A&P - 12.2 Neural Tissue (parts of a neuron)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
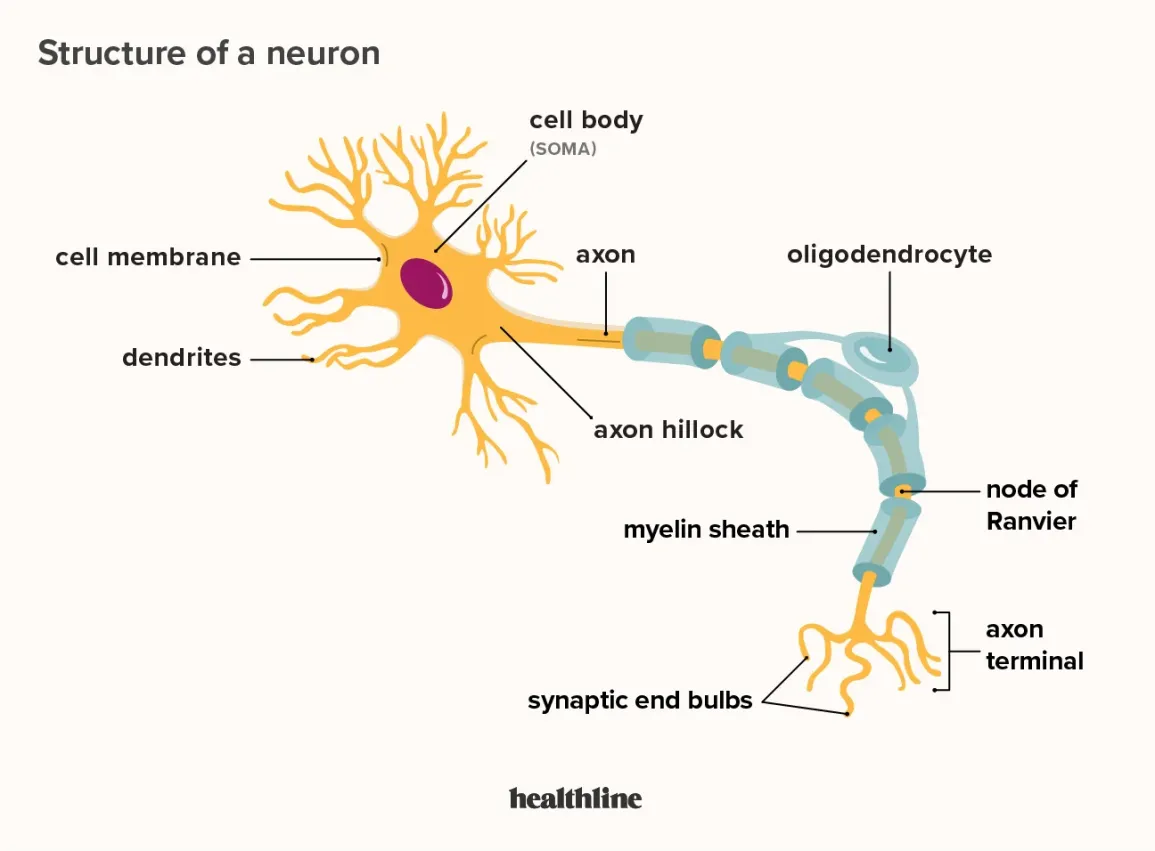
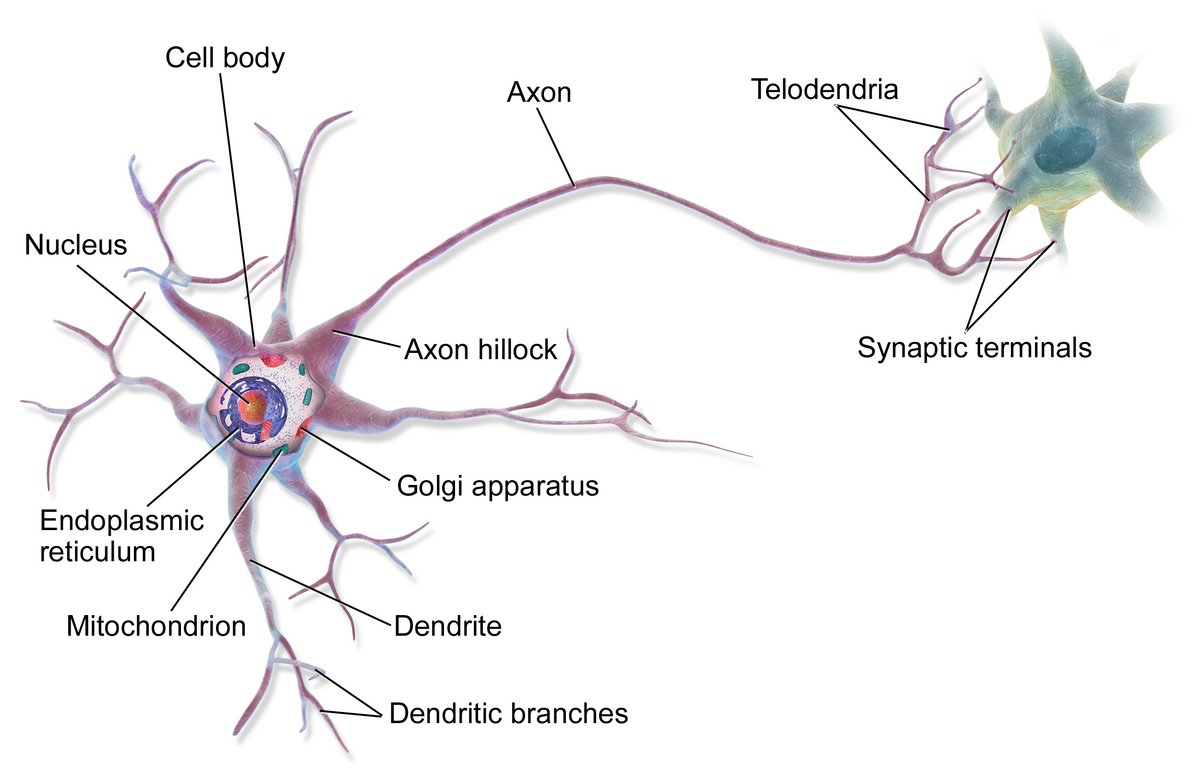
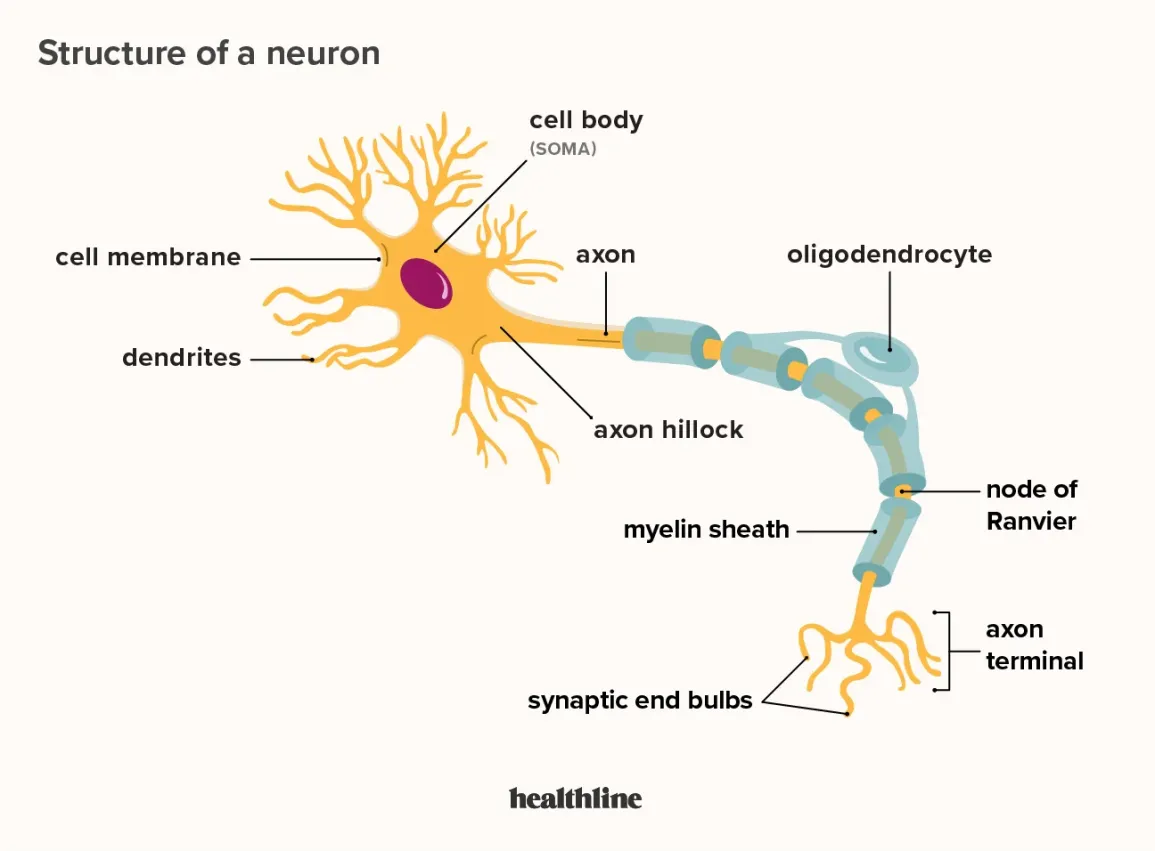
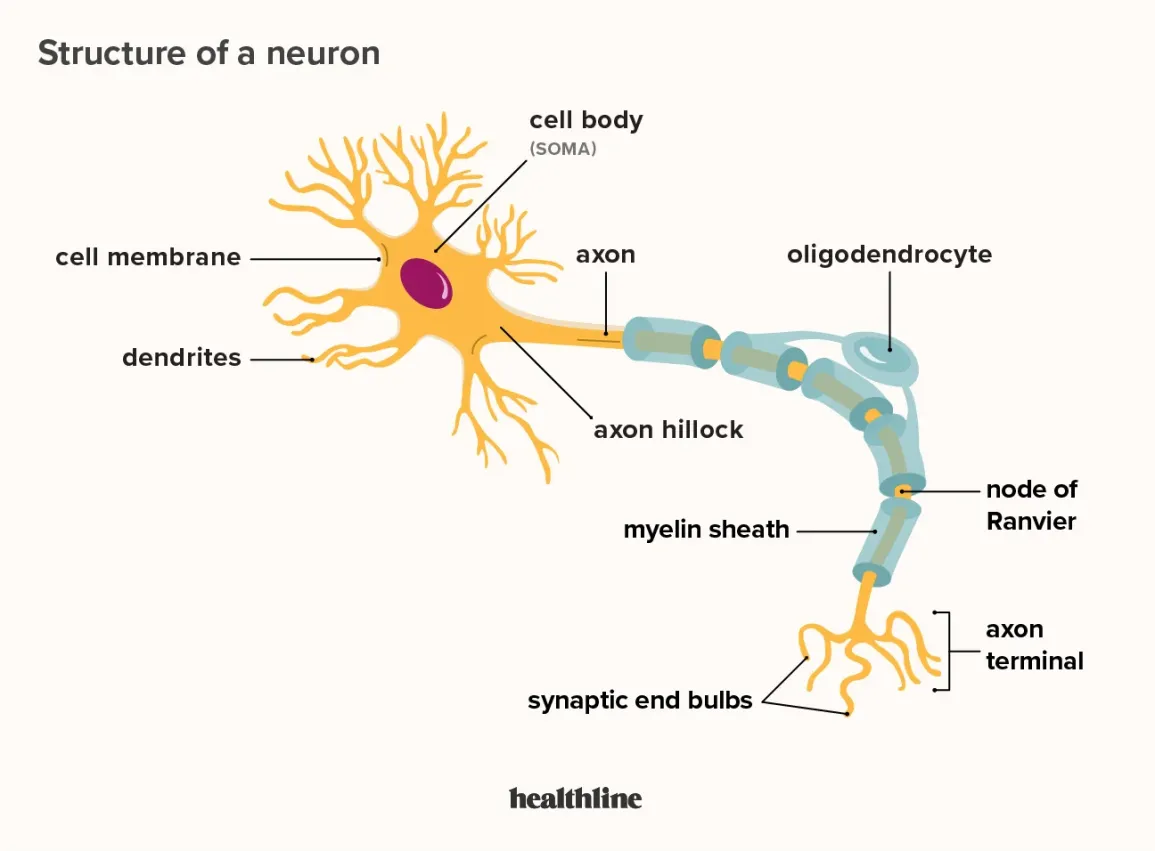
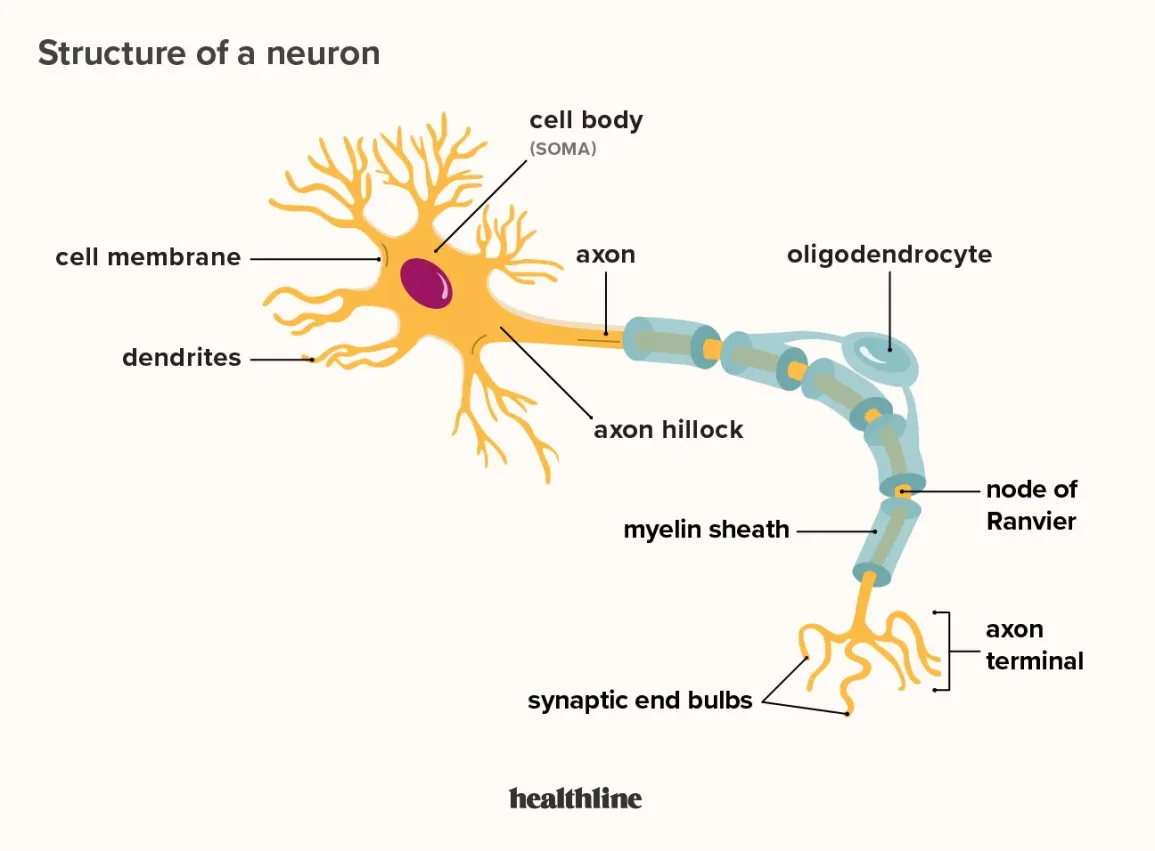
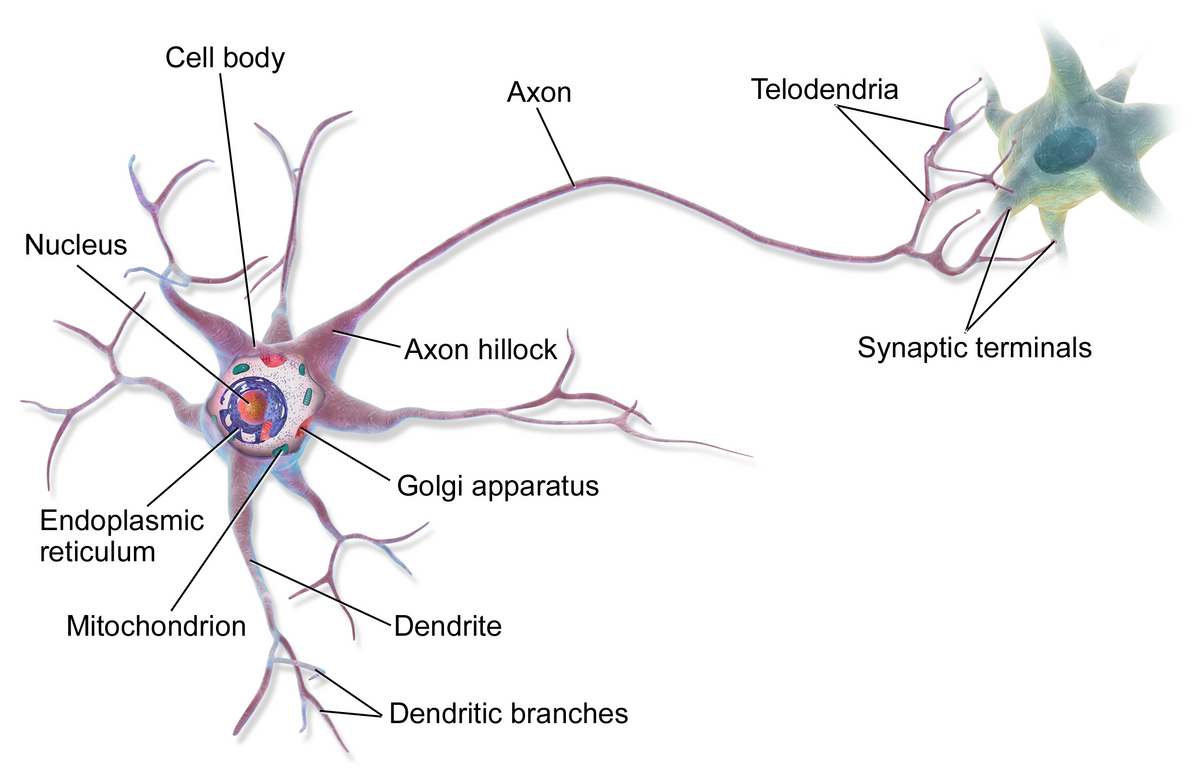
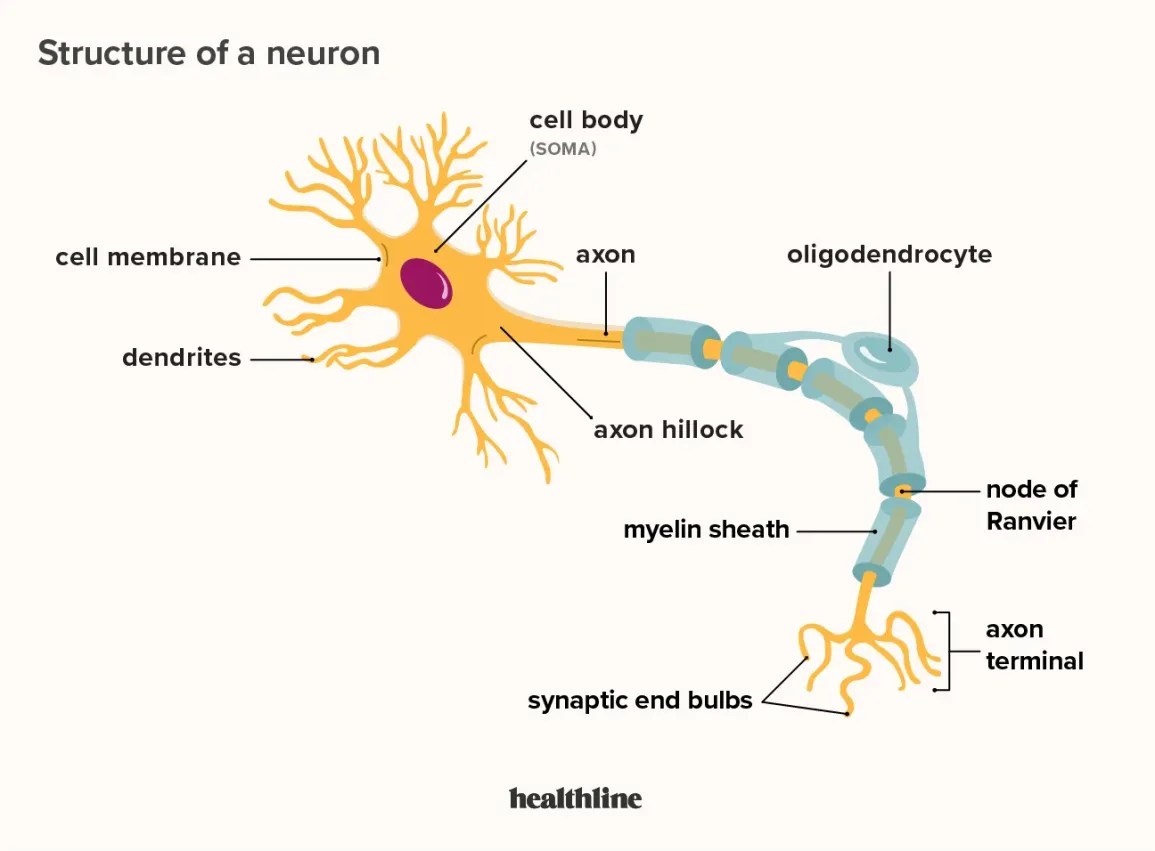
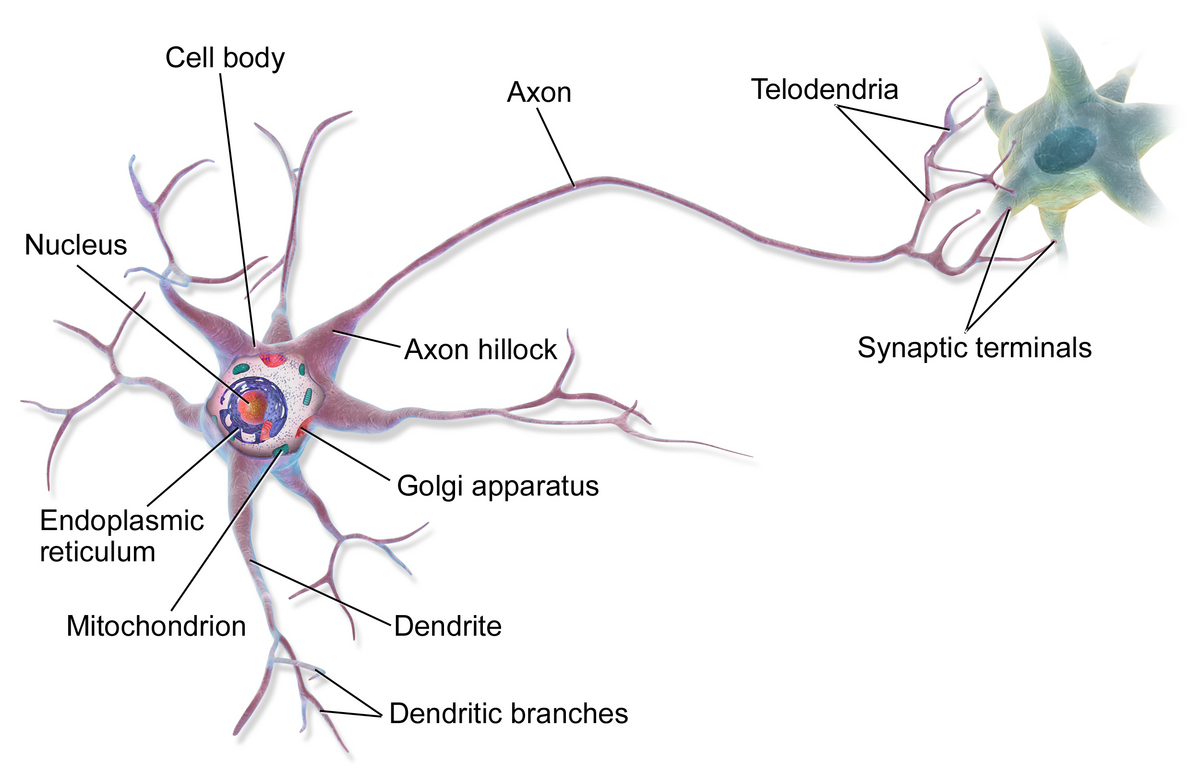
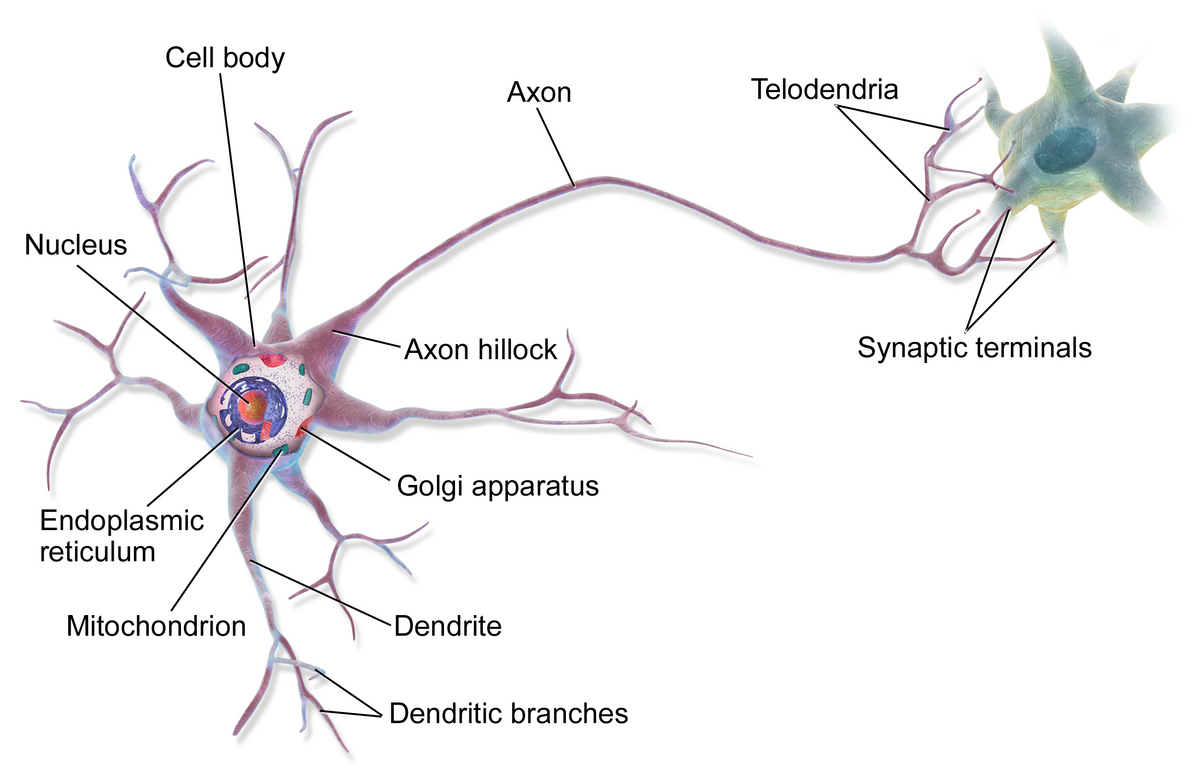
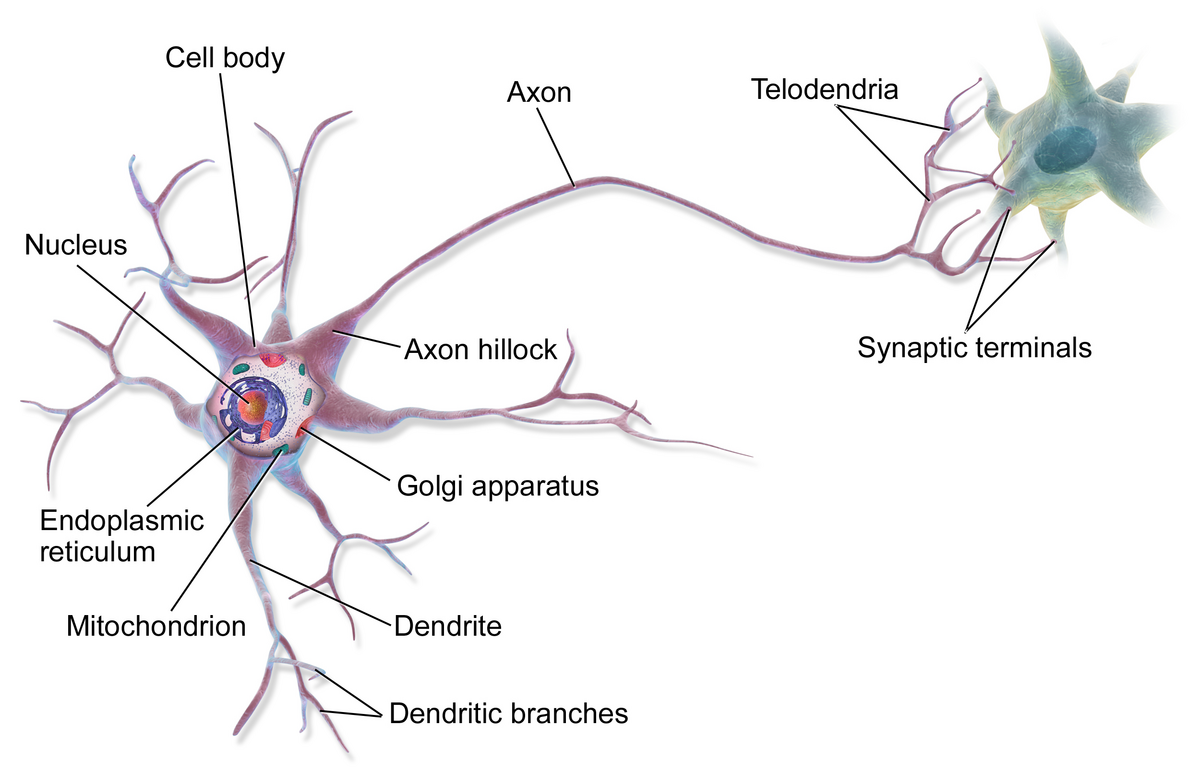
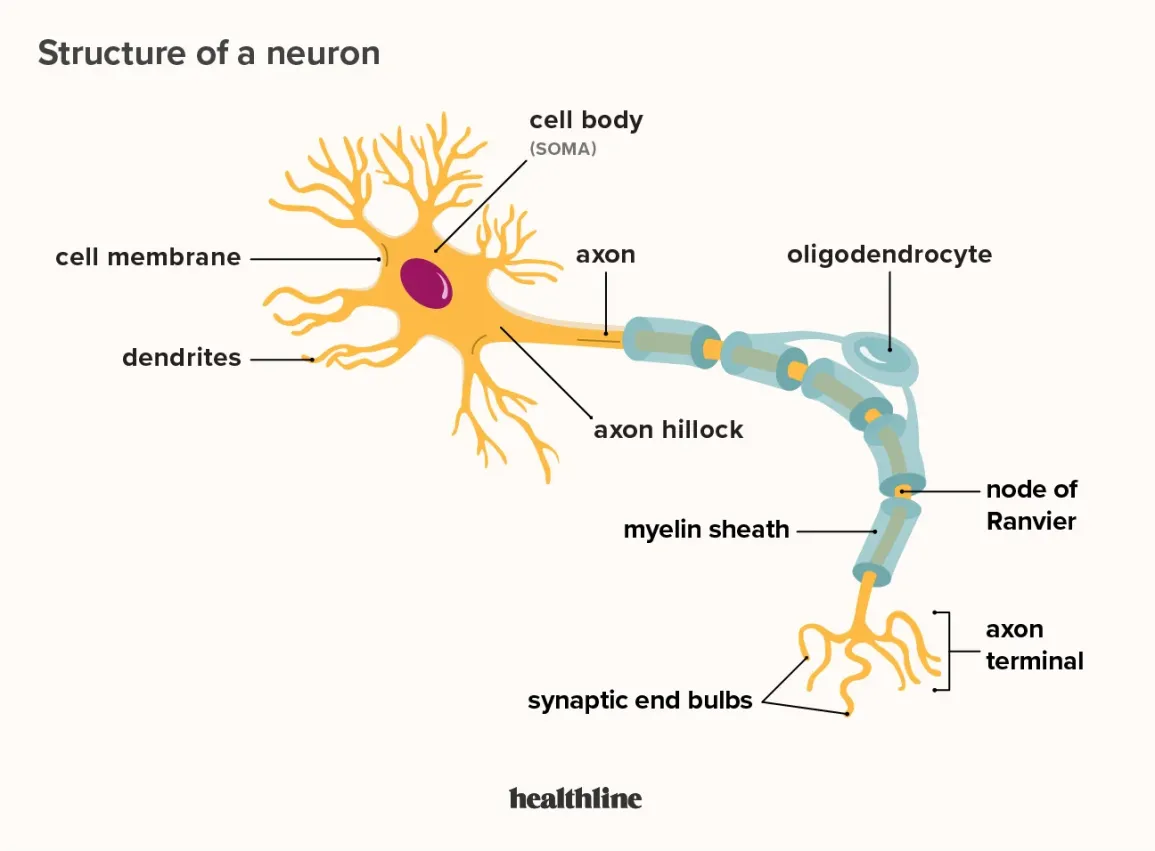
cell body (soma)
enlarged metabolic region of the cell where the nucleus and most the major organelles are located
FUNCTION: control center of neuron
has a single, centrally located nucleus with large nucleolus
cytoplasm contains mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi complex, inclusions, entensive rough ER, and cytoskeleton
mature neurons have no centrioles, no mitosis after adolescence
nucleus
localized collection of neuron cell bodies that are functionally related; a “center” of neural function
FUNCTION: controls the cell’s activities and stores genetic information
cell membrane
FUNCTION: protect the cell and control what enters and leaves it, also plays a key role in sending electrical signals
what makes neurons special is that they have many extensions of their cell membranes, which are generally referred to as processes
cell processes
called tracts within the CNS while they are called nerves within the PNS
dendrites
axon
tract
bundle of axons in the central nervous system having the same function and point of origin
nerve
cord-like bundle of axons located in the peripheral nervous system that transmits sensory input and response output to and from the central nervous system
dendrites
one of many branchlike processes that extends from the neuron cell body and functions as a contact for incoming signals (synapses) from other neurons or sensory cells (branches that come off the soma)
FUNCTION: receive chemical and electrical signals and conduct them towards the cell body (primary site for receiving signals from other neurons)
these electrical signals are not considered nerve impulses; they are called graded potentials rather than action potentials
the more dendrites the neuron has, the more information it can receive
graded potentional
change in the membrane potential that varies in size, depending on the size of the stimulus that elicits it
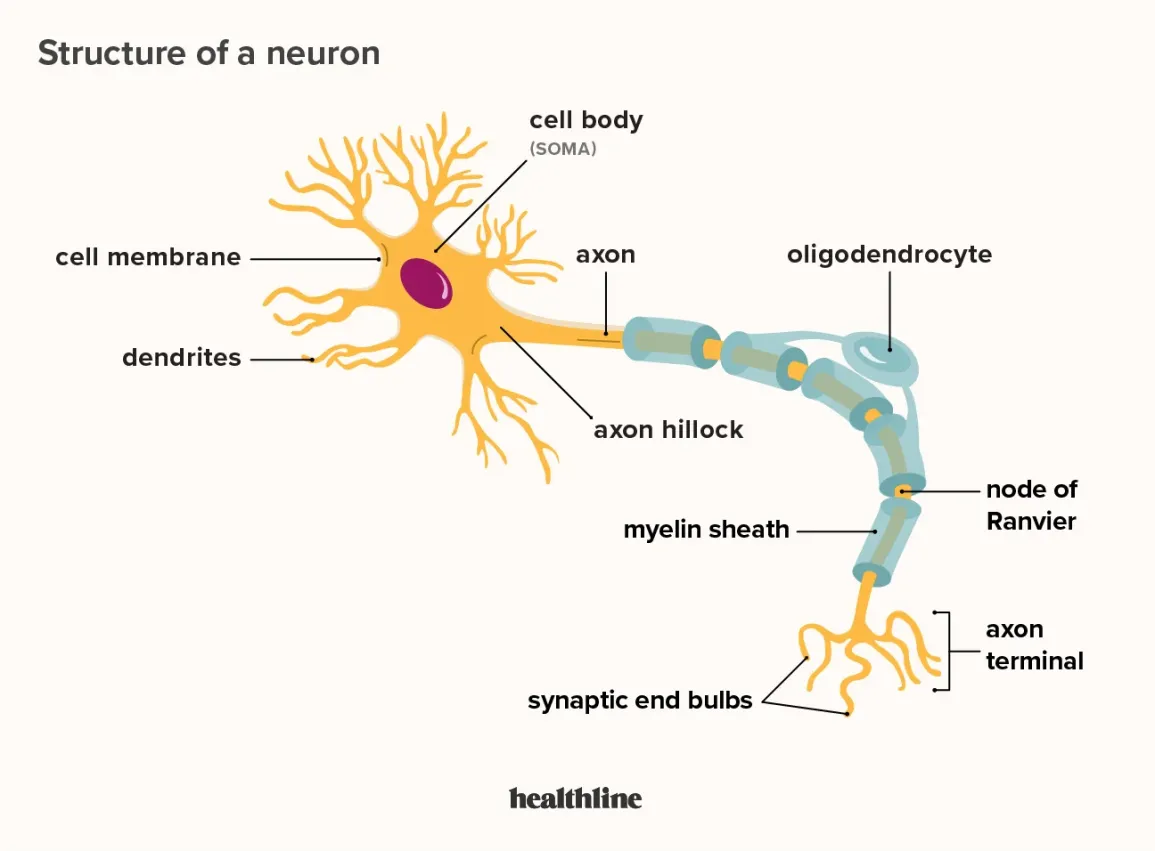
axon hillock
tapering of the neuron cell body that gives rise to the axon (axon forms at a tapered area called the axon hillock)
within the axon hillock, the cytoplasm changes to a solution of limited components called axoplasm
serves as the “trigger zone” because graded potentials must reach this area of the neuron before they can be converted into action potentials
axon (nerve fiber)
single process of the neuron that carries an electrical signal (action potential) away from the cell body toward a target cell - originates from one side of the soma called the axon hillock
FUNCTION: capable of generating action potentials and transmit them as nerve impulses away from the cell body towards the telodendria and axon terminals
only one axon per neuron
schwann cells and myelin sheath enclose axon
branches extensively on distal end
synaptic knob
specialized for rapid conduction of nerve signals from soma to remote points in the body
action potential
change in voltage of a cell membrane in response to a stimulus that results in transmission of an electrical signal; unique to neurons and muscle fibers
axolemma
the plasma membrane surrounding the axon is called the axolemma
axoplasm
cytoplasm of an axon, which is different in composition than the cytoplasm of the neuronal cell body
initial segment
first part of the axon as it emerges from the axon hillock, where the electrical signals known as action potentials are generated
myelin
lipid-rich insulating substance surrounding protein that is characterized by also binding to muscarine and is a metabotropic receptor
many axons are wrapped an insulating substance called myelin
made from glial cells
myelinated fibers
conduct impulses rapidly
these form the white matter of the nervous tissue
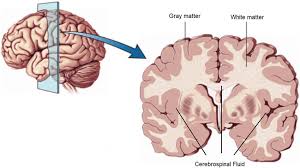
white matter
regions of the nervous system containing mostly myelinated axons
making the tissue appear white because of the high lipid content of myelin
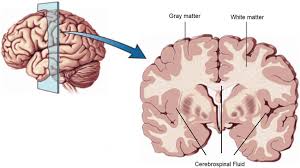
unmyelinated fibers
conduct impulse relatively slow compared to myelinated fibers
this type forms the gray matter of the nervous tissue
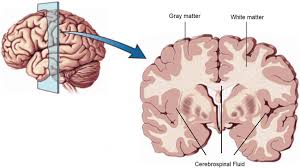
gray matter
regions of the nervous system containing cell bodies of neurons with few not no myelinated axons
actually may be more pink or tan in color, but called gray in contrast to white matter
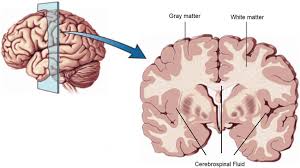
myelin sheath
axons are often covered with a whitish, fatty (protein-lipoid) material, myelin sheath
protects and electrically insulates neurons from one another
acts as insulation much like the plastic or rubber that is used to insulate electrical wires
there are gaps in the myelin covering of an axon
formed by glial cells - the linner layers of the glial cell form the insulating myelin sheath while the outer layer is called the neurolemma
in the PNS, Schwann cells envelop and then rotate around the axons forming the sheath while in the PNS, the myelin sheath is form by oligodendrocytes
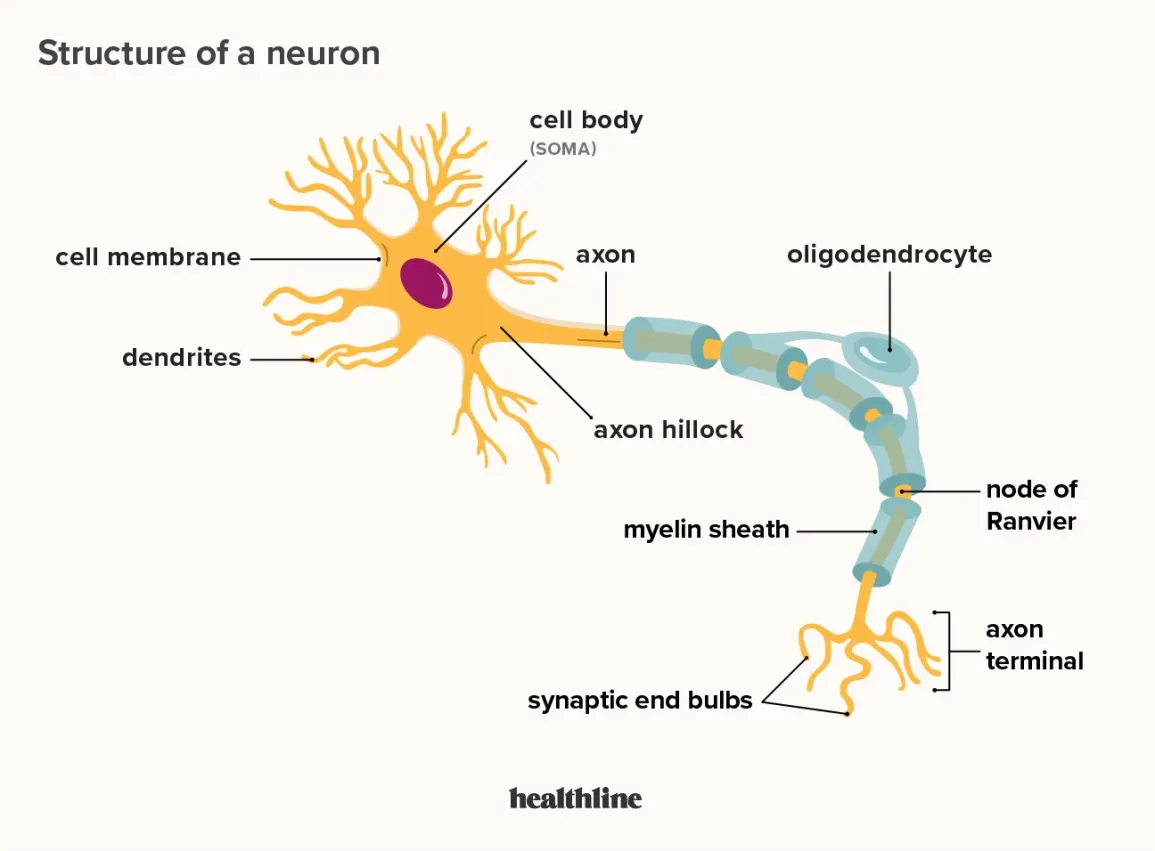
nodes of Ranvier
gapes within the myelin sheath are called nodes of Ranvier
gapes between two myelinated regions of an axon, allowing for strengthening of the electrical signal as it propagates down the axon
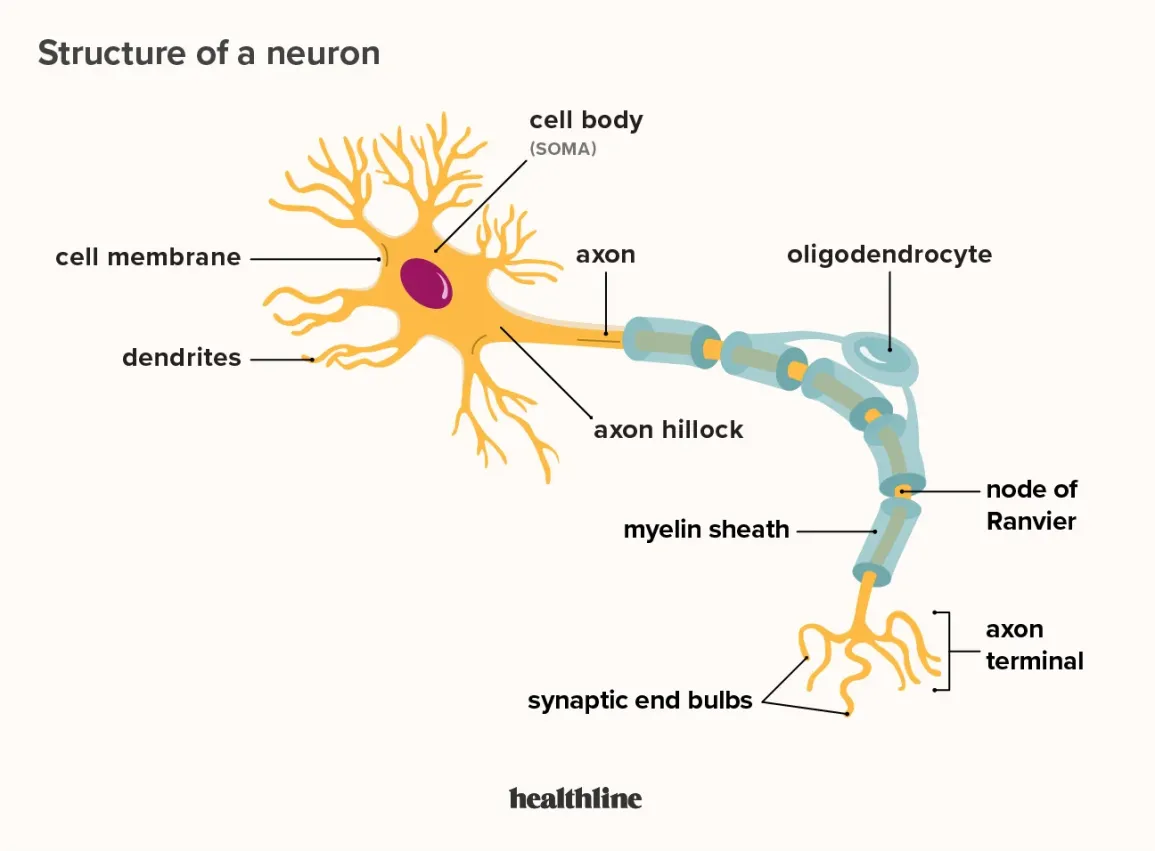
axon segment
the length of the axon between each gap, which is wrapped in myelin, is referred to as an axon segment
single stretch of the axon insulated by myelin and bounded by nodes of Ranvier at either end (except for the first, which is after the intital segment, and the last, which is followed by the axon terminal)
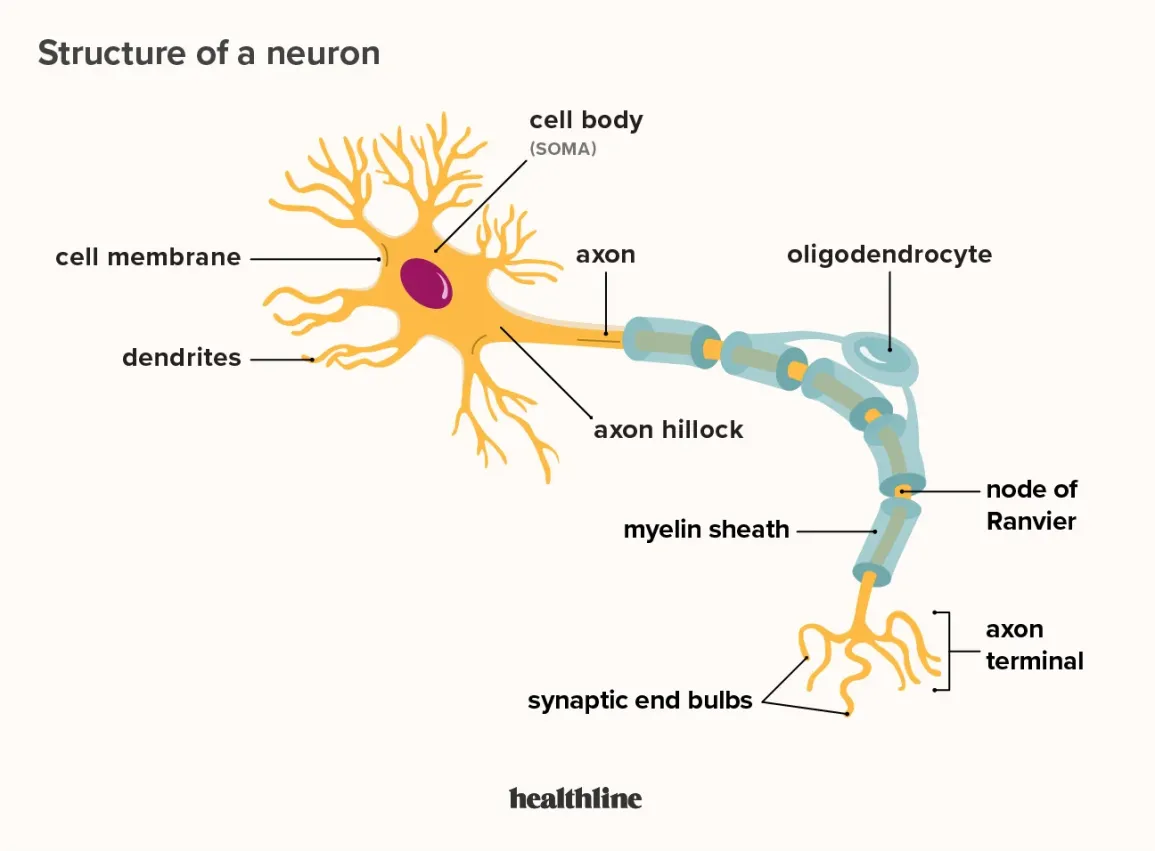
loss of myelination is a characteristic of which neurodegenerative disorders
multiple sclerosis (MS)
Guillain-Barre syndrome
multiple sclerosis
autoimmune disease
antibodies produced by lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) mark myelin as something that should not be in the body, this causes inflammation and the destruction of the myelin in the CNS
somatic and automic deficits, control of the musculature is compromised, as is control of organs such as the bladder
Guillain-Barre syndrome
demyelinating disease of the PNS
result of an autoimmune reaction but the inflammation is the the peripheral nerves
sensory symptoms or motor deficits are common, and autonomic failures can lead to changes in the heart rhythm or a drop in blood pressure, especially when standing, which causes dizziness
telodenria
smaller end branches of the axon
at the end of the telodenria are the axon terminals which have the synatic vesicles
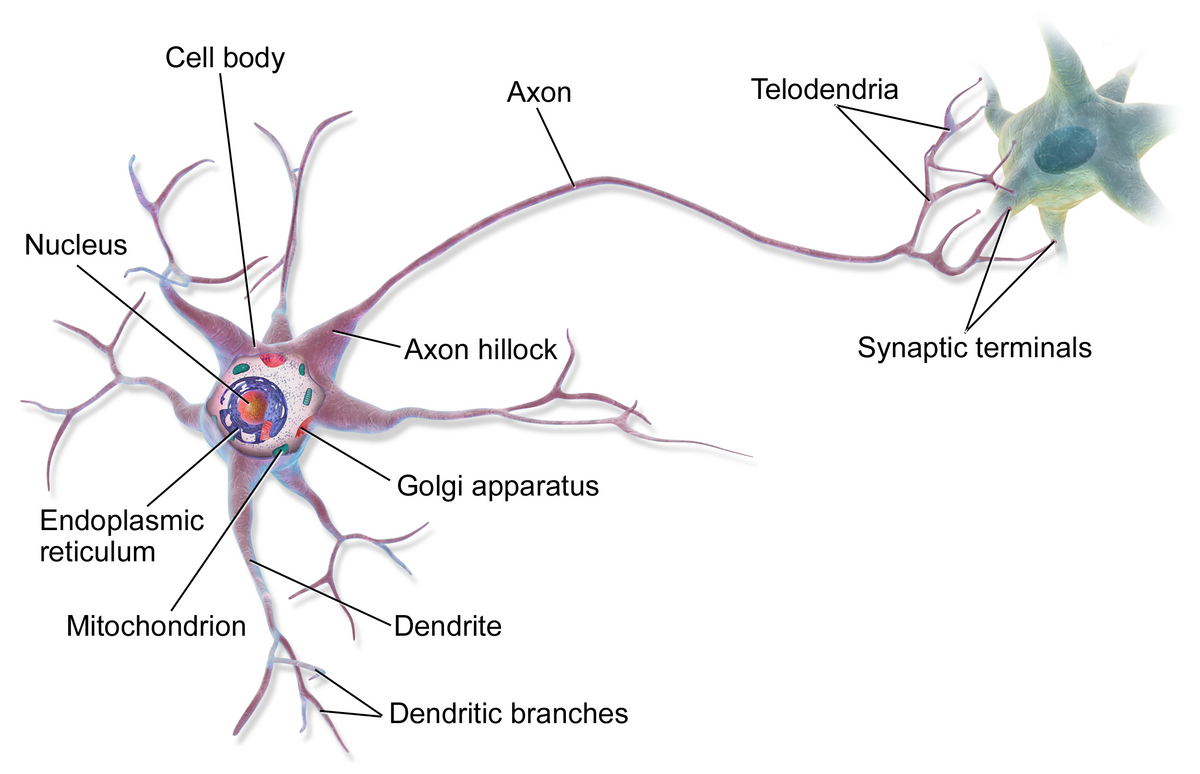
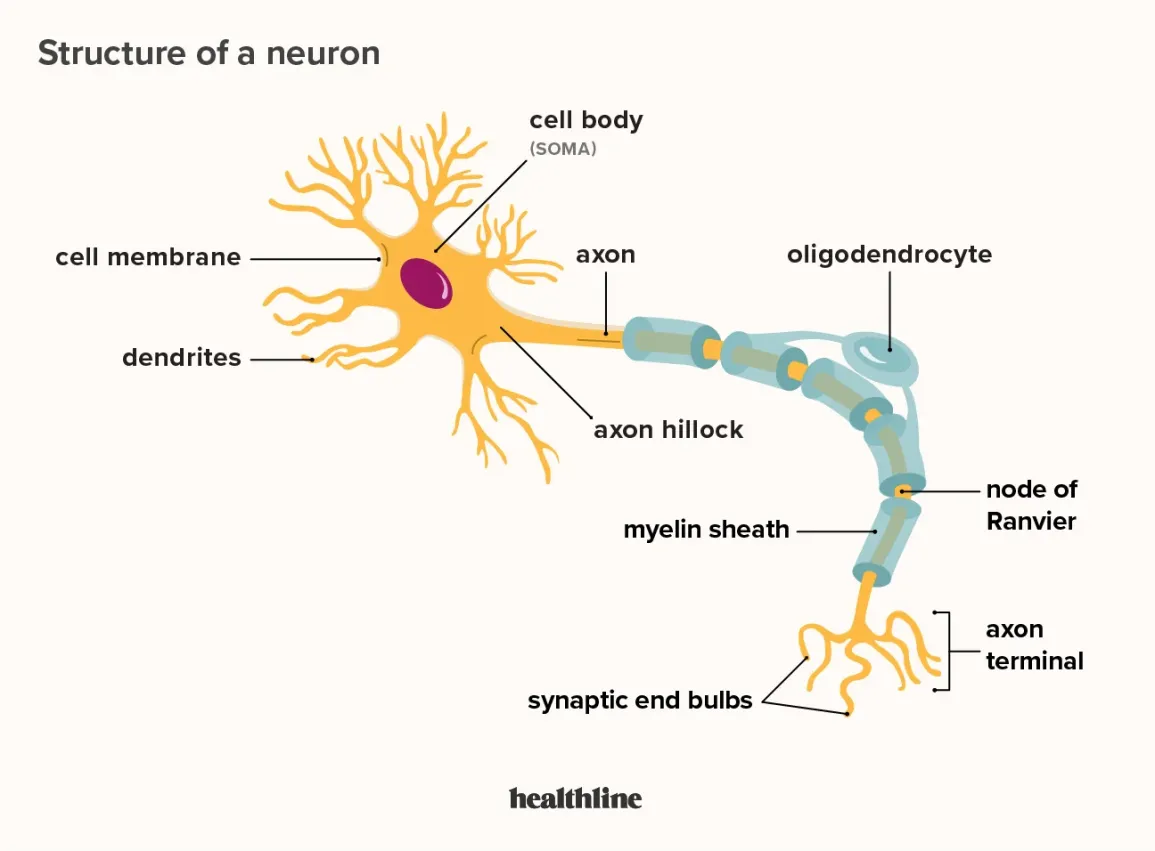
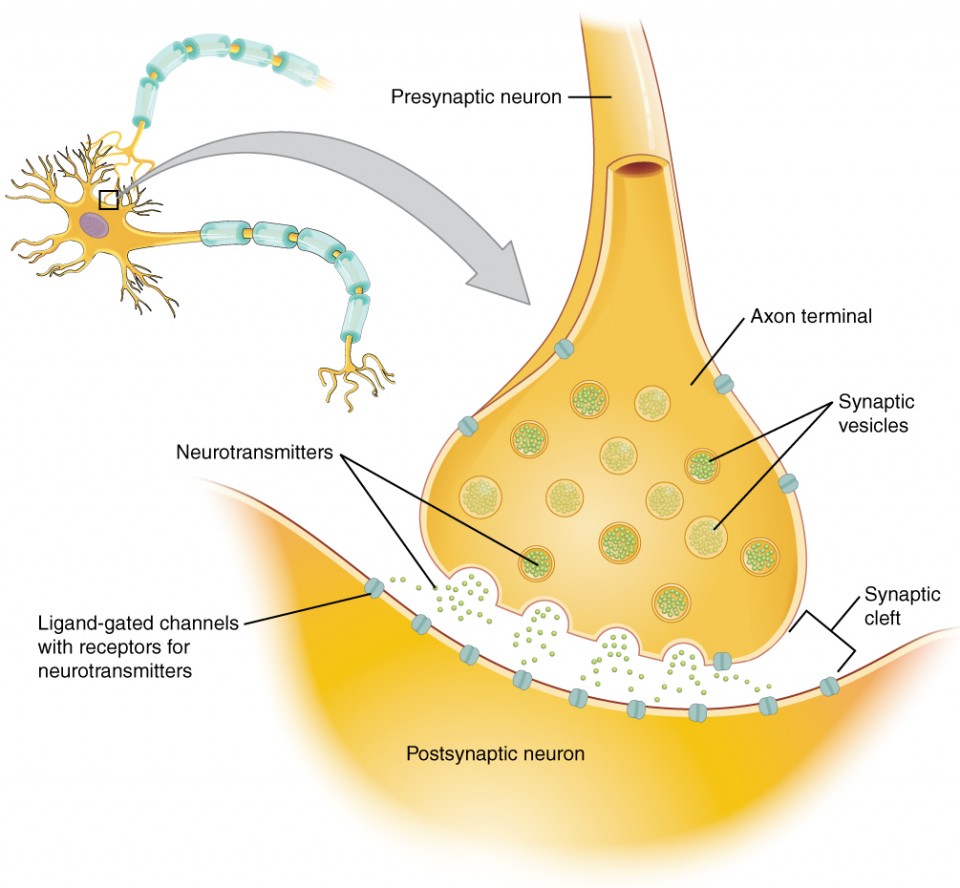
axon terminal
end of the axon, where there are usually several branches extending toward the target cell and posses many synaptic vesicles
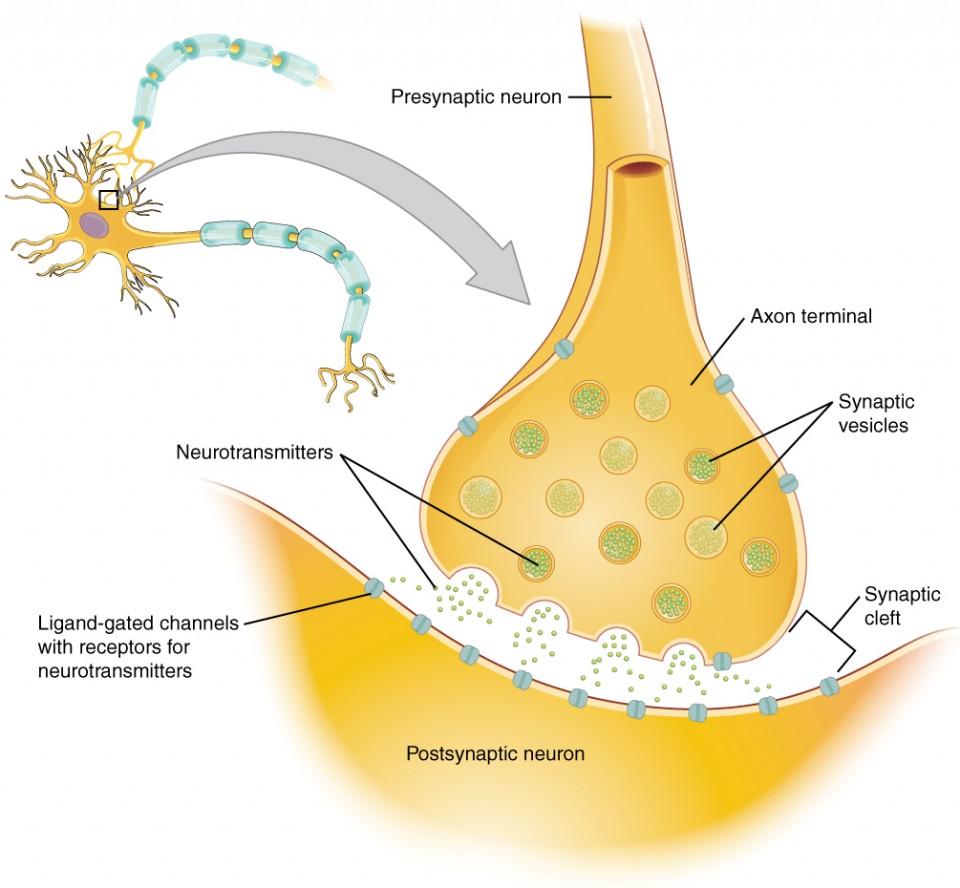
synaptic end bulb
swelling at the end of an axon where neurotransmitter molecules are released onto a target cell across a synapse
neurotransmitter
chemical signal that is released from the synaptic end bulb of a neuron to causes a change in the target cell
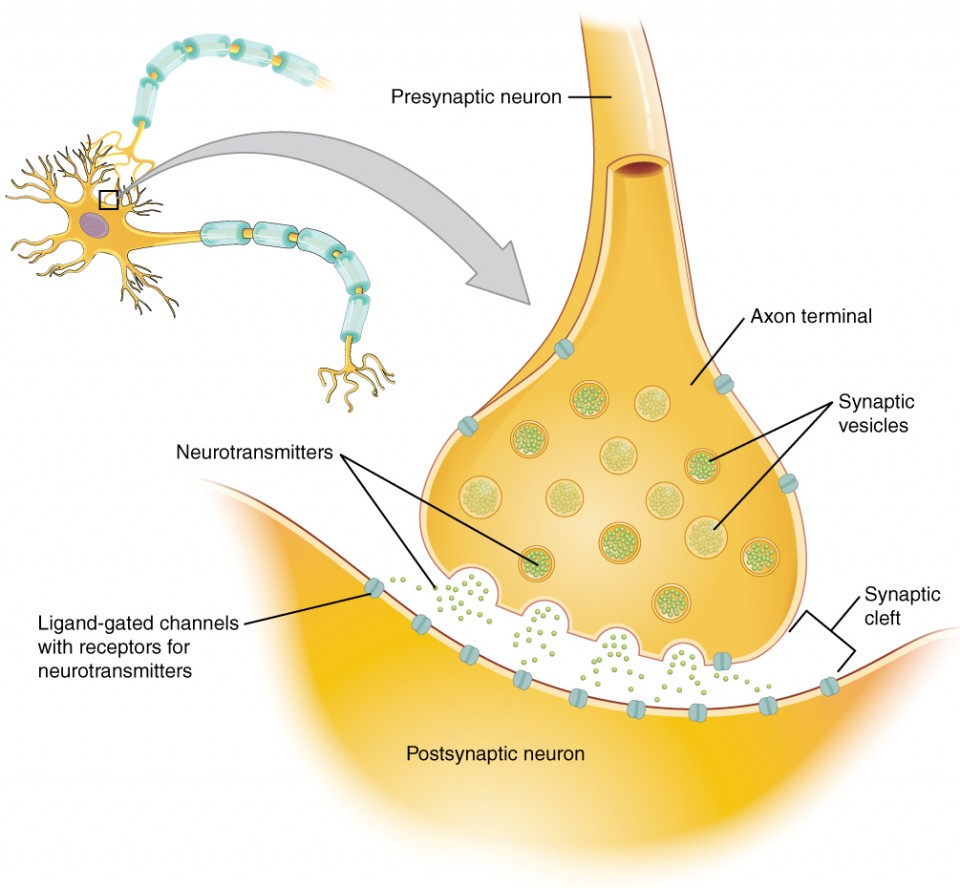
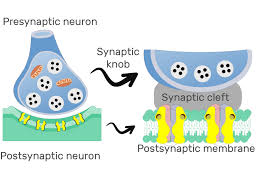
synaptic knob
(terminal button) - little swelling that forms a junction (synapse) with the next cell (nerve, muscle, gland)
contains synaptic vesicles full of neurotransmitters
synaptic vesicles
store and release neurotransmitters at the synapse
act like messenger packages that store, transport, and release neurotransmitters to help neurons communicate with each other
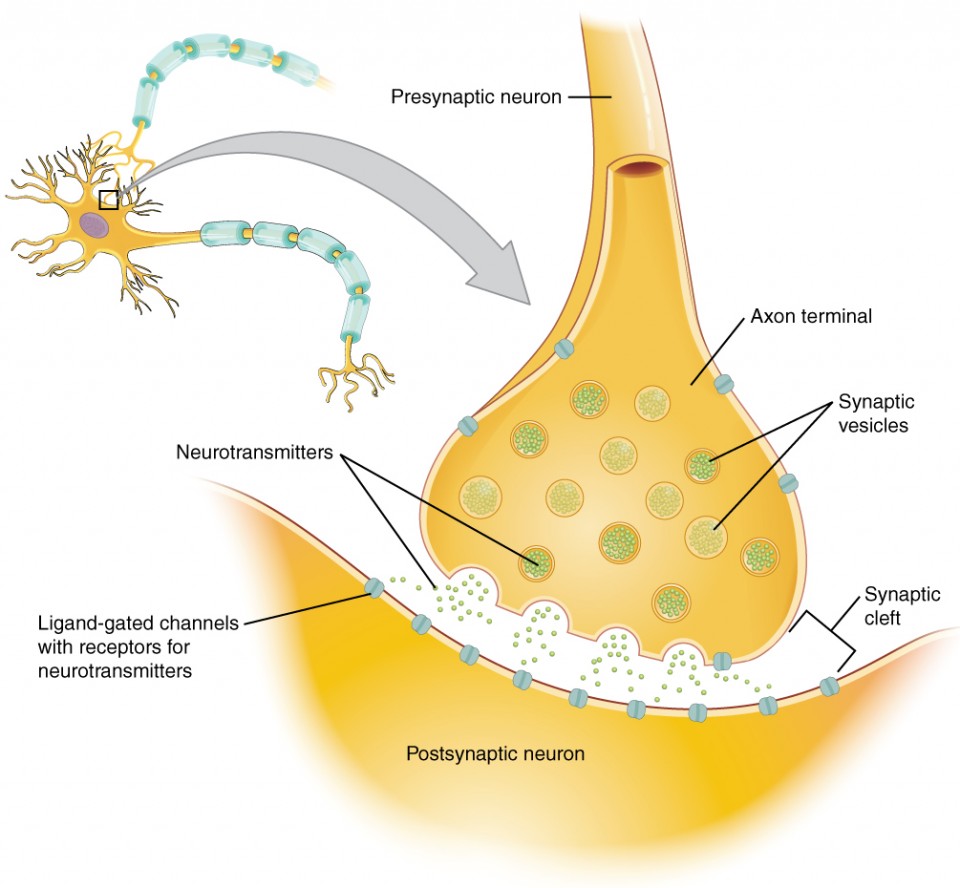
synapse
narrow junction across which a chemical signal passes from neuron to the next, initiating a new electrical signal in the target cell
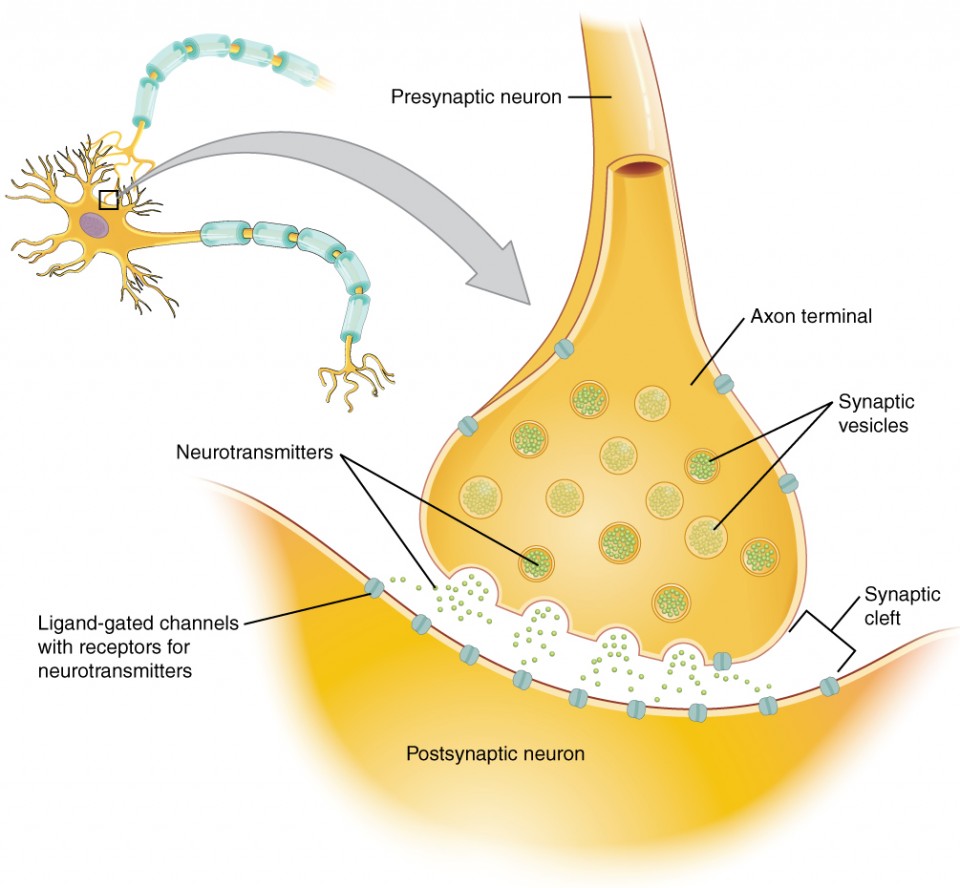
synaptic cleft
small gap between cells in a chemical synapse where neurotransmitter diffuses from the presynaptic element to the postsynaptic element
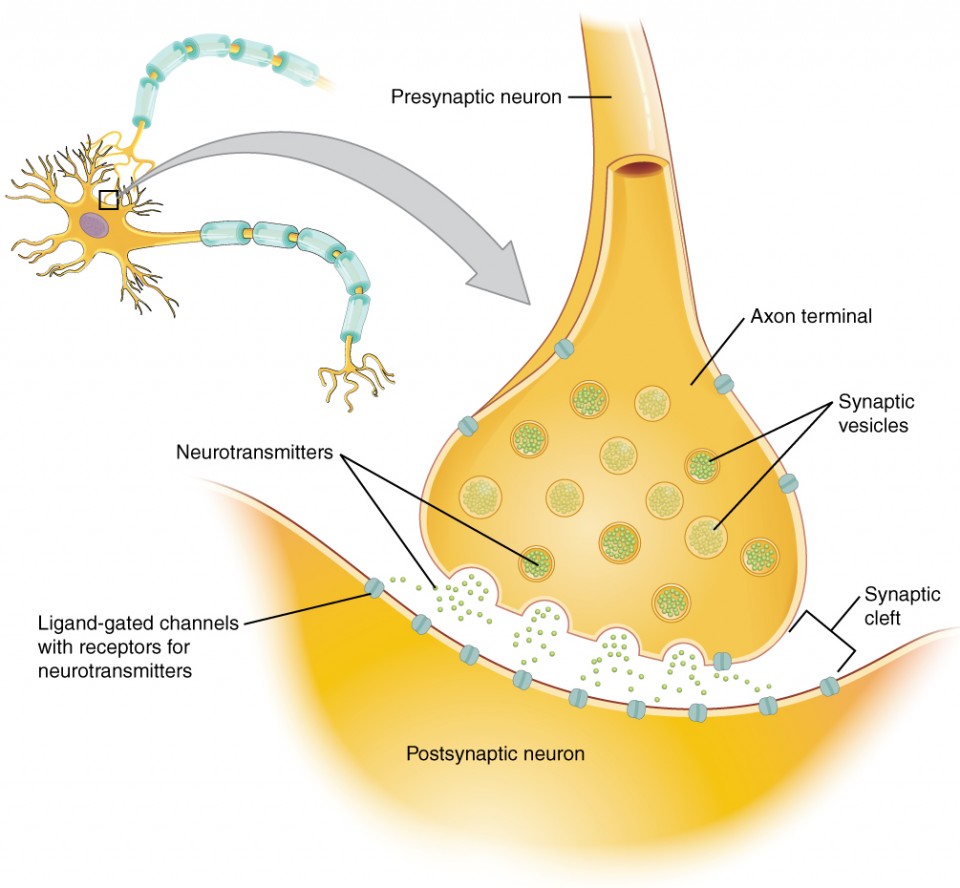
pre-synaptic neuron
nerve cell that sends a signal to another neuron across a synapse
before the synapse
responsible for transmitting information to the next cell
ends in a structure called the axon terminal
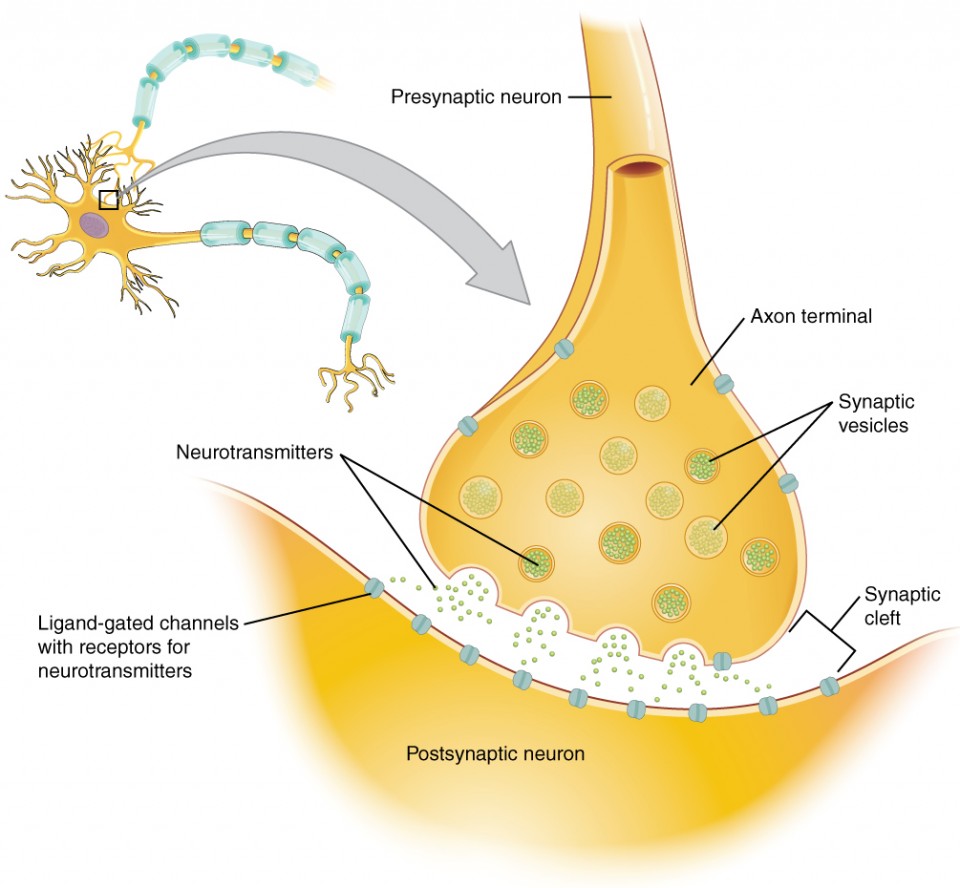
post-synaptic neuron
nerve cell that receives the signal from another neuron across a synapse
after the synapse
responsible for receiving and responding to the message sent by the presynaptic neuron
on the dendrites or sometimes the cell body
confusing terminology between the structures of the CNS and PNS
CNS
group of neuron cells bodies (i.e., gray matter) = nucleus
bundle of axons (i.e., white matter) = tract
PNS
group of neuron cells bodies (i.e., gray matter) = ganglion
bundle of axons (i.e., white matter) = nerve
ganglion
localized collection of neuron cell bodies in the PNS