 3
The Interest Income account appears in which area of the financial statements.
a. Asset
b. Equity
c. Revenue
d. Expense
c. Revenue
Ch 3
The Note Receivable account appears in which area of the financial statements.
a. Asset
b. Liability
c. Revenue
d. Expense
a. Asset
Ch 3
The Retained Earnings account appears in which area of the financial statements.
a. Asset
b. Liability
c. Equity
d. Revenue
c. Equity
Ch 3
An adjusting entry would adjust revenue so it is reported when earned and not when the cash was received.
True or False
True
Revenue is recognized when earned.
Ch 3
Salary & wage expenses are recorded when the cash is direct deposited into their bank accounts.
True or False
False
The expenses must be recorded in the period that the employee performs the services.
Ch 3
Salaries & Wages are recorded as expenses only when the employee receives their paycheck.
True or False
False
Expenses are recognized when incurred/used.
Salaries & Wages are incurred when the employee provides their services to the business.
Ch 3
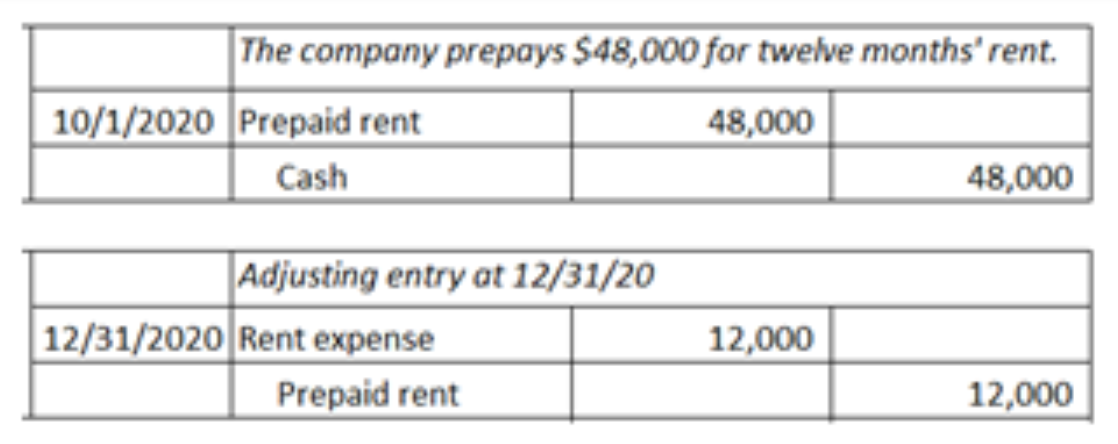
A company pays $48,000 for twelve months' rent on October 1, recording the prepayment as an asset. The adjusting entry on December 31 is a debit to Rent Expense, $12,000, and a credit to Prepaid Rent, $12,000.
True or False
True
Ch 3
A company buys a laptop for $3,600 on January 2nd. It plans to use the laptop for 3 years. It depreciates equipment using straight line (same amount of depreciation each year). The adjusting entry on December 31st is a debit to Depreciation Expense, $1,200, and a credit to Accumulated Depreciation.
True or False
True
⭐️ Ch 3
The matching concept:
a. addresses the relationship between the journal and the balance sheet
b. determines whether the normal balance of an account is a debit or
credit
c. states that expenses related to revenue be reported at the same time
the revenue is reported
d. requires that the dollar amount of debits equal the dollar
amount of credits on a trial balance
c. states that expense related to revenue be reported at the same time
Ch 3
Microsoft receives your payment for a 12 month subscription to Office 365. For Microsoft, this is a/an
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
c. unearned revenue
Ch 3
You pay Microsoft for a 12 month subsciption to Office 365. For you (the customer), this is a/an
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
a. prepaid expense
Ch 3
A company agrees to reimburse travel expenses next month for a business trip completed this month by an employee. For the company, this is a/an
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
d. accrued expense
Ch 3
A customer is interested in buying a soon to be released new version of an iPhone and pays for the phone in advance. From the customers’ point of view, this is a/an
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
a. prepaid expense
Ch 3
A customer is interested in buying a soon to be released new version of an iPhone and pays for the phone in advance. From the retailer’s point of view, this is a/an
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
c. unearned revenue
Ch 3
Retainers received in cash by a law firm in advance of providing legal services is an example of
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
c. unearned revenue
Ch 3
A law firm has provided legal services to a client but has not invoiced/billed the client. This is an example of
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
b. accrued revenue
Ch 3
Paying three months of rent in advance is an example of
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
a. prepaid expense
Ch 3
On December 31st a calendar year corporation owes employees for services performed during the last week of December.
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
d. accrued expense
Ch 3
Expenses result from selling services or products to customers.
True or False
False
Revenue is the result of selling services/products to customers.
Expenses are incurred/generated to provide the services.
Ch 3
Prepaid expenses are an expense & appear on the income statement.
True or False
False
Prepaid expenses are an asset on the balance sheet.
Prepaid expenses have future value.
Ch 3
When a business receives a bill from the utility company, no entry should be made until the invoice is paid.
True or False
False
GAAP requires the company be on the “accrual basis.”
Expense recognition cannot be delayed until the expense is paid.
Ch 3
An example of deferred (unearned) revenue is Unearned Car Insurance Premium Revenue on an insurance company’s balance sheet.
True or False
True
Ch 3
If the adjusting entry to recognize expired prepaid auto insurance at the end of the period is inadvertently omitted, insurance expense will be understated and net income overstated.
True or False
True
Ch 3
The difference between the balance of a fixed asset account and the balance of its related accumulated depreciation account is termed the book value of the asset.
True or False
True
Ch 3
Accumulated depreciation is reported on the income statement.
True or False
False
Accumulated depreciation is a “contra asset” account.
Ch 3
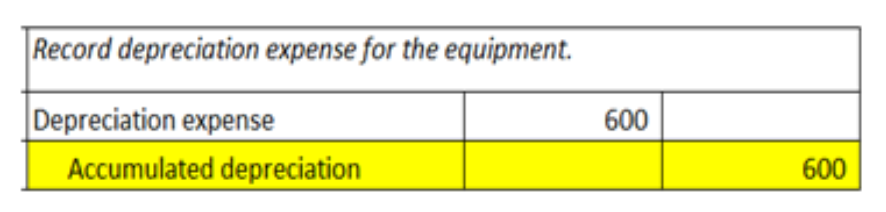
A company depreciates its equipment $600 a year. The adjusting entry on December 31 is a debit to Depreciation Expense, $600, and a credit to Equipment, $600.
True or False
False
The depreciation expenses is accumulated in the Accumulated depreciation “contra asset” account.
Ch 3
Office Furniture is an example of a current asset.
True or False
False
> 12 months is long term
Ch 3
Inventory is reported as a current asset.
True or False
True
Ch 3
Accrued expenses to be paid next month are listed on the balance sheet as a current asset.
True or False
False
Accrued expenses to be paid next month are current liabilities.
Ch 3
A company pays $12,000 for twelve months' rent on November 1st, recording the prepayment as an asset. The adjusting entry on December 31 is a debit to Rent Expense, $2,000, and a credit to Prepaid Rent, $2,000.
True or False
True
The asset prepaid rent is reduced each month by the amount of the rent for that month.
Ch 3
The company debits cost of goods sold when it buys merchandise to resell to its customers.
True or False
False
The company debits inventory when it buys merchandise.
The company debits Cost of Goods Sold when it sells merchandise,
Ch 3
Accruals are needed when:
an unrecorded expense has been incurred or
an unrecorded revenue has been earned.
True or False
True
Ch 3
Generally accepted accounting principles require cash‐basis accounting.
True or False
False
Must be accrual basis.
Cash basis doesn’t capture all of the economic activity.
Ch 3
The revenue recognition principle states that revenue should be recorded only when the cash is received from the customer.
True or False
False
Revenue recognized when earned. When the cash is received cannot be the rule since cash received in advance creates the liability unearned revenue and sales on account generate revenue before the cash is received.
Ch 4
The amount of the net income appears on both the income statement and the balance sheet for that period.
True or False
False
Net income appears on the Income Statement and the Statement of Changes to Equity becuz it is part of the changes to retained earnings.
Ch 4
Assets, liabilities, & stockholders’ equity accounts are permanent accounts & do not get closed at the end of the period.
True or False
True
Ch 4
Inventory will not appear on the post-closing trial balance.
True or False
False
Ch 4
Sales Revenue will not appear on the post-closing trial balance.
True or False
True
Ch 4
The matching concept:
a. requires that the dollar amount of debits equal
the dollar amount of credits on a trial balance balancing
b. states that expenses related to revenue be
reported at the same time the revenue is reported matching
c. addresses the relationship between the journal
and the balance sheet
d. determines whether the normal balance of an
account is a debit or credit
b. states that expenses related to revenue be reported at the same time the revenue is reported matching
Ch 4
The Unearned Revenues account is an example of a liability.
True or False
True
The unearned revenue must be “earned” before it can be recognized on the income statement.
Ch 4
The expense account “Salaries Expense” may have a credit balance.
True or False
False
Ch 4
Prepaid Supplies are an example of a temporary account since the supplies are used up in a short time.
True or False
False
Prepaid supplies are not zeroed out.
This is a balance sheet account.
Ch 4
When an account receivable is collected in cash, the total assets of the business increase.
True or False
False
Cash increases
Accounts receivable decreases
Total assets stays the same
Ch 4
Revenue - Expenses = Net Income
True or False
True
Ch 4
Microsoft receives a cash payment in advance for cloud services is an example of
a. prepaid expense
b. accrued revenue
c. unearned revenue
d. accrued expense
c. unearned revenue
Ch 4
A company’s accounts payable represents an amount that the company will collect from customers.
True or False
False
Accounts payable represents an amount the company must pay to its vendors/creditors.
Ch 4
The amount of the net income appears on both the income statement & the balance sheet for that period.
True or False
False
Net income appears on the income statement & the statement of changes to retained earnings (on statement of changes to equity)
Ch 4
Assets, liabilities, & stockholders’ equity accounts are permanent accounts & do not get closed at the end of the period.
True or False
True
Ch 4
Cash and other assets that are reasonably expected to be realized in cash, sold, or consumed through the normal operations of a business more than one year after the balance sheet date are called current assets.
True or False
False
> 12 months are long term
Ch 4
The accounting equation can be expressed as
Liabilities = Assets + Shareholder’s Equity
True or False
False
A = L + E
A - E = L
Ch 4
To determine the balance in an account, always subtract credits from debits.
True or False
False
If normal sign is a debit, debits - credits.
If normal sign is a credit, credits - debits.
Ch 4
A credit to the cash account will decrease the account.
True or False
True
Cash is an asset & the normal sign is a debit.
Increase cash with a debit & decrease cash with a credit.
Ch 4
Both debits & credit entries are posted to accounts like Accounts Receivable & Accounts Payable.
True or False
True
Ch 4
Debiting the asset account “Equipment” will increase the account.
True or False
True
Ch 4
Crediting the revenue account “Rent Income” will increase the account.
True or False
True
Ch 4
Inventory has a normal debit balance but it can have a credit balance?
True or False
False
A company cannot deliver more items than it bought/received.
Ch 4
If Equity is $12,000 & total Liabilities are $4000, then total Assets must be $16,000.
True or False
True
A = L + E
16000 = 4000 + 12000 ✅
Ch 4
The updating of accounts when financial statements are prepared is called the adjusting process.
True or False
True
Example: Cash - checking account fees.
Ch 4
Cost of Goods Sold
a. debit
b. credit
a. debit
Ch 4
Accounts Payable
a. debit
b. credit
b. credit
Ch 4
Cash
a. debit
b. credit
a. debit
Ch 4
Prepaid Expenses
a. debit
b. credit
a. debit