Quiz 1: Biomedical Sciences
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
What are the two major classes of cells in the central nervous system?
neurons (electrically excitable) and glia (supportive and regulatory)
Which cell type makes up the majority of brain cells?
Glia
What is the primary function of neurons?
to transmit information via electrical and chemical signals
What are the 3 main glial cell types in the CNS?
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia
What are dendritic spines and why are they important?
small protrusions where most synapses and drug targets are located
How do dendritic spines change with learning and memory?
they increase or decrease in number, density, and shape over time
What is a Purkinje neuron and where is it found?
a highly branched neuron in the cerebellum and the major output neuron there.
What are the three core structural components of a neuron?
dendrites, cell body (soma), and axon
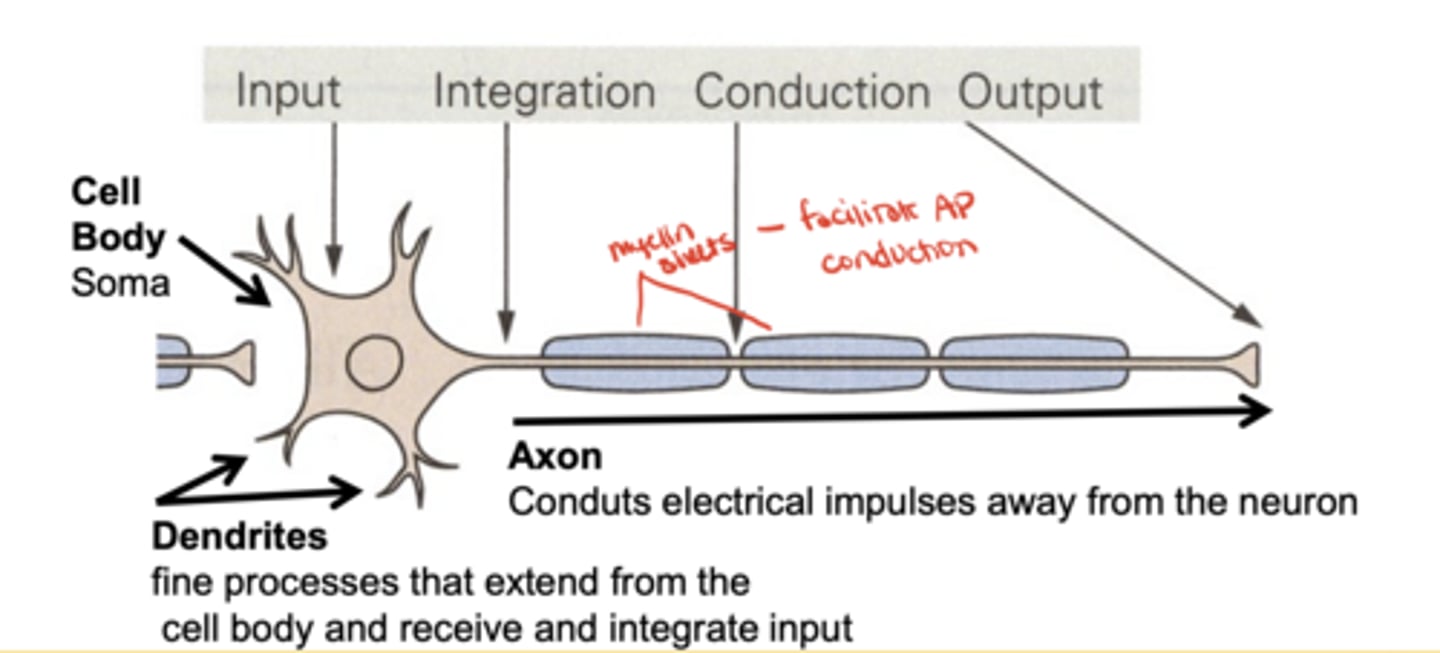
What is the function of dendrites?
receive and integrate input from other neurons
What is the function of the axon?
conduct electrical impulses away from the neuron
What structural feature distinguishes axons from dendrites?
axons lack dendritic spines
Do most neurons divide after development?
No, most neurons do not have the capacity to divide
How does the brain adapt if neurons don't divide?
through neuroadaptation / neuroplasticity (strengthening connections)
What percentage of brain volume is made up of astrocytes?
25-50% of brain volume
What protein uniquely identifies astrocytes?
GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein)
What are 2 developmental roles of astrocytes?
provide a migration scaffold and structural support
What key synaptic role do astrocytes play?
clear neurotransmitters from the synapse
How do astrocytes contribute to CNS disease?
involved in injury, inflammation, Alzheimer's disease, and chronic pain
What are microglia?
resident immune cells of the CNS
How do microglia respond to CNS injury?
change morphology and increase in number
Why can microglial activation be harmful?
excessive activation contributes to damage and neurodegeneration
What is the basic structure of a classical synapse?
presynaptic neuron → synaptic cleft → postsynaptic neuron
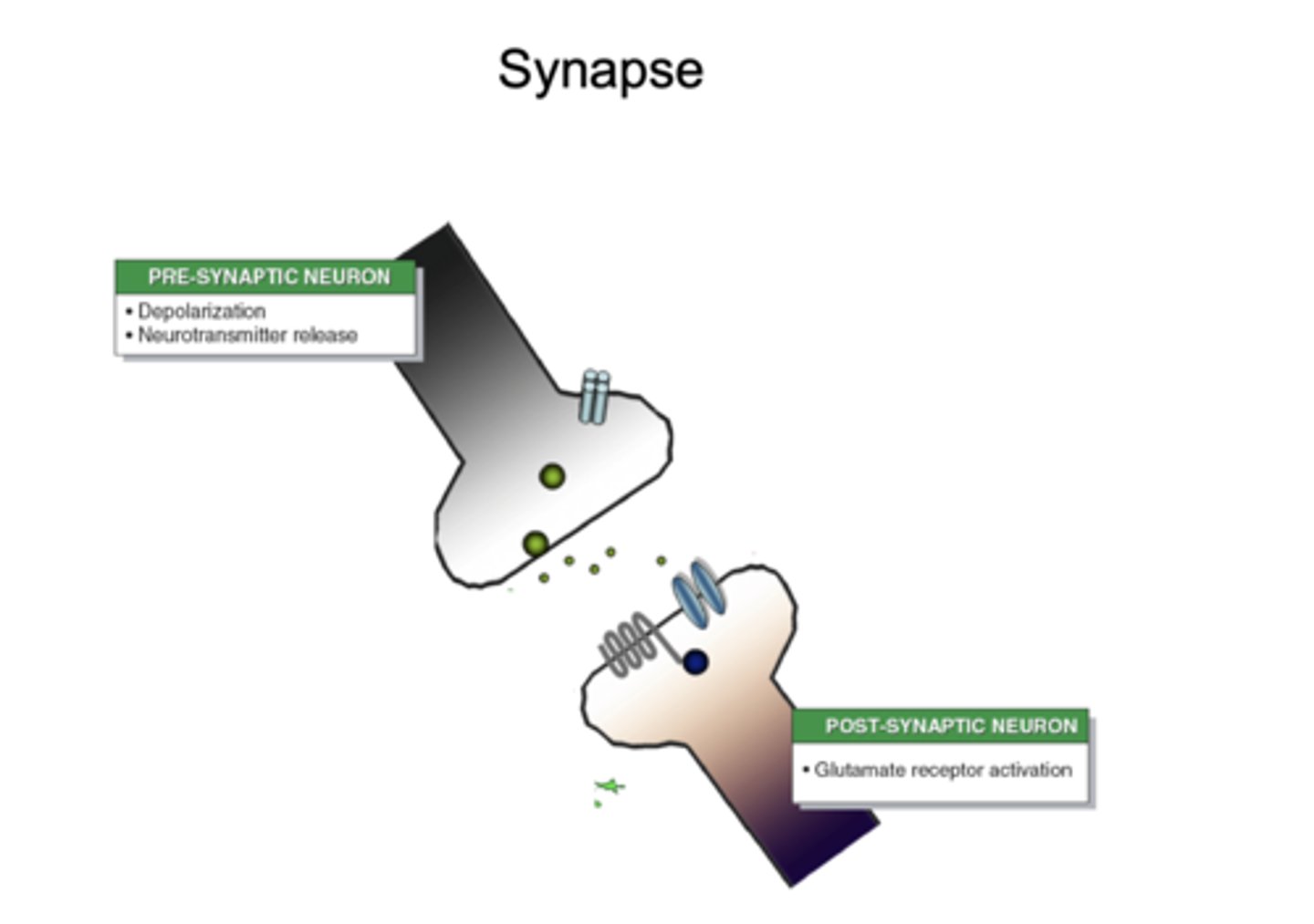
What two major receptor types mediate synaptic signaling?
ion channels and G-protein-coupled receptors
How can neurotransmission affect the postsynaptic neuron?
can activate or inhibit signal propagation
What is the "tetrapartite synapse"?
synapse involving neurons, astrocytes, and microglia
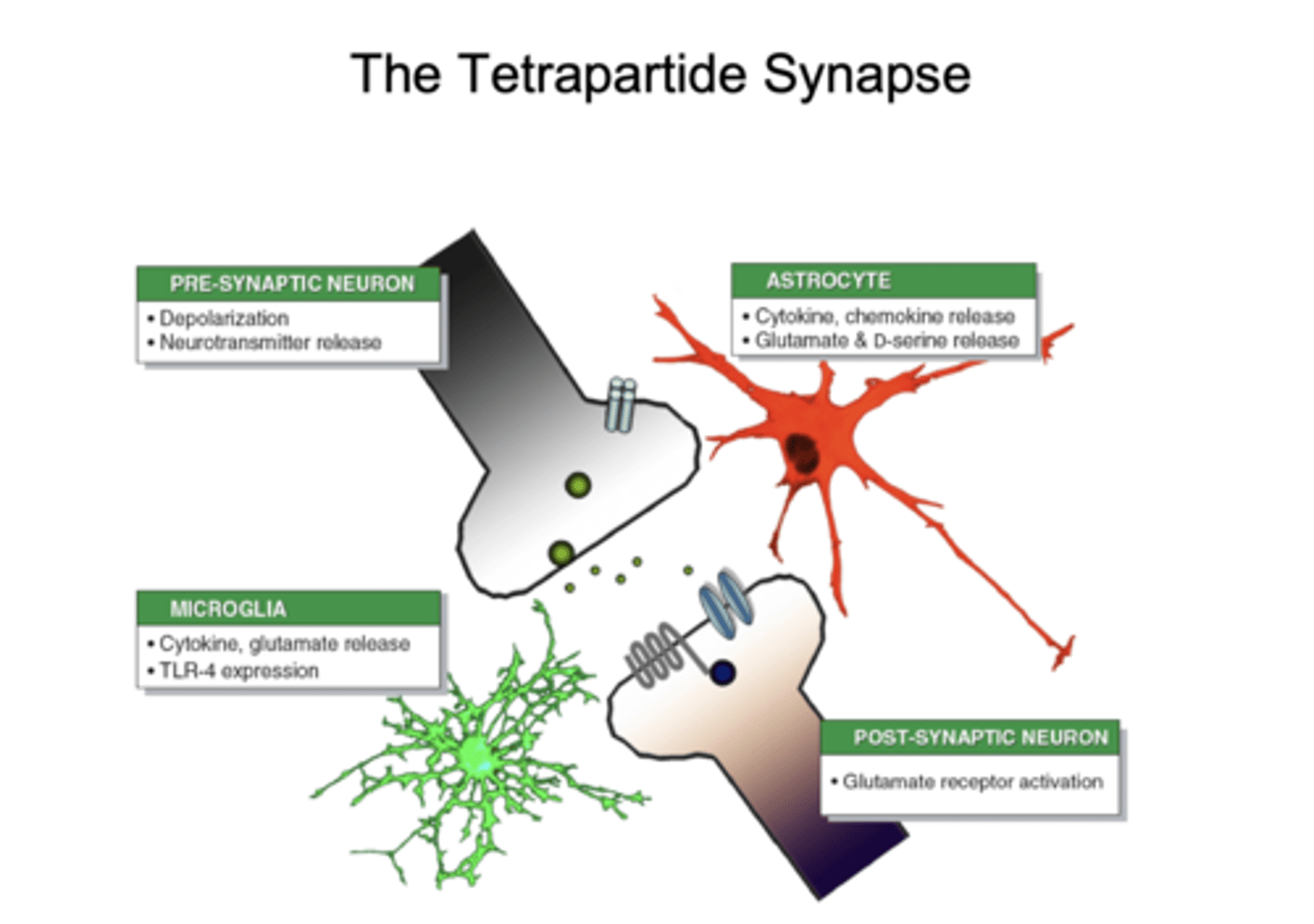
How do astrocytes actively modulate synaptic signaling?
release cytokines, glutamate, and D-serine
How do microglia modulate synaptic signaling?
release of cytokines, glutamate, and TLR-4 expression
Which glial cells produce myelin in the CNS vs PNS?
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Schwann cells (PNS)
How many myelin sheaths are produced by oligodendrocytes vs Schwann cells?
Oligodendrocytes: many
Schwann cells: one
Why is myelin essential?
enables rapid electrical conduction
What happens when myelin is destroyed?
slowed conduction and sensory/motor deficits
Which disease involves oligodendrocyte destruction?
Multiple Sclerosis
What is gray matter vs white matter?
Gray: cell bodies
White: axon tracts
Sulcus
a groove in the cortex
Gyrus
a fold in the cortex
What is a CNS nucleus (important distinction)?
a cluster of neurons, not a cell nucleus
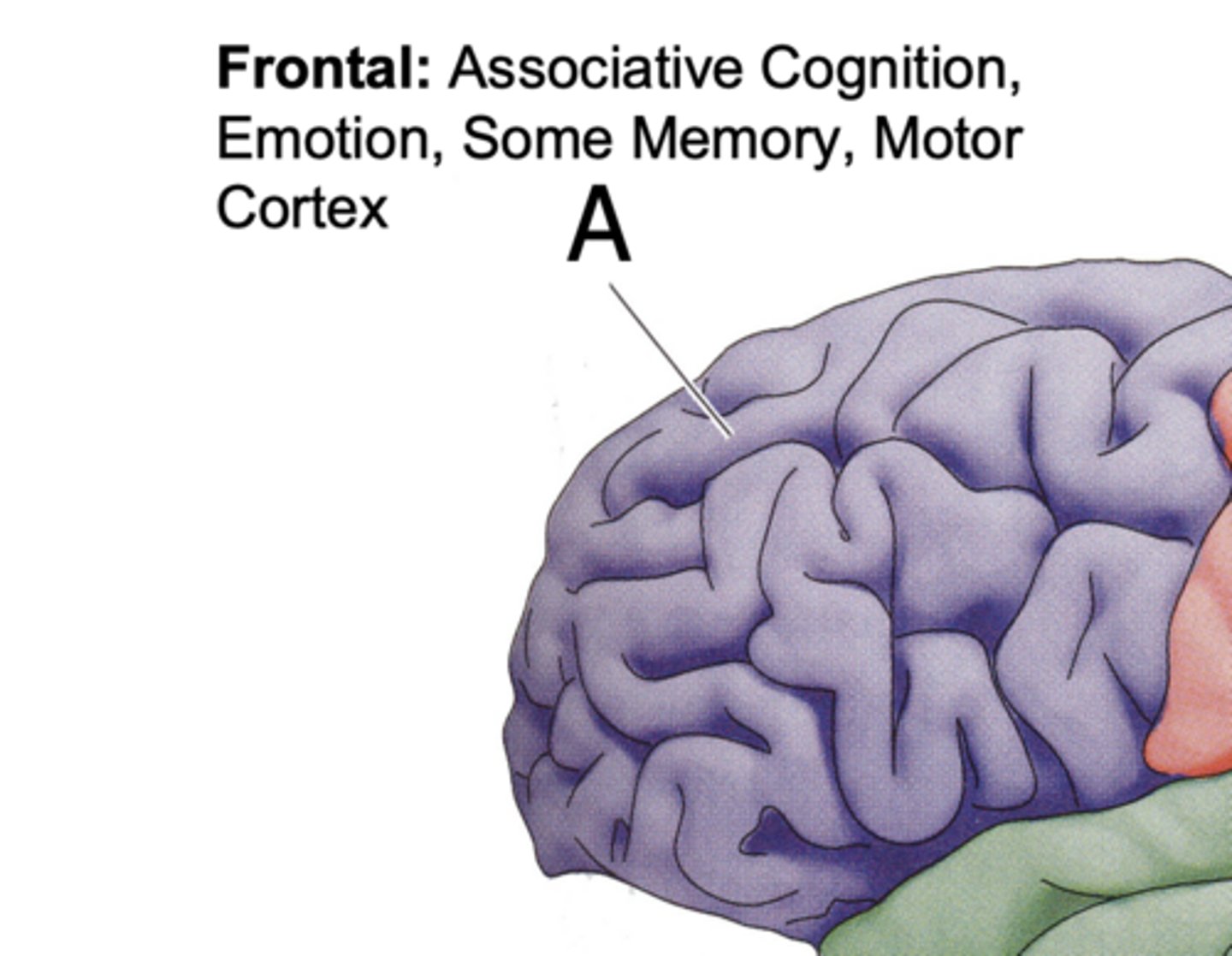
Frontal Lobe Function
associative cognition,
emotion, some memory, motor cortex
Temporal Lobe Function
memory, learning, auditory, and language comprehension
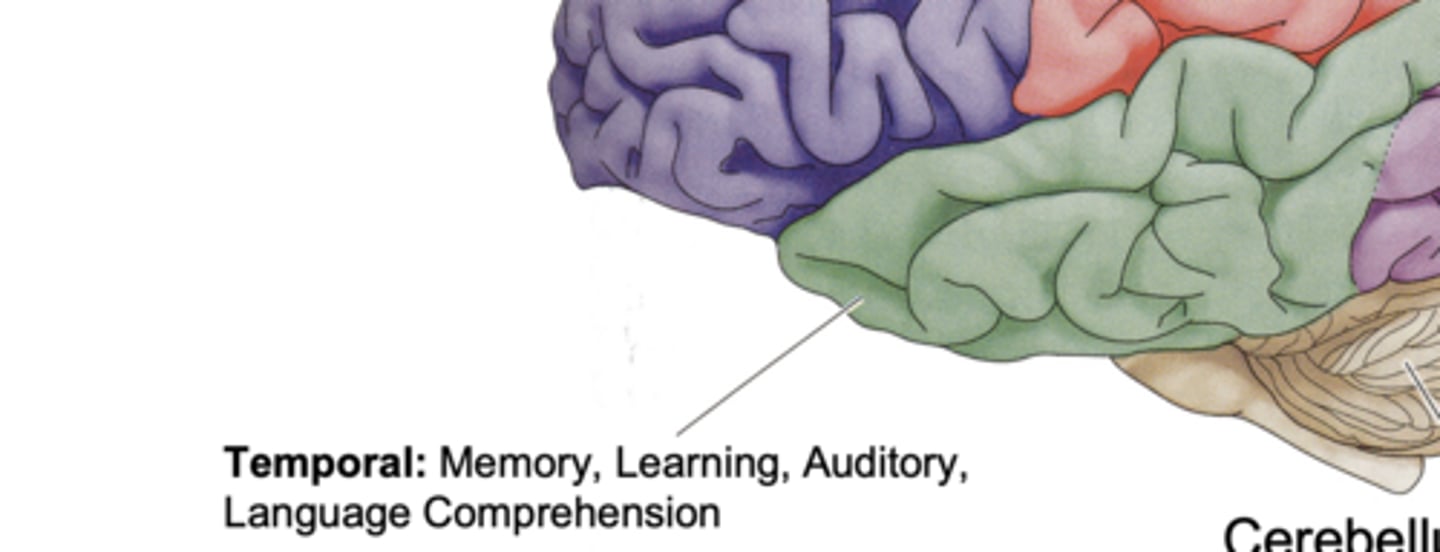
Parietal Lobe Function
somatosensory spatial integration, touch, temp, pain, some language processing
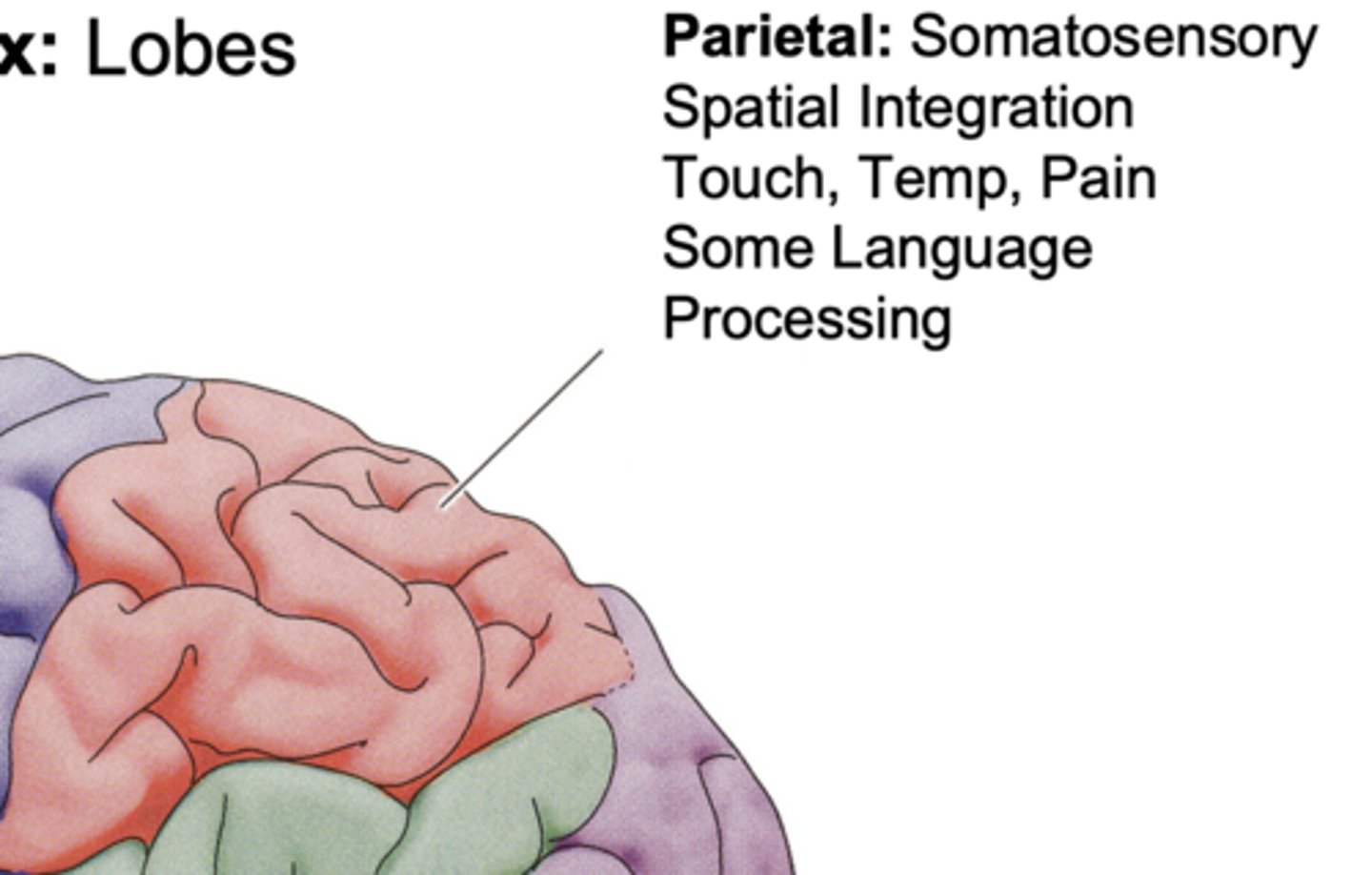
Occipital Lobe Function
primary visual cortex
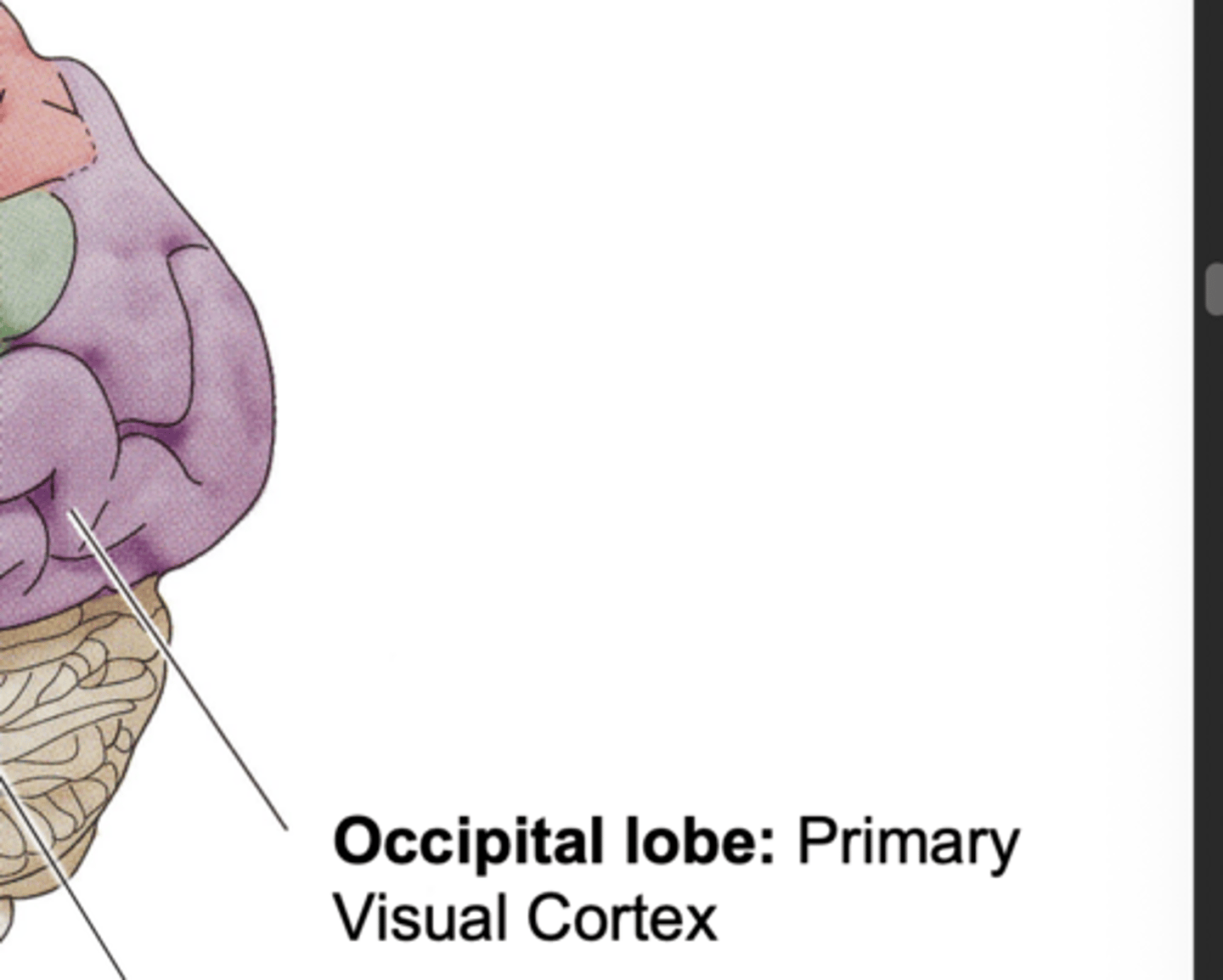
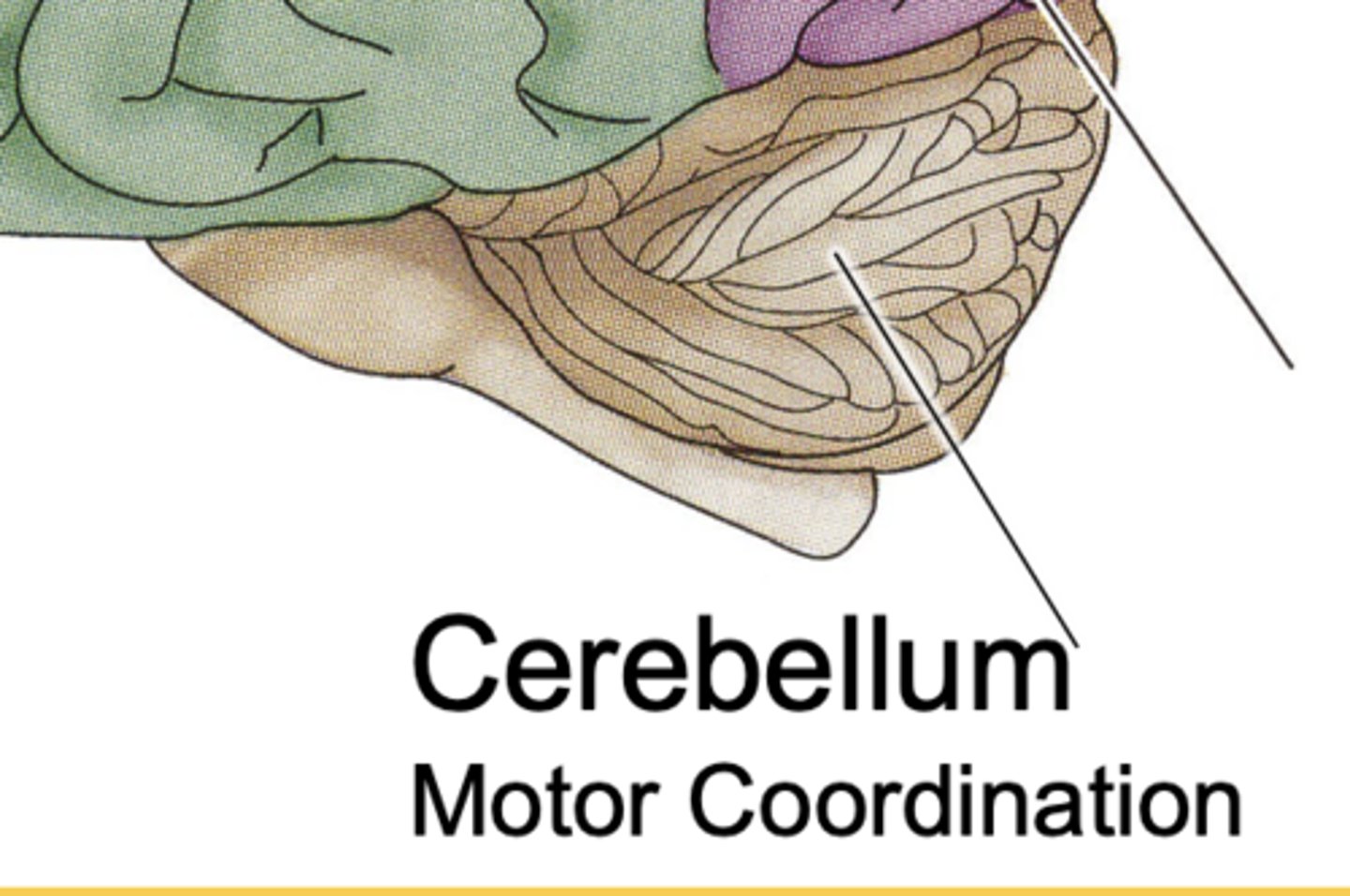
Cerebellum Function
motor coordination + balance
Optic Nerve Function
vision
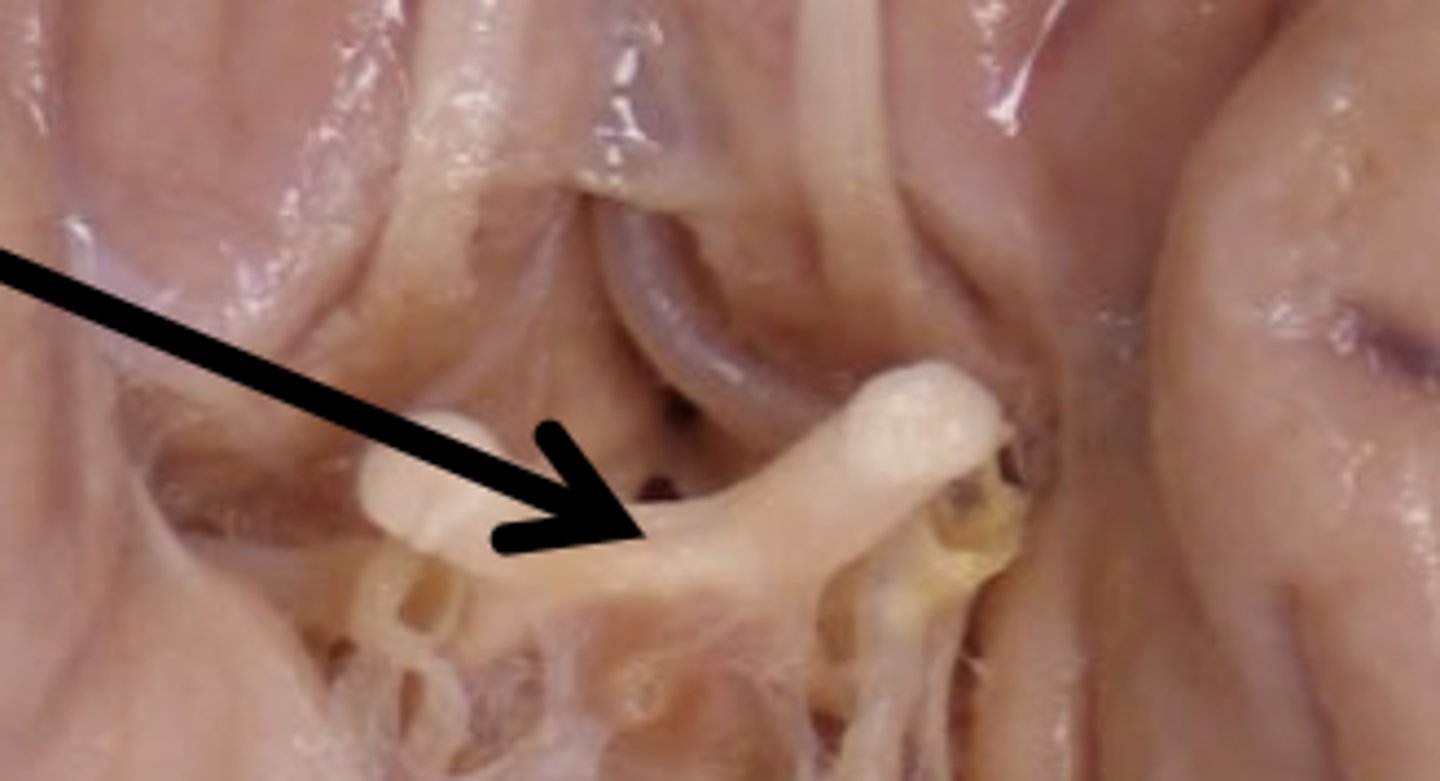
Pons Function
(bridge) relays information between brainstem, cerebellum
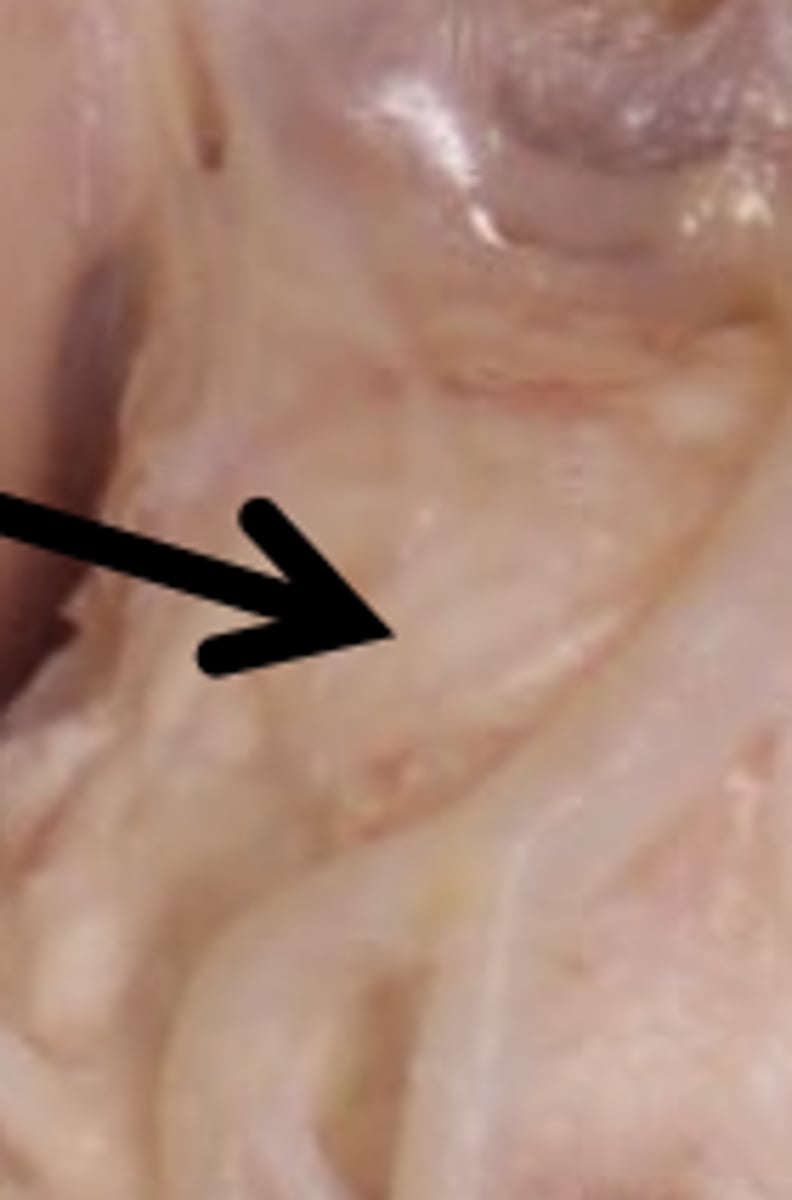
Cranial Nerves (7-10) Function
7: facial expression
8: hearing
9: oral sensation and taste
10: vagus (sensory and parasympathetic input)
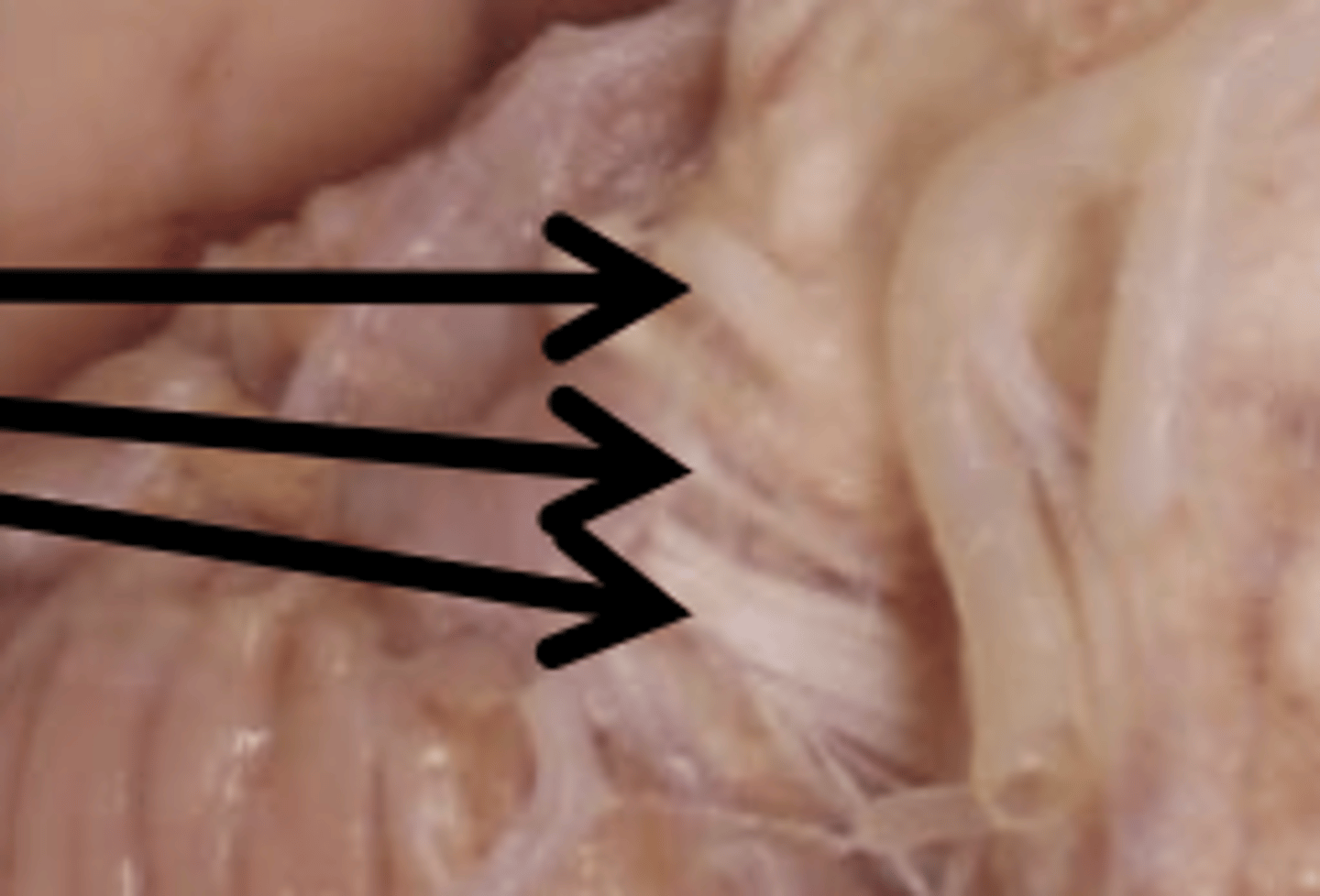
Olfactory Bulb Function
smell
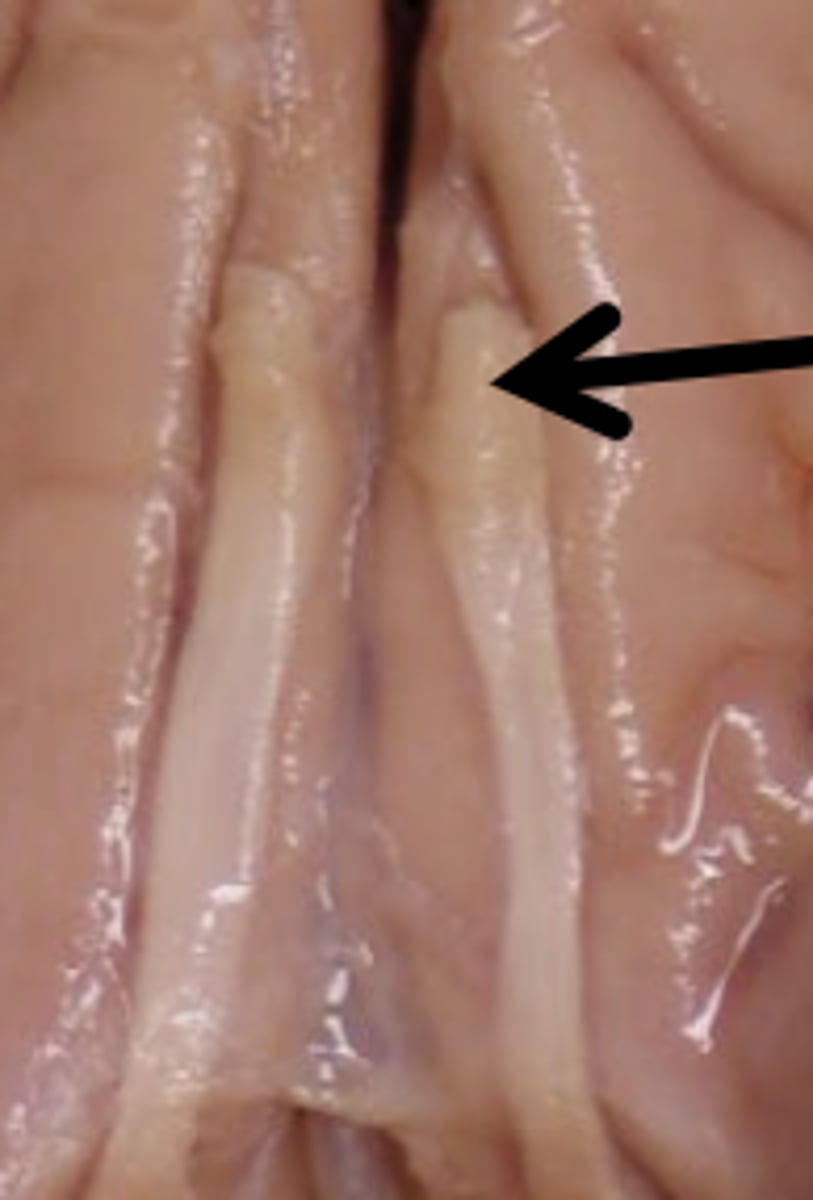
Basilar Artery Function
confluence of two vertebral arteries and main supply to cerebellum and brainstem
Cranial Nerves (5, 6) Function
5: sensation to face, mastication
6: abducens, eye movement
What structures make up the cerebral hemispheres (telencephalon)?
cortex, basal ganglia, amygdala, hippocampus
What are the primary functions of the cerebral hemispheres?
perceptual, motor, and cognitive functions
What two major structures comprise the diencephalon?
thalamus and hypothalamus
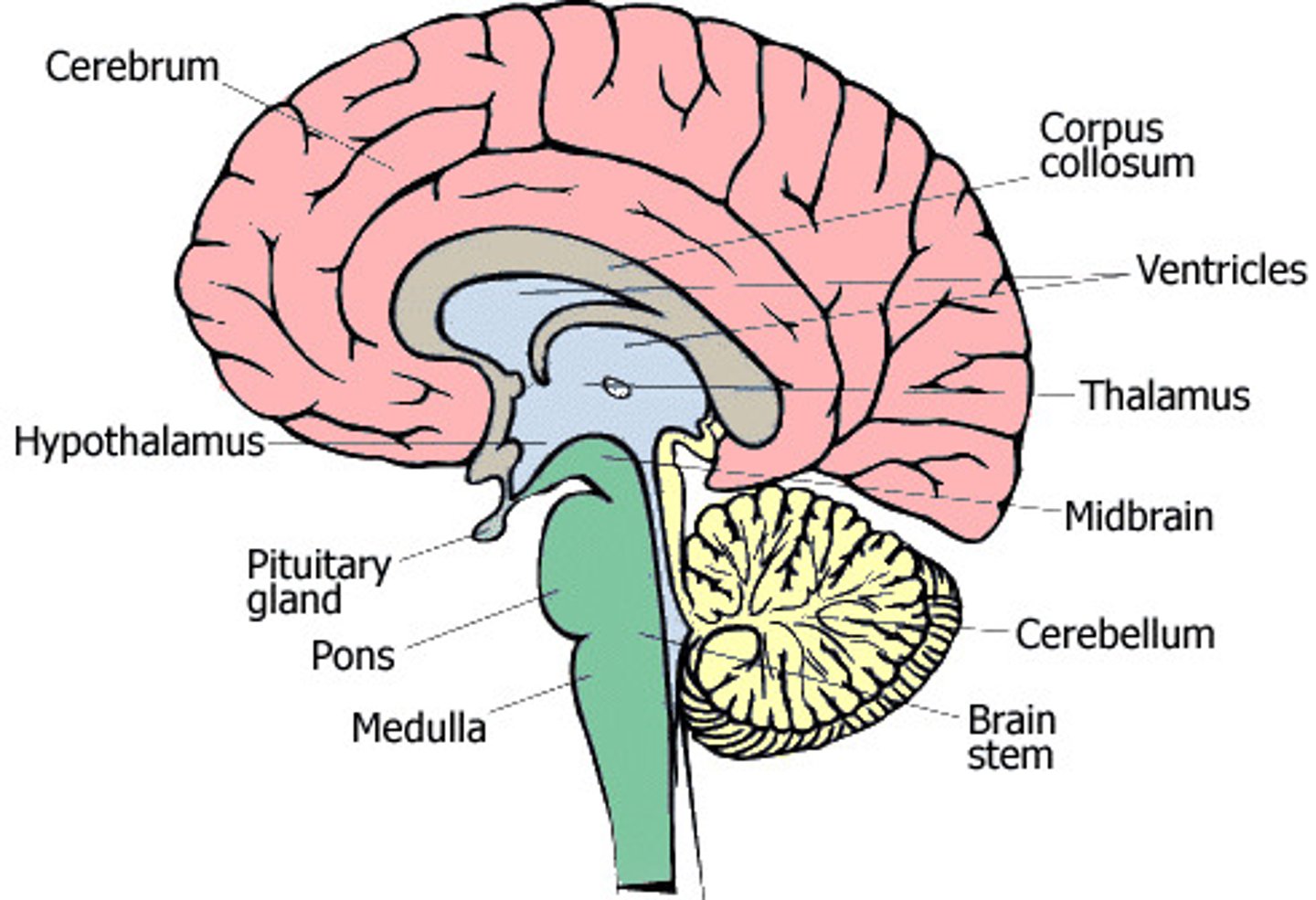
What are the primary functions of the thalamus?
relay and gating of sensory information and components of motor control
What functions are regulated by the hypothalamus?
autonomic regulation, feeding behavior, reproductive behavior, and motivation
What structures form the brainstem and what is its overall role?
Medulla, pons, midbrain → autonomic regulation, arousal, and integration of sensory and motor information
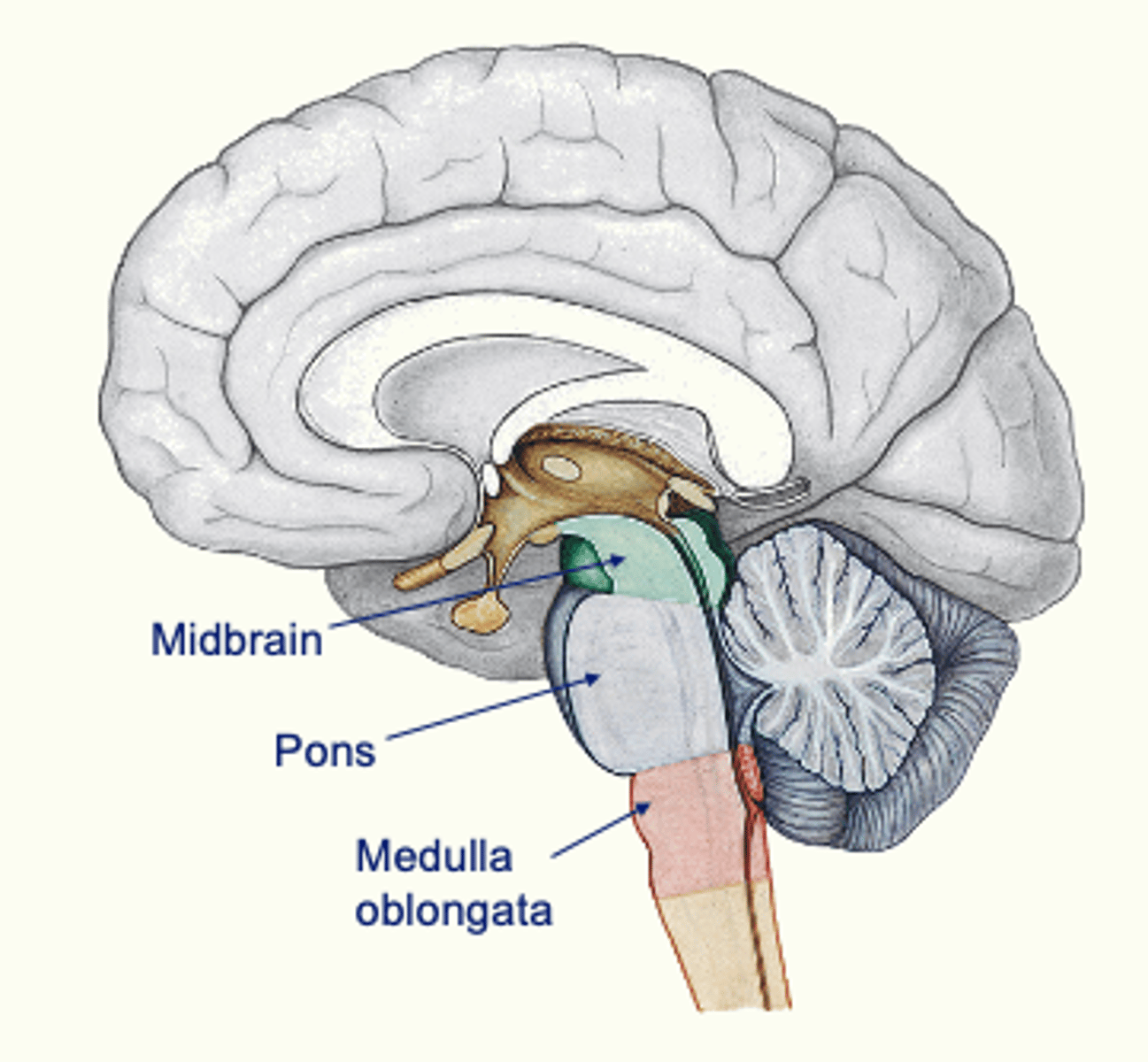
What specific systems does the brainstem contribute to?
motor control, visual and auditory systems, visceral sensory input, and head-related sensory/motor output
What are the primary roles of the spinal cord?
sensory input and processing and motor output
Which CNS subdivisions are most associated with autonomic control?
hypothalamus and brainstem
What is the corpus callosum?
major white-matter tract connecting hemispheres

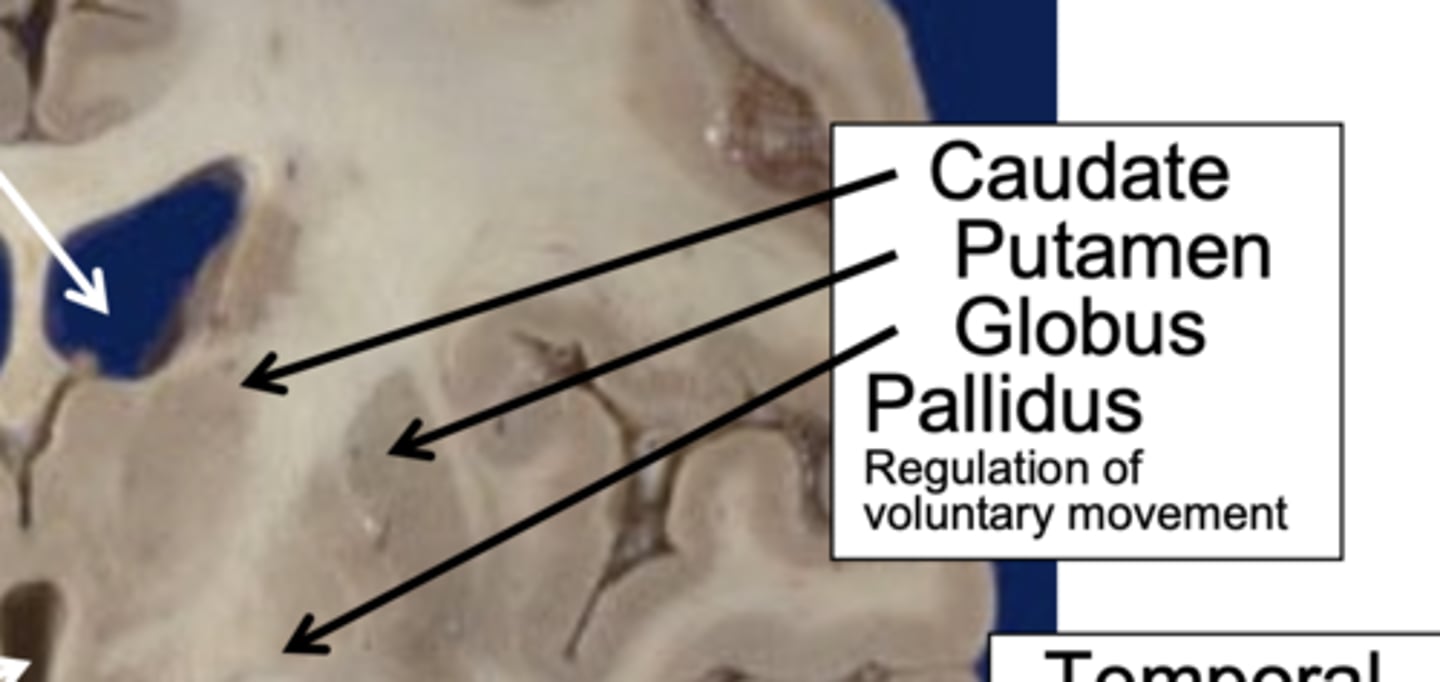
Which structures make up the basal ganglia and what is their role?
caudate, putamen, globus pallidus → motor control & inhibition
What is the hippocampus responsible for?
learning and memory formation

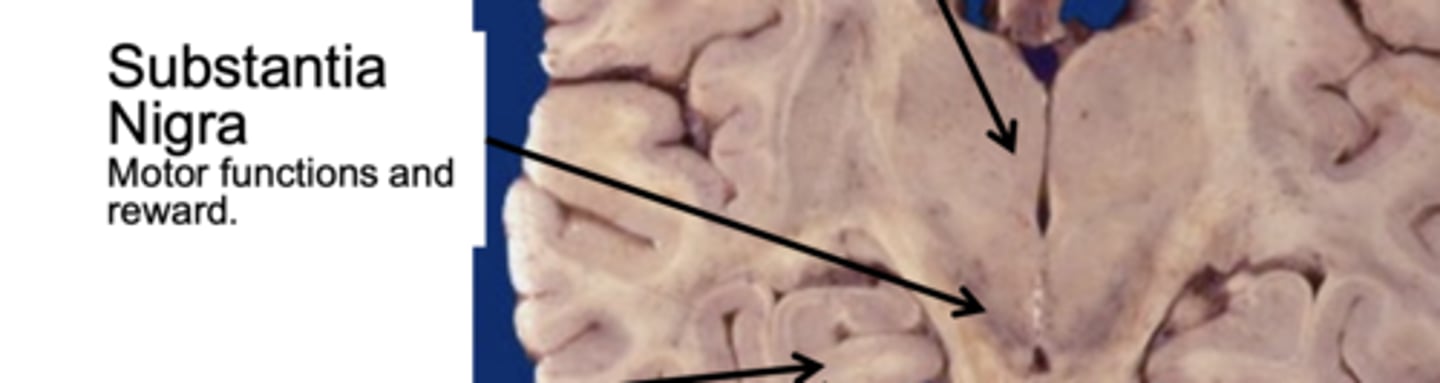
What is the function of the substansia nigra?
motor functions and reward
What is the ventricular system's primary function?
production and circulation of CSF
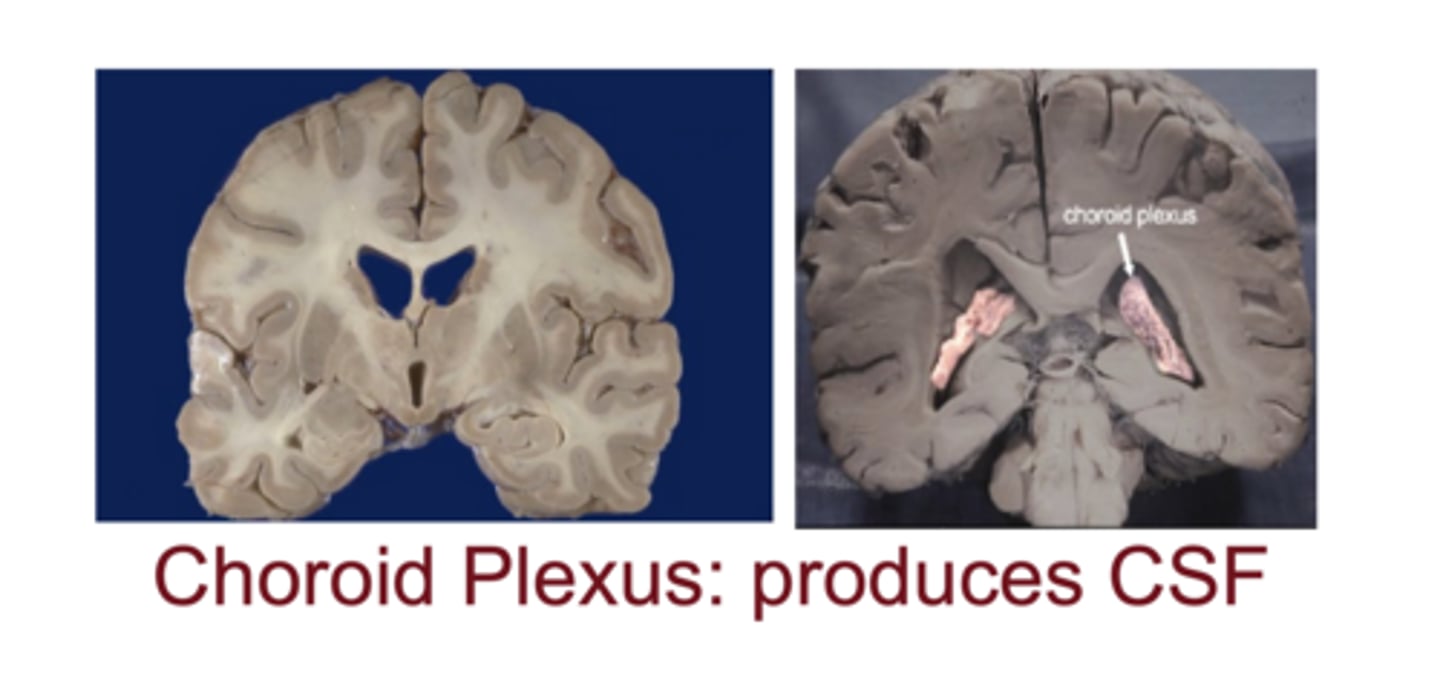
Which structure produces CSF and how much is produced daily?
choroid plexus; ~450 mL/day
**the CSF input
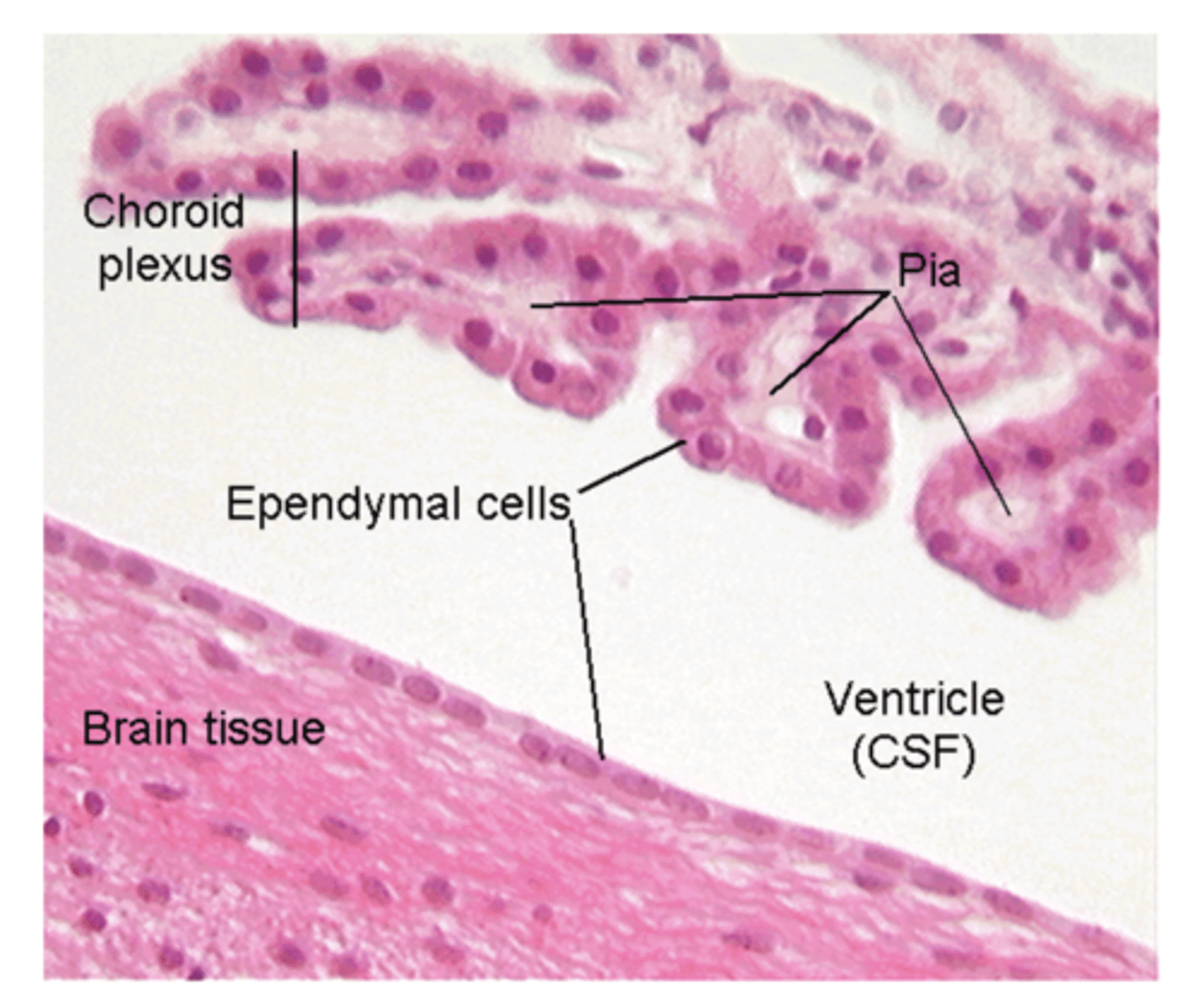
What is the ependymal layer?
layer of cells the lines the CSF-filled ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord
What is the function of the ependymal layer?
modified cells form the choroid plexus which produces CSF
What are the 3 meningeal layers that surround the spinal cord (from outer to inner)?
Dura mater(thick)→ Arachnoid mater(spidery) → Pia mater(thinnest)
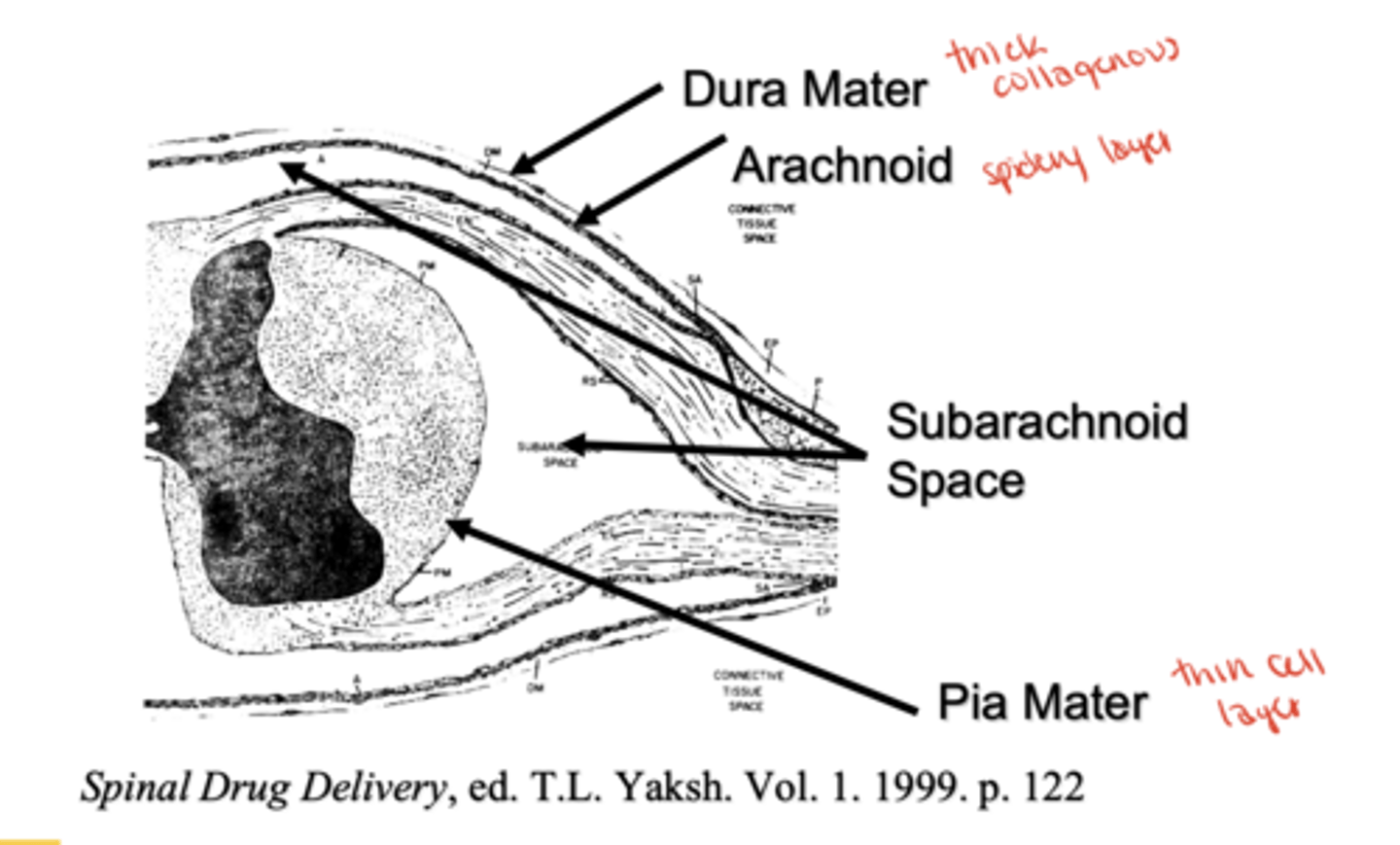
Which meningeal layer absorbs CSF and why is it clinically important?
Arachnoid villi; key for CSF resorption and CNS drug delivery
**the CSF output
What are the four major components of neurotransmission?
- resting membrane potential
- signaling/APs
- neurotransmitters (release and uptake)
- synapse (pre- and post- synaptic modulation)
What is the function of the cell body?
synthesis of neurotransmitters
What is the function of myelin sheaths?
covers the axon to speed up neural impulses through conduction
What makes neurons "electrically excitable" cells?
they can produce and respond to electrical signals due to polarized cell membranes created by ion gradients
What causes polarization of the neuronal membrane?
separation of opposite charges from different ion concentrations inside vs outside the cell
What defines an AP as a type of electrical discharge?
it is voltage-gated, all-or-none, transient, and involves ion flow through channels
What three factors establish the resting membrane potential?
unequal ion distribution, selective ion permeability, and the Na⁺/K⁺ pump
Which ions have the greatest membrane permeability at rest?
K⁺ >>> Na⁺ >> Cl⁻ > anions
What is the primary function of the Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase pump?
maintain low intracellular Na⁺ and high intracellular K⁺ to preserve polarization
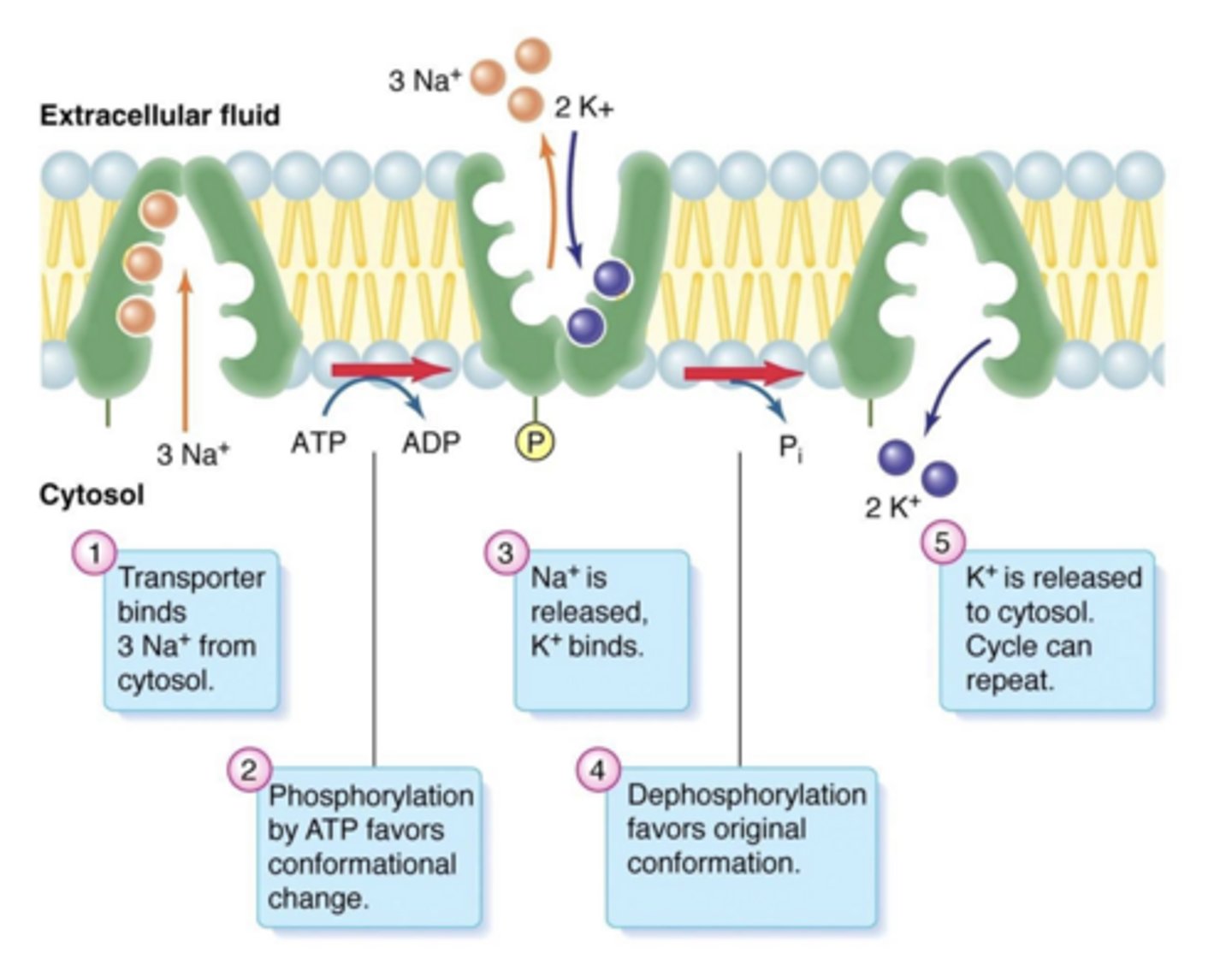
How does the Na⁺/K⁺ pump contribute to membrane potential energetics?
it creates potential energy via active transport against ion gradients
What is the effect of inhibiting the Na⁺/K⁺ pump (e.g., digoxin)?
reduced cellular polarization (depolarizing effect)
What is an action potential?
a brief reversal of the resting membrane potential used for neuronal signaling
What are the four phases of an action potential?
threshold, depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization
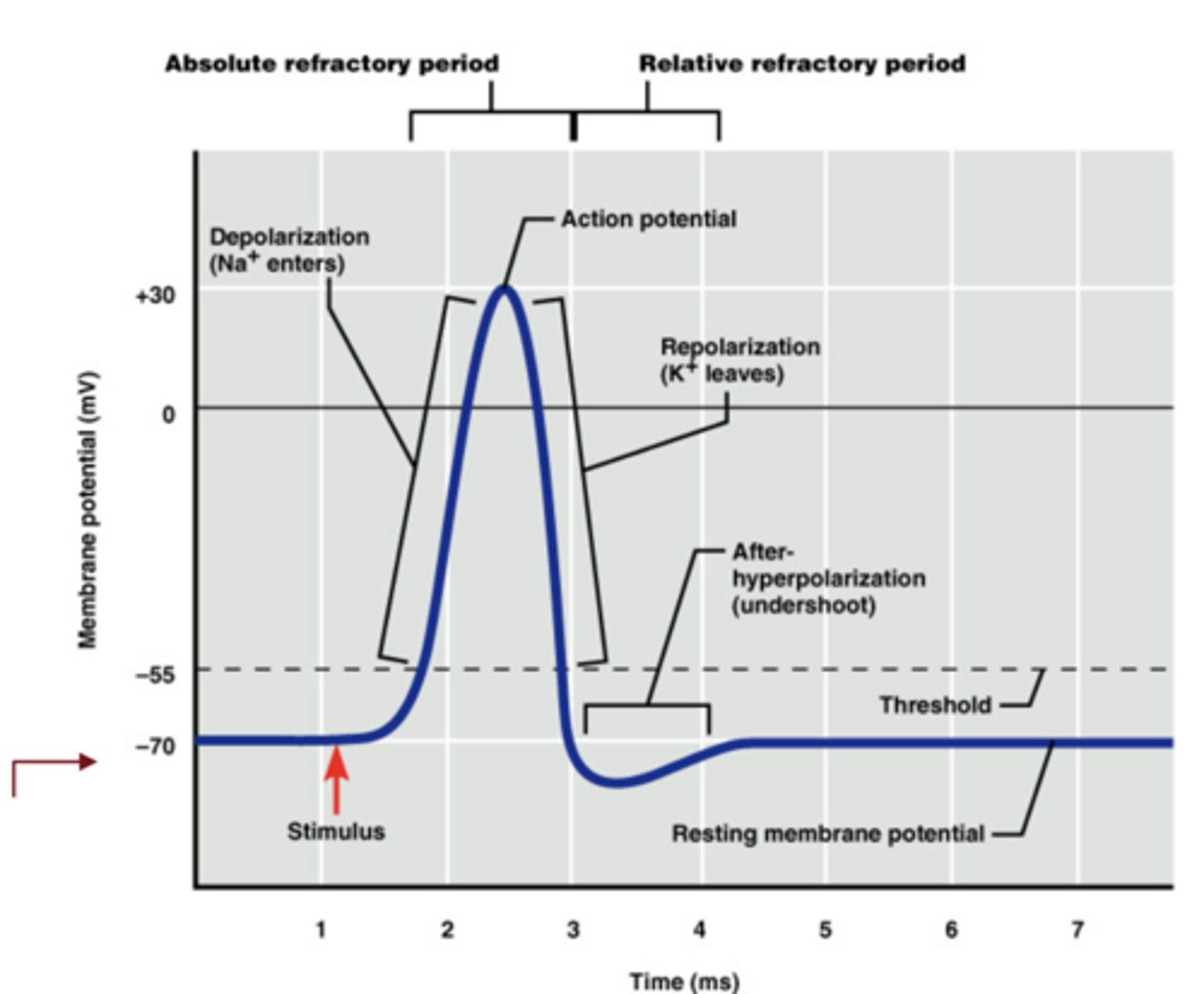
What ion movement drives the depolarization phase?
opening of voltage-gated Na⁺ channels and Na⁺ influx
What ion movement drives the repolarization phase?
opening of voltage-gated K⁺ channels and K⁺ efflux
How do Na⁺ and K⁺ conductance differ during an action potential?
Na⁺ conductance rises rapidly and briefly
K⁺ conductance rises more slowly and lasts longer
Which voltage-gated channels are involved in neuronal signaling?
Na⁺, K⁺, Ca²⁺, and Cl⁻ channels
How does an action potential propagate along an axon?
local Na⁺ influx depolarizes adjacent membrane segments, opening more Na⁺ channels
Why do local anesthetics block nerve conduction?
they block voltage-gated Na⁺ channels, preventing action potential propagation
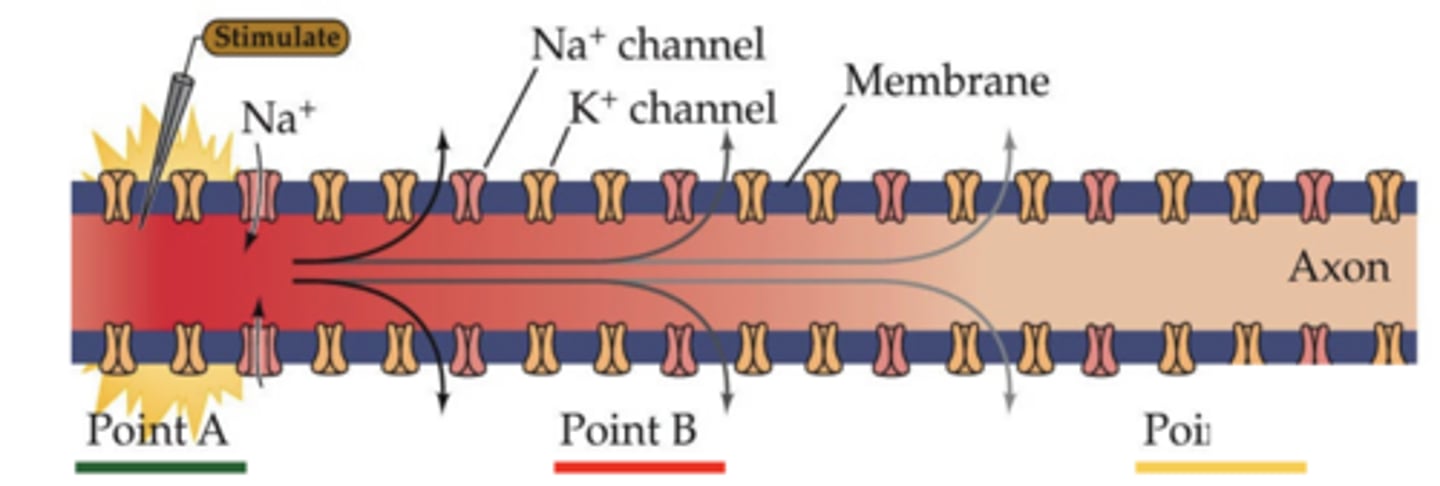
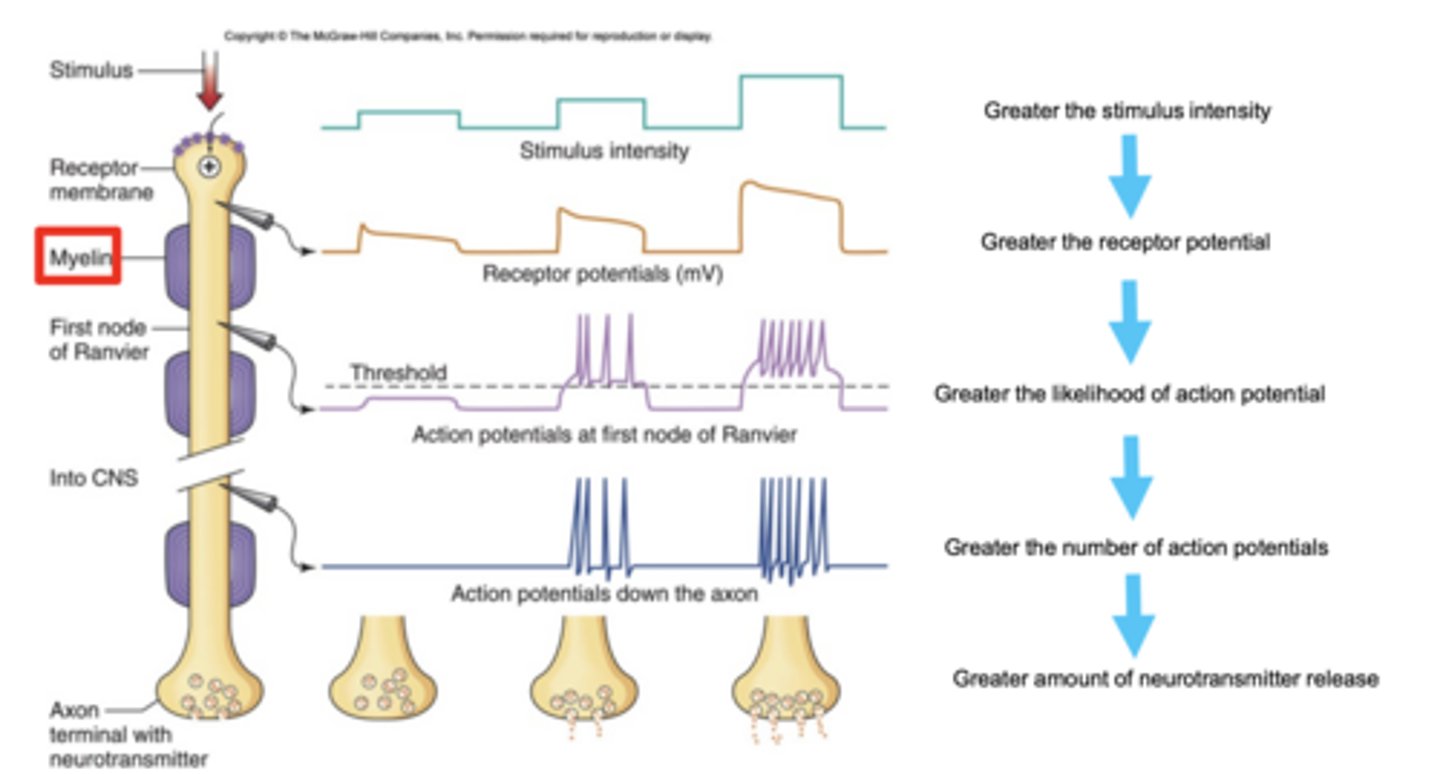
How does stimulus intensity affect neurotransmitter release?
stronger stimuli → more action potentials → greater neurotransmitter release
Which cells produce myelin in the CNS vs PNS?
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Schwann cells (PNS)
How does myelin increase conduction speed?
it forces current to jump between nodes of Ranvier (saltatory conduction)
What disease results from demyelination and why is conduction impaired?
Multiple sclerosis; current leaks and fails to reach threshold at downstream nodes
What triggers neurotransmitter release at the synapse?
an action potential invading the presynaptic terminal
What ion is essential for synaptic vesicle fusion?
Ca²⁺ influx into the presynaptic terminal
What are SNARE proteins and why are they important?
they mediate vesicle docking and fusion during neurotransmitter release
How does botulinum toxin (Botox) affect neurotransmission?
it disrupts SNARE-mediated vesicle fusion, blocking neurotransmitter release
What are sites on which neurotransmitters are released?
neurons, glands, organs, and muscles
What receptors mediate postsynaptic signaling?
ligand-gated ion channels and GPCRs
How does excitatory neurotransmission affect the postsynaptic neuron?
depolarizes it via Na⁺ or Ca²⁺ influx to reach action potential threshold
How does inhibitory neurotransmission affect the postsynaptic neuron?
hyperpolarizes it via Cl⁻ influx or K⁺ efflux, preventing action potentials
What are the major presynaptic targets where drugs can alter neurotransmission?
1. synthesis
2. transport
3. APs
4. vesicular storage
5. neurotransmitter release
6. presynaptic receptors
7. neurotransmitter reuptake
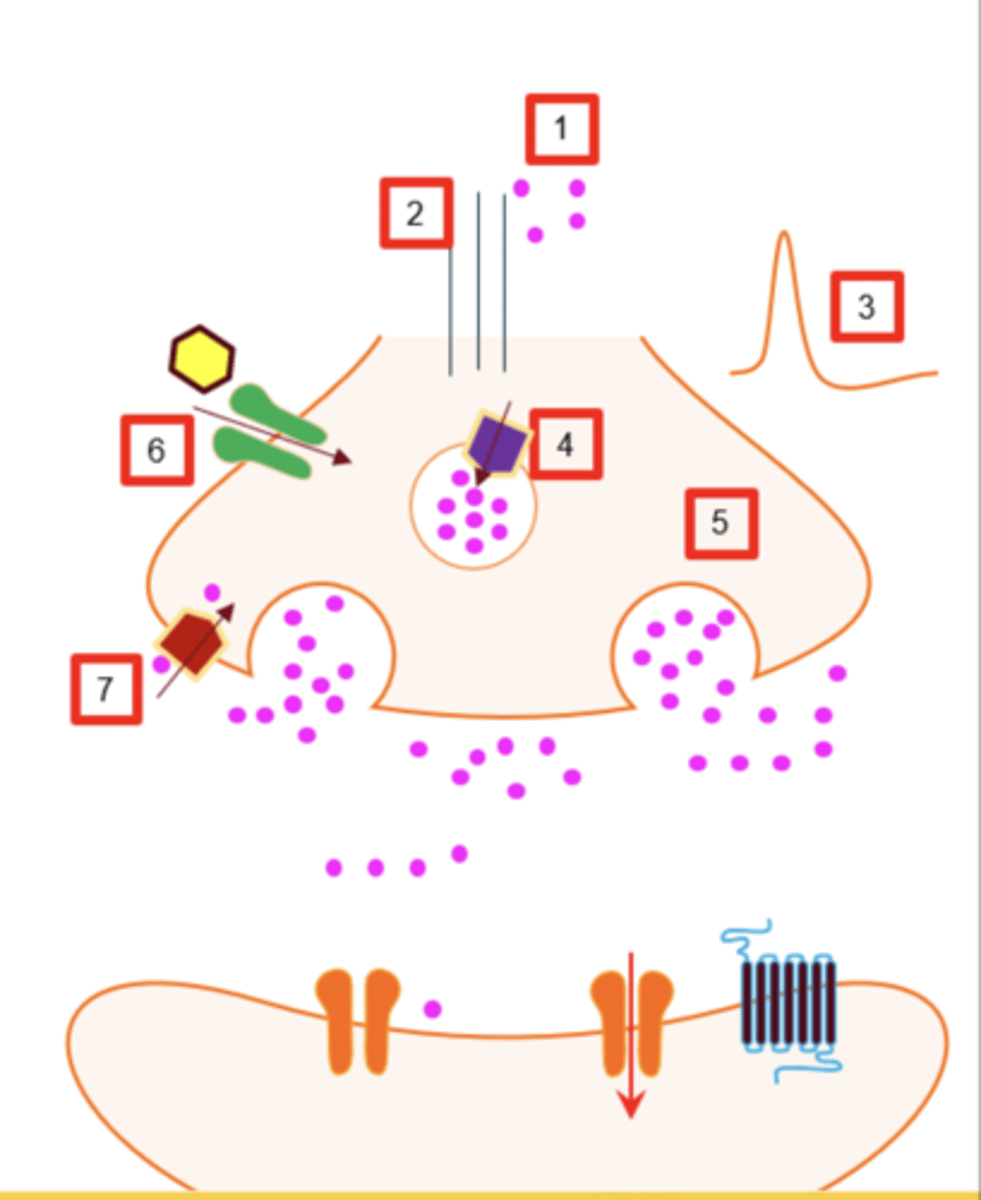
What are the major postsynaptic mechanisms by which drugs affect neurotransmission?
1. transmitter inactivation
2. # of receptors
3. blockade receptors
4. activation/modulation of receptors
5. second messengers
What are the two major classes of neurotransmitters?
small-molecule neurotransmitters (amino acids, biogenic amines, Ach, and purines) and neuropeptides (proteins)
