5 - Oxidation and Reduction
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Practice exam questions following revision of these cards as there are calculations etc to do. These cards are just definitions and short questions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Define reduction in terms of (i) electron transfer and (ii) change in oxidation number
i) gain of (increase in) electrons
ii) reduction (decrease) in oxidation number
Define oxidation in terms of (i) electron transfer, (ii) change in oxidation number.
i) Loss of electrons
ii) Increase in oxidation number
Reducing agent
Brings about reduction, it itself is oxidised
Oxidising agent
brings about oxidation, it itself is reduced
Oxidation number
Charge that an atom has or appears to have when electrons are distributed according to certain rules
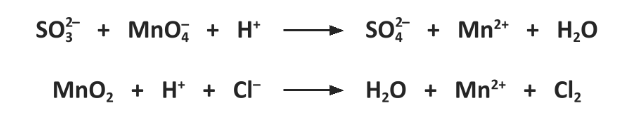
Use oxidation numbers to identify the reducing agent in the following reactions.
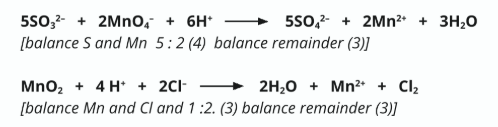
Equation 1: SO32- is Reducing agent // S+4 to S+6
Equation 2: Cl- is Reducing agent // Cl-1 to Cl20
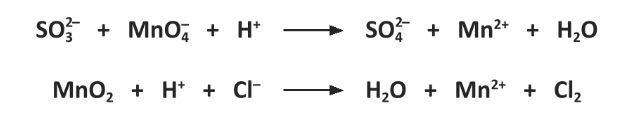
Hence, or otherwise, balance both the equations.
State the oxidation number of phosphorus in P4 and PO43- .
0, +5
State the oxidation number of nitrogen in NO3- and NO.
+5, +2
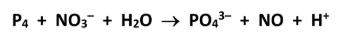
Hence or otherwise, balance the chemical equation

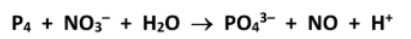
Identify the reducing agent in this reaction
P4
What are the oxidation numbers of iron in FeO, Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 respectively?
FeO : 2(+2, II) //
Fe3O4 : 8/3 (+8/3) //
Fe2O3 : 3 (+3, III)
The oxidation number of hydrogen in most of its compounds is +1. Explain why the oxidation number of hydrogen in the metal hydrides is -1
Hydrogen (H) more electronegative / metals less electronegative / metals more electropositive / more electronegative atom assigned gets negative charge
The oxidation number of oxygen in most of its compounds is -2. What is the oxidation number of oxygen in OF2?
+2
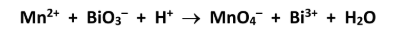
The following unbalanced equation describes a reaction that occurs in aqueous solution. Assign oxidation numbers and, hence or otherwise, balance this equation.
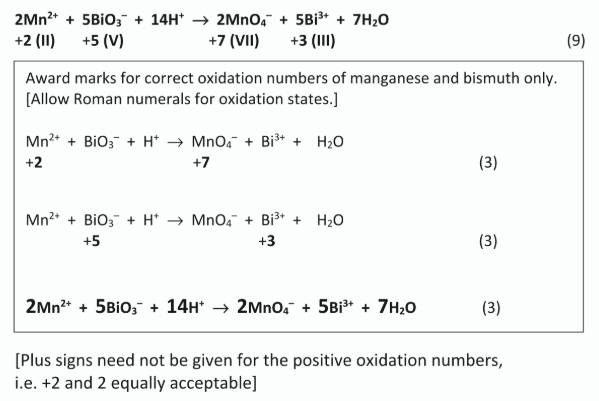
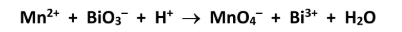
Identify the reducing agent in this reaction.
Mn2+ / Mn(II)
What is the oxidation number of sulphur in
(i) SO2
(ii) H2SO4
(iii) Na2S2O3?
i) +4 / 4 / IV //
ii) +6 / 6 / VI
iii) +2
Write the oxidation number for
(i) oxygen in OF2
(i) xenon in XeF4
i) 2 / +2 //
ii) 4 / +4