UTS: L1-L3
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Philosophy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Philosophy
This means “Love for wisdom”; overachieving inquiry into the nature of humane existence
Philo
This means love in Greek, one of the two words comprising philosophy.
Sophia
This means wisdom in Greek, one of the two words comprising philosophy.
Socrates
Athenian Philosopher. Father of westdsrn Philosophy. He was mainly concerned with the problem of the self. He believes that the true task of philosophers is to know oneself.
Socrates
He believed that every man is composed of body and soul. Every human person is dualistic.

Body
The imperfect, impermanent (changing) aspect of humans.

Soul
The perfect and permanent aspect of humans.
Rene Descartes
The Father of Modern Philosophy; believed that the human is a thinking being.
“COGITO ERGO SAM”= I think therefore I am.

3 types of soul/self
Rational Self/Soul
Appetitive Self/Soul
Spirited Self/Soul
Rational Self/Soul
A soul that is forged by reason.
Appetitive Self/Soul
Soul in charge of base desires (basic biological needs to survive)
Spirited Self/Soul
Soul in charge of emotions
John Locke
The Father of Modern Philosophy; believed that the human is a thinking being.
“COGITO ERGO SAM”= I think therefore I am.

David Hume
An emperisist who believed that one can know only what comes from senses and experiences.
He argued that there is no self. To him, self is but a bundle of impressions.

David Hume
Scottish; An emperisist who believed that one can know only what comes from senses and experiences.
He argued that there is no self. To him, self is but a bundle of impressions.

Impressions
The basic objects of our experience or sensation.
Ideas
Mere copies of impressions
Immanuel Kant
German; He believed tht we construct the self via experience.
Philospher in the age of enlightenment

Psychology
The study of the soul/mind.
Psycho
This means soul or mind
Logos
This means study.
Carl Jung
Proposed the archetypes and that self-realization is the process of attaining self.
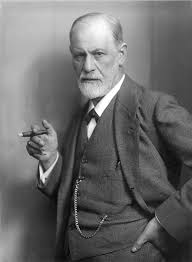
Id
The pleasure principle
Ego
Reality principle
Super-ego
Morality principle
Freud's Psychosexual Theory of Development
Oral
Anal
Phallic
Latency
Genital
Oral Stage
Stages Birth-12 months; Mouth
Anal Stage
1-3yrs; Anus
Phallic
3-6yrs; Gender Identification
Oedipus complex
Son's sexual attitude towards his mother and concomitant hostility toward his father

Electra complex
A girl's psychosexual competition with her mother for possession of her father.

Latency Stage
6-puberty; sexual impulses are repressed, leading to a period of relative calm.
Genital Stage
Puberty-adulthood; forming intimate relationships
Defense Mechanisms
unconscious resources used by the ego to decrease conflict within themselves, specifically between the superego and id. (They did not get what they want, basically)
10 Defense Mechanisms
Repression
Denial
Regression
Projection
Displacement
Reaction Formation
Rationalization
Sublimation
Introjection
Fixation
DM: Repression
Hiding feelings instead of confronting
DM: Denial
Refusal to accept reality
DM: Regression
Reverting to less mature thinking
DM: Projection
misattributing uncomfortable feelings to the other person.
DM: Displacement
Shifting blame to someone weaker
DM: Reaction Formation
Adaptation of views opposite of own/recognize how they feel, but they choose to behave in the opposite manner.
DM: Rationalization
Justification to please unpleasant feelings.
DM: Sublimation
Redirect strong emotions or feelings into an object or activity that is appropriate and safe.
DM: Introjection
Incorporating positive actions of another person to own ego.
DM: Fixation
Excessive attention to something
Carl Jung
Swiss; Proposed the archetypes and that self-realization is the process of attaining self.

Archetypes
Ancient images that derive from collective unconscious. Mainly expressed through dreams
Erik Erikson
A German-American psychoanalyst who made the Psychosocial Development Theory.
He recognized for the phrase ”identity crisis.”
Shadow
Darker side, Sex and life instincts
Anima/Animus
Masc/Fem aspects
Carl Rogers
Psyche
Erik Erikson
A German-American psychoanalyst who made the Psychosocial Development Theory.
He recognized for the phrase ”identity crisis.”

Psychosocial Development Theory
Stage 1: Trust vs. Mistrust (Infancy from birth to 18 months)
Stage 2: Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (Toddler years from 18 months to three years)
Stage 3: Initiative vs. Guilt (Preschool years from three to five)
Stage 4: Industry vs. Inferiority (Middle school years from six to 11)
Stage 5: Identity vs. Confusion (Teen years from 12 to 18)
Stage 6: Intimacy vs. Isolation (Young adult years from 18 to 40)
Stage 7: Generativity vs. Stagnation (Middle age from 40 to 65)
Stage 8: Integrity vs. Despair (Older adulthood from 65 to death)
Carl Rogers
American; Composed the Self Theory, where there is a real self and an ideal self.

Real Self
This is the self of who and what we really are

Ideal Self
The self that we expect ourselves to be, what we are not.

Self Image
View of the self in terms of weaknesses and strengths
Self Esteem
Positive and Negative thoughts about self
George Herbert Mead
Symbolic Interaction Theory. Believes in the social self that develops through interaction.
Sociology
the scientific study of human society

Society
A group of people, interacting, living atst in one place

Culture
This plays a vital role in self-development. Distinct and unique to parts of the world.

George Herbert Mead
American; Symbolic Interactionism Theory. Believes in the social self that develops through interaction.
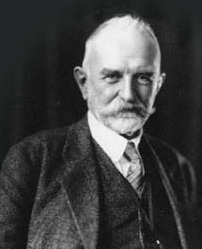
Symbolic Interactionism Theory
Importance of language and other symbols in human interactions
Preparatory Stage
Mimicy
Play stage
Role play
Leon Festinger
Consider myltiple roles
Significant Others
Influencive
Game stage
American; Looking glass self where it is how you asses urself based on others perspectives.

Self labelling
Vonsisten labeling
Leon Festinger
Amwrcian, Made the Social Comparison Theory, where the self is influenced by downward and upward social comparisons.

SCT: Downward Social Comparison
Compare self with lower which is ego boosting
SCT: Upward social comparison
compare self with higher; boosts motivation
Henri Tajfel & John Turner
made the Social Identity Theory. “Where do u belong?” social groups basically

Ervin Goffman
Self Presentation Theory; how u present urself to others.

Self-Presentation Theory
Ingratiation: 👍👍
Intimidation: ಠ_ಠ
Exemplification: ( ̄︶ ̄)↗
Supplication: <( _ _ )>
Self-Promotion: ╰(*°▽°*)╯
Geert Hofstede
Dutch psychologist. Individualism vs Collectivism

Individualism
Independency and self- reliance; relying on others is shameful.
Collectivism
All for one, one for all. Everyone supports each other!

Self-Realization
To Jung, this is the process of attaining selfhood
Selfhood
This means enabling all the psychological components to work in harmony and unity.