Unit Test #2 - Mrs. Williams
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GSCI-2010: Physical Science for Educators
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Basic Properties of Waves
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from place to place
Many require a medium to travel through
Waves only move energy
Mechanical Waves
Requires a medium
Two Types: Transverse and longitudinal
Transverse Waves
Move the medium at right angles to the direction of the wave movement
Longitudinal Waves
Move parallel to the direction of the wave movement
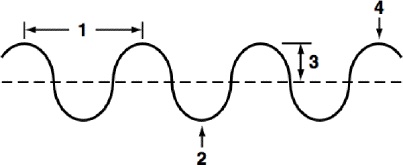
Parts of a Transverse Wave
Wavelength
Trough
Amplitude
Crest
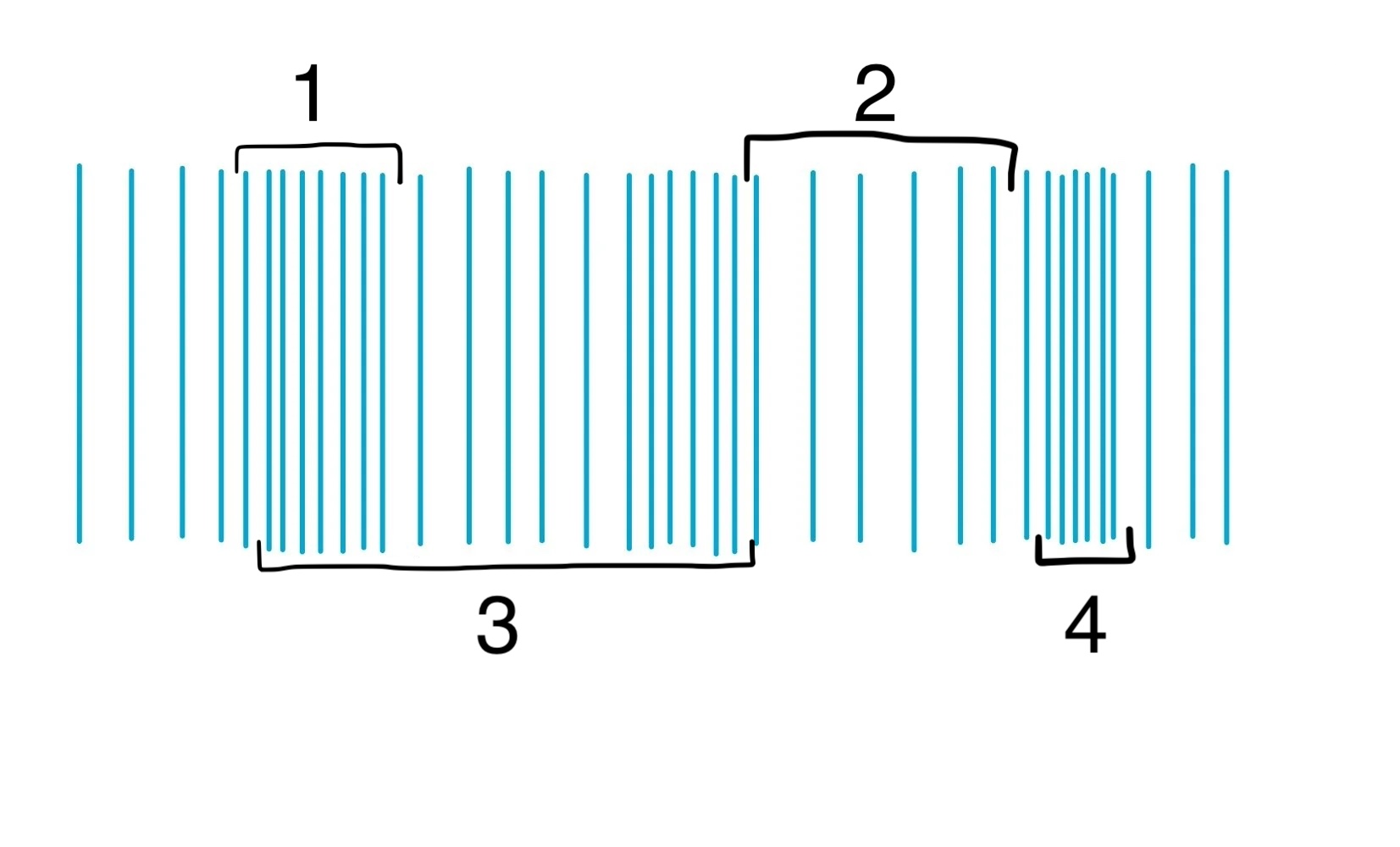
Parts of a Longitudinal Wave
Compression
Rarefaction
Wavelength
Amplitude
Amplitude in Waves
Transverse Wave - Maximum distance the medium moves up and down from its rest position
Longitudinal Wave - Measure of how compressed the compression is
Wavelength in Waves
Transverse Wave - Distance from crest to crest or trough to trough
Longitudinal Wave - Distance from compression to compression or rarefaction to rarefaction
Frequency in Waves
The amount of complete waves that pass a certain point in a certain amount of time and are measured in Hertz
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Radio, microwave, infrared, visible light, UV, x-ray, gamma ray
Red - longest wavelength/lowest frequency
Violet - shortest wavelength/highest frequency
When Light Strikes an Object
Light can be transmitted, reflected, or absorbed
How Light Passes Through
Transparent - All light passes through
Translucent - Some light passes through
Opaque - No light passes through
Reflection
Diffuse - Light bounces off in many different directions (Bumpy surface)
Specular - Light bounces off at a predictable angle (Flat surface)
Refraction
Light bends as wave changes speed and enters or exits into a new medium (Ex: Pencil in water)
Why we see Different Colors
The color of different objects is determined by the wavelengths of light that an object reflects and absorbs
Light to Heat Transfer
Black objects absorb all colors and transfers to thermal energy
Types of Mirrors
Plane - A flat mirror that produces an image upright and of the same size
Concave - A mirror that curves inward
Convex - A mirror that curves outward
Types of Lenses
Concave - Thinner in the center and causes light to diverge (spread out)
Convex - Thicker at the center and causes light to converge (come together)
Sound is….
vibration
How Sound Travels
Travels fastest in solids and warm air and slowest in gases and cold air
Intensity
Amount of energy a wave carries and how loud it is (Decibals)
Pitch
The human perception of the frequency of sound
The Doppler Effect
The change in frequency of a wave as its source moves in relation to the observer
Instruments and Pitch
The larger the object, the lower the pitch (tuba, bass drum)
The smaller the object, the higher the pitch (trumpet, snare drum)
Reverberation
The reflection of sound waves
Echo
When sound reflection is repeated
Practical Uses of Reverb/Echo
Sonar - Uses the reflection of sound waves to located objects under water
Echolocation - Used by bats and whales for food
Sonogram - Used to create images from reflected sound
Acoustics
The study of how sounds interact with each other and the environment
Resonance
When a material or object is made to vibrate at its natural frequency
Magnetism
Occurs because of electrons spinning in the same direction
Electricity
Occurs because of difference in charges in atoms
North and South Poles
Opposites attract, same sides repel
Charge of an Atom
More Protons (+)
More electrons (-)
Same amount (neutral)
Insulators vs. Conductors
Insulators - do not allow electricity to travel
Conductors - allow electricity to travel
Electric Force
An attraction or repulsion like and unlike charges have for each other
Static Cling
When two objects rub together, one loses some of its electrons to the other, causing attraction
Electric Discharge
The rapid movement of excess charge from one object to another
Units of Electricity
Amps - Measurement of the rate of flow of an electric current
Volts - Measure of the amount of electrical potential energy
Ohms - Measure of how difficult it is for electricity to flow
Watts - Measure of the rate of energy use or power
Circuit Basics
Parallel - A circuit that provides more than one path for electricity flow
Series - A circuit that provides one path for electricity flow
Resistance is Dependent on….
Type of material
Length of the conductor
Width of the conductor
Initial voltage