Ocular Side Effects of Systemic Medications - Clinical Ocular Pharmacology Spring 2026
1/232
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
233 Terms
clinicality
A med with high (criticality/clinicality) is commonly used and has commonly encountered side effects
criticality
A med with high (criticality/clinicality) can induce significantly detrimental and/or irreversible effects even if infrequently seen
1) Systemic drugs that activate/block similar receptors in the eye (autonomic nervous system)
2) Direct toxic effects of medication to the ocular tissues once its absorbed through the bloodstream (rich vascularization of the eyes)
3) Drug deposits that build up in an anatomical portion of the eye
How do Systemic Drugs Induce Ocular Side Effects?
1) Many ocular side effects induced by some systemic meds are readily visible in various ocular tissues during an ocular health assessment
Why is it important to know the ocular side effects of systemic medications?
true
True or False:
Many side effects have no impact on vision or eye health, they just alter the anatomy
true
True or False:
Some meds can present significant problems that require drug discontinuation
yes
Do we need to pay special attention to patients who report that they are taking certain meds during their hx to warn them of the potential risks of side effects and the need for regular monitoring?
false -- will always be bilateral
TRUE OR FALSE:
Ocular effects from systemic drugs can be unilateral
-Proton Pump Inhibitors
-Isotretinoin
-Oral anti-cholinergics
-Oral antihistamines
-Oral decongestants
-Tricyclic Antidepressants
-SSRIs
-Anti-Parkinson's Drugs
-Oral B Blockers
-Diuretics
-Oral Contraceptives
-Methoxsalen
What are the big categories of drugs that will DECREASE tear production in patients?
proton pump inhibitors
What are the most commonly prescribed drugs that contribute to dry eye symptoms?
thru an unknown mechanism
How do Proton Pump Inhibitors decrease tear production?
-Prilosec (Omeprazole)
-Protonix (Pantoprazole)
-Nexium (Esomeprazole)
-Prevacid (Iansoprazole)
What are some examples of Proton Pump Inhibitors?
clinicality
Do proton pump inhibitors have high (clinicality/criticality)?
acne treatment
What is isotretinoin used for?
-Accutane
-Zenatane
-Claravis
What are the current brands of isotretinoin?
criticality
Isotretinoin has high (clinicality/criticality)?
can induce SEVERE dry eye and CL intolerance, must often discontinue CL use for the 3 month course of the treatment of this drug
Why does isotretinoin have high criticality?
in patients with asthma & COPD (pulmonary dysfunction)
When is isotretinoin contraindicated?
decrease all glandular secretions (including tear production) and gastric motility
Why do oral anti-cholinergics decrease tear production?
in GI disease to reduce nausea and for treatment of IBS
Where are anticholinergics commonly used?
-Scopolamine for motion sickness
-Hyoscyamine for IBS
What are examples of anti-cholinergics that are commonly used?
side effects similar to anti-cholinergics
Why do oral antihistamines decrease tear production?
-Benadryl
-Claritin
-Zyrtex
-Allegra
-Clarinex (RX needed)
What are the common oral antihistamines that are prescribed?
for cold, sinus, and allergy symptoms
Oral decongestants are used for what?
Sudafed
Stand alone oral decongestant?
D
**Claritin-D for example
Antihistamine + oral decongestant agents have a ___ in their name?
-pseudoephedrine
-phenylephrine
What are typical decongestant ingredients?
for the treatment of systemic hypertension and arrhythmia
What do oral B Blockers treat?
decrease lysozyme and antibodies within the tears
How do oral B Blockers decrease tear production?
decrease overall fluid available for the tears
How do diuretics decrease tear production?
psoriasis
What is Methoxsalen (which decreases tear production) used for?
-Salagen (oral pilocarpine)
-Evoxac (cevimeline)
What is the medication that is known to INCREASE tear production?
prescribed in extreme cases of Sjogrens to increase secretory functions
When is Salagen and Evaxac prescribed to patients?
direct acting cholinergic agonists that bind acetylcholine receptors to increase exocrine secretions including tear production
What is the mechanism of action of Salagen and Evaxac leading to increased tear production?
in any instance of pulmonary dysfunction
When are Salagen and Evaxac contraindicated?
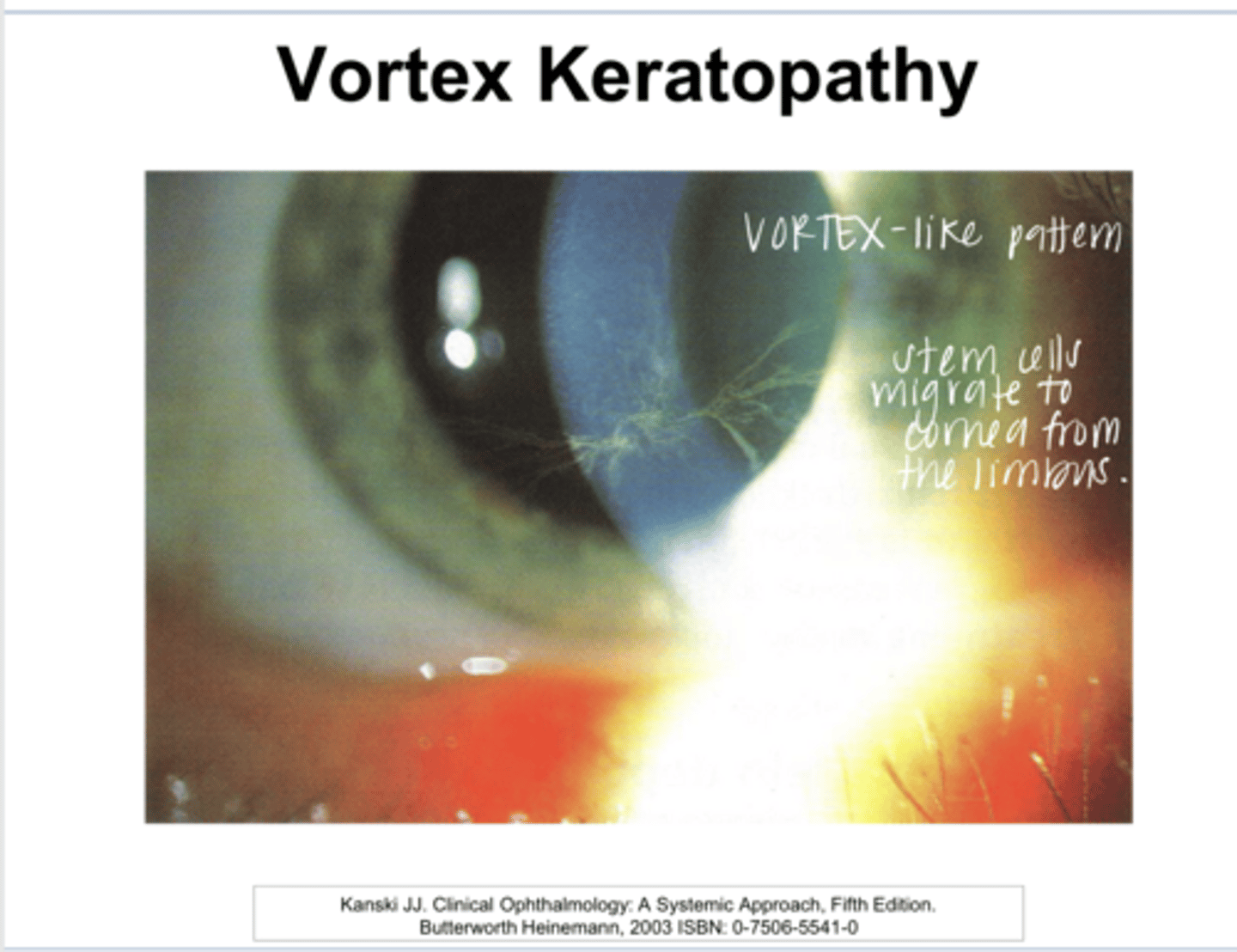
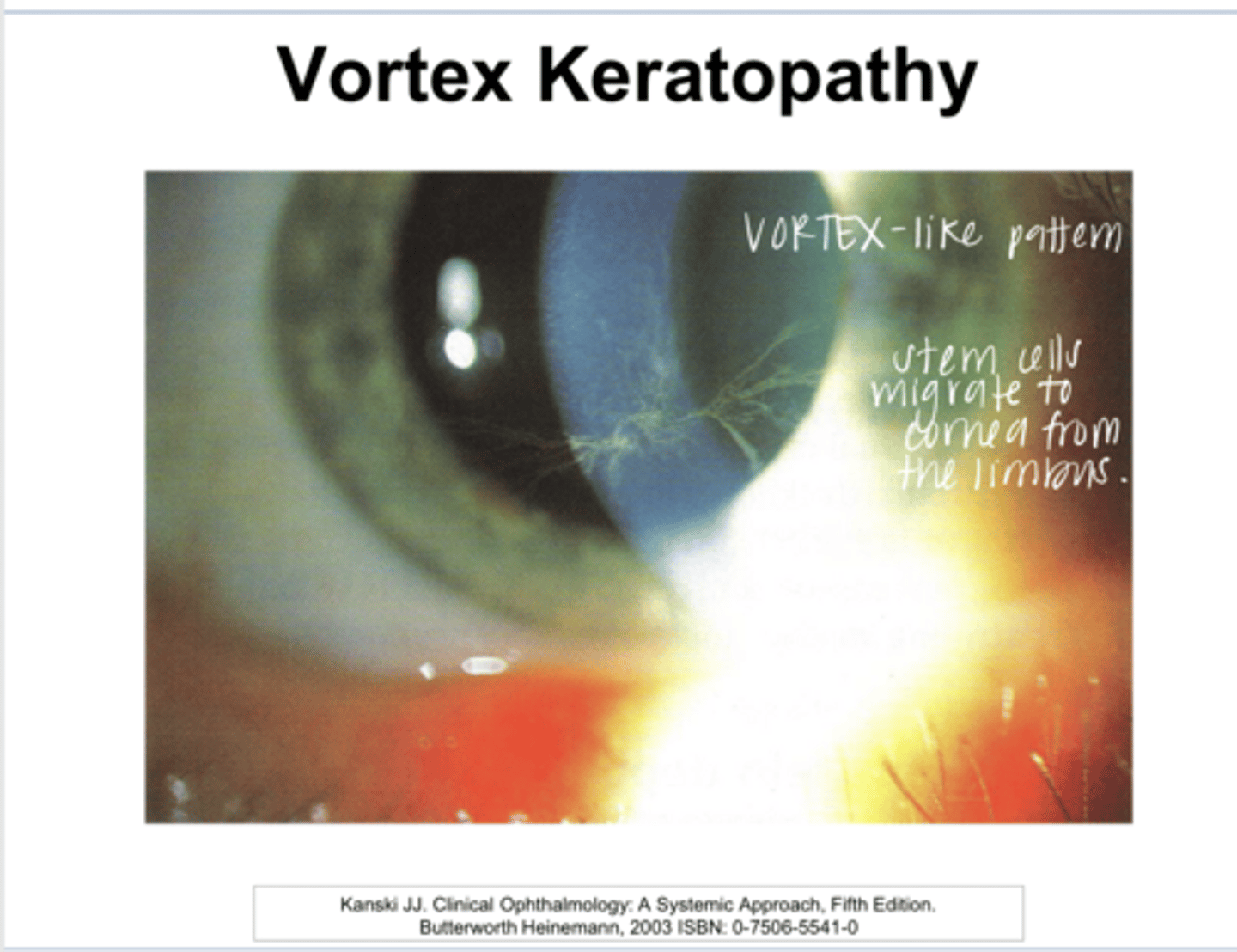
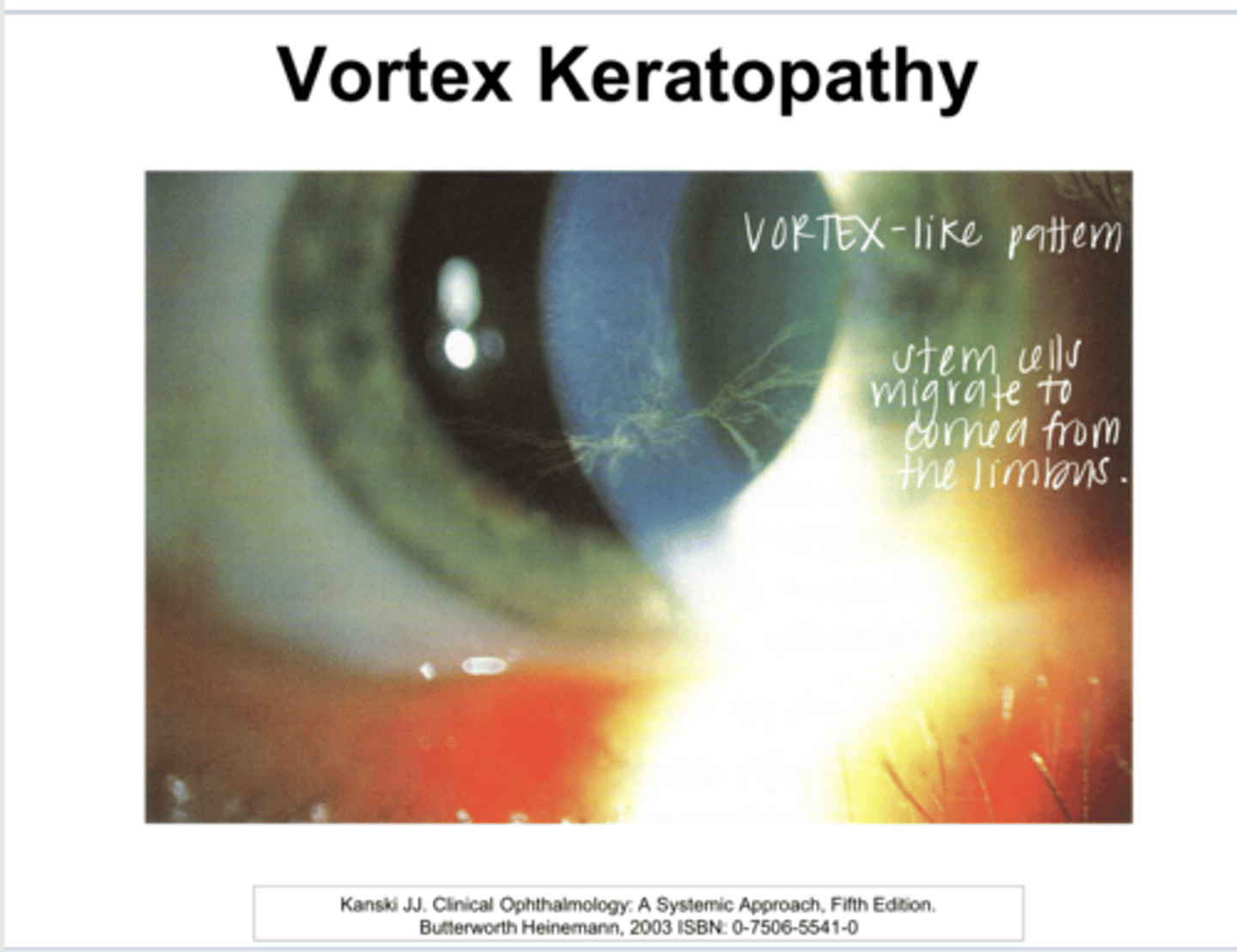
epithelial and subepithelial pigment deposits
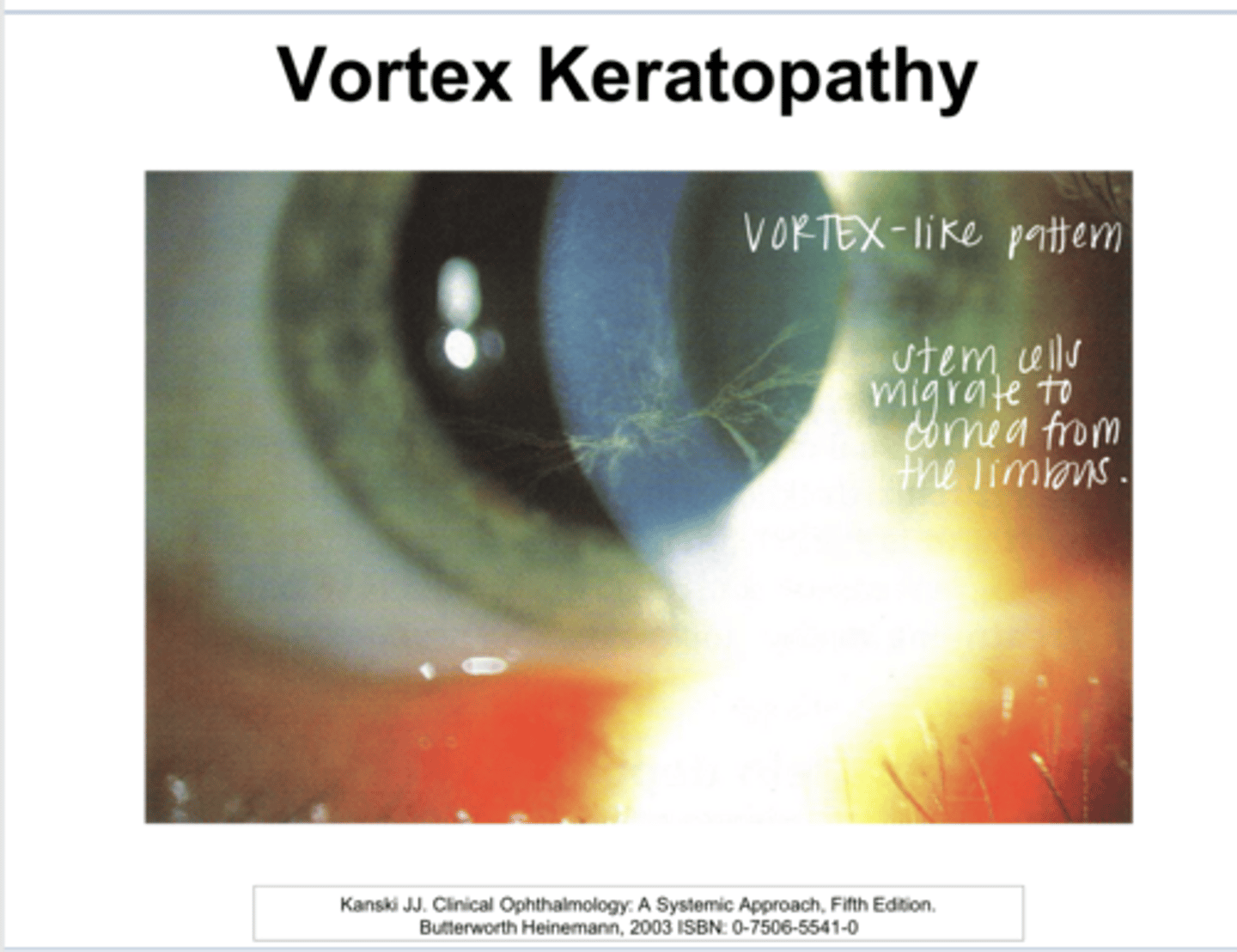
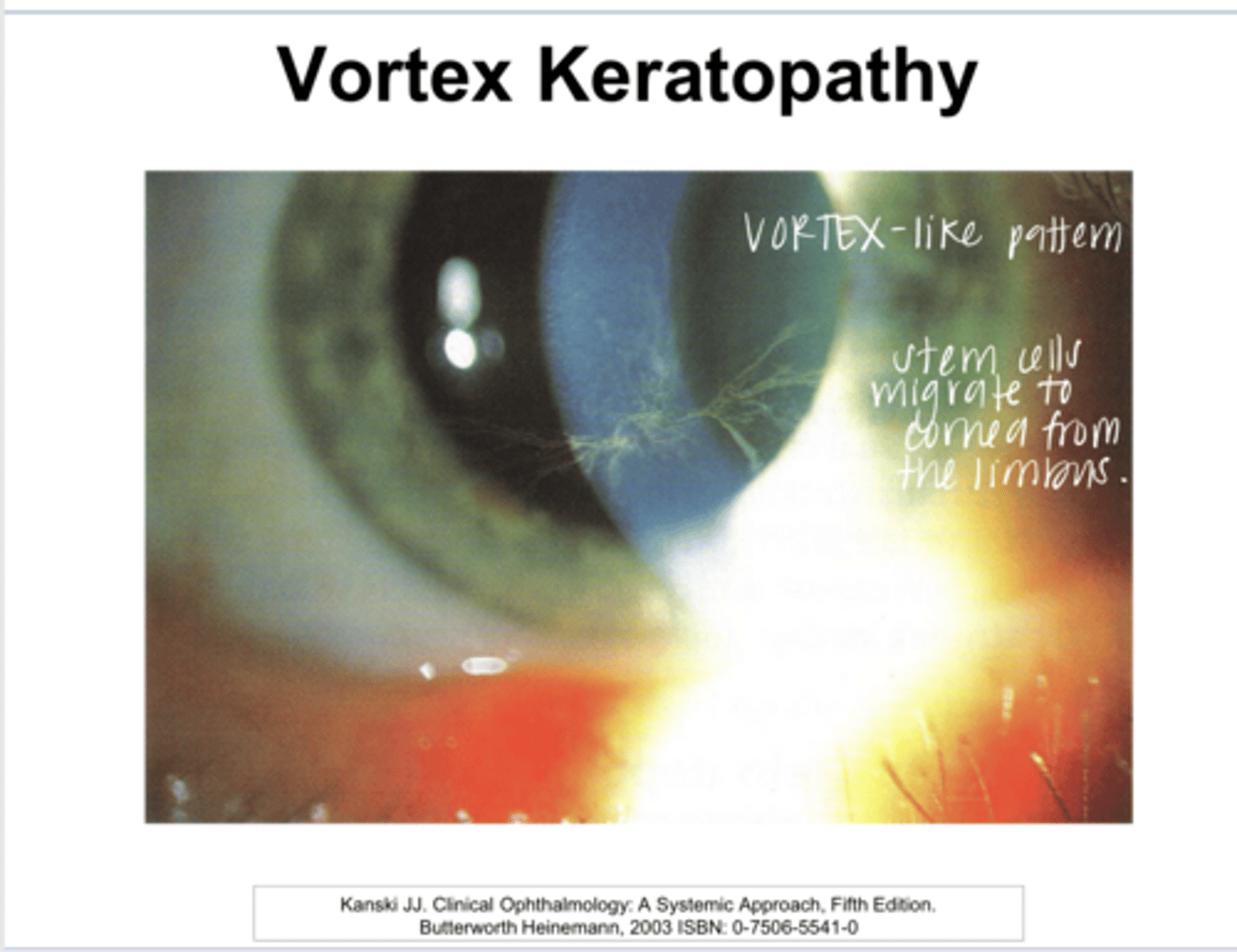
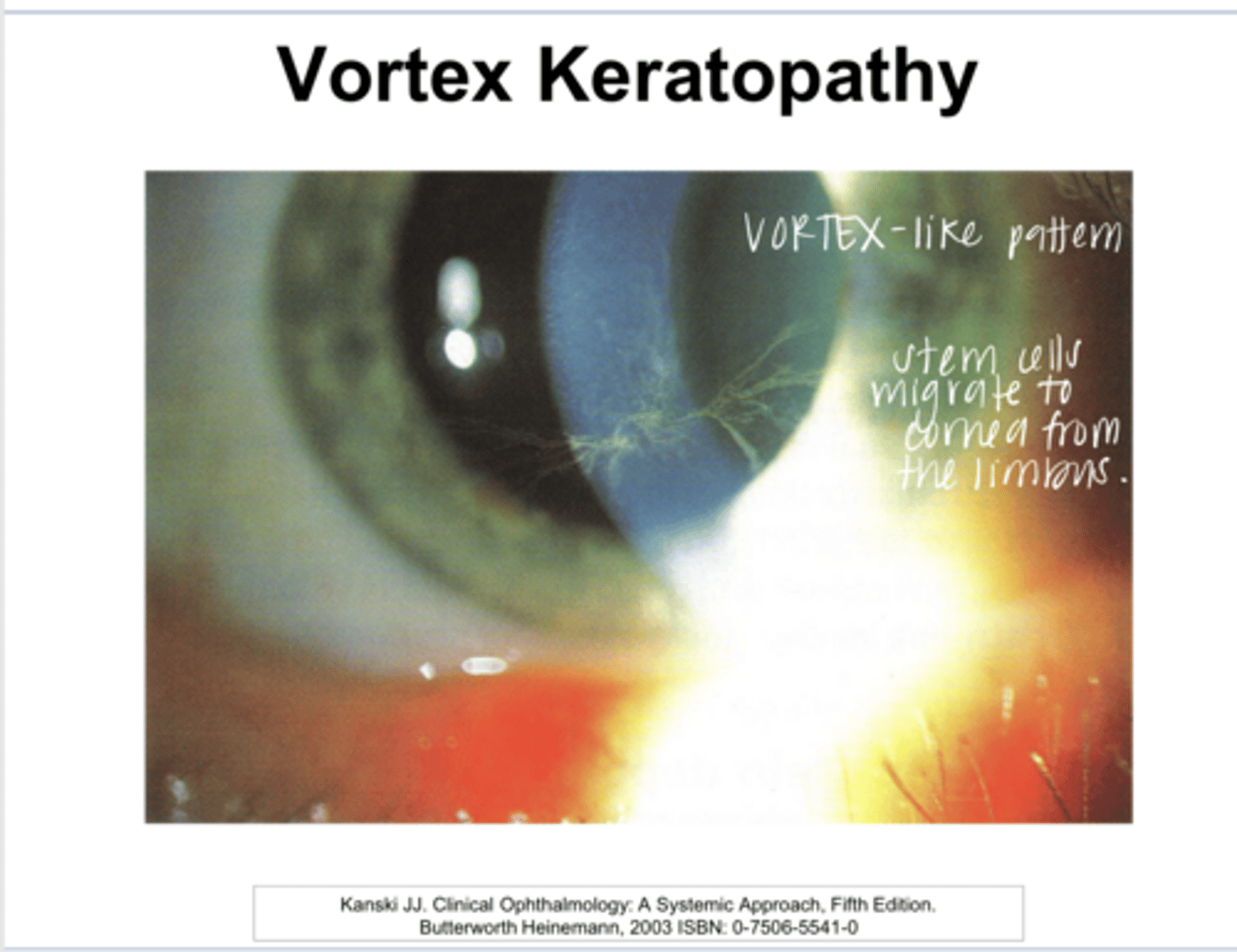
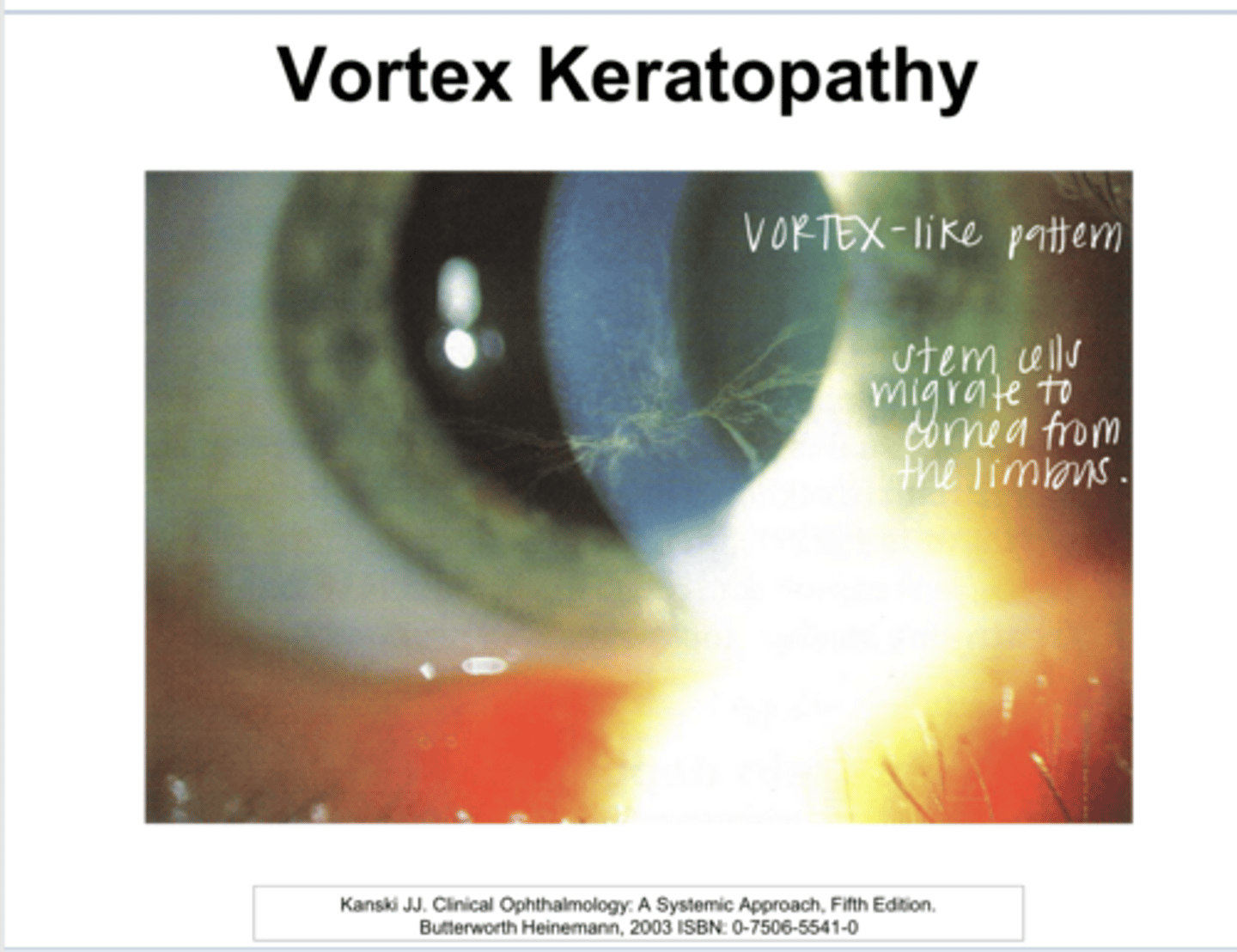
What is whorl/vortex keratopathy characterized by?
no -- may introduce glare and halos
Does whorl/vortex keratopathy affect VA?
yes
Do deposits of whorl/vortex keratopathy usually fade/resolve with drug discontinuation?
-Amiodarone
-Plaquenil (Hydroxychloroquine)
-Gold Salts
What drugs induce whorl/vortex keratopathy?
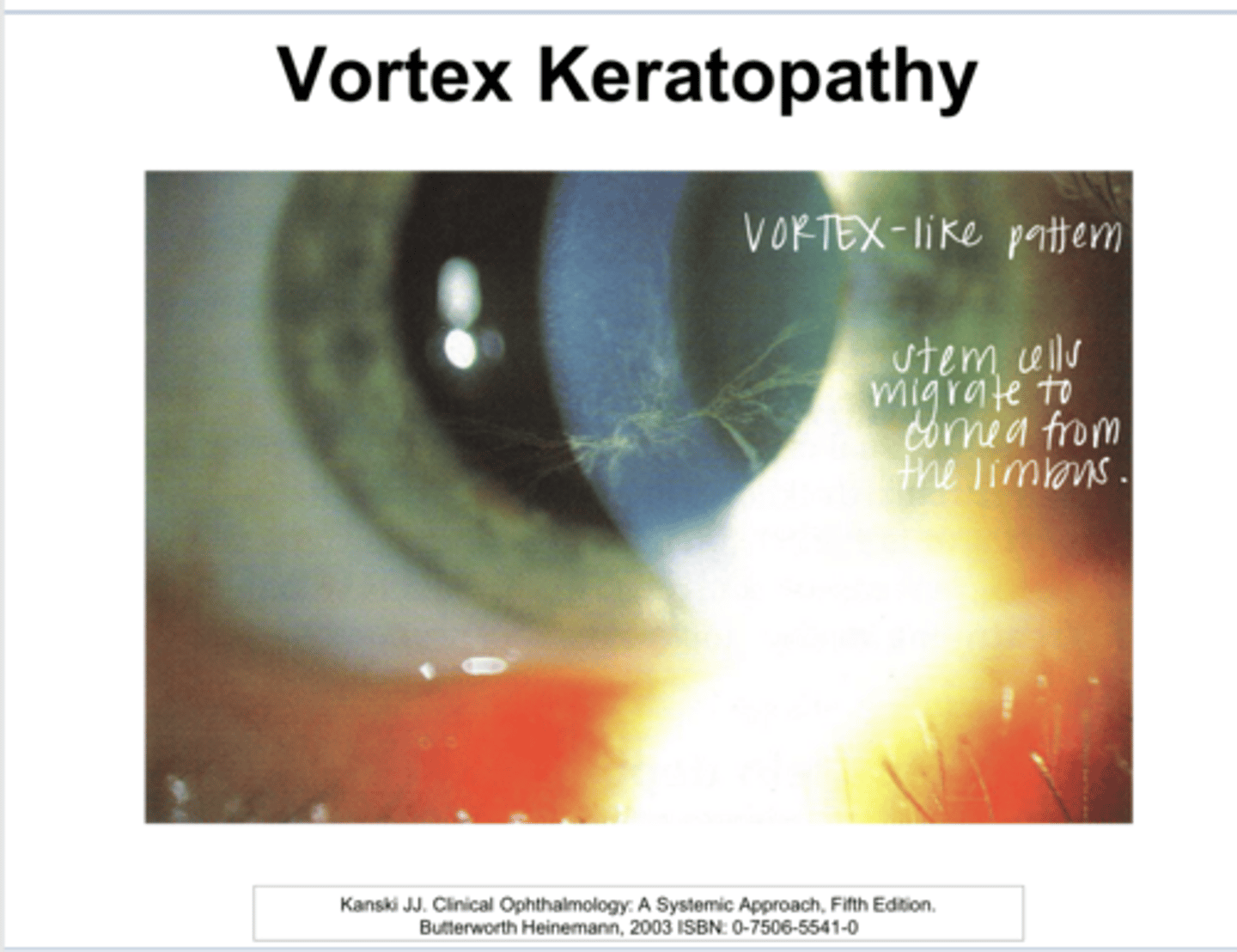
cardiac arrhythmias
What is Amiodarone used for?
true
True or False:
Virtually all patients who use Amiodarone will develop vortex keratopathy after 3 months of therapy
pigment deposits in the anterior subcapsular space of the lens
50% of patients with vortex keratopathy d/t Amiodarone use will develop what?
rarely -- but the deposits can be a sign of increased drug concentration that could decrease vision via optic neuropathy (these patient fit the systemic risk factors for NAION anyways)
Do the corneal deposits of vortex keratopathy d/t Amiodarone use ever cause a decrease in VA?
anti-malarial drug that is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and lupus
What is Plaquenil (Hydroxychloroquine) used for?
similar vortex keratopathy appearance
What can Plaquenil (Hydroxychloroquine) cause?
no -- very rare on the doses that are currently prescribed
Is vortex keratopathy common in patients who use Plaquenil (Hydroxychloroquine)?
potential for retinal toxicity
What is Plaquenil (Hydroxychloroquine) much more known for?
older drug taken for severe RA, not commonly used anymore
What are gold salts used for?
chrysiasis = deposition of gold deposits in the tissues similar to appearance of vortex keratopathy
What do gold salts cause?
in the posterior stroma of the cornea
Where will the gold deposits d/t gold salt use reside inthe cornea?
Chlorpromazine
What drug can affect the endothelium of the cornea?
anti-psychotic medication
What is the use of Chlorpromazine?
-corneal endothelial deposits in the interpalpebral fissure (rare)
-anterior lenticular changes are much more common
What can Chlorpromazine cause?
-Rifabutin
-Keytruda
-Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva, Reclast
What are the drugs that can induce uveitis?
for the treatment of tuberculosis
What is Rifabutin used for?
for cancer immunotherapy
What is Keytruda used for?
for the treatment of osteoporosis or Paget's disease
What are Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva, Reclast used for?
self-limiting conjunctivitis
Most patients will get a ______ within 2 days-2 weeks of starting therapy with Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva, Reclast?
uveitis/scleritis
Although rare, Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva, Reclast can cause what?
no -- typically will not resolve unless the drug is discontinued
Will the uveitis/scleritis resolve by itself when using Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva, Reclast?
yellow
Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva, Reclast can cause ____ colored visual disturbances?
Flomax (Tamsulosin)
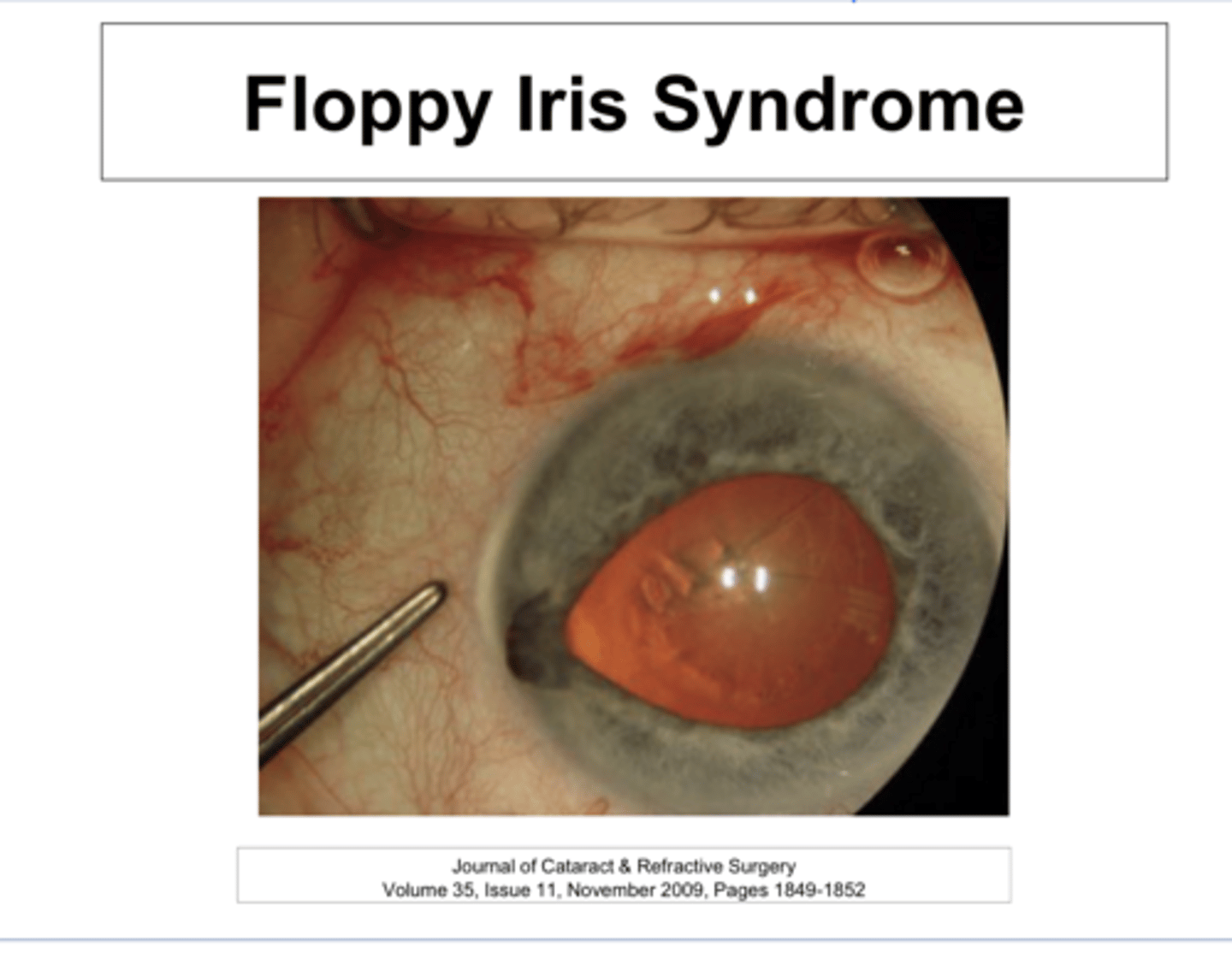
Drugs that Affect the Iris to Cause Floppy Iris Syndrome?
for Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH) and helps maintain a regular urinary flow
What is Flomax used for?
alpha adrenergic antagonist that relaxes the smooth muscle on the urinary sphincter (parasympathetic agonist)
What is the mechanism of action of Flomax?
Blocks alpha receptors on the iris dilator preventing full pupillary dilation (adrenergic antagonism). The alpha receptors of the iris are responsible for dilation of the pupil.
How does Flomax lead to Floppy Iris Syndrome?
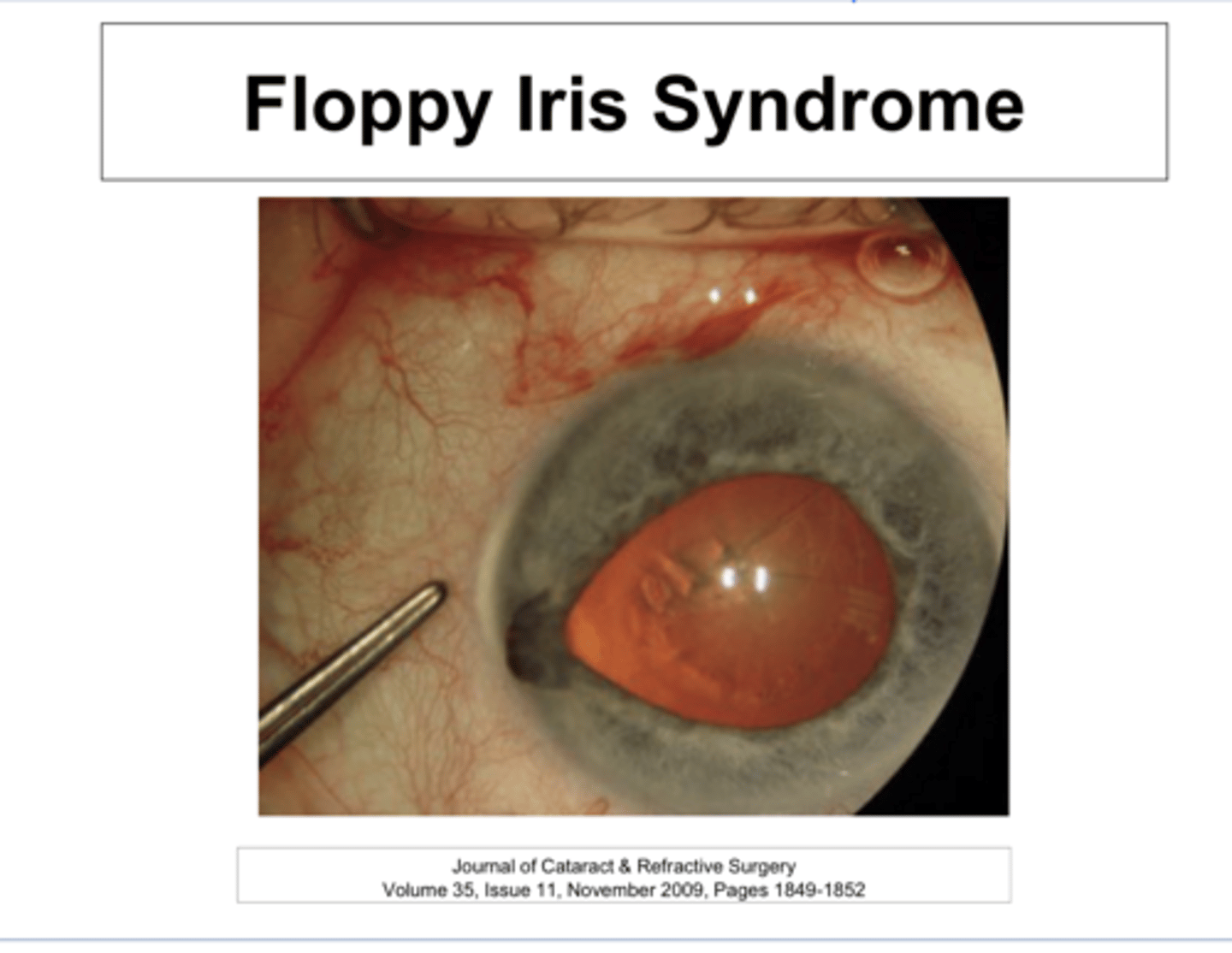
-Complications during Cataract Sx because the relative intraoperative pupillary miosis can cause the iris to "FLOP" and get in the way and become damaged by the phaco/probe instrumentation
-A smaller pupil can cause greater difficulty & posterior capsule rupture
What can Floppy Iris Syndrome cause?
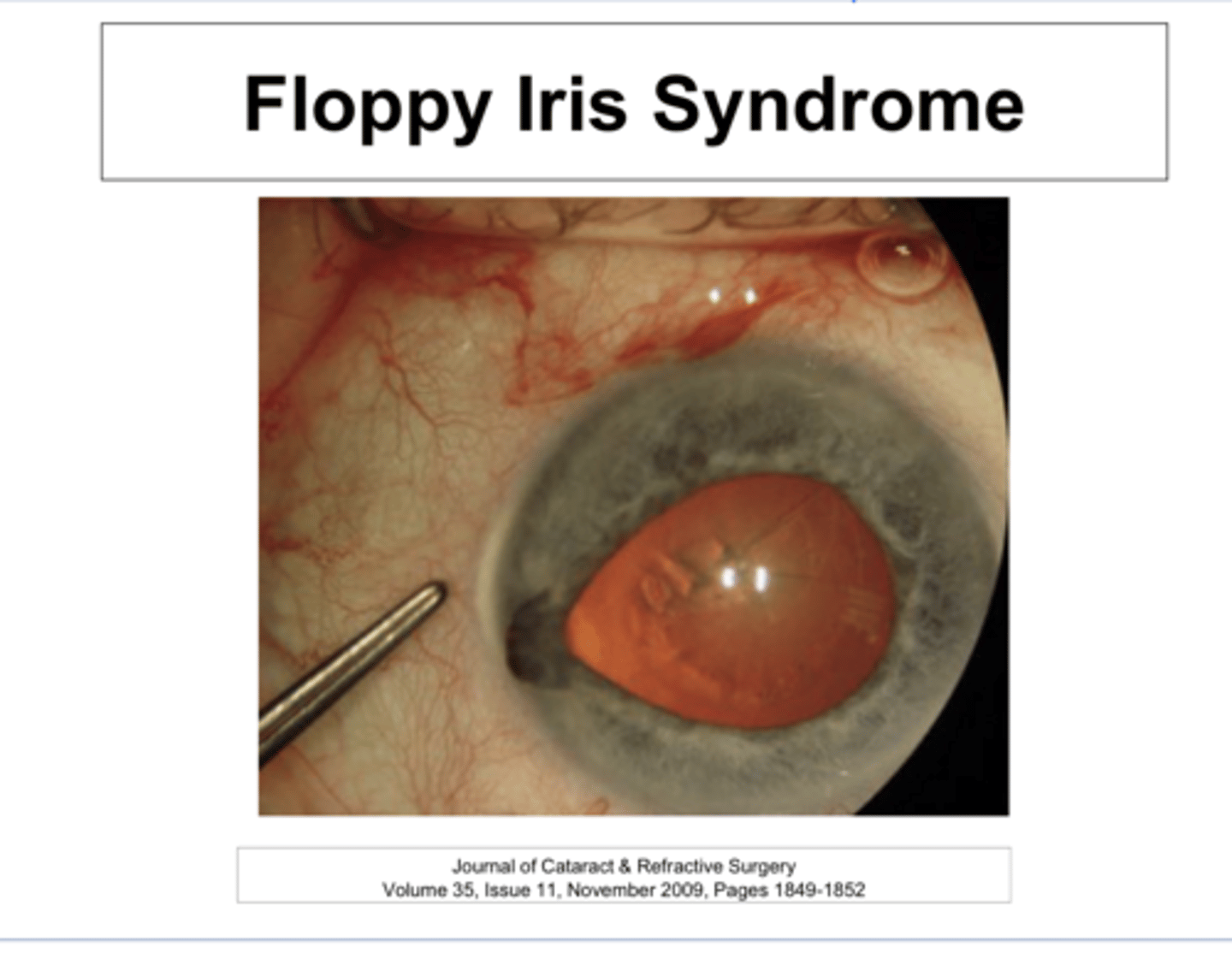
true - should discontinue meds 2-14 days prior to surgery but floppy iris syndrome can last for up to a year after discontinuation of the drug
True or False:
You MUST ASK all patients about their use of Flomax PRIOR to cataract sx
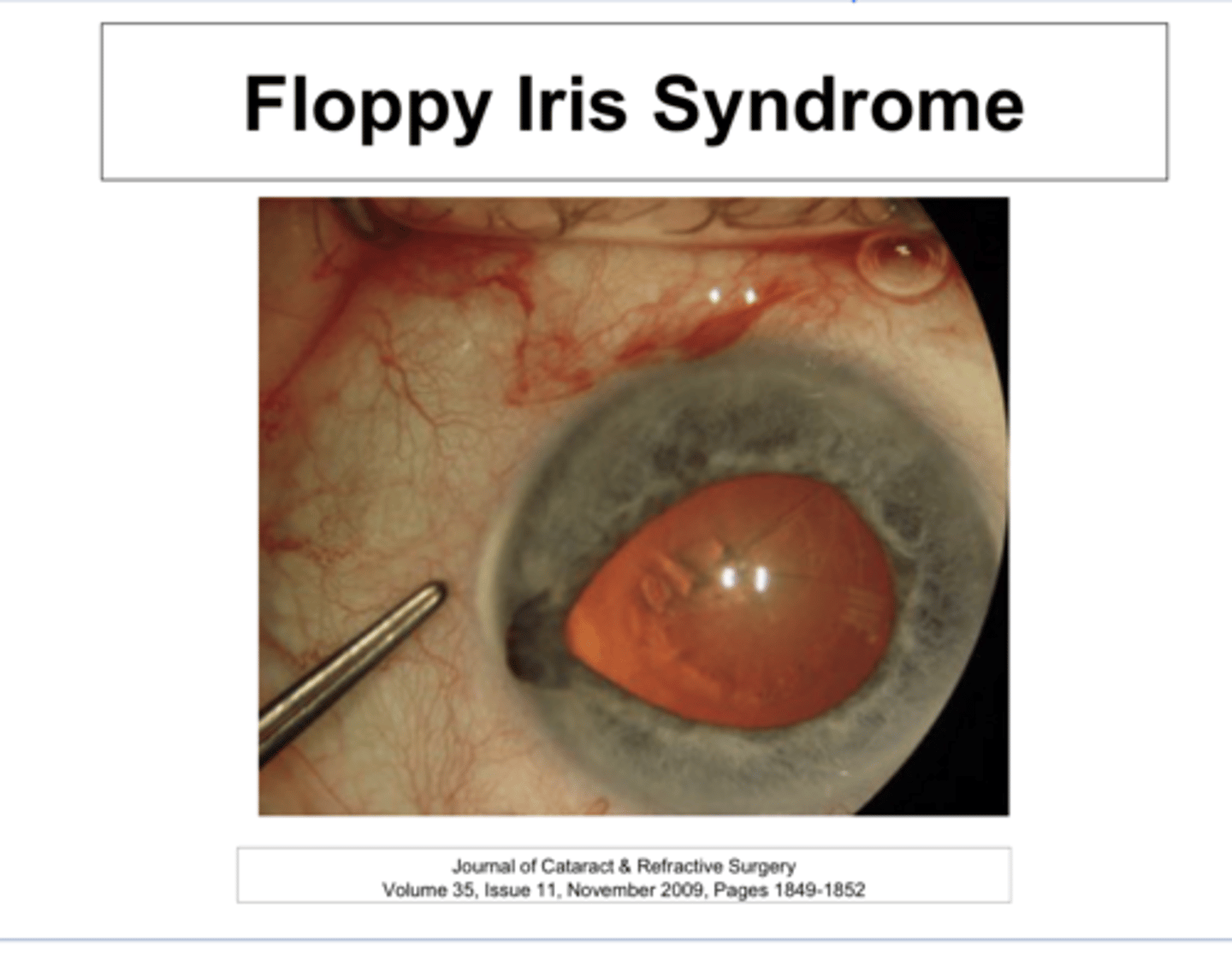
PCP to refer patients for eye exam PRIOR to Rxing Flomax. If they have an early cataract, remove the cataract 1st, then Rx Flomax after the sx is complete.
What is the current recommendation for PCP prescribing Flomax?
yes -- they will have to employ small pupil intraoperative techniques to minimize complications
If an existing Flomax patient develops a cataract, is it important to let the surgeon know this?
no -- does not affect alpha receptors and instead inhibits 5a-reductase that prevents breakdown of testosterone
Does Adodart (BPH med) cause floppy iris syndrome?
-Anticholinergics
-Anti-anxieties
-Anti-Depressants
-Anti-Histamines
What medications can cause pupillary mydriasis AND cycloplegia (and thus will cause blurred vision)?
parasympatholytics
Medications that cause pupillary mydriasis AND cycloplegia will be _______?
for the treatment of asthma
What is the anticholinergic Atrovent used for that can cause pupillary mydriasis AND cycloplegia?
for IBS
What is the anticholinergics Levbid, Anaspaz, and Levsin used for that can cause pupillary mydriasis AND cycloplegia?
for motion sickness
What is the anticholinergic Scopolamine used for that can cause pupillary mydriasis AND cycloplegia?
-Valium
-Xanax
What are the anti-anxiety drugs that can act as an anticholinergic and can cause pupillary mydriasis AND cycloplegia?
-Tricyclic Antidepressants
-SSRIs
-SNRIs
What Antidepressants can act as an anticholinergic and can cause pupillary mydriasis AND cycloplegia?
increase IOP via angle closure
All drugs that act as anticholinergics and can cause pupillary mydriasis AND cycloplegia can also do what?
sympathomimetics (adrenergic agonists)
Medications that cause pupillary mydriasis WITHOUT cycloplegia will be _______?
-amphetamines
-cocaine/methamphetamines
-methylphenidate/amphetamine/dextroamphetamine
-wellbutrin
-oral decongestants
What are the medications that will cause pupillary mydriasis WITHOUT cycloplegia?
Dexedrine (Dextroamphetamine)
What is an amphetamine that is used commonly for weight loss and can cause pupillary mydriasis WITHOUT cycloplegia?
ADD/ADHD
What are methylphenidate/amphetamine/dextroamphetamine
commonly used for?
NRDI antidepressant
What is Wellbutrin used for commonly?
-Anticholinesterase
-Opiates
-Salagen/Evoxac
What are examples of drugs that can cause pupillary miosis?
-prevents the breakdown of natural ACh
-ACh will bind to muscarinic receptors of the pupil
-pupil constriction d/t parasympathetic stimulation
What is the function of anticholinesterase & how does it cause pupillary miosis?
pinpoint
Opiates create ____ pupils
mechanism occurs through the CNS not on autonomic receptors directly
What is the mechanism by which opiates cause pinpoint pupils?
direct acting cholinergic agonists
How do Salagen/Evoxac cause pupillary miosis?
Dilantin (phenytoin)
What is a drug that can affect the EOMs?
anti-seizure med
What is Dilantin (Phenytoin) used for?
-gaze evoked nystagmus
-downbeat nystagmus
What can Dilantin (Phenytoin) cause?
-Chlorpromazine
-Seroquel (Quetiapine)
-Corticosteroids
Drugs that can Affect the Lens?
anti-psychotic med
What is chlorpromazine used for?
for bipolar disorder
What is Seroquel (Quetiapine) used for?
dopamine (D2) antagonists used as antipsychotic agents
What type of drug are Chlorpromazine and Seroquel?
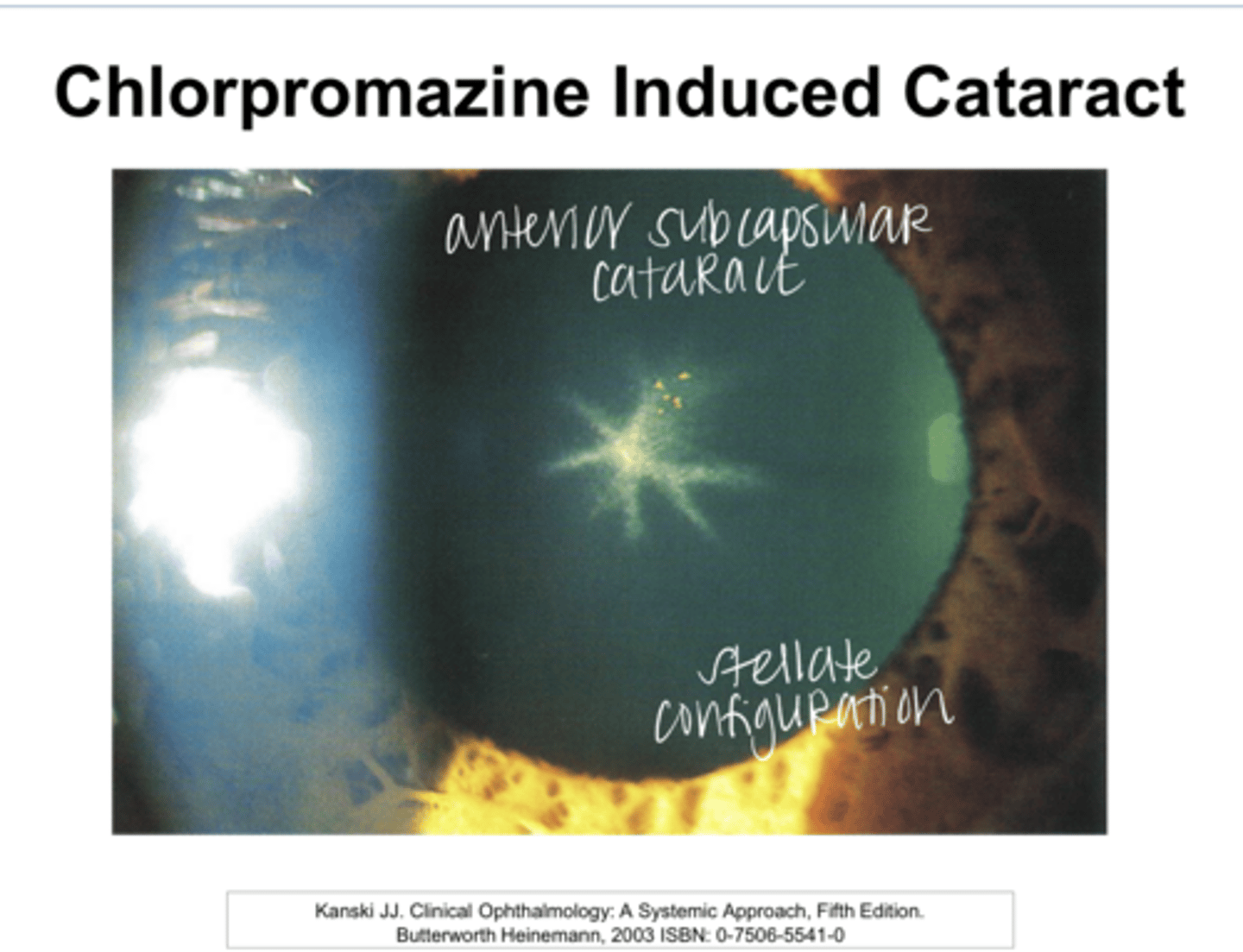
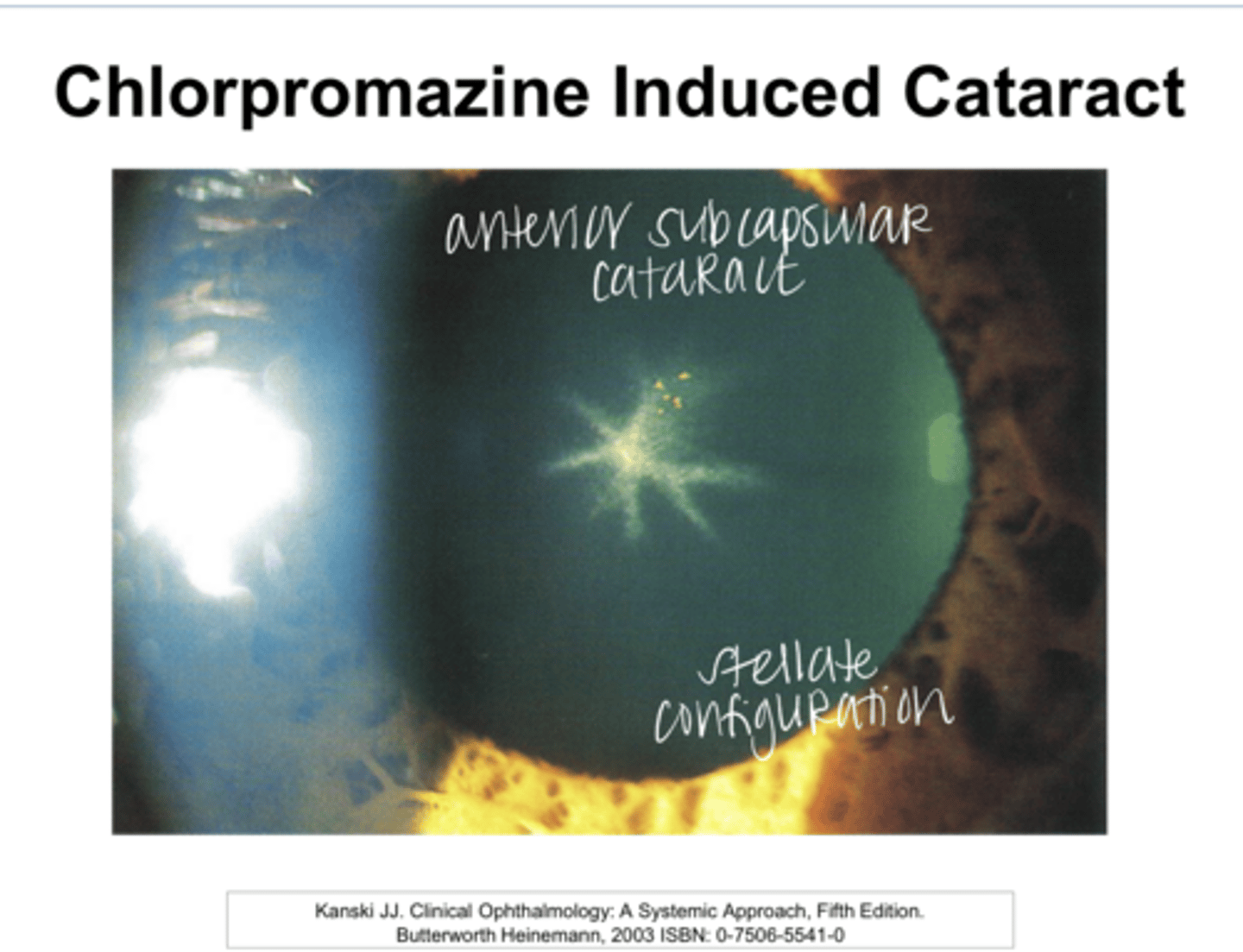
Anterior lenticular opacities in stellate appearance
How will lens opacities appear in patients on Chlorpromazine or Seroquel?
-corneal endothelial deposits in the interpalpebral fissure -- but this is rarely seen
-blue hue to sclera and conj
Aside from lens opacities, what can also appear in patients who are taking Chlorpromazine or Seroquel?
no
Is the opacity that is a result of Chlorpromazine and Seroquel use reversible?
no
Does the opacity that is a result of Chlorpromazine and Seroquel use decrease VA?
Chlorpromazine Induced Cataract Pic
Chlorpromazine Induced Cataract Pic