Macroeconomics
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I will get an A
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Scarcity implies…
Choice
Ceteris paribas
Other things the same
Positive economics
Is or will statements
Normative economics
Ought statements
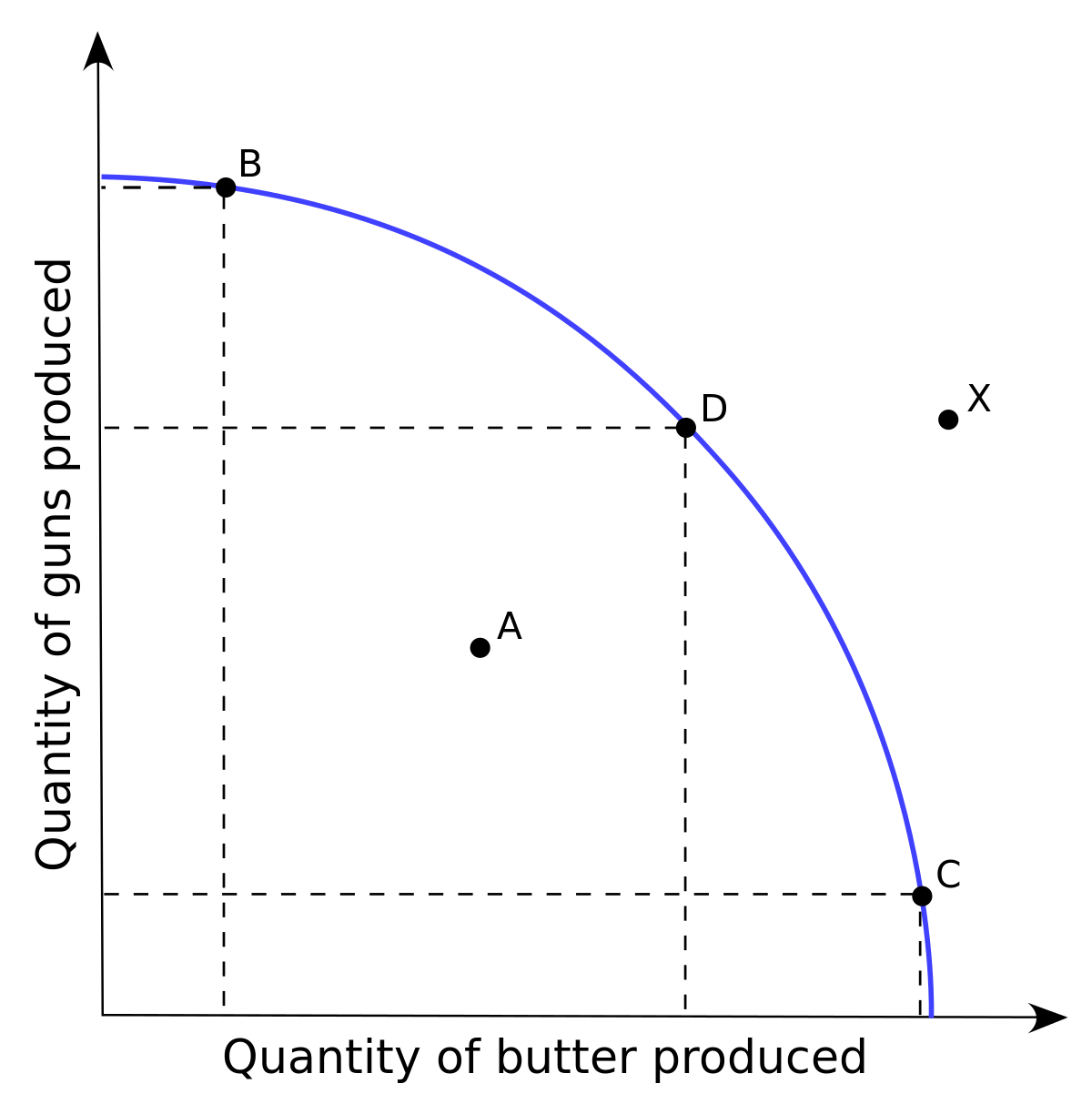
Production possibilities frontier
Graphical representation of possible outcomes of two products
Law of Demand
The lower the price, the higher the QUANTITY demanded is
Demand schedule
Table of relationshio between prices and quantity demand
A change in quality demand
A movement along the demand curve
Price and quantity demanded have a _____ relationship
Inverse
Land
Natural resources
Labor
All physical/mental activity devoted to producing goods
Capital
Tools, machinery, infrastructure, and knowledge used to produce goods
Entrepreneurial ability
Ability to combine resources to produce goods
Society's ability to produce goods is permanently reduced when
Resources are used too quickly
Scarcity
A condition that results from limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants
Relative scarcity
Comparison of scarcity between goods/services
Opportunity cost
Value of lost opportunity when you choose one activity over another
Marginal Benefit (MB)
Additional benefit associated w/ 1 more unit of activity
Marginal Cost (MC)
additional cost associated w/ 1 more unit of activity
Marginal Cost Formula
change in total cost/ change in quantity
Decreasing MB
the more a good is consumed, the lower MB gets
Example of MB
each additional hour spent studying instead of sleeping decreases MB
Increasing Marginal Cost
condition where additional costs associated w/ each successive unit of an activity increases
Marginal Decision
weighing MB and MC
Optimal Level of Output
MB=MC
Market Demand
Overall/Total Demand for a good/service/resource
Graphical Market Demand is represented by
the horizontal summation of all demand curves
When a nonprice determinant changes
the entire demand curve shifts
a shift in the demand curve suggests
a change in demand
increase in demand results in a
shift to the right
decrease in demand results in a
shift to the left
normal goods
as income rises, demand rises
inferior goods
as income rises, demand decreases
substitutes
goods consumed in place of each other
compliments
goods consumed together
when a substitute decreases
demand increases
when a compliment increases
demand increases
height of the demand curve represents
consumers’ willingness to pay for a unit of the good
consumer surpus
the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay and what they actually pay
the area below the demand curve and above price is
consumer surplus
Law of Supply
as prices rise, so does supply
as income decreases, the demand curve shifts right
inferior good
Diminishing Marginal Productivity
if atleast one input is fixed, the marginal productivity will fall
decrease in input results in
increase in supply
equilibrium price
price of when QD=QS
disequilibrium
shortages and surpluses
surplus
QD<QS
shortage
QD>QS
a good is more affordable
when the supply curve shifts right
when demand and supply move in the same direction
equilibrium price is INDETERMINANT
when demand and supply move in opposite directions
equilibrium quantity is indeterminant
when demand increases and supply decreases
equil. price increases
height of supply curve
cost of making additional units
producer surplus
difference between the price producers get for selling and the marginal cost for producing it
total surplus
consumer surplus + producer surplus
economic efficiency
no reallocation on goods that has benefits greater than cost
the area above the supply curve and below the price is
producer surplus
another name for total surplus
economic surplus or social welfare
deadweight loss
value of economic surplus lost when market can’t be adjusted to its competitive equilibrium
productive efficiency
producing output at lowest possible avg. total cost
allocative efficiency
producing goods that are most wanted by consumers
elastic demand
price elasticity of demand is greater than 1
inelastic demand
price elasticity of demand is less than 1
perfect inelastic demand
price elasticity of demand is 0
Unit elastic
price elasticity of demand is 1
own-price elasticity of demand
measure of how much quantity demand responds to prices
price elasticity demand of -1.25
if prices decrease by 10% QD increases by 12.5
elasticity
how responsive a variable is to a change
elasticity formula
percentage change of QD(or QS)/percentage change in price
elasticity ____ over time
increases
price controls
legal restrictions on prices
price cieling
max price
price floor
min price
if a price floor is placed above equilibrium price
a surplus occurs
if a surplus or shortage occurs, then the price is
binding
binding prices are
not efficient
if supply curve shifts left
prices rise
adam smith’s invisible hand
people pursuing their own self-interest results in benefits for everyone
market failure
individuals pursue rational self interest but result in inefficient
lack competition
when there is few firms, they may charge high prices
solution to lack of competition
antitrust laws, regulations
public goods are
nonrivalrous and nonexcludable
national defense is an example of a
public good
positive externaility
unpaid benefit enjoyed by a 3rd party not directly involved in the production/ consumption
private demand
demand for a good that only considers private benefits
social demand
demand for a good that reflects private and external benefits
social marginal beneit
full benefit to society of consuming an additional unit
negative externaility
uncompensated cost imposed on a 3rd party
private supply
supply of a good that only reflects private costs
social supply
supply of a good that reflects both private and social costs
private good
any good that is rivalrous and excludable
free rider problem
those who benefit from resources, public goods and common pool resources do not pay for them or under-pay
solution to free-rider problem
government tax revenues that provide public goods
information problems
if one or both sides of a transaction lack important information, some exchanges will not
solution to information problems
inspections, certifications, licensing, and records
public interest view of gov
a democratic government translates votes into effective beneficial policy action
public choice view of gov
gov is made up of rationally self-interest individuals and policies are the result of their decisions and the incentives they promise
voters are like
consumers
voters
vote for politicians who promise bundles of policies they like
rational ignorance
voters choose to be poorly informed about politics and policies