Lab F: Fischer Esterification for chris fixed
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
yo chris did yk ily ?! (pls make more sets (u left while the class was still young))
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
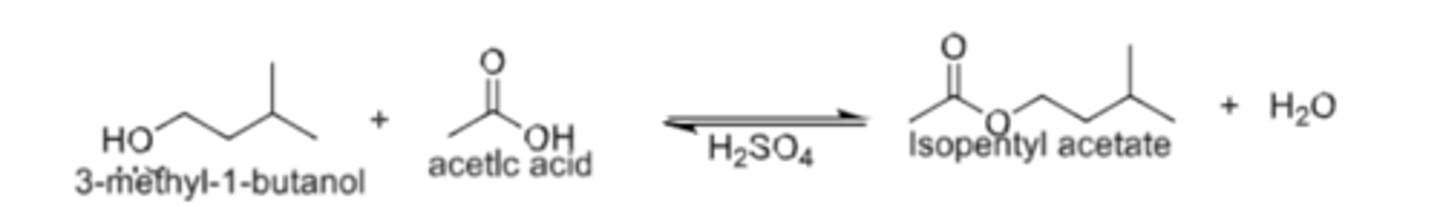
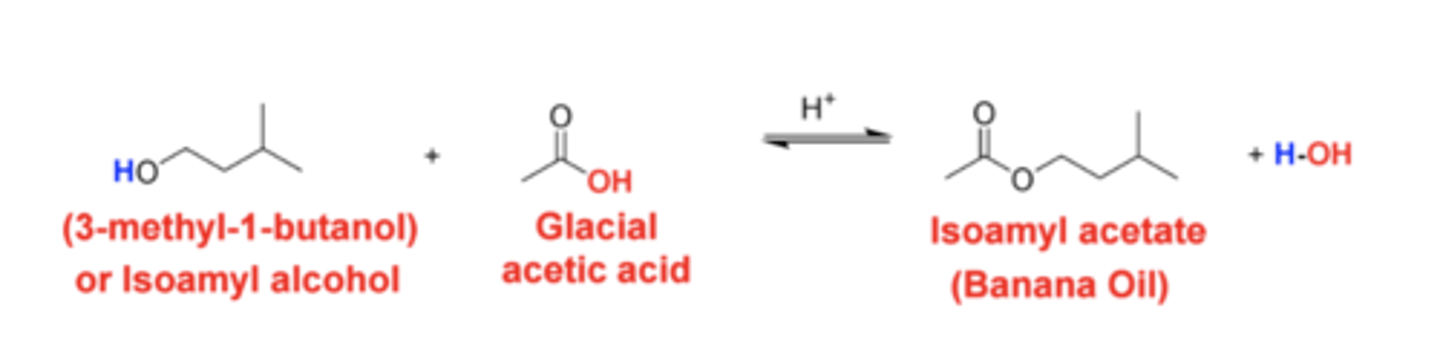
Purpose
synthesizing Isopentyl acetate (3-methylbutylacetate ) using a Fischer esterification reaction between acetic acid and isopentyl alcohol (3‐methyl‐1‐butanol).
Scheme 1. Synthesis of Isopentyl acetate
example of lower molecular weight esters
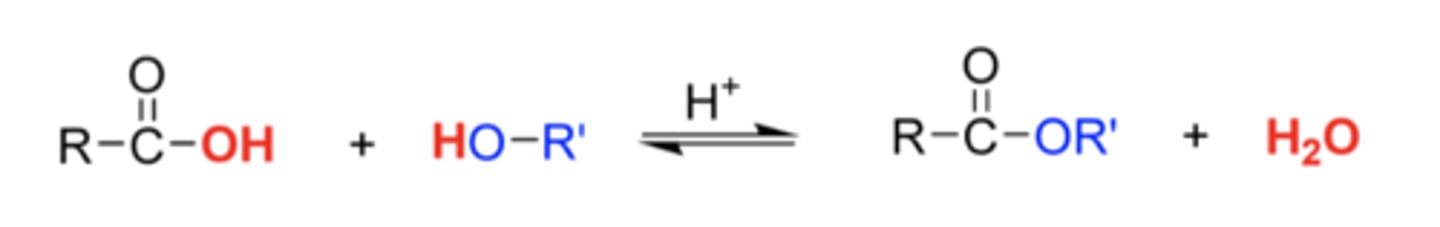
What is Fischer esterification?
is an acid‐catalyzed equilibrium reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, usually sulfuric acid, to produce the corresponding ester and water as a by‐product.
Is the reaction reversible or irreversible?
reversible. The ester can react with the acid and water to go back to the starting materials.
In order to get a good yield of the product
it is necessary to push the equilibrium by either removing water as it forms, or by using an excess of one of the reagents
The Fischer esterification is a reliable method to make esters
on an industrial scale,
because it requires very simple reagents and the reaction can be driven to completion by using a large excess of whichever starting material is less expensive
why do we reflux the rxn
to increase the rate of rxn
When a reaction is refluxed in an organic solvent,
the boiling point of the solvent is the reaction temperature.
what is the excess reagent we use in this experiment
glacial acetic acid
By using an excess of one of the reagents (glacial acetic acid, in this experiment) and refluxing for 50 minutes,
we will be able to drive the equilibrium reaction to the product side and attain a good yield of the ester.
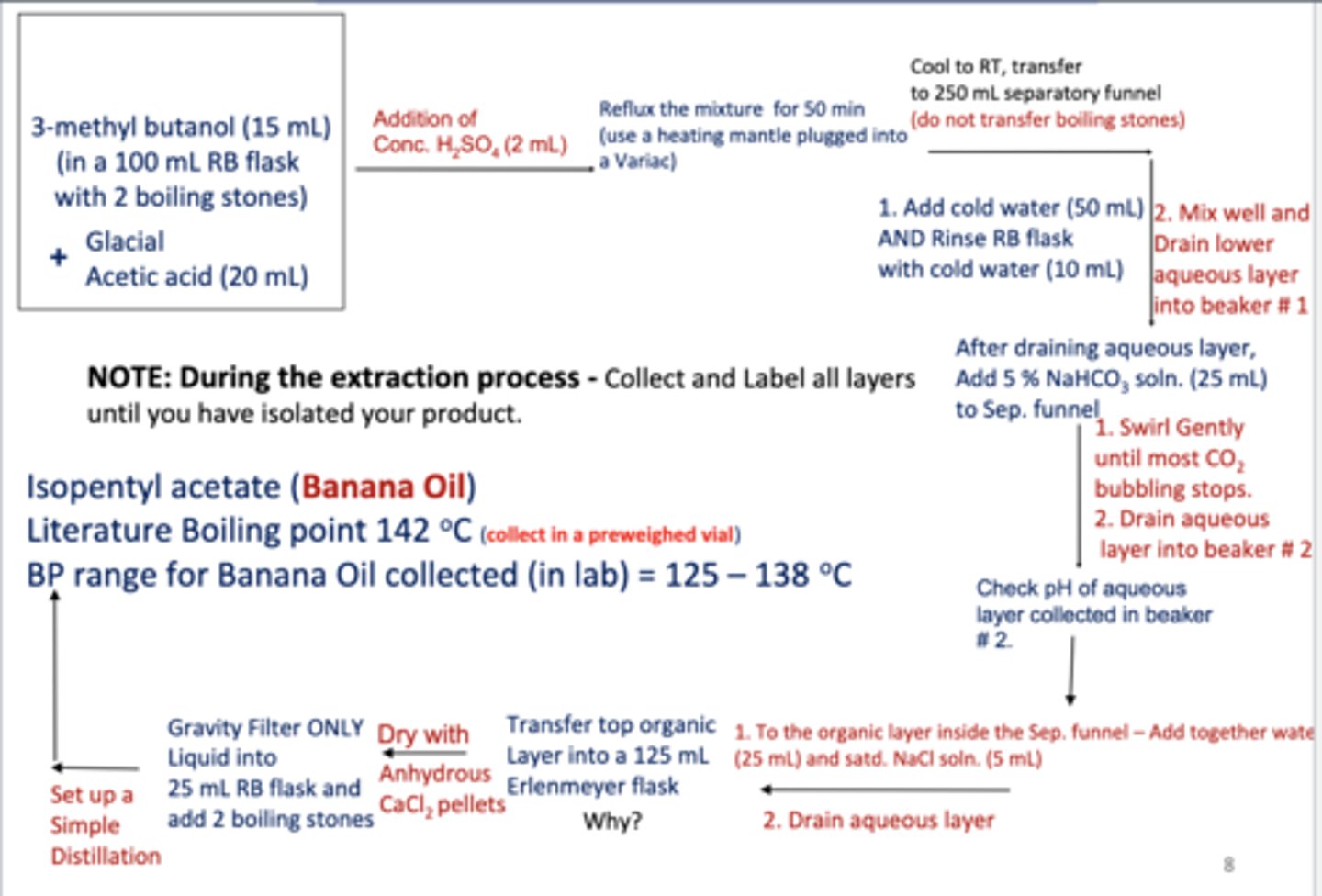
After an initial purification by extraction,
the crude product will be distilled to give pure Isopentyl acetate.
In order to remove all of the acetic acid, we can take advantage of the fact
It is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids typically have pKa values near 5, and can be easily deprotonated.
The organic layer will be washed with sodium bicarbonate
to convert acetic acid into sodium acetate salt. In this way, we can move all of the acetic acid into the aqueous layer, where sodium acetate has greater solubility
The deprotonation reaction that occurs generates
carbon dioxide, making it important to vent your separatory funnel frequently. If you fail to do so, your stopper may pop out, leading to a large loss in yield.
After removing the acetic acid, you are left with
isopentyl acetate, and maybe a trace amount of isopentyl alcohol, and a trace amount of water.
You will begin by washing the organic layer with
a saturated brine solution. Saturated salt solutions are often used to draw water out of the organic layer as a first step in the drying process
All extractions are then dried with
an inorganic drying agent. The drying agent is an anhydrous inorganic salt (devoid of water) that binds to the water and can then be filtered away.
what is the drying agent we use and why do we use it.
anhydrous CaCl2. Because we want to lose as little as possible of our product in the drying step without using additional solvent
how should the anhydrous CaCl2 be seperated
gravity filtration
what do you have at this point
isopentyl acetate with maybe a trace of isopentyl alcohol —two products that have boiling points only 13 oC apart.
what would a difference of 13 oC require
a fractional distillation. However, the difference is so small that even a fractional distillation would need a Vigreux column with many theoretical plates, and in using such a column, we would lose a large amount of material to column holdup and the vapor that is left in the system.
to make seperation easier
we want to significantly limit that amount of isopentyl alcohol that we have to separate from the product.
two basic starategies to drive an equilibrium reaction
One strategy is to remove products as they form in order to continue pushing t h e equilibrium toward more products, and the second is to use an excess of one of the starting materials.
what strategy will we use
We will use more than two equivalents of acetic acid in order to drive the equilibrium towards the products. By driving the equilibrium to the products, we may only have a small amount of isopentyl alcohol if any , at all to remove, which can be accomplished by a simple distillation
will pure alcohol be obtained
No. the material that distills will be mostly isopentyl acetate which maybe contaminated with a small amount of the isopentyl alcohol.
because there is only a very small amount of isopentyl alcohol contaminant, the amount of isopentyl acetate lost in this case is most likely
less than what would be lost to column holdup and the vapor pressure in a fractional distillation with a sufficient number of theoretical plates to obtain pure separation.
In order to characterize a compound by its boiling point range, you will need to note the temperature range during which
your product distills over
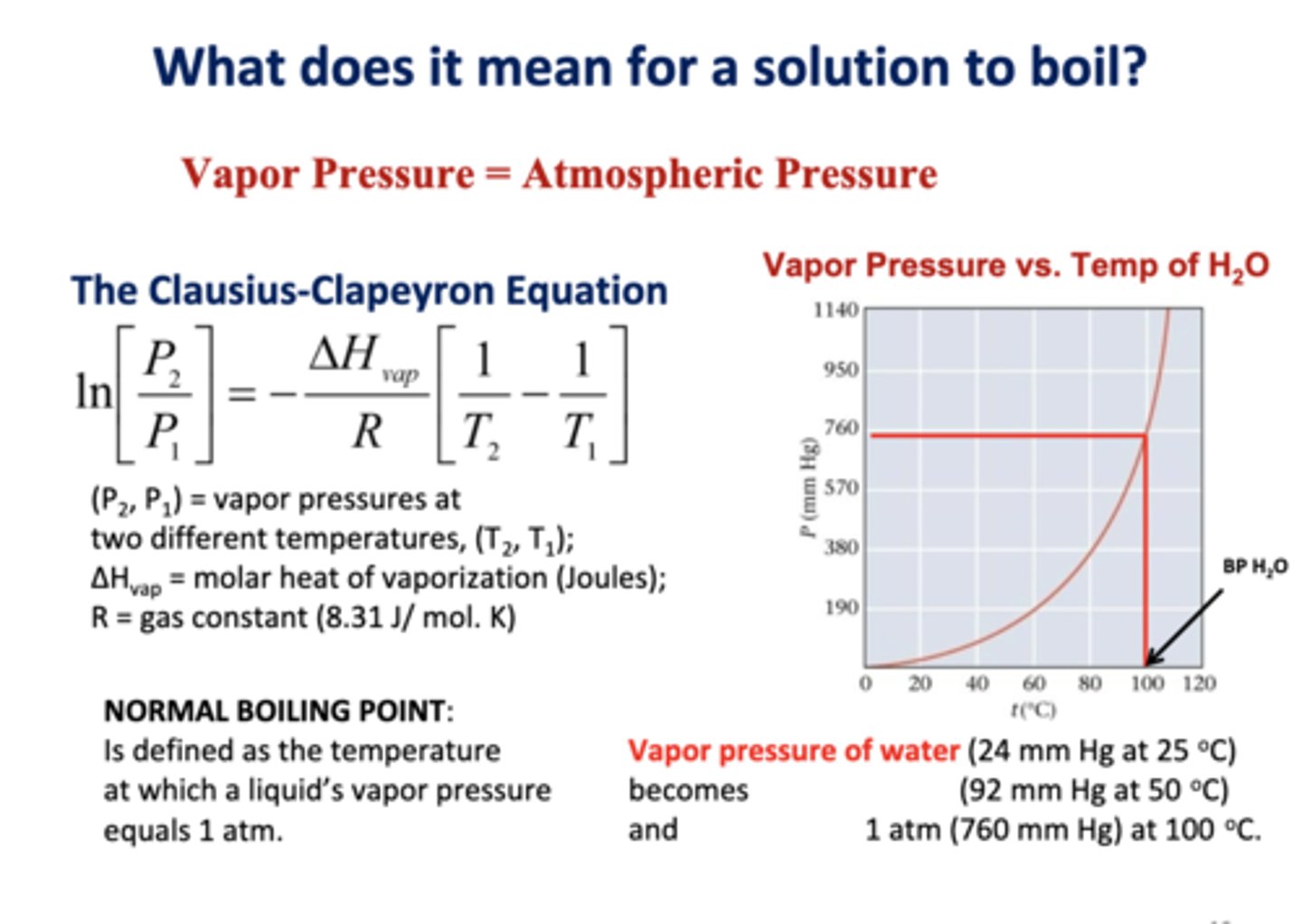
why will our bp be different from literature
Unfortunately, the alcohol thermometers that we use tend to be poorly calibrated at temperatures over 100 °C. Our bp will be about 125-138, while literature is 142.
concerted sulfuric acid hazard
extremely corrosive
since this is an equilibrium rxn
we use glacial acetic acid in excess to push the rxn toward the formation of the product, isopentyl acetate.
why do we use concentrated sulfuric acid
serves as acid catalyst
this rxn is
acid catalyzed esterifcation rxn
do we add stir bar
NO.
do we add boiling chips
YES. add 2
do we use a stir plate
no because don't use stir bar. have heating mantle sitting on base of ring stand.
what is the purpose of doing boiling stones
the pores in the boiling stone help prevent solution from bumping too vigoursly during the reflux process and helps to maintain an even boiling of the solution
what funnel do we use to add liquids to seperatory funnel
pyrex
why don't we want to transfer boiling stones to sep funnel
to prevent sep funnel from clogging
can boiling stones be reused
NO
at end of reflux process
we will have product, isopentyl acetate, excess glacial acetic acid, re-generated acid catalyst, and maybe some unreacted isopentyl alcohol.
when add water
aq layer (bottom layer): light redish color
organic later (top layer): yellowish-brown color
when add aq sodium bicarbonate
observe fizzing due to formation of carbon dioxide gas. Need to vent
purpose of adding aq sodium bicarbonate
to neutralize any leftover glacial acetic acid in the mixture
when add aq bicarb:
aq layer: clear color
org layer: yellowish color.
what should pH be after add aq bicarb
5 to 6 (neutral
purpose of adding tap water
remove any leftover acid
purpose of adding brine or saturated sodium chloride solution
to begin drying process. Being a saturated salt solution, can draw out large amounts of water mixed in with organic layer.
adding tap water and brine:
same layers as one below.
purpose of adding anhydrous CaCl2 pellets
serves as drying agent to cap drying process by drawing out any residual water that is mixed in with organic layer
after gravity filtration
liquid that drains through will contain isopentyl acetate and trace amounts of any isopentyl alcohol
why carry out distillation
assuming final product may contain isopentyl alcohol. Isopentyl acetate has bp of 142 while bp of isopentyl alchol is 132. a diff of 10 will require fractional distillation. However, diff in bp is so small if use fractional distillation which req using vigerux column which has many indentations or threoretical plates. Each theoretical plate corresponds to simple distillation cycles. This would result in losing a large amount of product due to column holdup and the vapors left in system. Use simple distillation to sep product on assumption that any leftover isopentyl alchol is small enough or none compared to losing product if doing fractional distillation instead.
since final product is liquid
look at bp.
which liquid do we collect
the liquid that distills at 125 and end at 138.
the larger ring of the keck clip goes
on the outermost piece of glassware (condenser on left side)
in simple distillation, heating mantle is supported by
ring clamp
do we foil for simple distillation in this experiment
yes until comes up to a boil
isopentyl acetate appearance
clear. Smells like banana oil
glassware for distillation
3-way distillation adapter, thermometer adaptor, 2 keck clips, thermometer, vacuum adaptor, labeled vial, and 2 new boiling stones
where do we collect liquid that boils at lower temp.
in a different beaker and discard into a C, H, O non-halogenated container.
from which side should we start removing distillation set up
from right side.
where should all aqueous waste be disposed
special container aqueous waste (Fischer Lab)
where should Anhydrous Calcium chloride pellets and gravity filter paper be disposed.
the biohazard box
where should boiling stones be disposed of
biohazard box
where does red bulb of thermometer lie
below 3-way distillation side arm
fischer esterification reaction
lower molecular weight Esters:
- Have pleasant fruity odors
- Used as Flavoring agents and in the Perfume Industry
general method for preparation of esters
reflux, extractions, simple distillation
-
what type of rxn is this
• Acid catalyzed reaction , meaning that the acid is regenerated and is never consumed.
• Impossible to obtain a 100% yield.
Our Esterification Reaction - Synthesis of Isopentyl acetate (Banana Oil)
glacial acetic acid hazard
flammable, corrosive
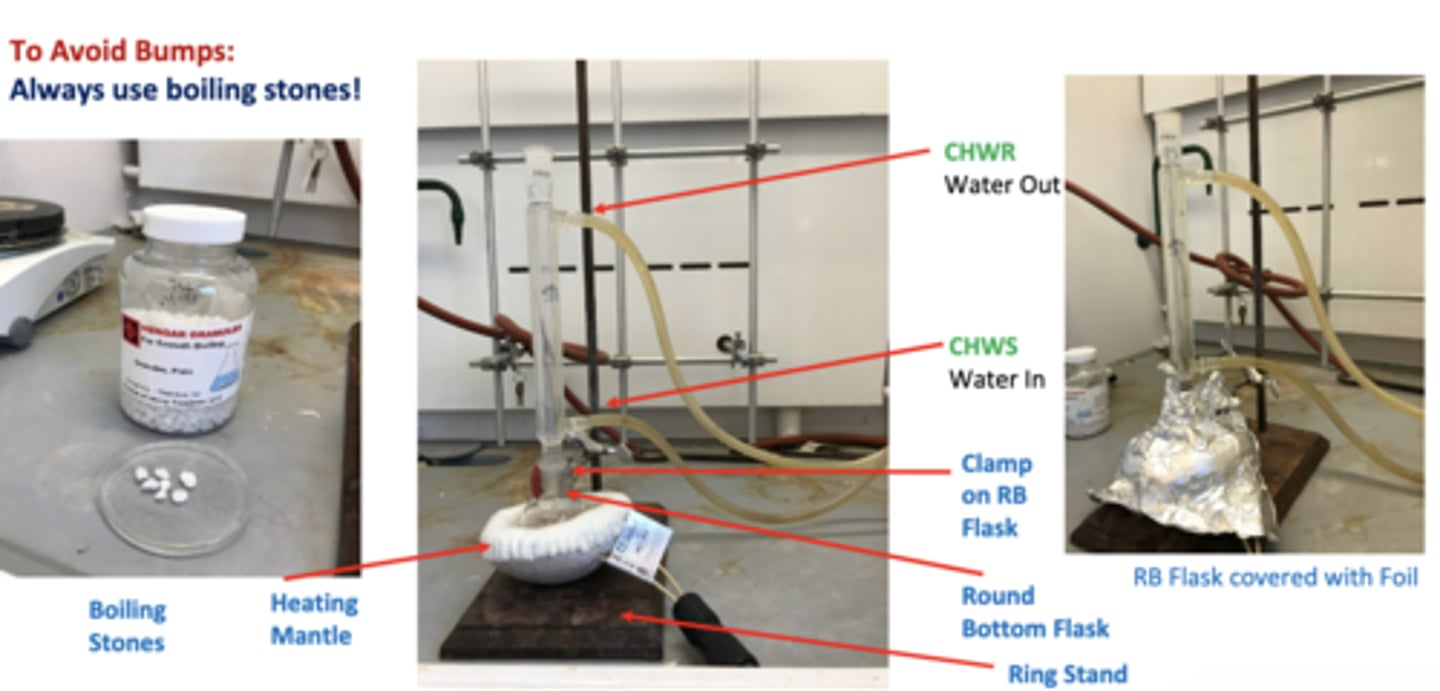
Fischer Esterification - Reflux Schematic

Flow Chart - Fischer Esterification Reaction
simple distillation set up

why shouldn't we distill to dryness
leaving a small amount of residue will prevent overheating and breaking the flask, and also prevent formation of pyrolytic tars that are difficult to wash out.
purpose of reflux
- To heat a reaction mixture at its boiling temperature (the boiling point of the solvent, or in this case, excess reactant used in the reaction) to form the product, without losing any material inside the reaction flask.
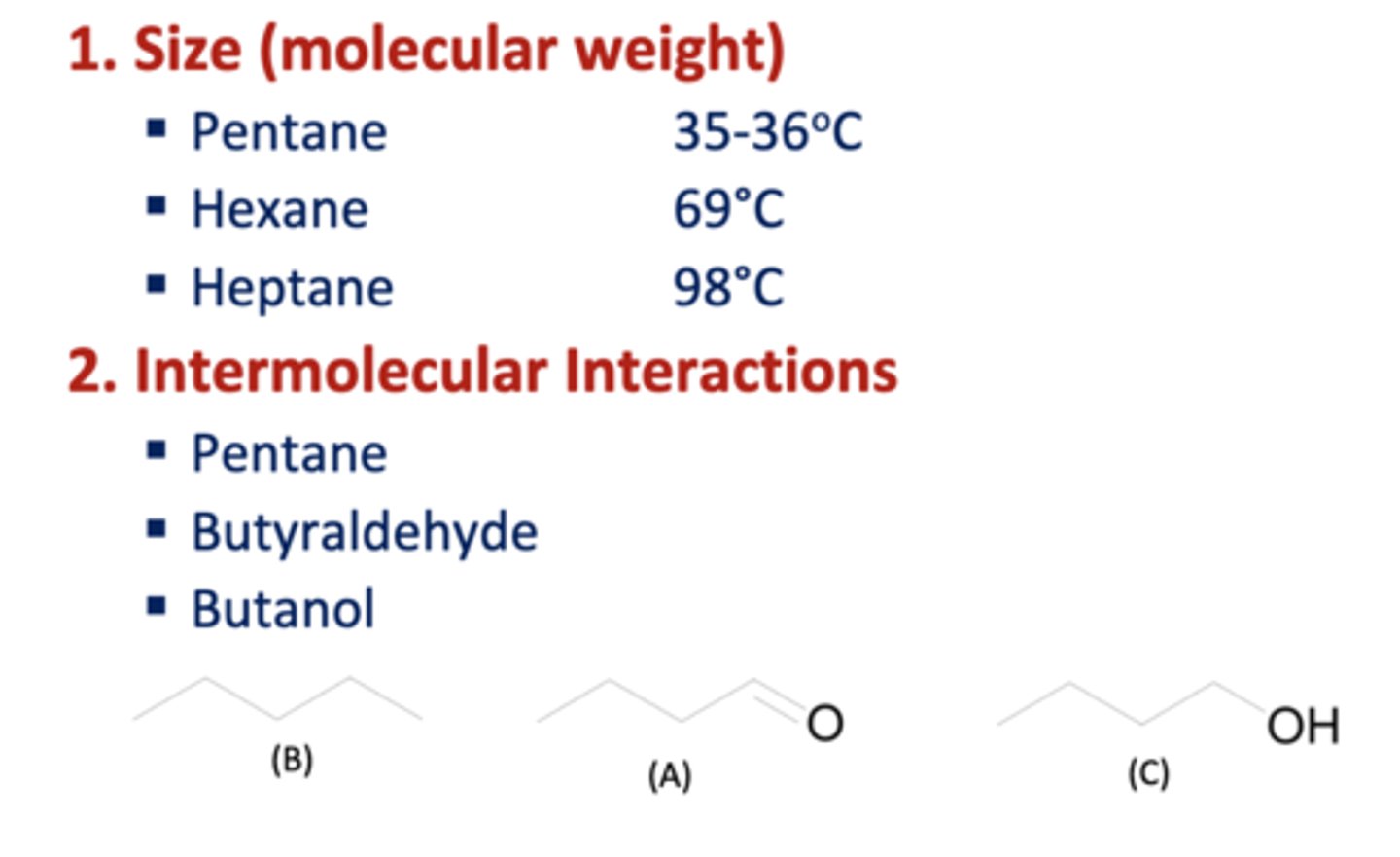
Factors affecting Boiling Points
size and intermolecular interactions
-bigger has higher bp
what does it mean for a solution to boil
fractional distillation
-A fractional distillation is used to separate liquid mixtures that are miscible in each other, and that boil at less than 25 oC from each other at 1 atm.
-A fractionating column (Vigreux column) is inserted between the 3-way distillation adapter and the round bottom flask (distillation flask) - providing a larger surface area over which a number of separate liquid-vapor equilibria can occur.
-Many vaporizations and condensations take place before the distillate is collected.
one theroetical place is equivalent to
one simple distillation cycle.
Efficiency of a fractionating column
expressed by number of theoretical plates
Vacuum Distillation
Used for compounds that either boil at too high a temperature, or that decompose near their boiling points.
-Under vacuum - compounds can be distilled at temperatures lower than their atmospheric boiling points.Only feasible solution for distilling compounds with BPs > 200 oC.
Simple Distillation:
-Used to separate liquids boiling below 50 oC at 1 atm from: a. non-volatile impurities or b. another liquid that boils at least 25 oC higher than the first.
-A technique in which a liquid is vaporized by boiling, then re-condensed back to a liquid (distillate), and collected in a receiving flask.
Schematic -Simple Distillation

What does NRM stand for
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
What does NMR show
That nuclei posses charge and can spin
Spinning charge generates a magnetic dipole
What are magnetic dipoles
Characterized by nuclear magnetic spin quantum number "l"
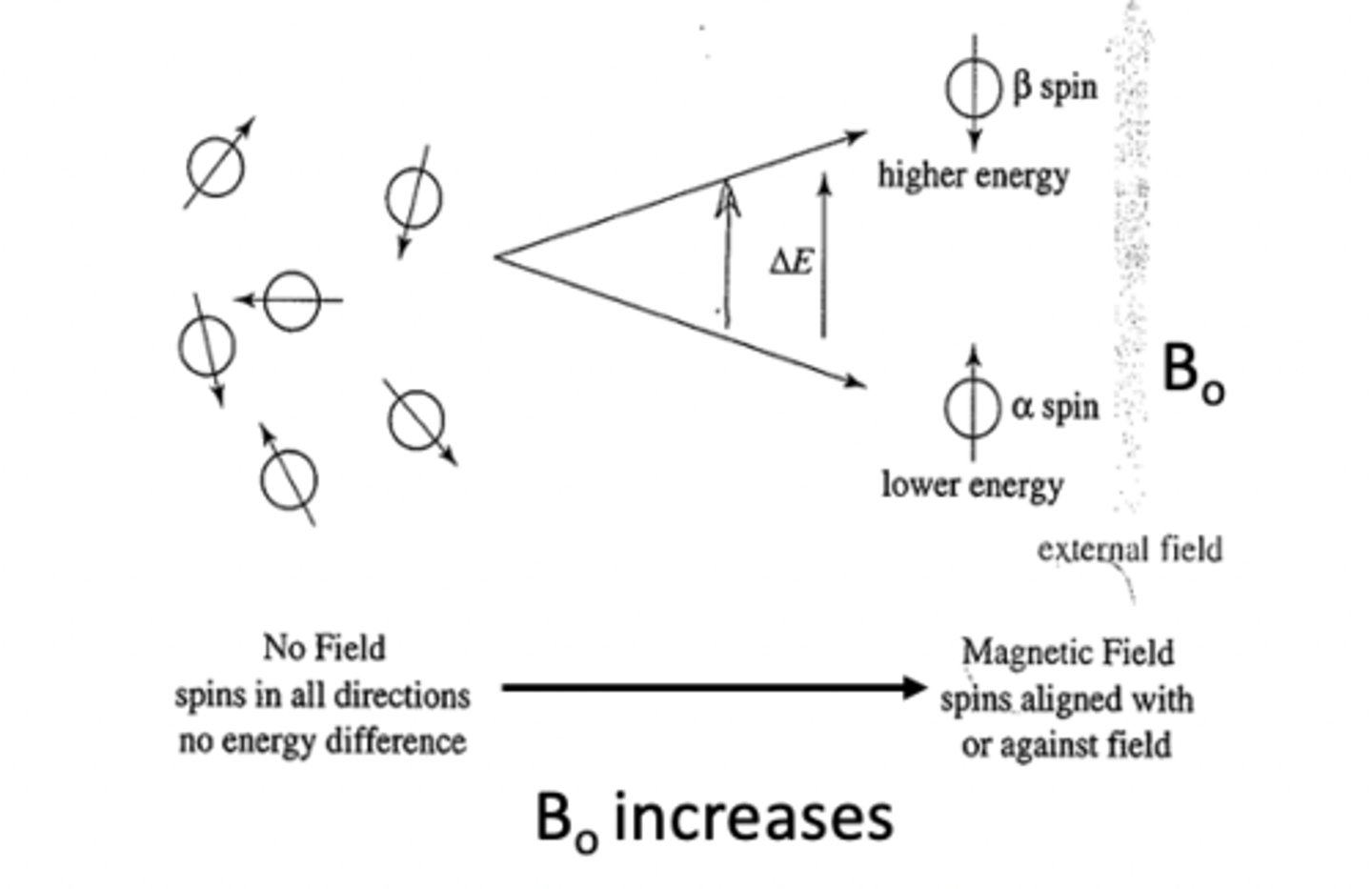
What happens as Bo increase
•More nuclei are aligned with the externally
applied magnetic field or the lower energy
α-spin state.
•∆E = Energy difference between α and β-spin states
•Increasing the applied magnetic field = Increasing ∆E
between spin states
•Nuclei can absorb energy and flip from the
α-spin state to the β-spin state. When this happens,
the nucleus is said to be in RESONANCE with the
applied magnetic field, hence the term
“Nuclear Magnetic Resonance”.
•The difference in energy ΔE between the two
spin states corresponds to a frequency in the Radiofrequency
region of the EM spectrum.
What is Plank's equation
∆E = hν
∆E = γ Boh/2π = hν; ν = γBo/2π
γ = gyromagnetic ratio; a constant that depends on the magnetic moment of the nucleus.
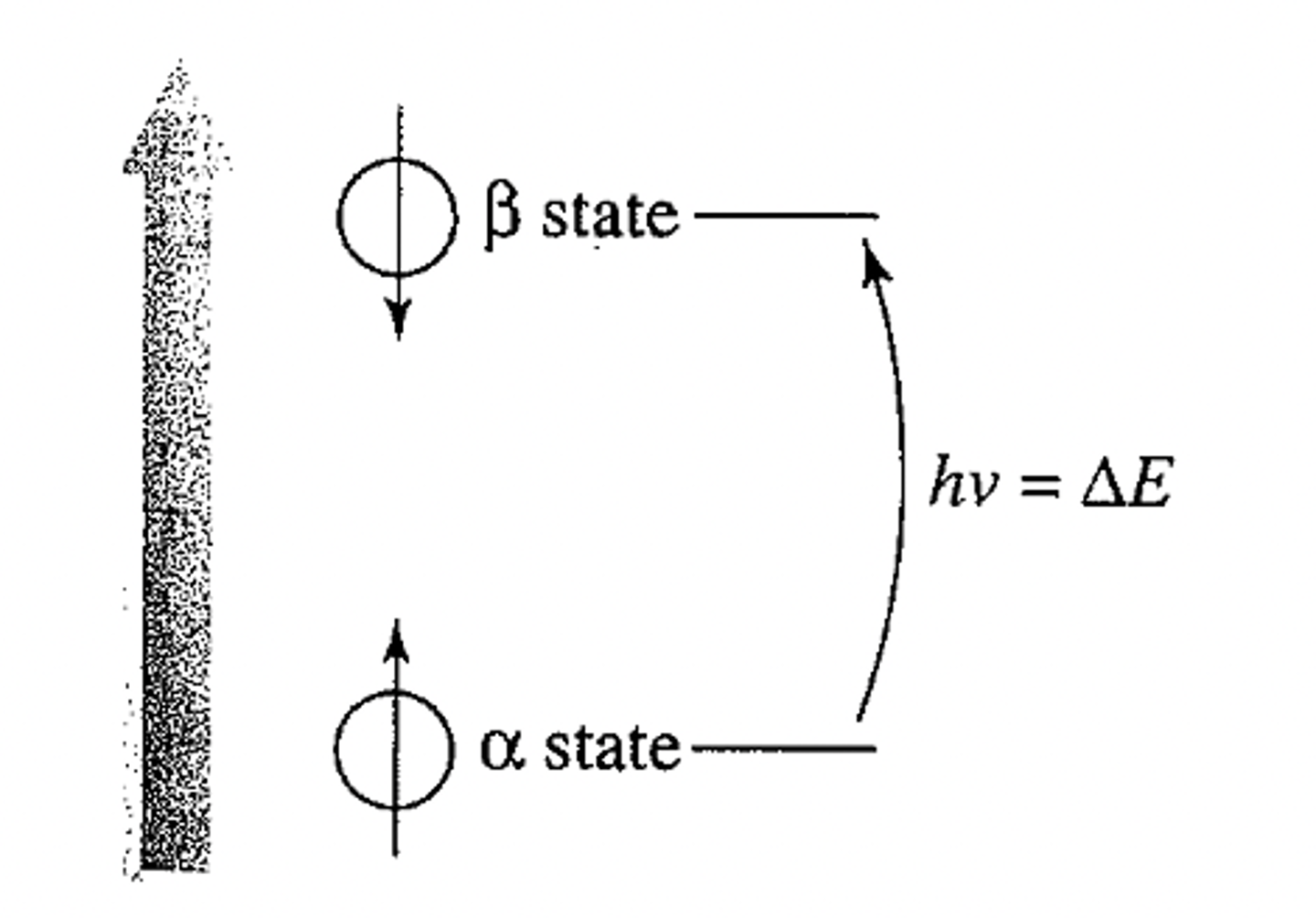
What are the conditions for resonance
Larmor equation: ν = γ Bo /2π or
ω = γ Bo; where ν= ω/ 2π
ν is in hertz and ω is in radians/second
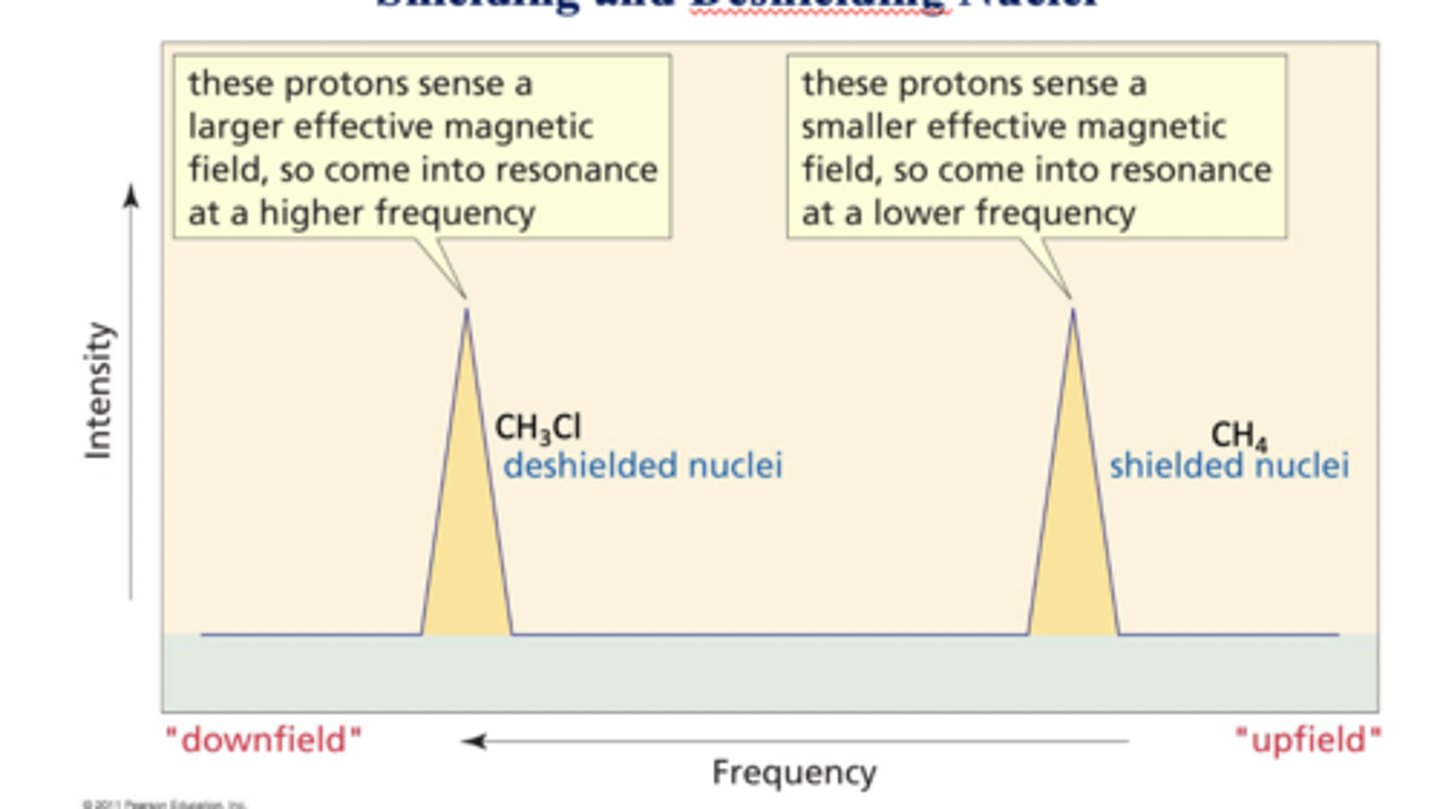
Shielding and deshielding nuclei
Electronegative Cl withdraws e-1 density from the 'C' and 'H' atoms - thus DESHIELDING them
Deshielding or Lesser shielding = more of the applied magnetic field strength experienced
= higher (DOWNFIELD) Frequency absorbed
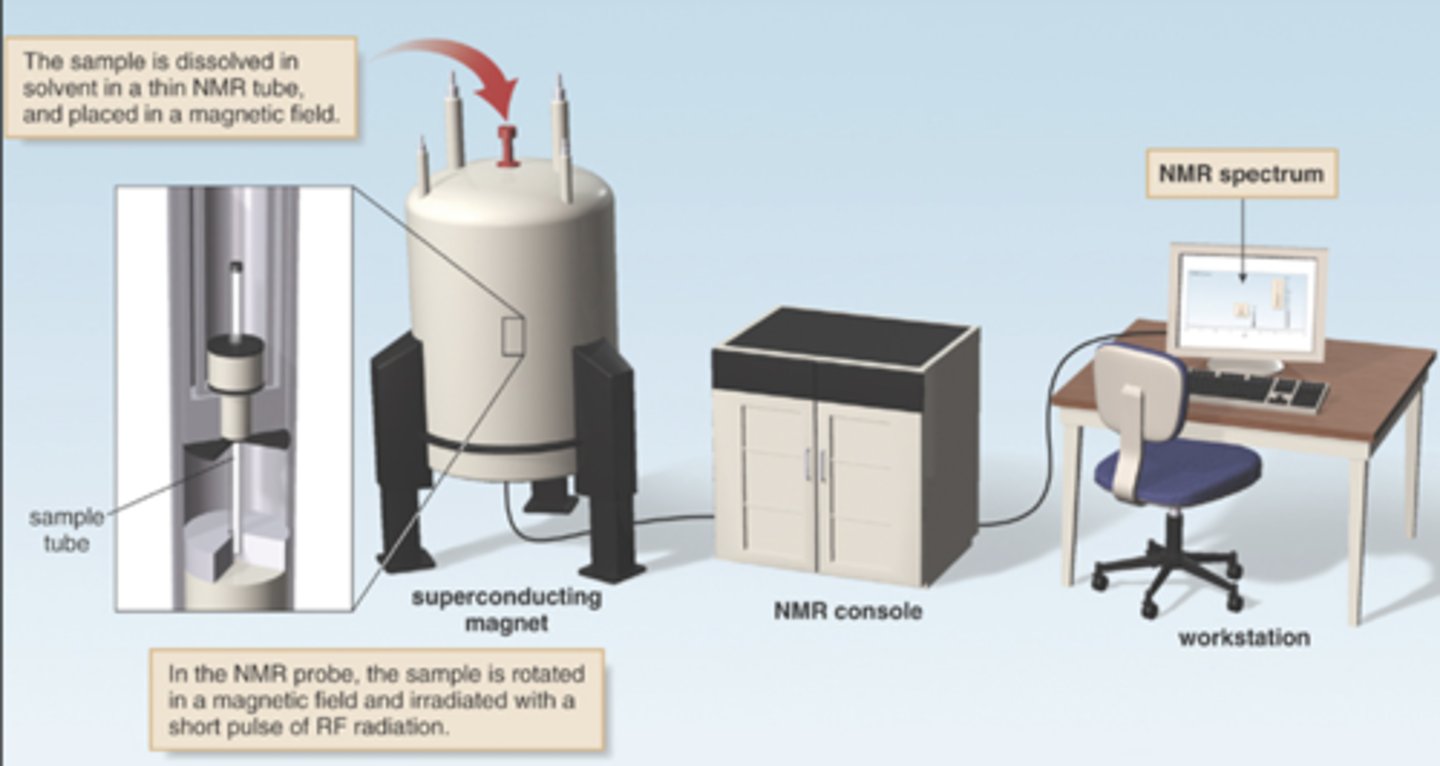
Schematic of an NMR spectrometer
NMR spectrum is
A plot of the intensity of an observed
NMR signal Vs the frequency, measured
relative to a reference compound;
typically Tetramethylsilane (TMS)
Advantages of TMS
1. TMS HAS 12 equiv. H's
2. NMR Signal due to protons in TMS appears as a singlet at 0 ppm (way upfield from other signals).
3. It is low-boiling and inert.
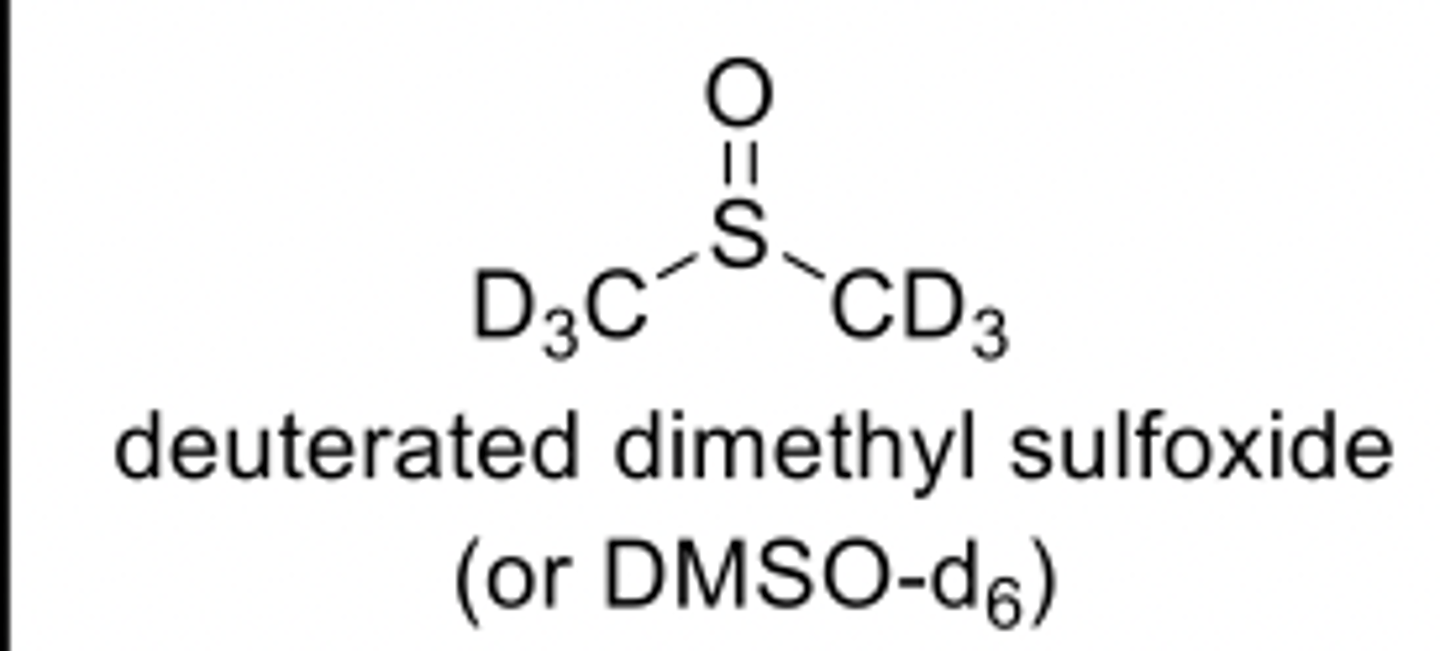
Common NMR solvents
CDCl3 deuterated chloroform
(typically used for non-polar compounds)
(typically used for
polar compounds)
A Typical NMR Sample Prep:
10-20 mg compound + 0.5-0.6 mL CDCl3
Chemical shift (position of the peak)
frequency difference between the resonace observed for the nucleus and the resonance observed for the reference compound (usually TMS)
Degrees of unstaruation
2 (No. of C atoms) + 2 + (No. of N atoms) – (No. of Halogen atoms) - (No. of H atoms)
2
For a DU ≥ 4 = 3 double bonds + 1 ring (= 1 Aromatic ring)
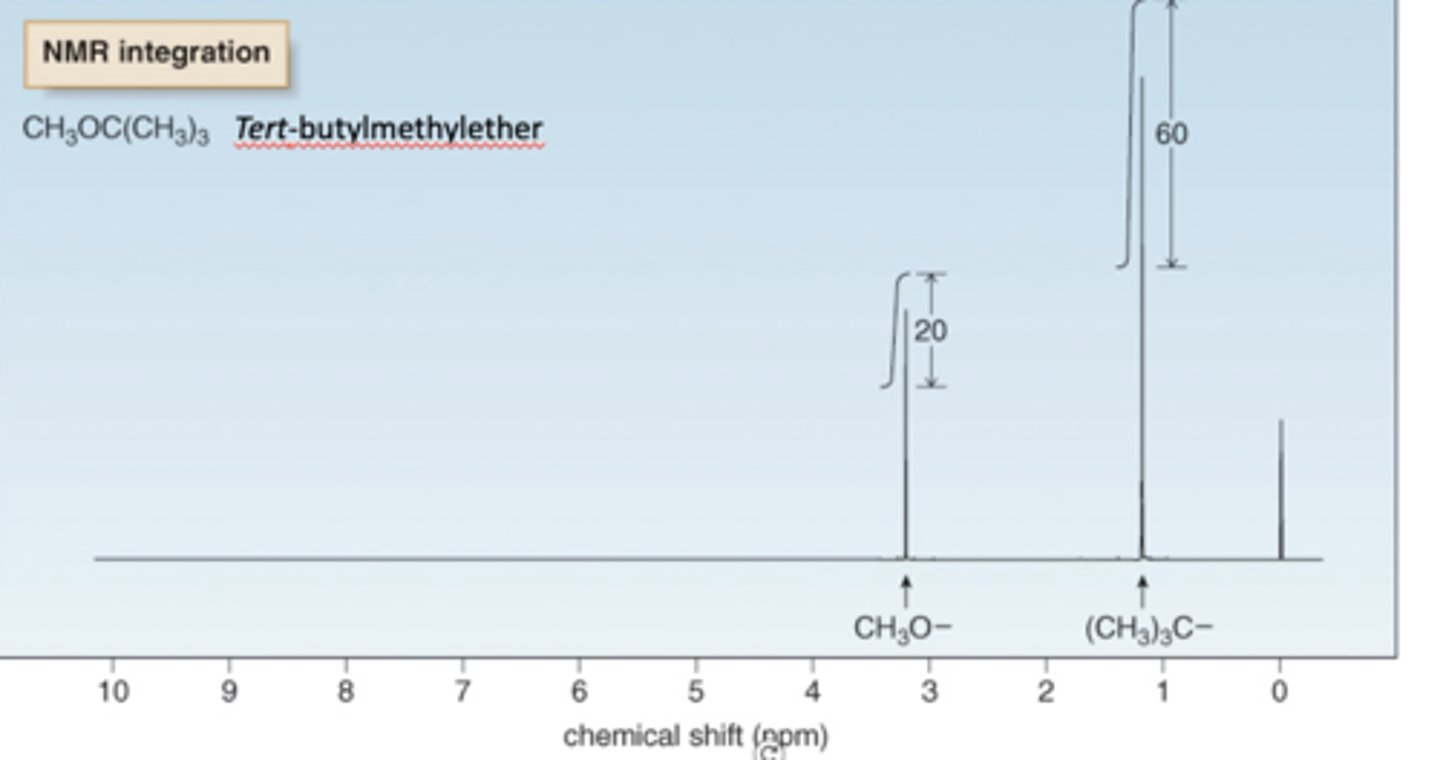
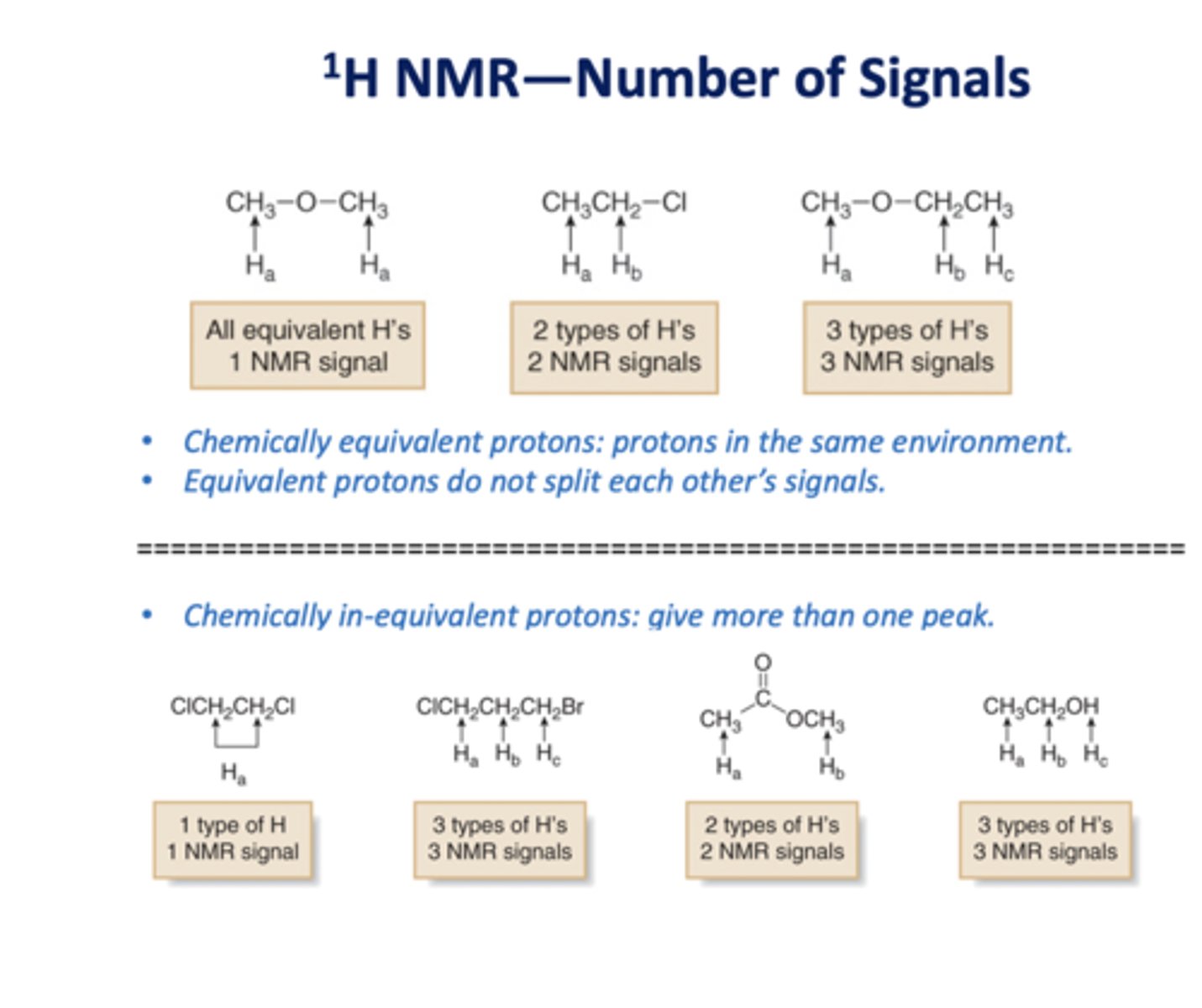
Features of a 1H NMR spectrum that provide information about a compound's structure:
a.Size of/ area under the peak ((Integration) of NMR signals = is indicative of the relative number of identical protons in a particular environment.
b.Number of signals = corresponds to different groups of non-equivalent protons.
c. Position of signals = is indicative of the kind of proton/ s responsible for the signal.
d. Spin-spin splitting of signals = indicates the number of neighboring protons
= calculated using the N+1 rule)
NMR number of signals
NMR intensity signals
•Area under an NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
•Height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak which in turn is
proportional to the number of absorbing protons.