control and coordination. concept one. objections
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
By Anthony Hernandez. Bio 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
obj 1) Describe the overall function of the nervous system and summarize the overall process used to accomplish these functions
the nervous system is the control center of the body overseeing all communication among the other organs. It uses sensory input, receives stimuli via millions of sensory receptors throughout the body. Integration processes the input stimuli and decides what should be done. Motor output, activates effector organs to cause a response.
obj 2) differentiate between the two main types of cells that make up nervous tissue.
nerve cells are excitable cells that respond to stimuli by conducting impulses to transmit signals. Glial cells that provide nutrition, insulation, and help with signal transmission.
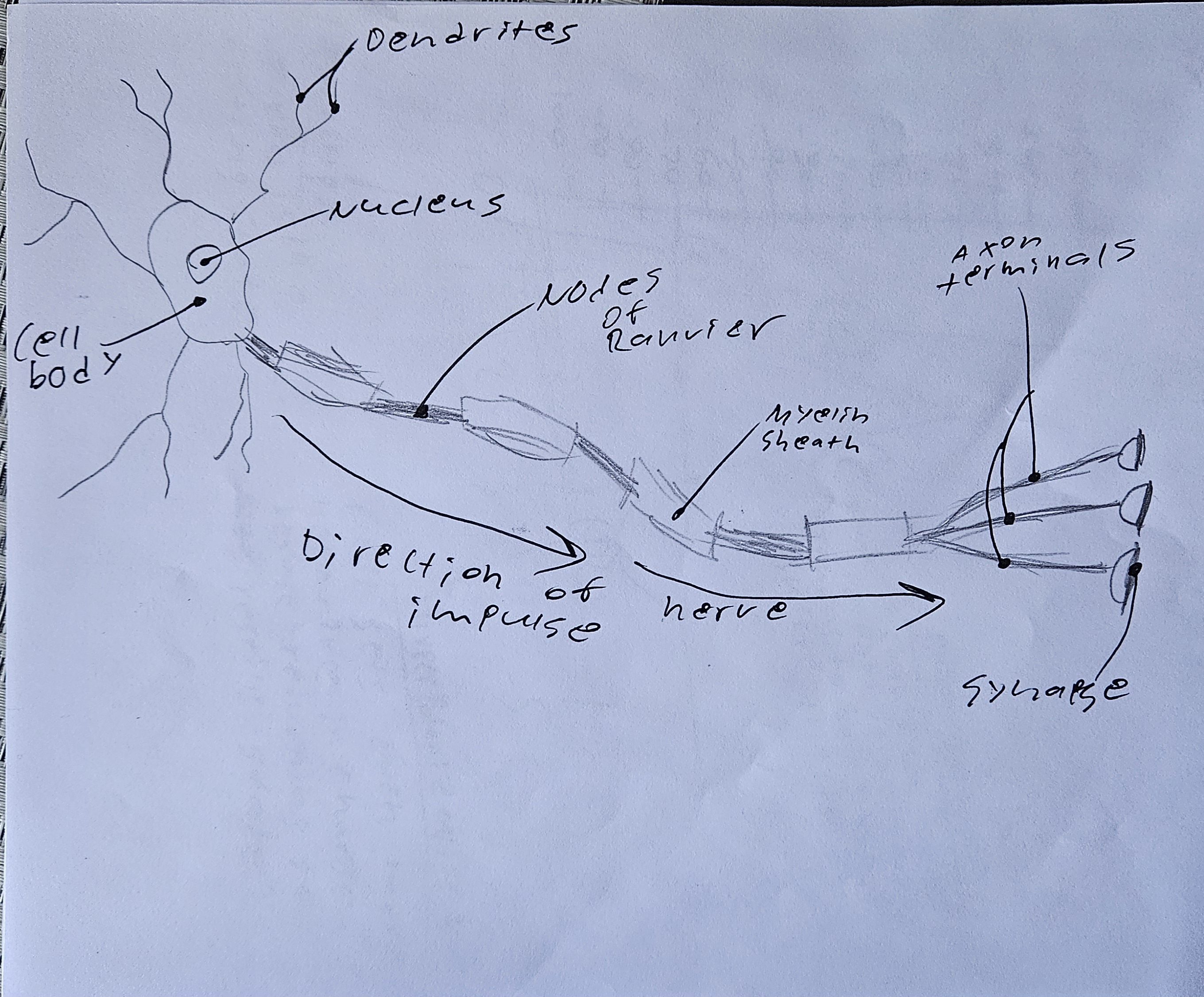
obj 3) draw a picture of a neuron and label its key parts
obj 4) explain how neurons can be classified based on their structure and function
structure:
based on number of processes
multipolar= 3processes. one axon and two dendrites
bipolar= 2 processes. 1 axon and one dendrite
unipolar= 1 process divides from cell body like a T
function:
based on the way an impulse travel through a neuron with regards to brain and spine
sensory neurons= transmit info from sensory receptors to CNS
motor neurons= transport info from CNS to rest of the body
interneurons= housed in CNS. transports info between the sensory and motor neurons. structurally multipolar
obj 5) summarize how a signal is transmitted from one neuron to another, including what happens at a synapse and how to increase the strength of the signal
sensory stimuli is received between the CNS and the rest of the body. motor nerve fibers send out information to the rest of the body. the junction between two neurons is called the synapse, where transfers signals from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron. Acetylcholine is released in order to stimulate contractions and it is even released to the synaptic cleft for stimulation.
obj 6) explain the role of protein channels, specifically including the Na+/K+ pump, in the conduction of a nerve impulse
protein channels act as ion channels to allow specific ions to cross the membrane. the movement of a few ions result in a graded potential. potassium and sodium ions can be positive or negative. the opposite charges attract and create potential energy. The movement of lots of ion exceed the threshold and creates an action potential.
obj 7) difference between the three main ways protein channels can be gated
voltage channels open and close in response to changes in the membrane. ligand gated channels opens when a neurotransmitter binds to the protein channel. Mechanically gated channels open if the membrane is stretched of deformed physically. movement of ions through the mechanically gated channels are essential to all electrical events in neurons.
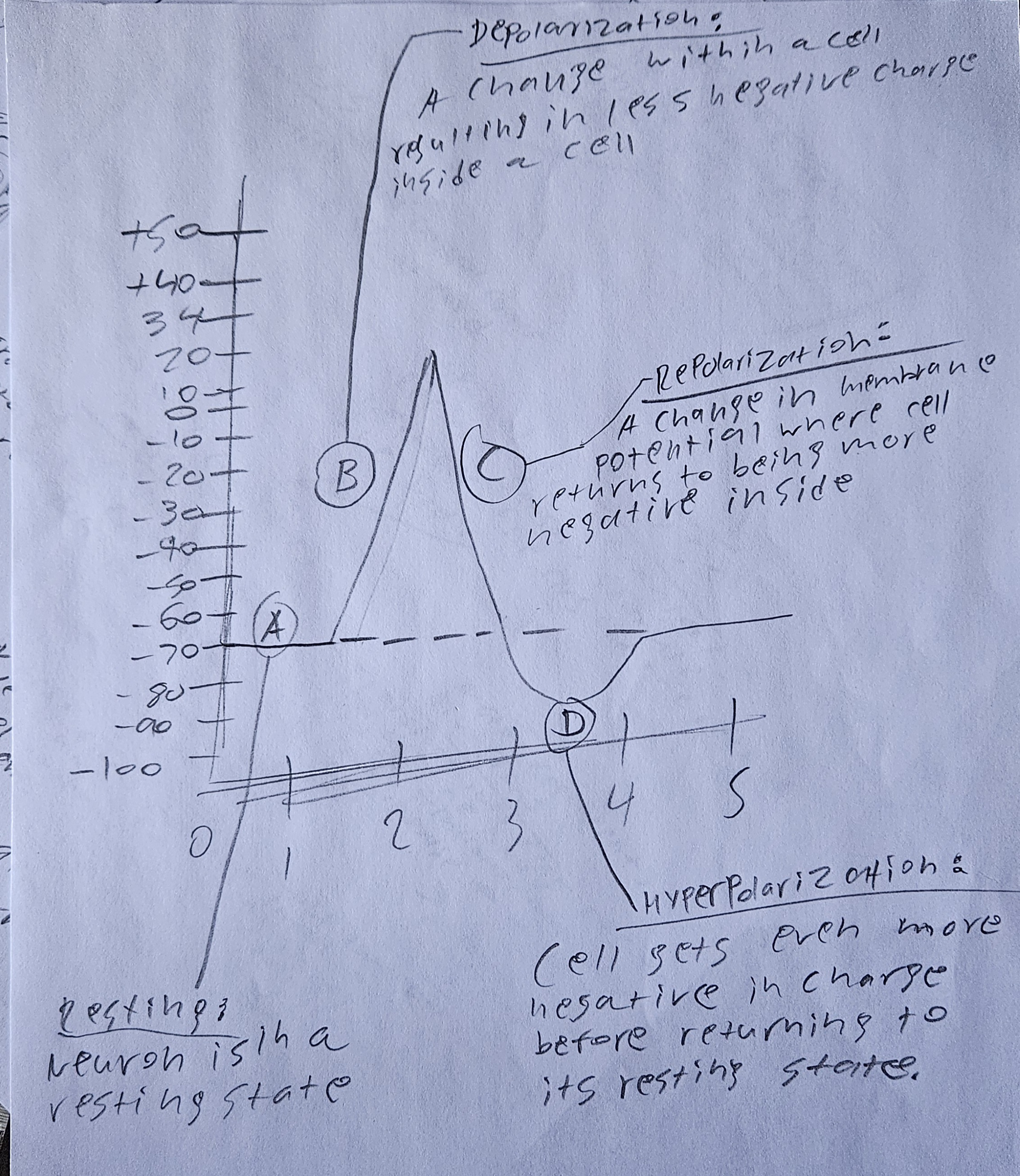
obj 8) sketch a graph of how the voltage changes across the cell membrane during an action potential. label and briefly explain what each section of the graph shows in terms of what is happening.
obj 9) explain how excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters function differently
excitatory neurotransmitters open the ion channels and depolarize the postsynaptic neuron, causing the action potential to be sent on. inhibitory neurotransmitters can hyperpolarize the postsynaptic neuron so it cannot send on the action potential.
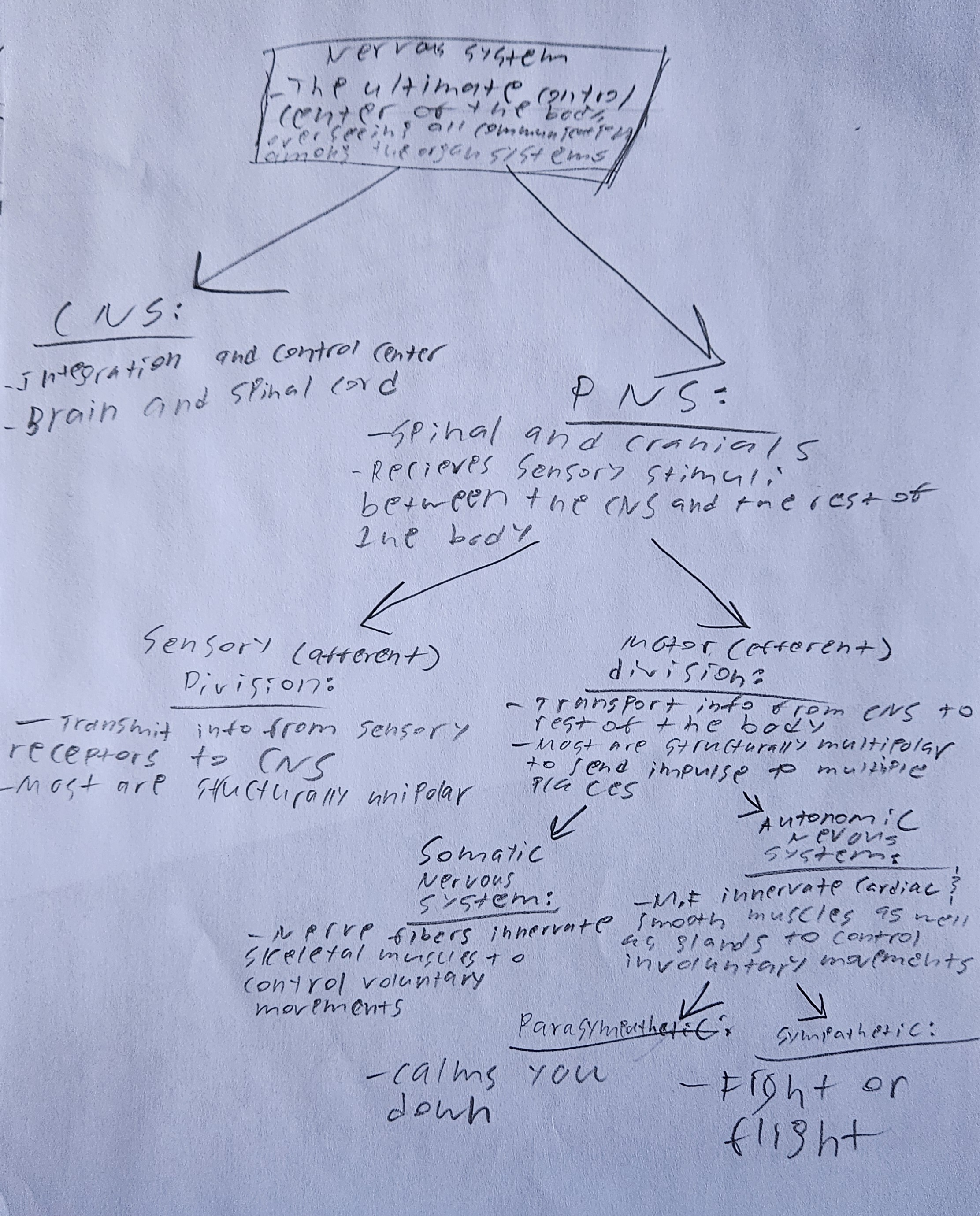
obj 10) sketch a flowchart showing the organization of the different divisions of the nervous system. include short phrases or pictures under each division to help you remember the differences.
obj 11) distinguish the roles and components of the central and peripheral nervous systems
the central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. it is the integration and control center. brain is protected by the skull and surrounded by layers of tissue. meninges and cerebrospinal fluid cushion the brain from injury. the peripheral nervous system consists of the spinal and cranial nerves. it receives sensory stimuli between the CNS and the rest of the body.
obj 12) summarize the location and role of the three main parts of the brain
Cerebrum: the largest part of the brain and made of the left and right hemispheres. functions in learning, speech, emotion, reasoning, vision, hearing, and fine movements
Cerebellum: under the cerebrum. it maintains posture and balance. coordinates timing and patterns for smooth and agile subconscious movements
Brainstem: base of the cerebrum and anterior to the cerebellum. relays info between rest of the brain and the spinal cord. coordinates a lot of automatic functions like respiration, circulation, body temperature, sleep, digestion and swallowing
obj 13) distinguish between the sensory and motor divisions of the peripheral nervous system
Motor Division:
Efferent
motor nerve fibers
sends out information from the brain to effector organ like muscles (contraction) and glands (secretion)
Sensory Division:
Afferent
sensory nerve fibers
take in sensory stimuli to send back to the CNS/Brain
somatic sensory fibers carry info from the skin, skeletal muscles and joints
visceral sensory fibers carry info from the visceral organs
obj 14 a) distinguish between somatic and autonomic nervous systems of the motor division. explain the Somatic nervous system
somatic nerve fibers innervate skeletal muscles to control voluntary movements
neuron’s cell body starts in the CNS, and the axon extends all the way to the skeletal muscle it affects
acetylcholine is released in order to stimulate contractions
nerve impulses are sent to the neurotransmitter junction
Ach is released to synaptic cleft for stimulation
Ach binds to receptors on the skeletal muscle cell, transmits action potentials to conduct muscle contraction
obj 14 b) distinguish between somatic and autonomic nervous systems of the motor division. explain the Autonomic nervous system
muscle fibers innervate the cardiac and smooth muscles as well as glands to control involuntary movements
A two-neuron chain is used to connect the CNS to effector organs
the first neuron starts in the CNS and the synapses with a second neuron that extends to the effector organ
Norepinephrine is released into the sympathetic nervous system, while ACh is released into the parasympathetic. both can be stimulatory or inhibitory
15a) explain how the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system work in opposition to one another. explain PARASYMPATHETIC SYSTEM
calms you down’
rest and digest'
maintains your body and conserves energy for later
communicates to one effector organ at a time
paraganglia cells are longer than postganglionic
uses neurotransmitter Ne and hormones for stimulation and inhibition
15b) explain how the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system work in opposition to one another. explain SYMPATHETIC SYSTEM
excites you
fight or flight
one stress signal is sent to responses in multiple effector organs at once
focuses on what your body needs right now
preganglionic cells are shorter than postganglionic
Uses Ne and hormones for stimulation and inhibition
obj 16) explained the difference between an innate and learned reflex
innate reflex is a rapid and predictable motor response to a startling stimulus while a learned reflex is a response resulting from practice, repetition, or experience.
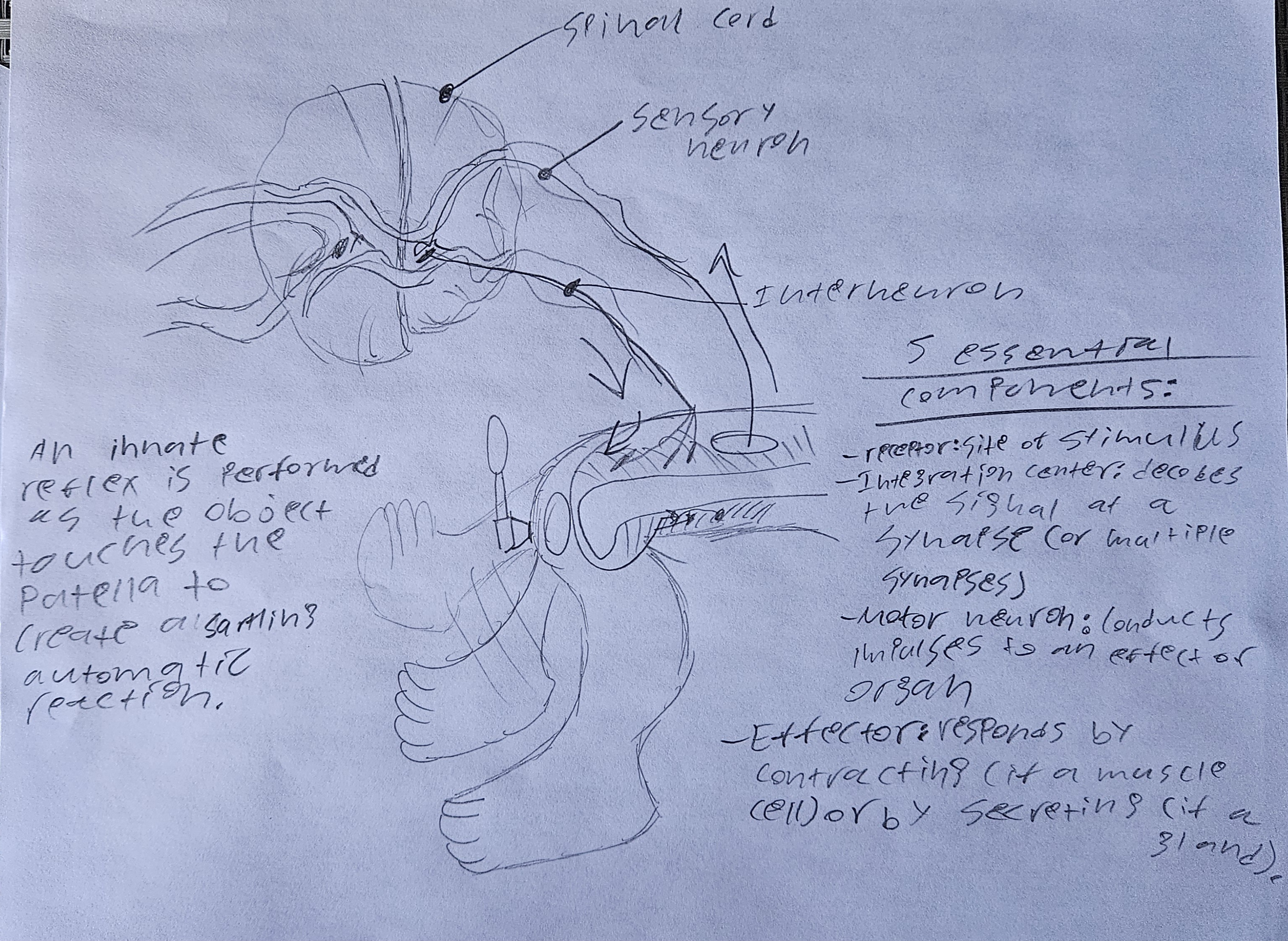
obj 17) draw and interpret or describe an example of a reflex arc. within your drawing or description, identify the 5 essential components of all reflex arcs