LAB:Digestive, Respiratory, and Urinary Systems
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of vocabulary flashcards covering the anatomy and functions of the digestive, respiratory, and urinary systems.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
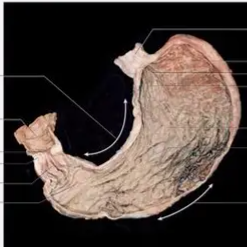
A pouch in your upper belly that holds and churns food; digestion starts here.
Stomach
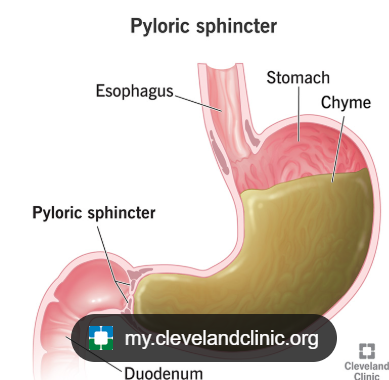
A muscle valve at the bottom of the stomach that controls food moving out.
Pyloric Sphincter
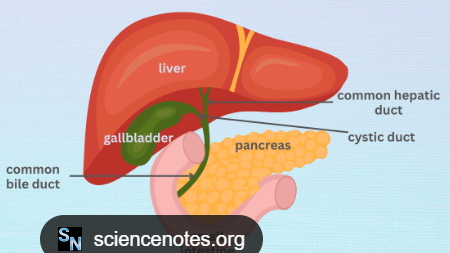
A small bag under your liver that stores bile, which helps digest fats.
Gallbladder
The first part of your small intestine, right after the stomach; food mixes with digestive juices here.
Duodenum
A long, coiled tube in your belly where most food nutrients are absorbed into your blood.
Small Intestine
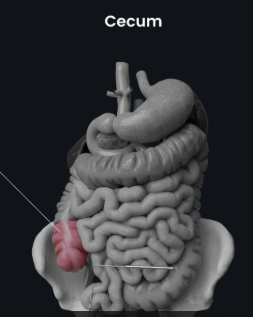
A small pouch where the small intestine meets the large intestine in your lower right belly.
Cecum
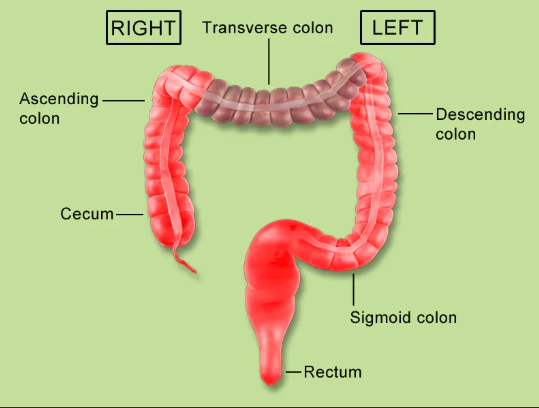
The first part of your large intestine that goes up on the right side; it takes water from digested food.
Ascending Colon
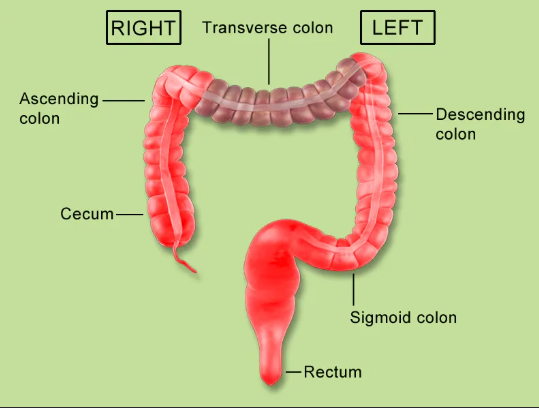
The part of your large intestine that goes across your upper belly; it keeps taking water.
Transverse Colon
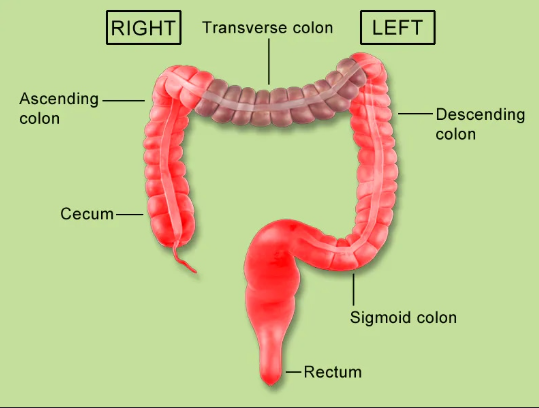
Part of your large intestine that goes down on the left side; it stores waste.
Descending Colon
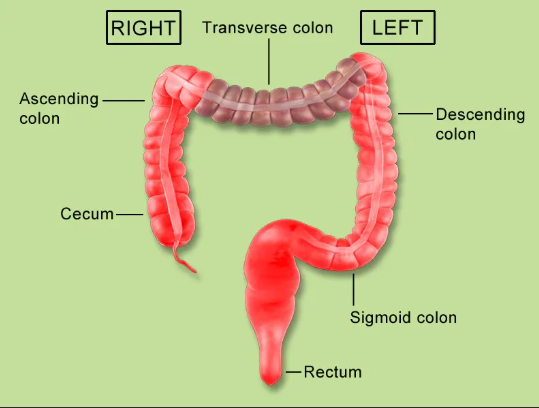
The last part of your large intestine, in your pelvis; it holds poop before you go to the bathroom.
Rectum
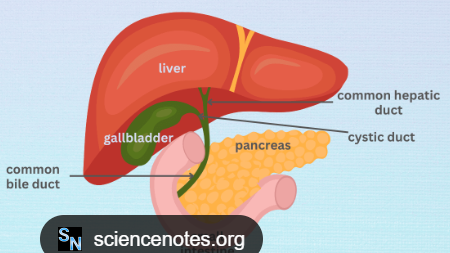
A big organ in your upper right belly that cleans blood, makes bile, and helps with body processes.
Liver
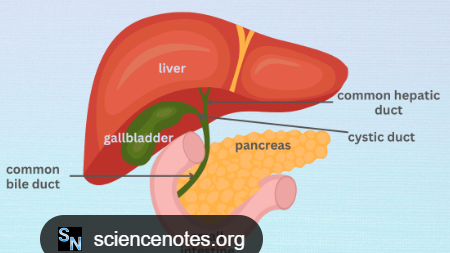
A gland behind your stomach that makes juices to digest food and hormones like insulin.
Pancreas
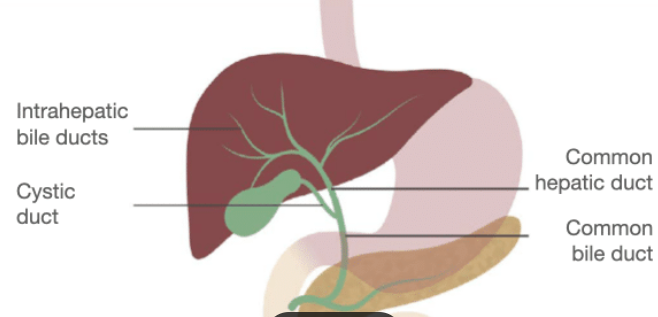
A tube connecting your gallbladder to the main bile duct.
Cystic Duct
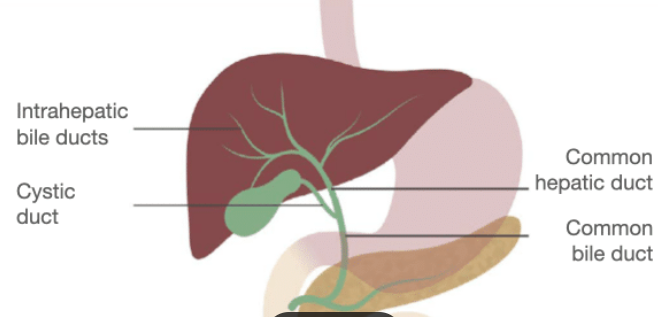
The main tube that carries bile from your liver and gallbladder to your small intestine.
Common Bile Duct
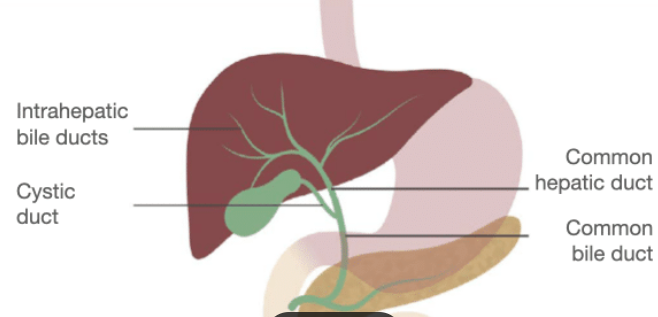
A tube that carries bile from your liver.
Common Hepatic Duct
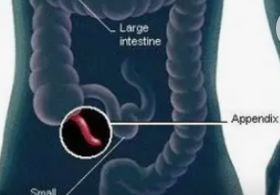
A small, worm-like organ attached to the cecum; its exact job is unclear but might help your immune system.
Appendix
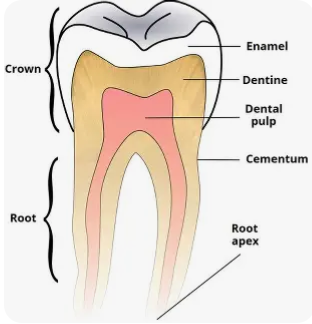
The part of your tooth you can see above the gum.
Crown
The part of your tooth hidden in your jawbone.
Root
The main, soft part of your tooth, under the hard outer layer.
Dentin
The hard, white outer layer of your tooth crown, protecting it.
Enamel
A tiny hole at the tip of the tooth root where nerves and blood enter.
Apical Foramen
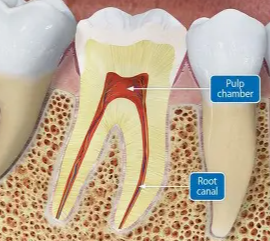
The space inside the tooth root that holds nerves and blood vessels.
Root Canal
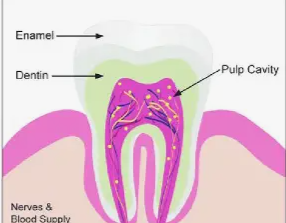
The main space inside your tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels.
Pulp Cavity
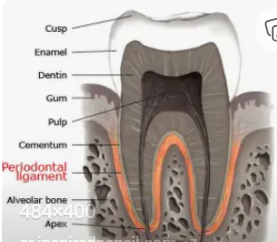
Tiny fibers that hold your tooth firmly in its socket in the jawbone.
Periodontal Ligament
The flat, sharp front teeth for biting and cutting food.
Incisors
The pointy teeth next to your incisors for tearing food.
Canines
Teeth between canines and molars with two bumps, for crushing food.
Premolars (Bicuspids)
The wide, flat back teeth for grinding food.
Molars
In your neck, helps you breathe, speak, and stops food from going down the wrong way.
Larynx (Voice Box)
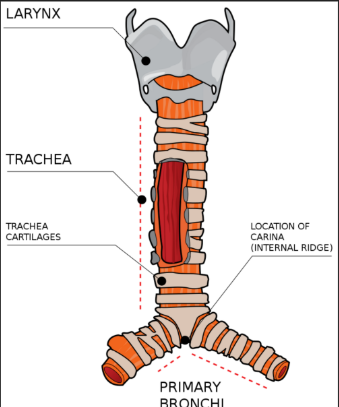
The main tube from your voice box to your lungs, carrying air.
Trachea (Windpipe)
Your main breathing organs that take in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide.
Lungs
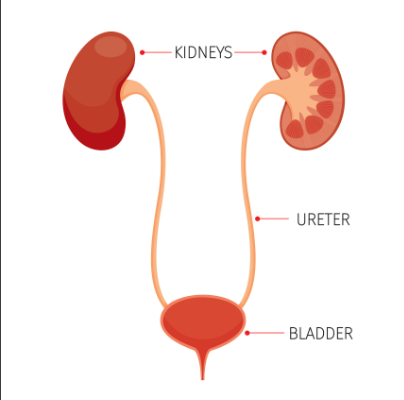
Two bean-shaped organs that clean your blood, make pee, and control blood pressure.
Kidney
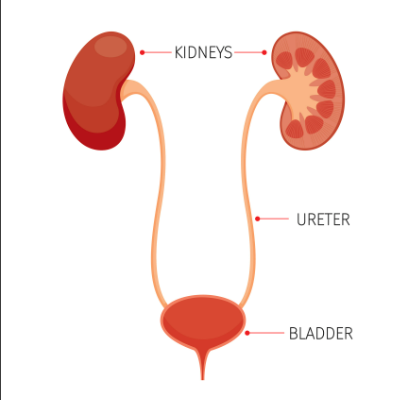
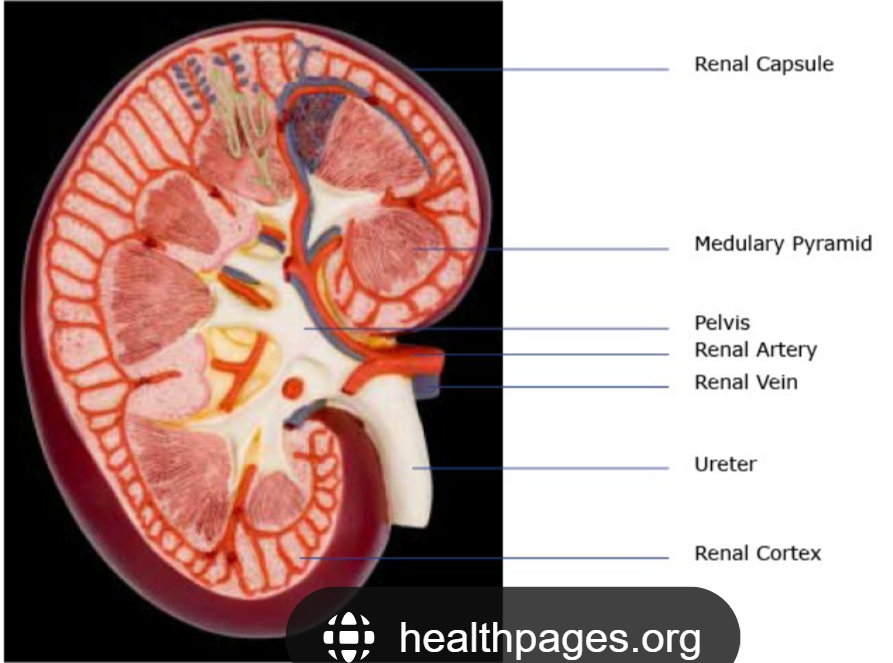
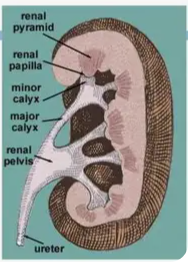
Tubes that carry pee from your kidneys to your bladder.
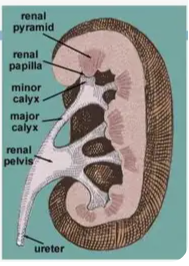
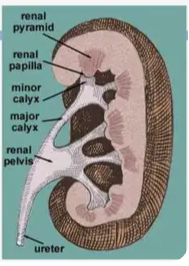
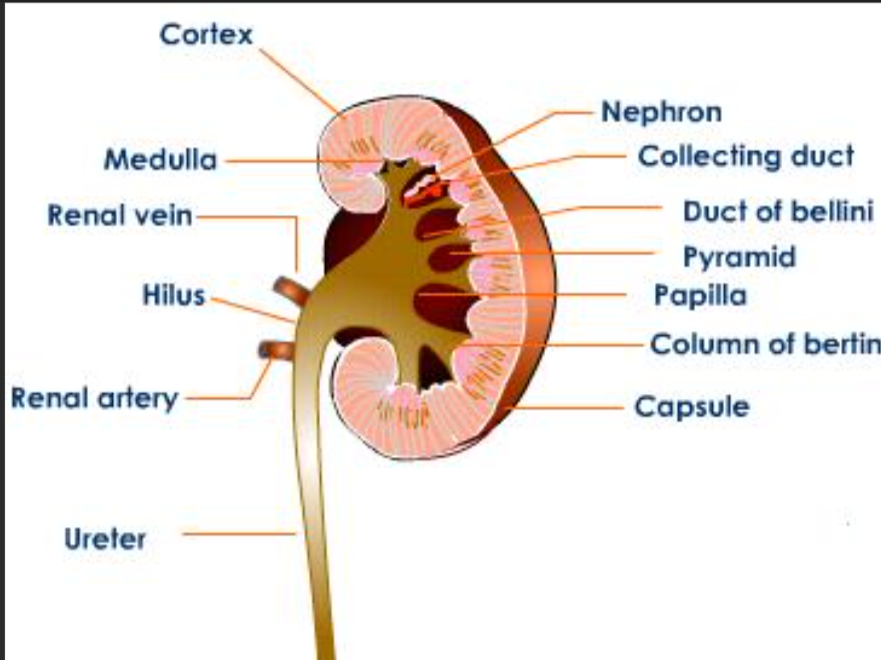
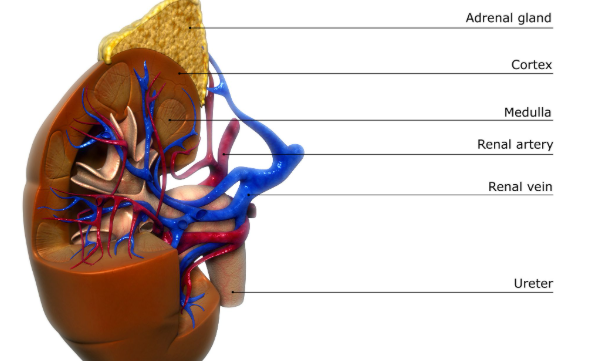
Ureter
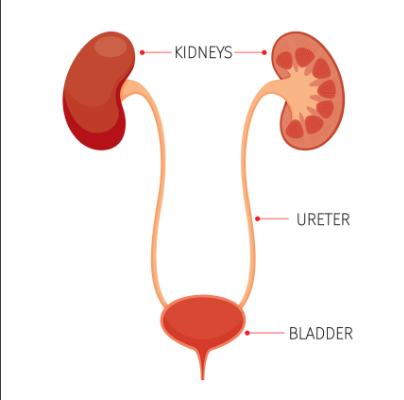
A bag in your lower belly that stores pee until you go to the bathroom.
Urinary Bladder
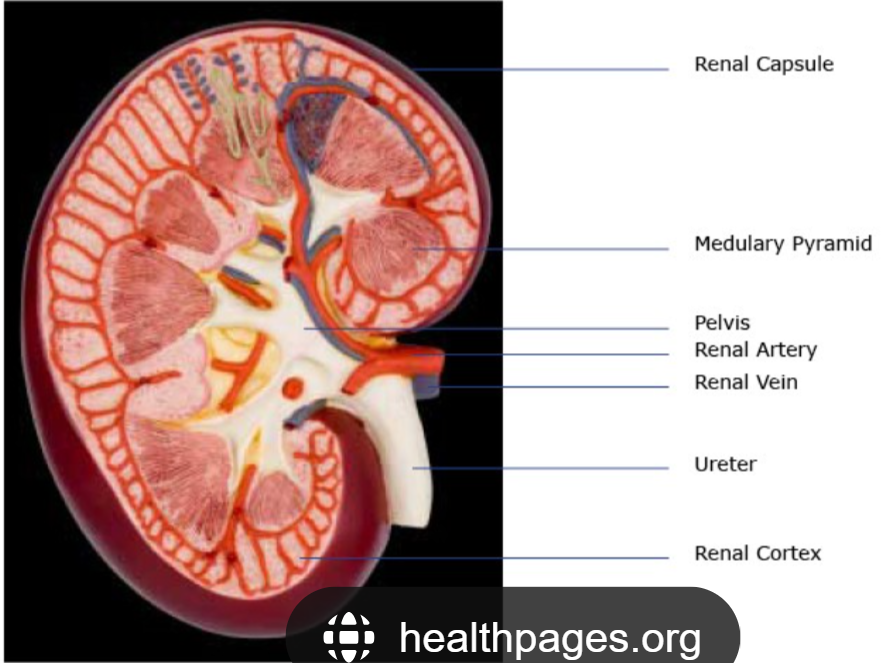
The tough outer skin covering your kidney, protecting it.
Renal Capsule
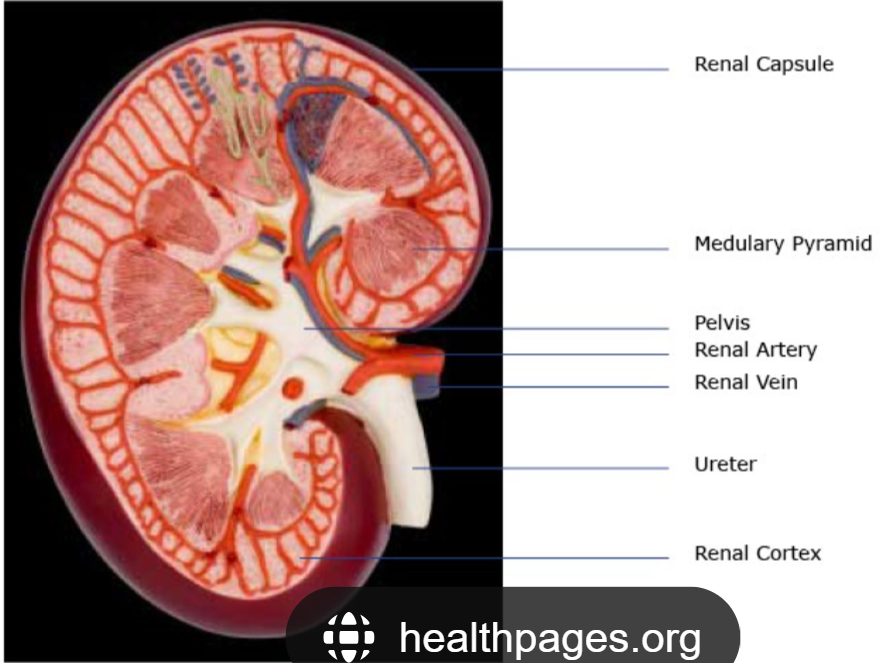
The outer layer of the kidney, where blood is mainly filtered.
Cortex
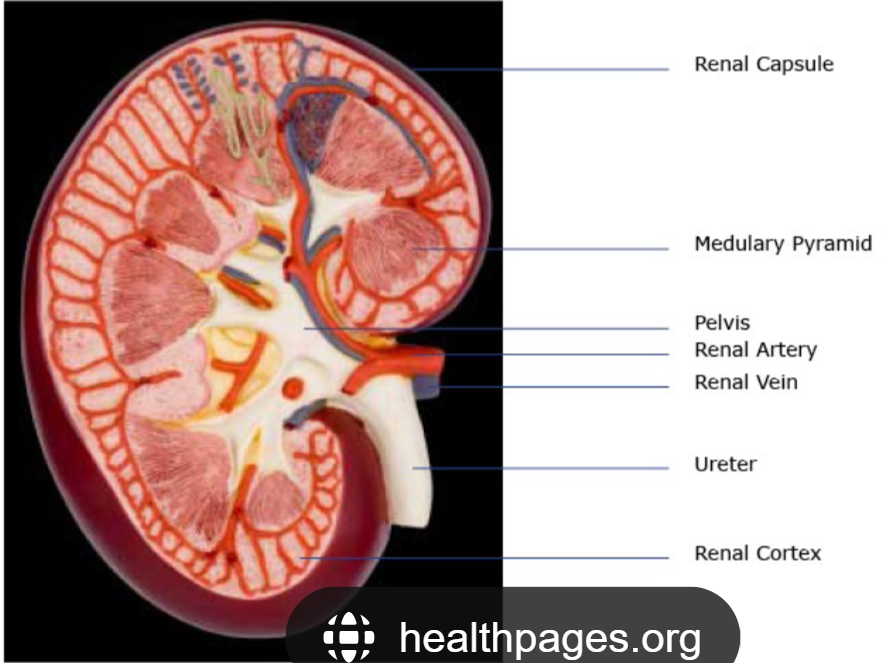
The inner part of the kidney, where pee is made more concentrated.
Medulla
Cone-shaped sections in the medulla that help collect pee.
Renal Pyramid
Parts of the cortex that go between the renal pyramids.
Renal Column
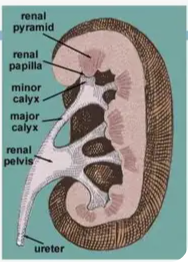
The tip of a renal pyramid, where pee drips into collecting cups.
Renal Papilla
Small cups that collect pee from the papilla.
Calyx (Major and Minor)
The main funnel in the kidney that collects all the pee and sends it to the ureter.
Renal Pelvis
The blood vessel that brings dirty blood to the kidney to be cleaned.
Renal Artery
The blood vessel that takes clean blood away from the kidney.
Renal Vein
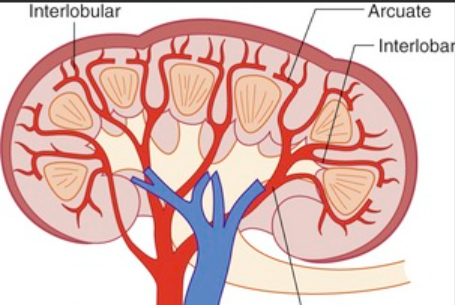
Blood vessels running between the kidney's pyramids.
Interlobar Arteries
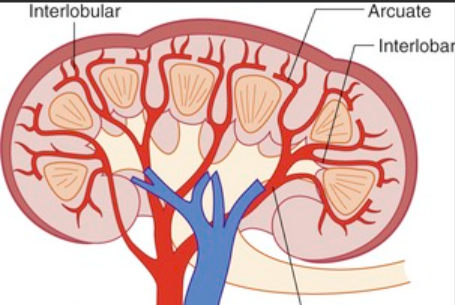
Blood vessels running next to the interlobar arteries.
Interlobar Veins
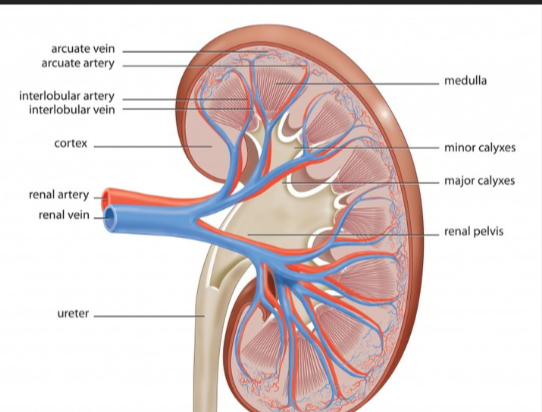
Blood vessels that curve over the bases of the kidney pyramids.
Arcuate Arteries
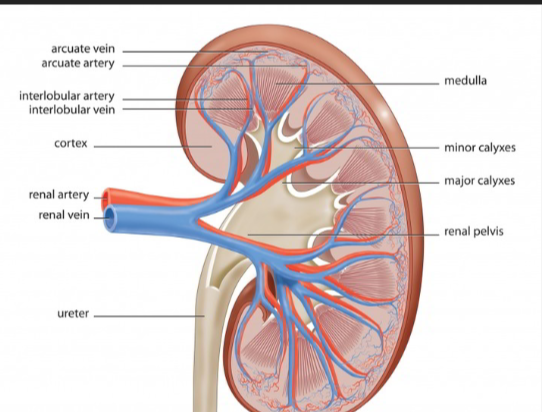
Blood vessels that run next to the arcuate arteries.
Arcuate Veins
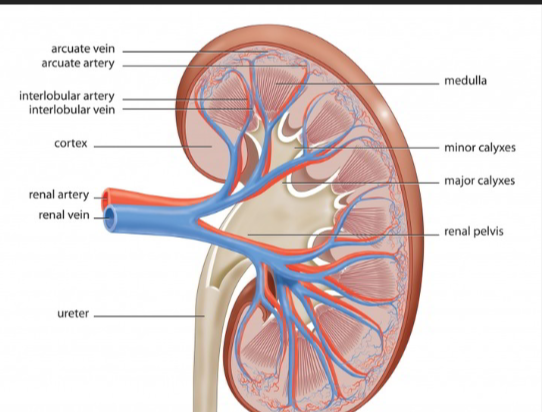
Smaller blood vessels in the outer kidney layer.
Interlobular Arteries (Cortical Radiate Arteries)
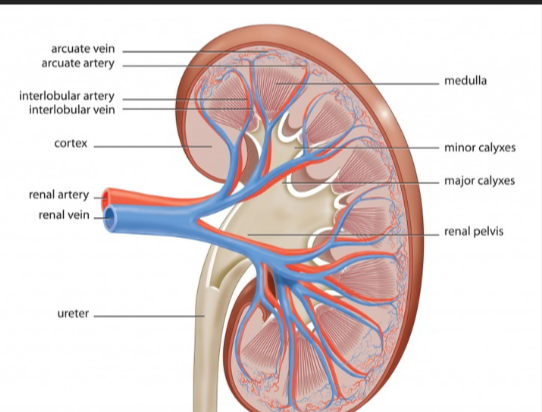
Smaller blood vessels in the outer kidney layer that carry blood away.
Interlobular Veins (Cortical Radiate Veins)
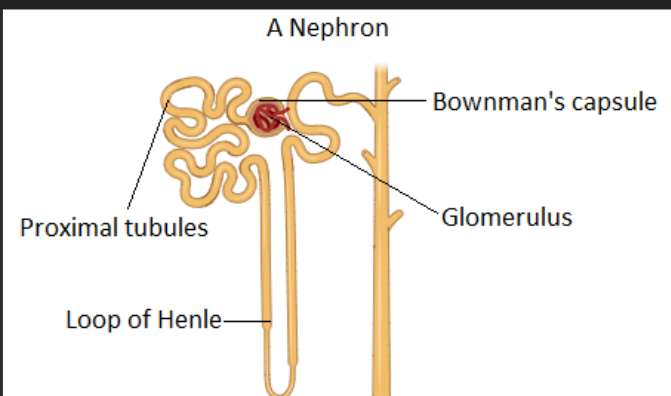
A cup-like structure that surrounds a tiny ball of blood vessels, collecting the first liquid filtered from blood.
Glomerular Capsule (Bowman's Capsule)
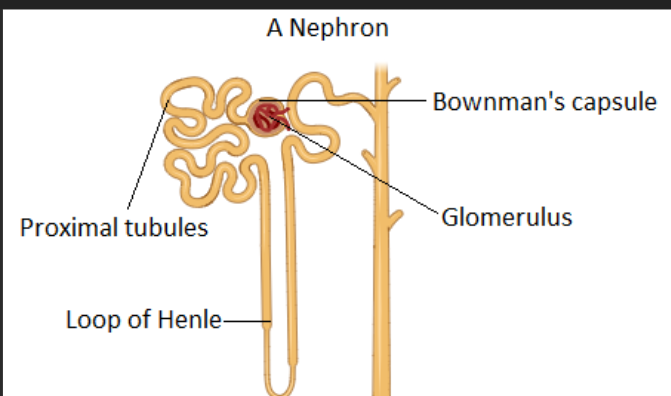
A tiny ball of capillaries inside the glomerular capsule that filters blood.
Glomerulus
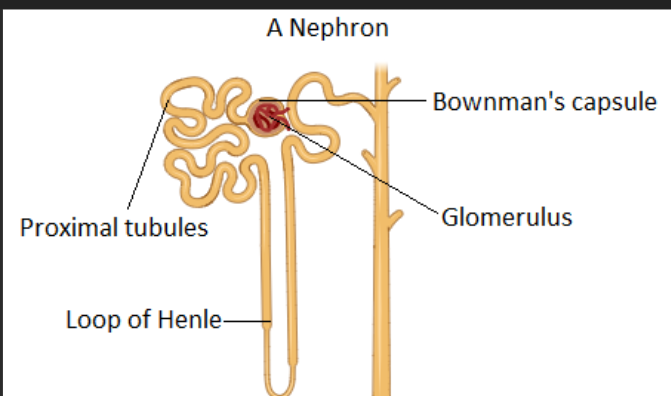
A U-shaped tube in the kidney that helps save water and salt.
Loop of Henle
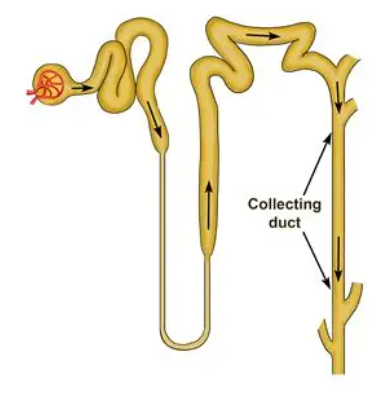
Tubes that gather pee from many filters and send it out of the kidney.
Collecting Duct (Tubule)
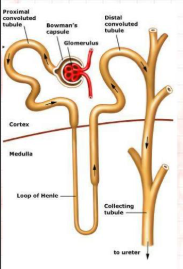
The first twisted tube after the filter, where most useful things are reabsorbed into the blood.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
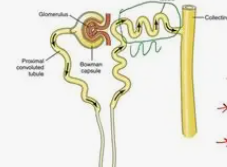
A twisted tube further down, where the kidney fine-tunes what goes back into the blood or stays in the pee.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
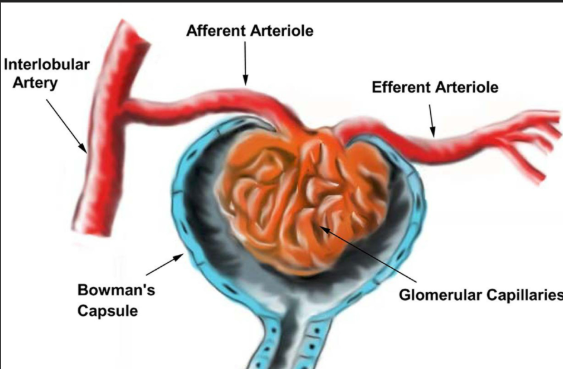
A tiny blood vessel that brings blood into the glomerulus for filtering.
Afferent Arteriole
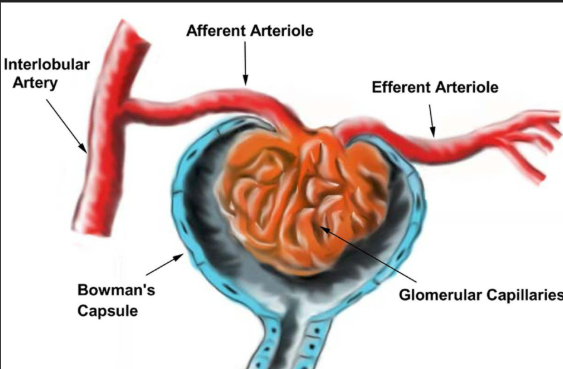
A tiny blood vessel that carries blood away from the glomerulus.
Efferent Arteriole
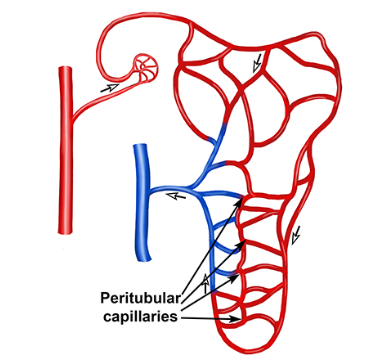
Tiny blood vessels that surround the kidney tubules, helping to take back useful things.
Peritubular Capillaries
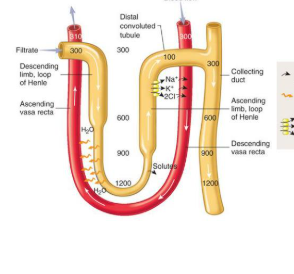
Straight blood vessels that run along the loop of Henle, helping the kidney concentrate pee.
Vasa Recta