Forces and their interactions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
magnitude
size/distance
displacement
distance moved in a straight line in a given direction
vector
direction+ magnitude
scalar
magnitude
power
rate at which work is done/ energy transferred
force
push or pull on an object (vector quantity)
contact force
when 2 objects are physically in contact with each other
non-contact force
when the objects are not touching
weight
force that acts in mass due to gravity
gravity
force that attracts an object towards the centre of the earth
resultant force
overall force acting on an object taking into account all the forces acting on it
equilibrium
when all the forces acting on an object balance out
work done
energy transferred
forces
push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object
Name as many forces as I can + state if it is contact or non-contact
Friction-contact
gravity- non-contact
upthrust- contact
magnetic- non-contact
weight- non-contact
normal contact force- contact
tension- contact
electrostatic- non-contact
compression- contact
drag- contact
the strong force- non-contact
how to name forces (3marks)
type of force
what the force is acting on
what it is interacting with
e.g force of gravity on the ball from the earth
name vector quantities
force
acceleration
velocity
displacement
name scalar quantities
length
pressure
mass
resistance
work done equation
work done(J) = force(N) x distance (m)
elastic deformation
the object will return to its original shape when the deforming force is removed
inelastic deformation
the object will not return to its original shape when the deforming force is removed
Hooke’s law (law of elasticity)
the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied to it, provided the law of proportionality is not exceeded
extension
length of the material when its force is applied
extension equation
f= kx
force applied on the spring= spring constant x extension of the spring
what is spring constant
measure of stiffness of the spring
What is the required practical for force and extension
investigate the relationship between the weight hung from the spring and the extension
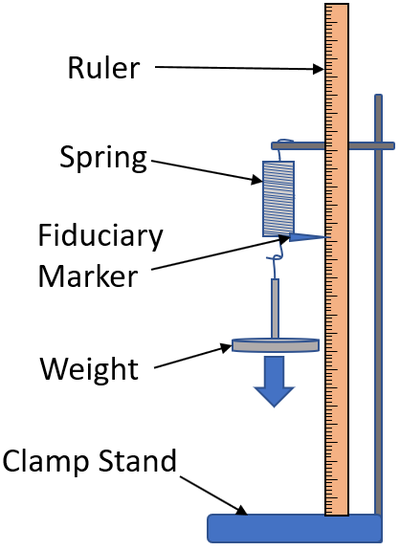
how to find spring constant (from a graph)
1/ gradient
elastic potential energy
the energy stored as a result of deformation of an elastic object, for example the stretching of a spring
elastic potential energy equation
Ee= ½ ke²
elastic potential energy(J) = ½ spring constant (n/m) extension² (m)