Comprehensive Review of Respiratory, Hematologic, and Oncologic Conditions for Nursing
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What is the primary assessment focus in chest trauma?
Meticulous respiratory/chest assessment and monitoring ABC's (hypoxemia and hypovolemia).
What are the risks associated with rib and sternal fractures?
Laceration to organ risk and the need for conservative treatment.
What is a critical management strategy for pain in chest trauma?
Manage pain to prevent atelectasis.
What defines flail chest?
Multiple rib fractures at two or more sites leading to chest wall instability and respiratory distress.
What is the treatment approach for flail chest?
Supportive care, possible ventilation, and surgery for severe cases.
What is a pulmonary contusion?
Hemorrhage and tissue edema in the lung, requiring airway maintenance and pain control.
What is a pneumothorax?
The presence of air in the pleural space.
What is the incubation period for SARS-CoV-2?
Up to 14 days, with an average onset of symptoms at 4-5 days.
What are common symptoms of COVID-19?
Fever, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, and loss of taste or smell.
What diagnostic tests are used for COVID-19 monitoring?
Chest X-ray, CBC with differential, CMP, lactate, CRP, D-Dimer, ECG, MEWS scoring, swab, and antibody tests.
What is the recommended treatment for COVID-19?
Supportive care, supplemental oxygen, and management of ARDS.
What is the purpose of prone positioning in ARDS treatment?
To improve oxygenation and lung mechanics.
What antiviral therapies are recommended for COVID-19?
Paxlovid and molnupiravir; monoclonal antibody Bamlanivimab for early diagnosis and outpatient use.
What is pulmonary edema?
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in interstitial spaces and alveoli, often associated with heart failure.
What are the clinical manifestations of pulmonary edema?
Shortness of breath, low oxygen saturation, and abnormal lung sounds upon auscultation.
What defines acute respiratory failure (ARF)?
PaO2 < 60 mmHg, PaCO2 > 50 mmHg, and pH < 7.35.
What are the underlying causes of ARF?
Ventilation and/or oxygenation failure due to trauma, neurological issues, or other conditions.
What is the role of mechanical ventilation?
To maintain ventilation and oxygenation in cases of respiratory failure or airway compromise.
What is the difference between positive-pressure and negative-pressure ventilators?
Positive-pressure ventilators inflate the lungs using positive pressure, while negative-pressure ventilators create a vacuum to assist breathing.
What is the nursing role in managing patients on mechanical ventilation?
Assessing LOC, ABGs, pulse oximetry, vital signs, lung sounds, and skin color.
What is the significance of the ABG values in respiratory assessment?
They help determine the acid-base balance and respiratory function of the patient.
What is the expected auscultation finding in a patient with pulmonary edema?
Crackles or wheezing due to fluid accumulation in the alveoli.
What are the goals of care in respiratory conditions?
Early intervention, infection prevention, and supportive care.
What is the recommended cuff pressure for an endotracheal tube (ETT)?
20 to 30 mmHg
What are the key components of ventilator settings?
Mode, tidal volume/rate settings, FiO2, inspiratory-to-expiratory ratio, PEEP
What nursing interventions can help prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)?
Daily oral care, maintaining proper ETT and vent tubing position, and turning/repositioning the client.
What does the ABCDEF Bundle stand for in ICU care?
Awakening, Breathing (SBT), Coordination/Choice of analgesia, Delirium (CAM-ICU), Early mobility, Family engagement.
What is the purpose of the VAP Bundle?
To reduce the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia through specific interventions like elevating the head of the bed and daily sedation vacations.
What is a common complication associated with mechanical ventilation?
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) or ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI).
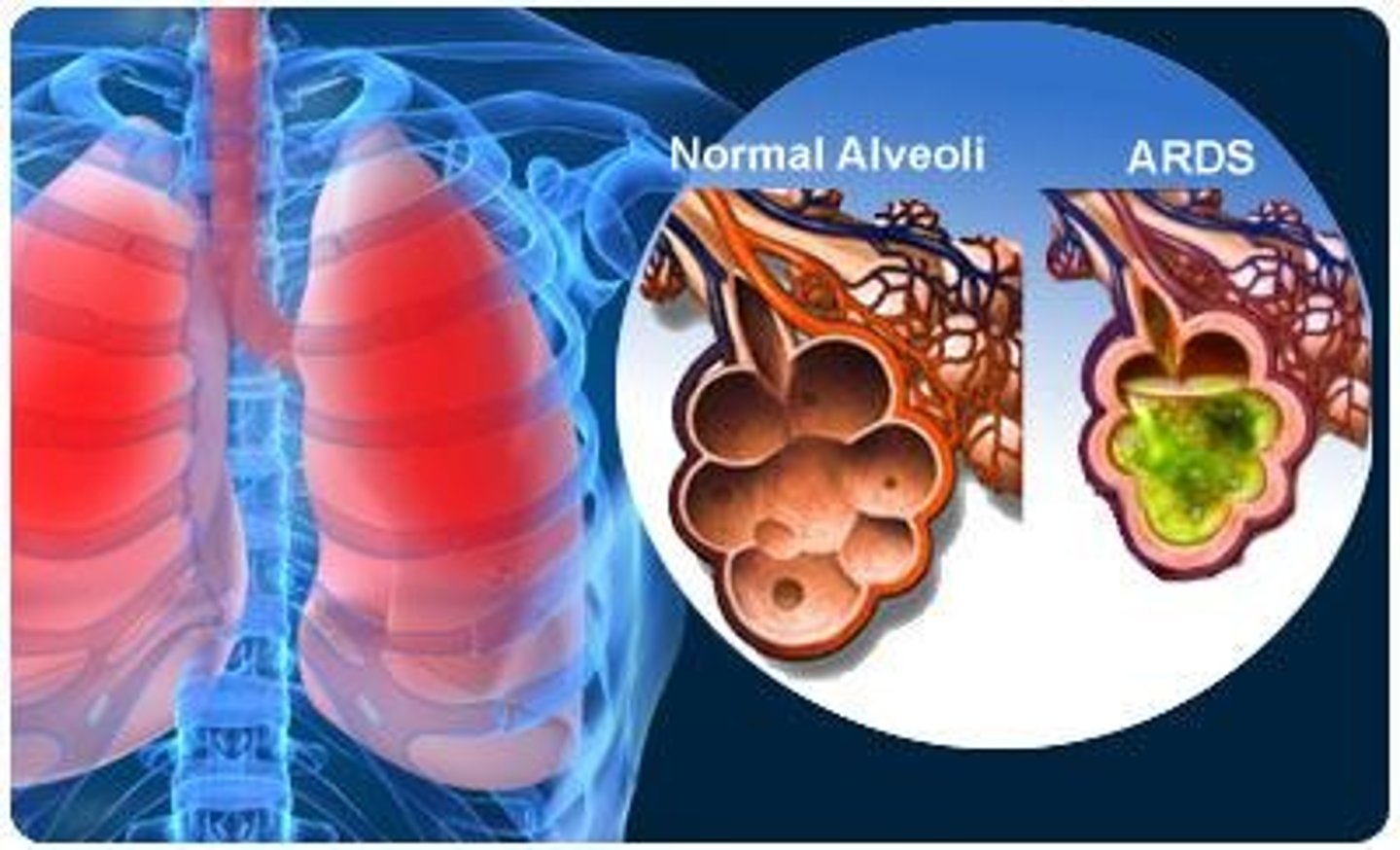
What are the manifestations of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)?
Progressive hypoxemia, respiratory distress, tachycardia, tachypnea, and crackles.
What is the Berlin Criteria used for?
To classify the severity of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS).
What is the primary medical management for ARDS?
Identification and treatment of the underlying cause, aggressive respiratory support, and intubation with mechanical ventilation.
What is the role of PEEP in mechanical ventilation?
PEEP helps to keep the alveoli open and improve oxygenation but may cause the patient to fight the ventilator.
What should be monitored closely during weaning from mechanical ventilation?
Respiratory changes, exhaustion, changes in condition, and ability to clear secretions.
What is a unique characteristic of ARDS?
It is characterized by non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema and severe ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch.
What pharmacologic measures are used in the management of ARDS?
Supportive measures including inotropic/vasopressor support, analgesics, sedatives, and neuromuscular blocking agents.
What should be done if a patient with ARDS has low oxygen saturation despite supplemental oxygen?
Intubate the client and control breathing with mechanical ventilation.
What is the significance of daily sedation vacations in ICU care?
They help assess the patient's readiness for extubation and reduce sedation-related complications.
What is the importance of communication with the patient and family during mechanical ventilation?
To keep them informed about the plan of care, provide support, and help navigate complex medical terminology.
What are the potential effects of implementing the ABCDEF Bundle in ICU patients?
It can reduce the prevalence of delirium in intensive care unit patients.
What is the role of bronchodilators in mechanical ventilation?
To promote airway patency and improve ventilation.
What is the purpose of humidification in mechanical ventilation?
To maintain mucosal integrity and prevent airway dryness.
What factors influence the time it takes to wean a patient from mechanical ventilation?
Patient's condition, ability to breathe independently, and need for respiratory support.
What is the significance of monitoring lung sounds and ABGs in ventilated patients?
To assess respiratory function and detect complications early.
What is the primary goal of nursing care for clients with ARDS?
To ensure effective respiratory support and monitor for changes in condition.
What is the origin of the hematologic system?
It originates in the hematopoietic stem cell, either from the myeloid or lymphoid stem cell.

What are the three main types of hematopoietic malignancies?
Leukemia, Lymphoma, and Multiple Myeloma.
What is Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)?
A defect in the hematopoietic stem cell that differentiates into all myeloid cells; it is the most common nonlymphocytic leukemia.
What are common manifestations of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)?
Fever, infection, weakness, fatigue, bleeding, bone pain, gum hyperplasia, and petechiae.
What is the treatment for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)?
Aggressive chemotherapy (induction therapy) and hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
What characterizes Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)?
A mutation in the myeloid stem cell leading to uncontrolled proliferation of cells.
What is the common treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)?
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (imatinib), chemotherapy for acute phase, and stem cell transplant.
What is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)?
Uncontrolled proliferation of immature lymphoblasts from the lymphoid stem cell, common in young children.
What are the manifestations of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)?
Pain from enlarged liver/spleen, bone pain, CNS symptoms like headache and vomiting.
What is Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)?
A common malignancy of older adults characterized by a malignant clone of B lymphocytes.
What are the 'B symptoms' associated with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)?
Fever, night sweats, and unintentional weight loss.
What is the average survival time for patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)?
Survival varies from 2 to 14 years depending on the stage.
What is Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)?
A disorder of the myeloid stem cell causing dysplasia, commonly in erythrocytes.
What are common treatments for Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)?
Bone marrow stimulating agents, blood transfusions, immunosuppressive therapy, and iron chelation therapy.
What is Hodgkin Lymphoma characterized by?
The presence of Reed-Sternberg cells and a high cure rate.
What are common manifestations of Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Painless lymph node enlargement, B symptoms, fatigue, pruritis, and anemia.
What differentiates Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) from Hodgkin Lymphoma?
NHL is more common, has unpredictable spread, and is associated with various risk factors.
What are the clinical manifestations of Multiple Myeloma?
Hypercalcemia, renal dysfunction, anemia, and bone destruction.
What is the primary treatment for Multiple Myeloma?
There is no cure; treatment focuses on managing symptoms and complications.
What are the major complications associated with leukemia?
Neutropenia, bleeding (thrombocytopenia), stomatitis/mucositis, and fluid/electrolyte imbalances.
What is the purpose of a Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (SCT)?
To collect hematopoietic stem cells for treatment, either from the patient (autologous) or a donor (allogeneic).
What is Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)?
A complication of allogenic transplants where donor lymphocytes attack the patient's tissues.
What triggers Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)?
Sepsis, trauma, cancer, shock, and other underlying disorders.
What is the first step in treating DIC?
Treat the underlying cause to improve tissue ischemia.
What are the signs of acute toxicity during a transplant?
Nausea, vomiting, severe diarrhea, mucositis, and hemorrhagic cystitis.
What nursing interventions are appropriate for a patient with acute myeloid leukemia?
Private room, soft bland diet, oral hygiene after meals.