ECON 248 2.1 The Scientific Method: Observation, Theory, And More Observation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
The dispassionate development and testing of theories about how the world works.
Scientific Method
Economists try to address their subject with a ().
Scientist’s Objectivity
Although economists use theory and observation like scientists, a challenge they face is that conducting economic experiments is (). This is because they usually can’t manipulate values on a whim.
Impractical
() can simplify the complex world and make it easier to understand.
Assumptions
Economists use () in the form of diagrams and equations, ignoring certain parts of the real-world economy to focus on what’s important.
Economic Models
An economic model which is used to show how money flows between households and firms in goods/services market and the factors of production market.
Circular Flow Diagram
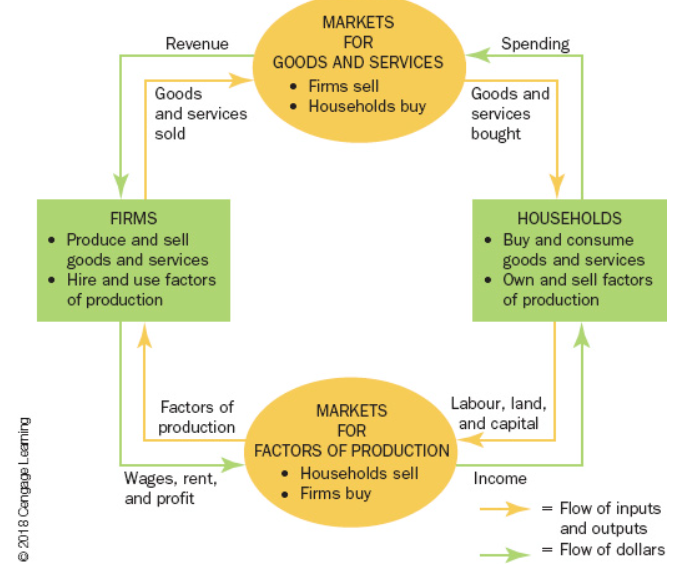
Within a circular flow diagram, the only decision makers are () and ().
Households, Firms
Firms produce goods and services via using inputs like land, labour, and capital, called (), which are offered by households. This is also called the market for factors of production.
Factors Of Production
Goods and services made by factors of production are purchased by (). Also called the market for goods and services.
Households
A economic model which shows the various combinations of output for different goods/services in the form of a graph.
Production Possibilities Frontier
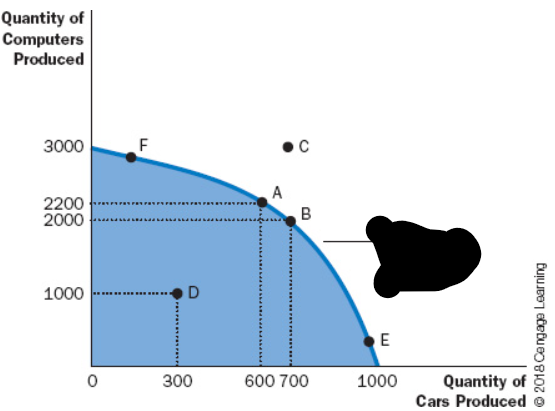
The production possibilities frontier allows us to know the maximum amount of (1) and/or (2), that can be made at the sacrifice of making less of a another (1) and/or (2).
Goods, Services
An outcome is said to be () if the economy is getting all it can from the scarce resources it has available.
Efficient
A scenario where an economy is producing less than what it could with the current resources available. For a ppf, inefficient production of goods would be points () the curve.
Inefficiency, Inside
The cost of one thing to receive another thing.
Opportunity Cost
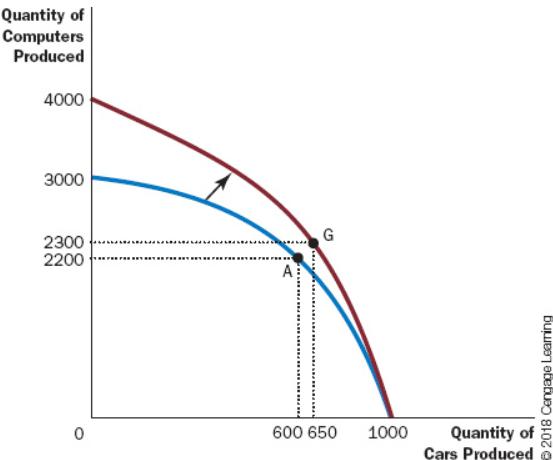
The red line represents a () in the production possibilities frontier, which allows more of both goods to be made.
Shift
The study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in specific markets.
Microeconomics
The study of economy-wide phenomena, such as national inflation.
Macroeconomics