Tissues Microscope Long Quiz
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
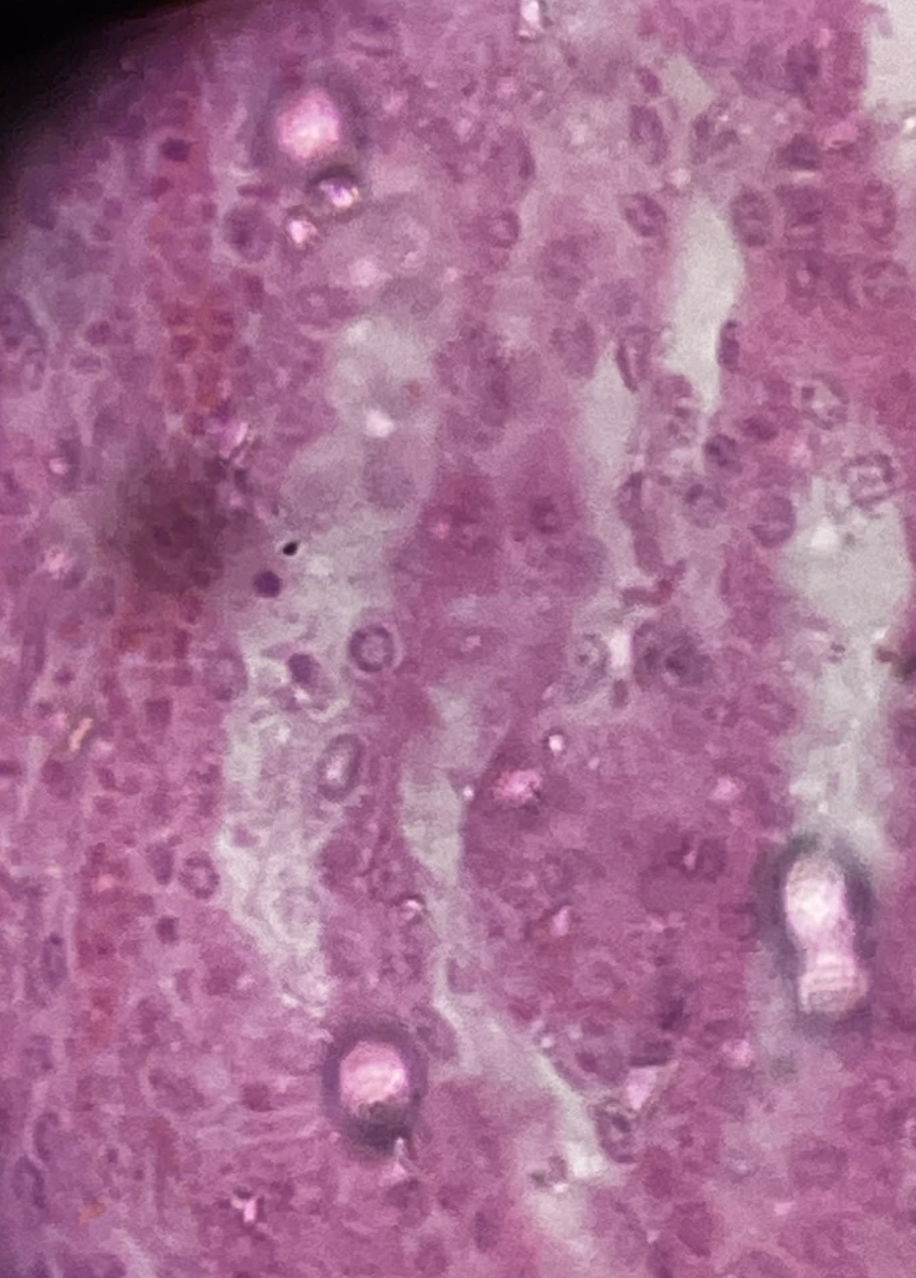
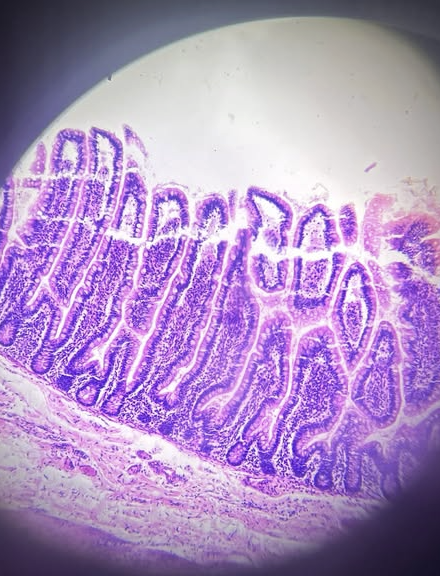
Small Intestine
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Small Intestine Tissue?
Absorption of nutrients and secretion of enzymes and mucus.
Simple Columnar Epithelium Function?
Columnar (tall, rectangular cells)
Intestine Cell Shape?
Cells have elongated nuclei usually located near the basal region
Columnar Cell Description?
Digestion and absorption of nutrients
Carbohydrates → sugars
Proteins → amino acids
Fats → fatty acids and glycerol
Absorbs vitamins, minerals, and most water from food
Small Intestine Function?
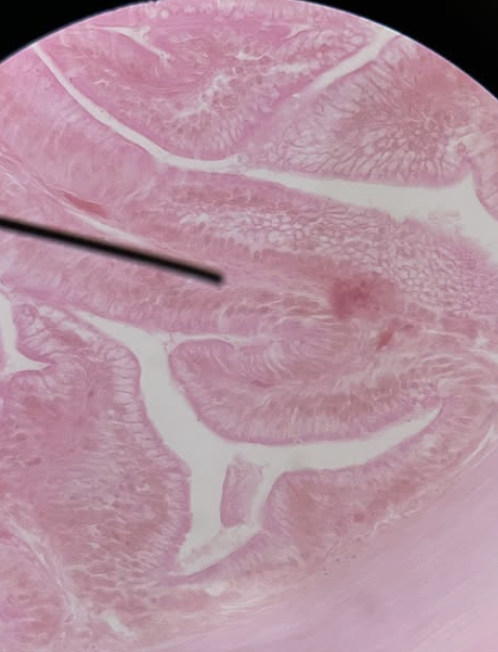
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary, rhythmic contraction to pump blood throughout the body.
Cardiac Muscle Function?
Pumps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
Maintains circulation and blood pressure throughout the body
Heart Function?
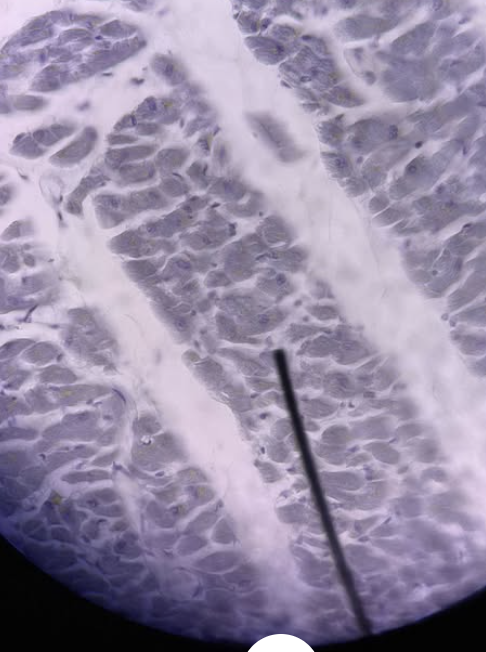
Kidney
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Kidney Tissue?
Secretion and absorption
Simple Cuboidal Function?
Cuboidal
Kidney Cell Shape?
Filters blood to form urine
Kidney function?
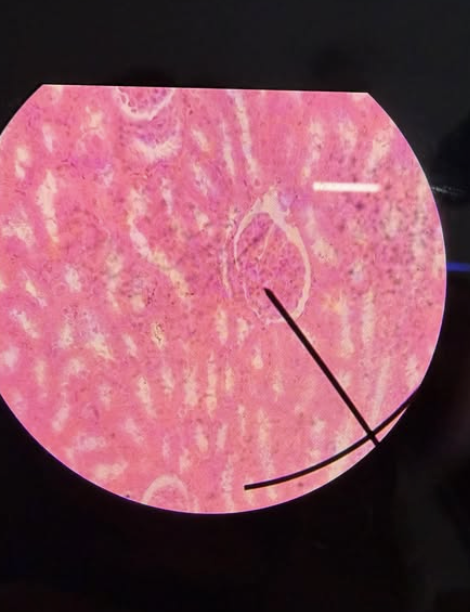
Intestine
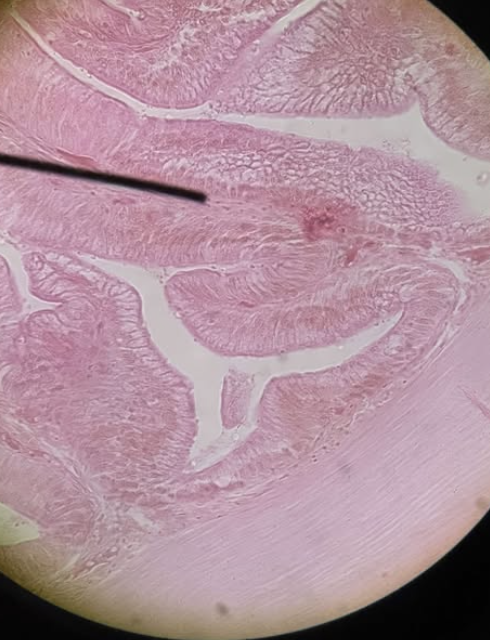
Small Intestine - Ileum
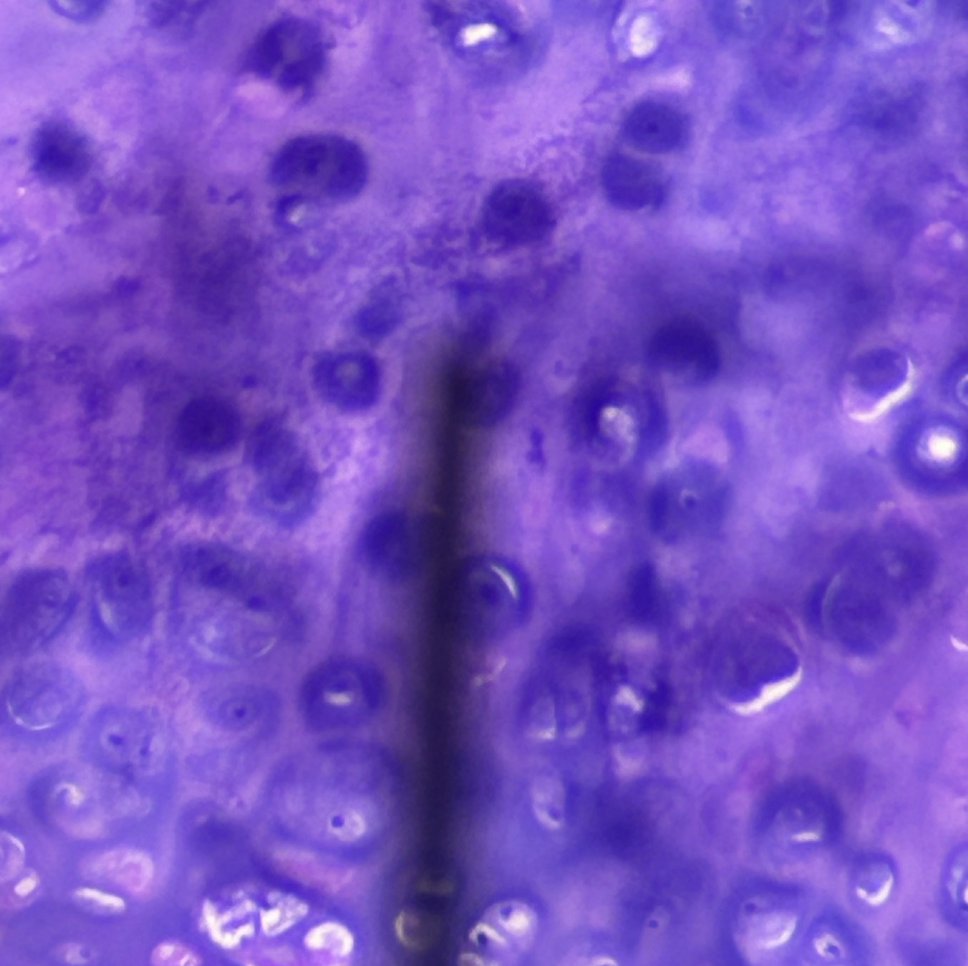
Cartilage
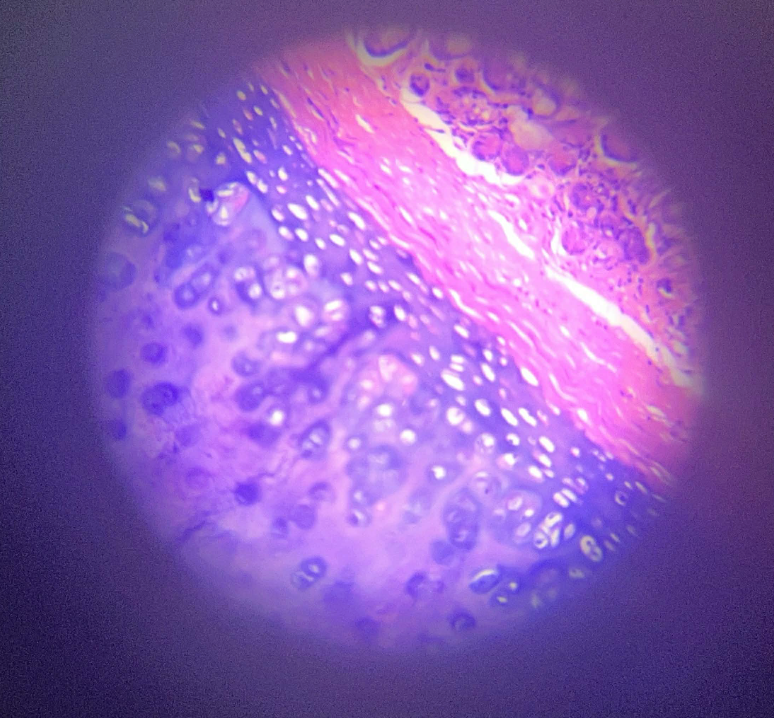
Cartilage Den
Intestine
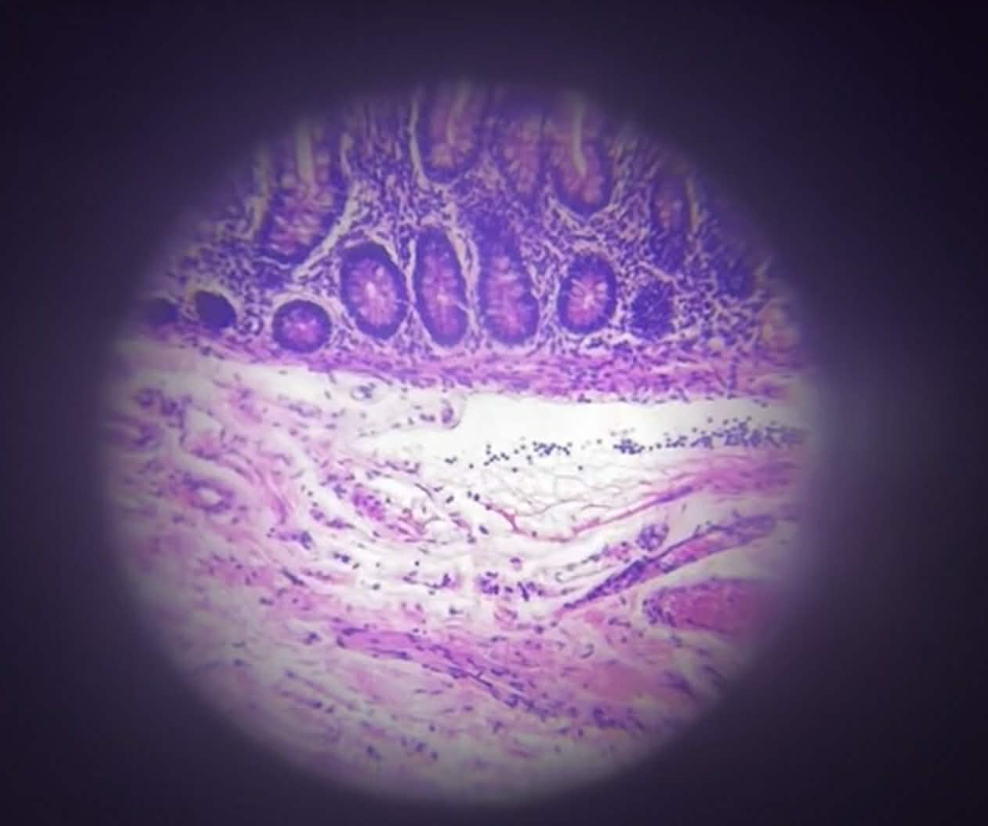
Oval
Cartillage cell shape?
Provides support, flexibility, shock absorption, and reduces friction at joints
Cartilage Function?
Chondrocytes
Cartilage Cell?
Bone / Osseous Tissue
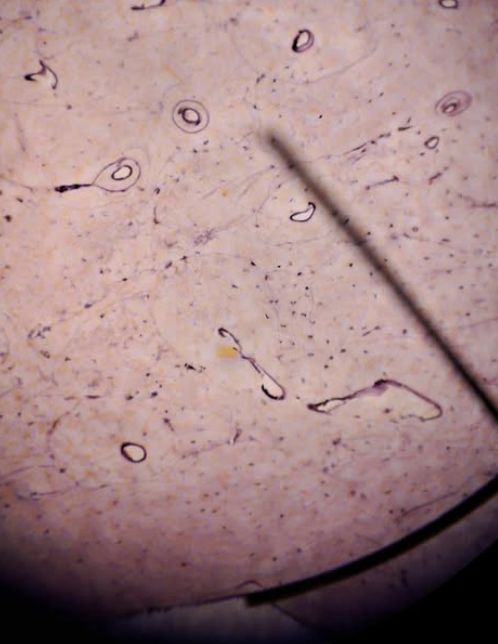
Support, protection, mineral storage (calcium & phosphorus), and blood cell formation
Provides structural support and protects vital organs
Enables movement (acts as levers for muscles)
Stores and releases minerals
Houses bone marrow for hematopoiesis (blood cell production)
Bone Tissue function?
Spider-Like
Bone Cell Shape?
Areolar Connective Tissue
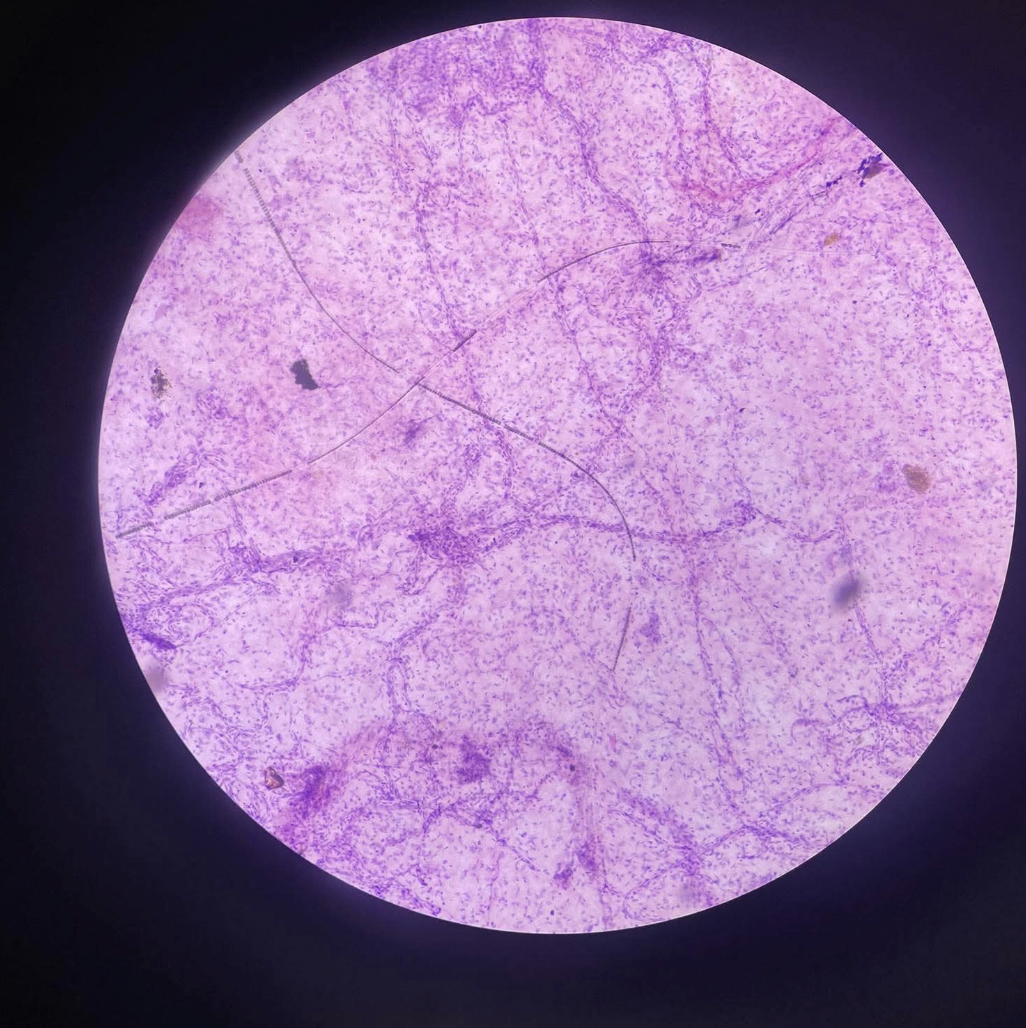
Binds and supports other tissues, wraps organs, holds tissue fluid, and allows diffusion of nutrients and wastes
Areolar Connective Tissue Function?
Muscular Striated Tissue
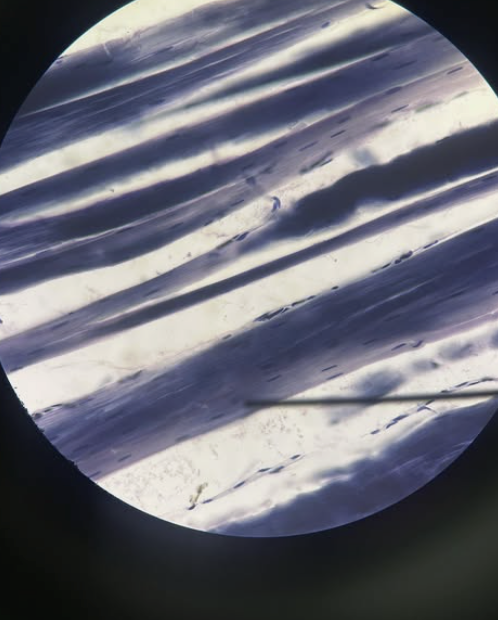
Voluntary movement, posture maintenance, and heat production
Muscular Striated Tissue Function?
Muscles attached to bones (most common)
e.g., biceps brachii, triceps, quadriceps, gastrocnemius
Tongue
Pharynx
Upper part of the esophagus
Extraocular (eye) muscles
Diaphragm
Muscular Striated Tissue Organs?
Areolar Connective Tissue Den
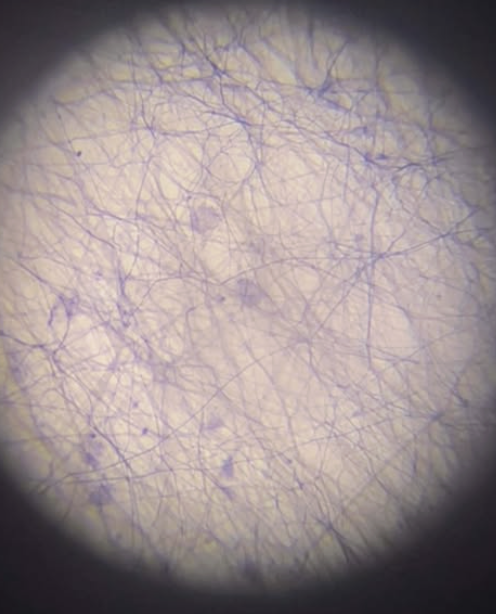
Human Cardiac Muscle
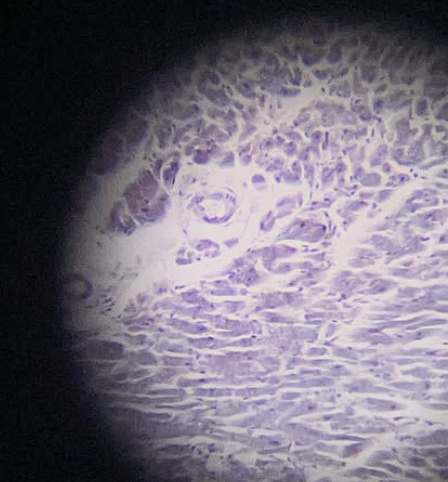
Human Bone Decalcified
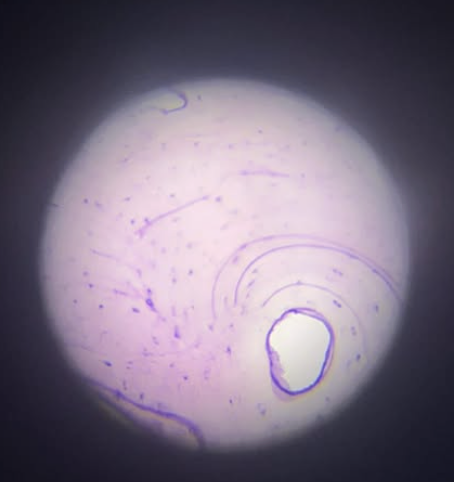
Esophagus
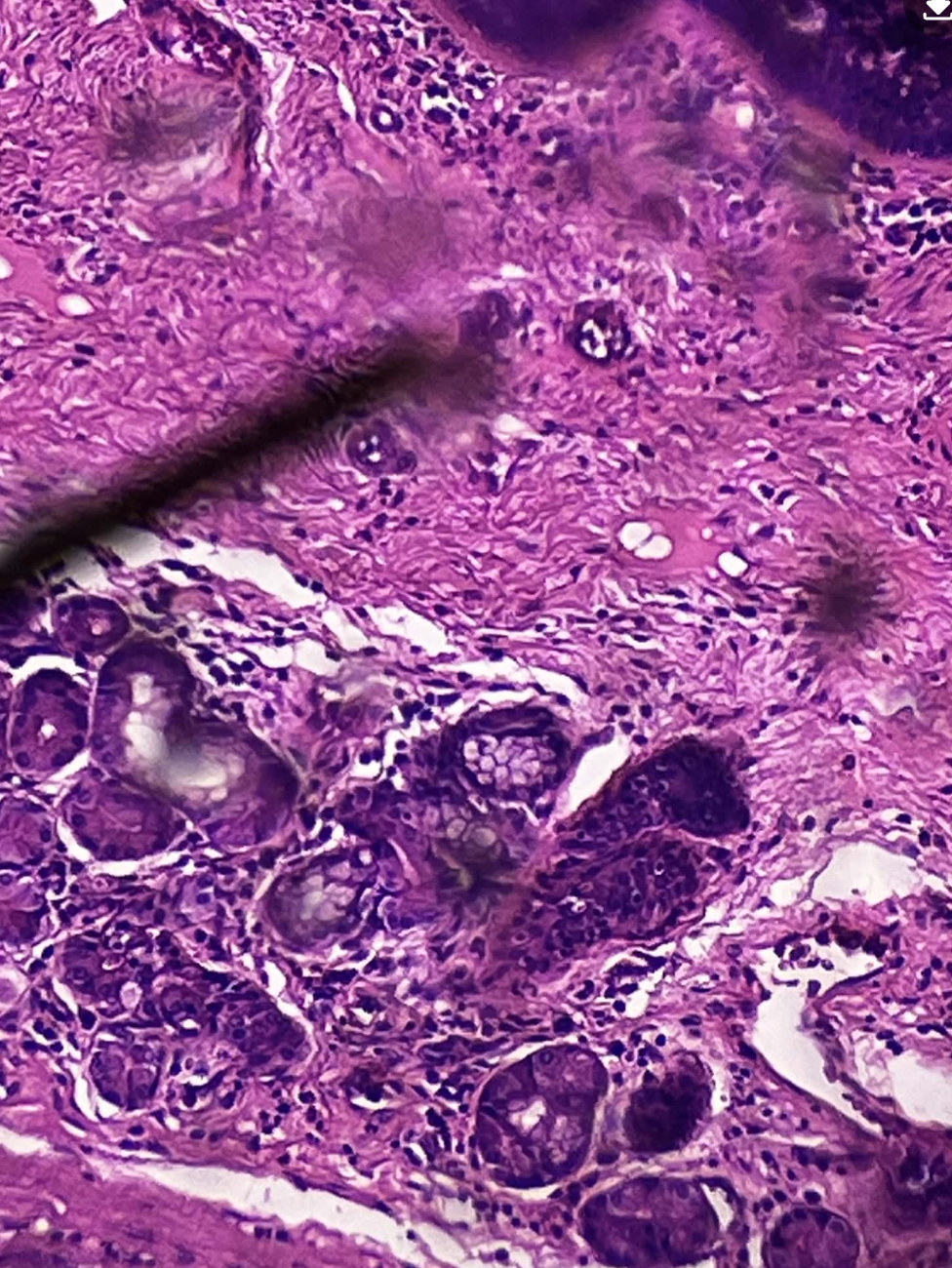
Stratified Squamous
Esophagus tissue?
Squamous
Esophagus cell shape?
protects against mechanical abrasion
Stratified Squamous function?
Conducts food from mouth → stomach (peristalsis)
Protects mucosa from abrasion by swallowed food
Secretes mucus from submucosal glands to lubricate the passage
Esophagus Function?
Intestine
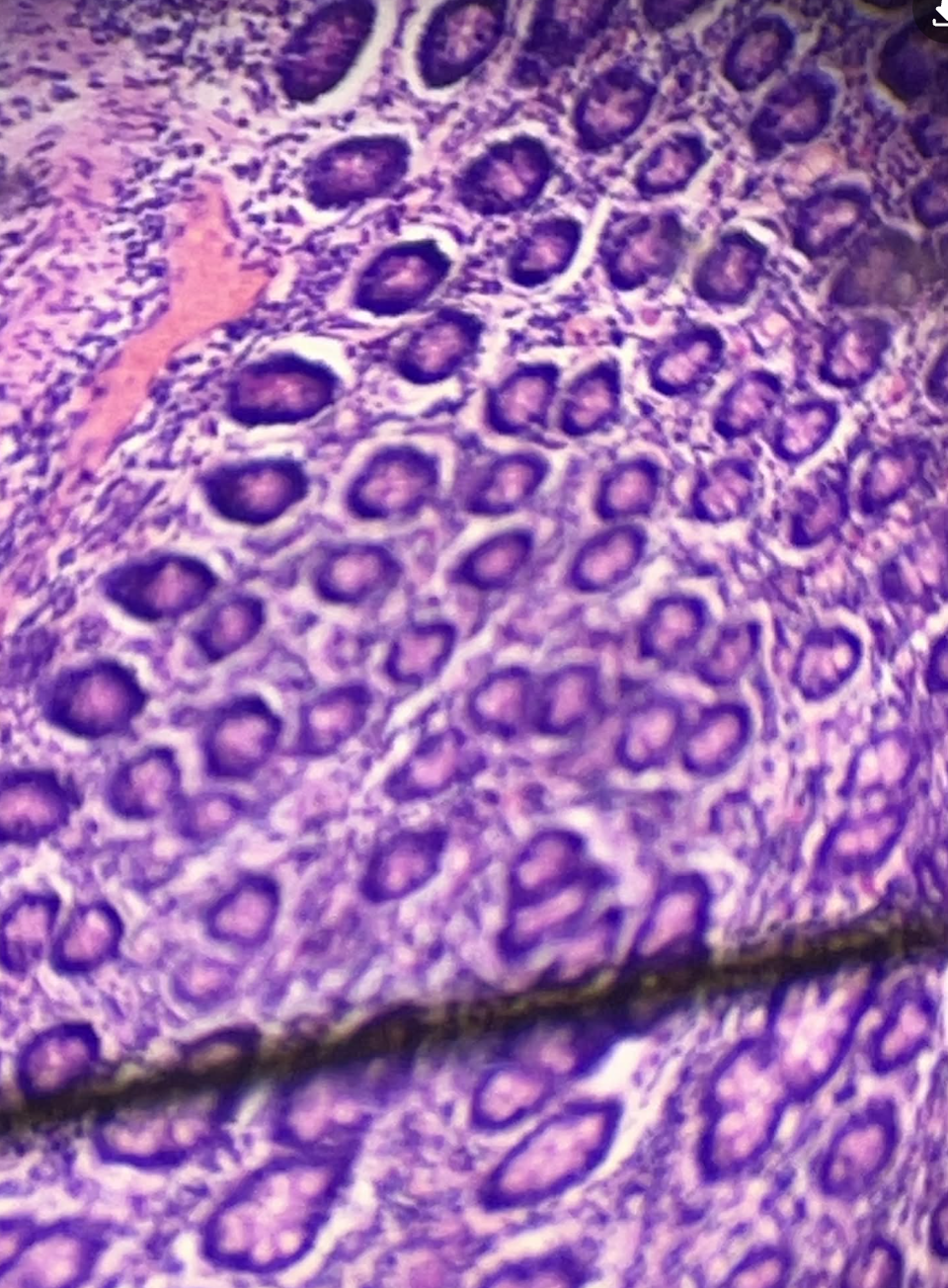
Kidney