Biodiversity and Conservation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
4 ways to measure biodiversity
Species diversity
Genetic diversity
Endemic species (only here)
Ecosystem diversity
Benefits of biodiversity
Intrinsic: They have a right to exists
Economic: Provide essential ecosystem for the global economy
10% US GDP 300 bill to the world 125 trill
Yuan Longping (Heterosis)
Crossed native wild rice with conventional rice
They hybrid rice yeilded almost 30% higher than conventional strains
David Tilman
Planted a bunch of plants different species of perennial grass
After a couple of years the soil fertility and plant biomass increased
Ecotourism
Big business in developing countries
Mass extinction
Late Ordovician (60%)
Late Devonian (50%)
Late Permian (70%)
Late Triassic (50%)
Late Cretaceous (75%)
end of the Cretaceous period
66 million years ago
75% of all plants and animals disappeared
180 kilometer wider crater (Chicxulub) hit Yucatan
Walter Alvarez
Found 1-in layer of iridium
proof of Chicxulub
Conservation Biology goals
Document biodiversity
Understand threats
Develop solutions
Hot spots
High number of endemic species
Must contain > 1500 endemic plants species and at least 70% of its original vegetation coverage
5 major threats to biodiversity
Over harvesting
non-native species
pollution
habitat loss/fragmentation
global climate change
Over harvesting
Atlantic cod overfishing after the 70s and the population dropped in1992
Implement catch limits
Stop fishing cod
Create refuges
Stop recreational fishers from killing cod
Non-native species causing ecological and economic harm
Lampreys kill trout
Emeral Ash borer kills ash trees in north america
Wild pigs damage native plants and create stagnant water
Zebra mussels ….
4 Types of pollution
Air, water, soil, and noise
Habitat fragmentation
Cut up habitats
Costa Rica improved of 65 years
island biogeography
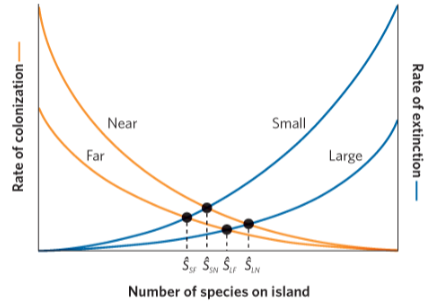
Nick Haddad Corridors
Help connect “islands” formed by habitat fragmentation
Connected plants pollinated
connected
isolated (- seed production)
isolated winded
reduced plot area and increased isolation
indirect relashionship
Types of conservation
In-situ: In natural habitat
Ex-situ : placing them in controlled environments
In-vitro: Conserving genetic material
Royal Chitwan national Park (Nepal)
Balances conservation with local communities
grass harvesting
Success storys
Ball eagle recovery (Chesapeake Bay)
Marine protected areas “spillover”
Ongoing challenges
Amphibian population decline (due to fungus)
Bleaching of coral (algae leave)