Medieval Europe - APAH
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Antique Rome
2nd Century - 8th Century
Constantine the Great adopts Christianity
Edict of Milan 313 - ends Christian persecution
says its OK to be Christian, but does not make it the main religion
Art is more STYLIZED, less Greek idealized naturalism

“Santa Sabina” Rome, Italy; 430 CE; Antique Rome; Brick, stone, wooden roof
Basilica Plan (Forum of Trajan) → originally, Basilica Ulpia = SECULAR law court → Basilica plan turned into a sacred church
SPOILA - reused Roman capitals and bricks
Roman influences - Corinthian columns, roman barrel arches
Built on TOP of Temple of Juno
Amun-Ra influence - Clerestory, focuses light on nave
Originally contained mosaics- illustrated stories from the Bible
the mosaics reflect light, symbolizing the spiritual nature of Jesus being the light
Look in binder for the architecture plan

“Catacomb of Priscilla” Rome, Italy; 200 CE; Antique Rome
Catacomb = underground burial chambers (groups)
5 miles of chambers, 40k tomb
land donated by wealthy Roman woman named Priscilla
Buried underground because they needed space to bury people due to the Christian practice of burying dead bodies
Contains earliest known Christian Artwork
We know Christian artworks were being made before, but Christians were persecuted before, therefore the artworks likely didn’t survive or were kept secret
Frescoes - made PERMANENT paint/paintings/art
More stylized and narrative-focused
Artwork made by PRIEST (Priests had power and could read, therefore they were the ones to read the stories in the Bible and the ones to draw the stories)
Content - Christ’s death, resurrection, and with Madonna (Mary)
Greek roundels
Check Venn Diagram in binder

Byzantine Empire
Roman capital moved to Istanbul, renamed Constantinople
Justinian I takes throne 527-565
Population is newly mobile
Orthodox Christianity is official state religion
You HAVE to be Christian
MASSIVE building projects - churches
propaganda =— large, visible

“San Vitale” Italy; Byzantine; 530 CE
Built on the grounds of martyr St. Vitalis
Construction sponsored by local banker and architect Argentarius
to show piety
Function - martyrium, church, relic, visitation (circumbulation)
Didactic art - educate illiterate public
Central plan - looks like the Pantheon
central plan allows the travelers/pilgrims to walk around the surrounding aisle to visit the relics
MOSAICS - reflect light, enhance spiritual experience of pilgrims
Central plan, more windows to let in more light
Vines and nature - represents heaven
MOSAIC; VISUALS:
Gold background - timelessness, divinity
Frontal view
Overlapping figures
Stylize figure, individualized faces
HOTI - (Justinian I) center, grown, purple, fibulae, holds a bowl for the Eucharist, military power (soldiers), halo
FUNCTION - Asserts POWER of Justinian, even if not physically present in Ravenna, Italy -PROPAGANDA


“Hagia Sophia” Constantinople, Turkey, 530 CE
Central plan
Built to rival Jewish Temple of Solomon
PENDENTIVE - dome on a square of arches
Floating halo of light
Huge central plan space- filled with light
Filled with Mosaics
VISUAL: Didactic art = educates illiteratie public
Frontal View
Focus on the narrative
Stylized
Later turned into a mosque from the conquering Ottoman Turks who practiced Islam
Qibla placed near the apse, but it was off-center to point towards Mecca

“Merovingian Looped Fibulae” Medieval Europe; 6th century; gilt metal
Fibulae = brooch to fasten clothing and was originally worn by Roman soldiers to fasten cloath
Establishes status
Semi-circle shape represents a victory wreath, specifically victory over death, symbolizing the resurrection of Jesus
Fish is a symbol of Christianity and Jesus
Cloissone - inlaid with semi-precious stones
establishes status, precious stones and gold
Symbol of status for mobile population
People can go visit other places, and a brooch can communicate a visiting person’s status
Fibulae - typical cross and cross-bow shape

“Virgin (Theotokos) Mary and Child between Saints” Byzantine EMpire; 6th century; Encaustic on wood
Encaustic = wax painting on wood, allowed for mobile art; This is the beginning of the use of encaustic
Previously, frescoes were used for its permanence, but it was used on walls and not portable, thus encaustic was an upgrade because it allowed for portability
Theotokos - Virgin Mary enthrone with baby Jesus
sitting on a gold chair
Icon - small portable painting depicting sacred figures; private worship; healing powers
people would privately pray in their homes to these icons that were believed to have healing powers → People no longer went to churches, thus no longer giving donations to the church. Additionally, it was believed that it was a sin to pray to these icons because it was a sin to worship graven images
STARTS ICONOCLASM
Eyes = stylized and functioned to receive prayers and send it to heaven
Evidence of Roman ideals

“Vienna Genesis” Byzantine Empire; 6th century; Illuminated Manuscript
Story = “Jacob Wrestling the Angel” - Jacob becomes Israel
Continuous narrative - Jacob is travelling with his family to Canaan. However, after crossing the river, he wrestles an angel. After the struggle, he emerges righteous and changes from Jacob to Israel
Codex - first book, elimnates scrolls
Greco-Roman = contrapposto stance, curvilinear, drapery
Assembly line of artists worked to create it
Illuminare - to make ornate
Vellum dyed with purple, lined with silver ink
Vellum = an old form of paper made form animal hide, but was expensive. THUS, the use of vellum shows wealth AND piety

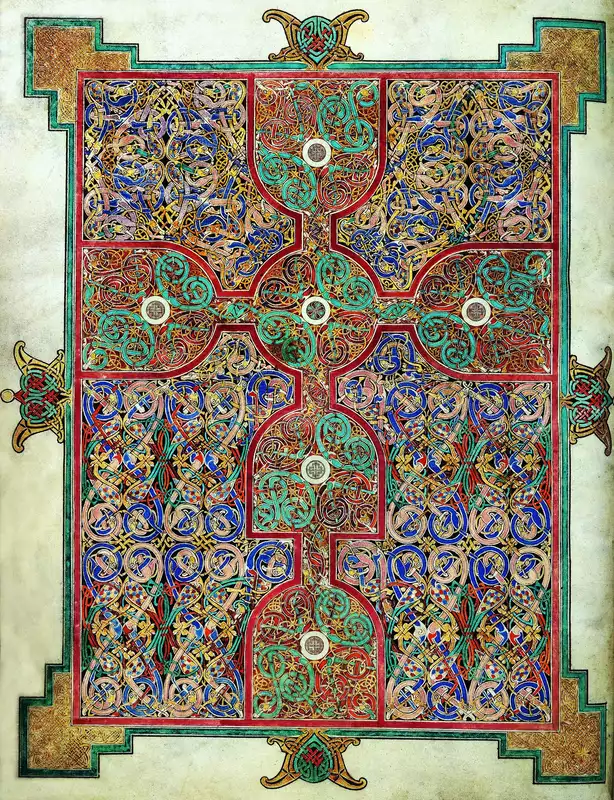
“Lindisfarne Gospels” Hiberno-Saxon
Conversion - books and luxury items
looks successful
Lindisfarne Island - off coast of Britain
Placed at altar in church - legitimized transactions
domestic/secular (real estate, marriage) events turned sacred
Like Lady Xoc in a way taht it turned a political event sacred (husband Shiled Jaguar becomes King
Interlacing lanes - references Celtic work
Completed by ONE monk over 6 years - meditation
970 CE - contains earliest surviving English translation of the bible
Zoomorphic - animal and animal
Blue = royalty
Red = the wine that → Blood of Christ through transubstantiation
Cross made of wine goblets - represents the Eucharist

Romanesque Europe
800-1200 CE
Increased travel from pilgrimage routes
more international style - things become homogenized
Influenced by Roman culture

“Bayeux Tapestry” Romanesque Europe; 1066
Embroidery - made by women
Norman (France) conquest of England
William (Norman) vs Harold (England)
Patron - Bishop Odo (Will’s half brother)
History from viewpoint of the victor - William of Normandy → BIAS → not entirely historically accurate
HISTORICALLY ACCURATE PARTS:
- the 11th century dining practices
-military armor (like Night Attack)
Tapestry popular in medieval times because it’s portable, making them practical for the mobile population

“Church of St. Foy” Romanesque; Conques, France; 11th century
Located along the pilgrimage route of Santiago de Compostela
Church built BEFORE it had a relic
people would stay and donate
nearby church had a relic of Saint Foy → That church was dilapidated and on the outskirts of the route, so people didn’t visit that church often either → monks from Conques steail it at night
68 feet high Barrel with a vaulted nave
1: lets in LIGHT
2: Makes you look towards the heavens
3: echoed the choir’s magical singing, enhancing the spiritual experience
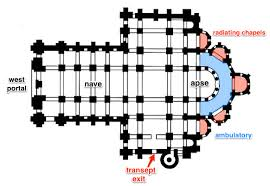
Cruciform plan - adds transepts where a pilgrim can enter through a side door and go behind the apse to visit the relics (and drop off offerings), then leave through the other transept without disturbing the nave

Tympanum of Last Judgement faces courtyard
Jesus' hands go up and down, representing heaven and hell
Parishioner’s have a CHOICE - pay offerings to go to heaven or do not and go to hell
Devil is ALSO a judge
each sinner represents a sin to avoid - adultery, gluttony, abuse of office, etc.

Reliquary of St. Foy
Saint Foy is a martyr
Saint Foy was a 12 year old girl who was killed from Roman persecution of Christians. She was arrested, tortured with a hot brazier, and finally beheaded. However, even while being tortured, Saint Foy never surrendered her faith, demonstrating her religious devotion to Christianity
Her reliquary was originally in Agen but stolen by monks from Conques in order to attract more welath and visitors
Bernard Angers first spoke about this reliquary in 1010 and expressed his concern about idolatry, where the pilgrims would worship the reliquary for its jewels and beauty rather than its contents and what it represented
pilgrims donate gemstones → dress covered in different gems
Head thought to have been the head of a Roman statue of a child → spoila → made object more important by associating it with past riches of Roman Empire
Common belief: reliquary cannot be relocated unless saint gives permission → its relocation to Conques was seen as Saint Foy’s willingness to be moved → Conques gains influx of pilgrims
Lamb and crucifix represent sacrifice
GOTHIC PERIOD
12th-16th century
Gothic Period the derogatory term from later Renaissance artists, means “ugly and non-classical” (classical = Greco-Roman)
Economic prosperity due to pilgrims → invest in churches
Emphasis on morality → biggest and nicest building in a town is usually the church
Renovation of St. Denis kickstarts stained glass, highly ornate, and asymmetrical church design

“Chartres Cathedral” French Gothic; 12th century; Limestone and stained glass
Asymmetrical, highly ornate
looks interesting, captures attention
Built on a Roman Temple
like Santa Sabina
Relic - Virgin Mary’s tunic
leads to Rise of Cult of Mary → artwork more feminine- seen in the floral designs and rose windows
Perpendicular style; emphasized verticality
Original church built in 7th century; burned down in 1194
Tunic miraculously survives after going missing for 4 days → leads people to believe that the tunic truly is a divine relic
Cruciform plan - enter through transept, go visit relics behind the apse, leave offerings (typically monetary), leave through other transept. This plan and process allowed the pilgrims to not disturb the nave
Golden Ratio - perfect proportion, Represents Gods PERFECT creation in the universe
The Golden Ratio often seen in nature, and nature was created by God
Groin Vault
Flying Buttresses - support large building, allows light through the stained glass
Key Gothic Visuals - ELONGATED FIGURES
Individualized saints → focus on the narrative→ for the illiterate public→ NOT to educate (stories of the Bible are known by now), INSTEAD it is for the illiterate public to recognize the Saints
NEW CONCEPT: LUX NOVA (lux = light; nova = new): transforms the light of God like a projector → colored light
pilgrims described the feeling as being inside a jewelry box
Enhance spiritual experience of pilgrims
Tracery = sacred geometry
Blue = represents royalty → Virgin Mary, who is depicted with a crown, is the Queen of Heaven
Rose Window = sacred femininity
Pointed arch = leads the eye up and stops to the eye looking up to the heavens
Roman Barrel differs because it goes up but then down instead of staying up
