Determination of salicylic acid in Acylpirin® by spectrophotometry
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
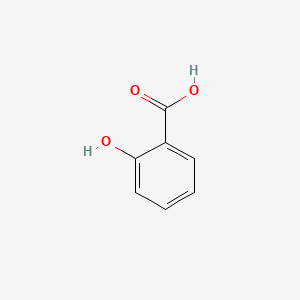
Salicylic Acid
A precursor to aspirin; a plant hormone used in pain relief and the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals.
Structural Formula of Salicylic Acid
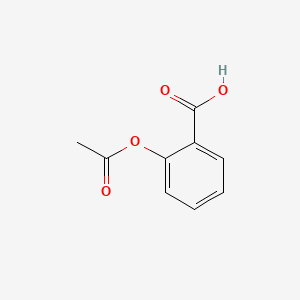
Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid)
A common pain reliever and anti-inflammatory drug synthesized from salicylic acid and acetic anhydride.
Structural Formula of Acetylsalicylic Acid
Synthesis of Aspirin
The chemical reaction where salicylic acid reacts with acetic anhydride in the presence of an acid catalyst to form aspirin and acetic acid.
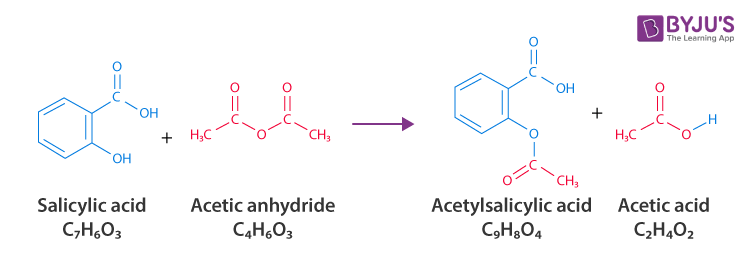
Acetylation
The process of introducing an acetyl group into a compound, such as the conversion of salicylic acid to aspirin by reacting with acetic anhydride.
Acetic Anhydride
A reagent used in the synthesis of aspirin from salicylic acid; it reacts with the hydroxyl group of salicylic acid.
Spectrophotometry
An analytical technique used to measure the absorbance of light by a sample at specific wavelengths to determine the concentration of the analyte.
Spectrophotometric Determination with Iron(III)
A method where salicylic acid reacts with iron(III) ions to form a colored complex, which can be measured using spectrophotometry.
Rection scheme of reaction of salicylic acid with iron (III)
Spectrophotometer Zuzi 4101

Components of Spectrophotometer
The include a light source (usually a tungsten or deuterium lamp), a monochromator (to select specific wavelengths), a sample holder (cuvette), a detector (such as a photomultiplier tube), and a digital display or output device.
Scheme of Spectrophotometer (single beam)
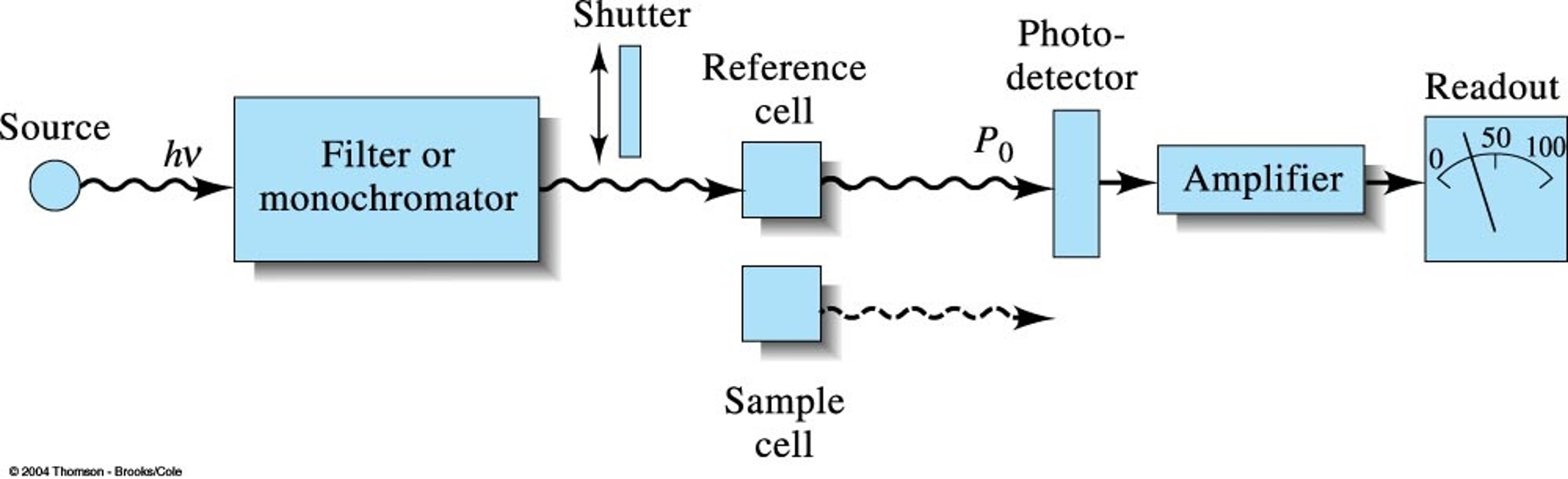
Single Beam Spectrophotometer
A type of spectrophotometer where a single beam of light passes through the sample, and absorbance is measured by comparing light intensities before and after.
Double Beam Spectrophotometer
A spectrophotometer where the light source is split into two beams, one passing through the sample and the other through a reference, allowing for more accurate measurements.
Monochromator
A device in a spectrophotometer that isolates a specific wavelength of light from a broad spectrum by using a diffraction grating or prism.
Cuvette
A small, transparent container used in spectrophotometry to hold liquid samples for light transmission measurements.
Photomultiplier Tube (PMT)
A highly sensitive detector used in spectrophotometers that amplifies the signal of light detected, making it possible to measure very low light levels.
Absorbance (A)
A measure of the amount of light absorbed by a solution, calculated as the negative logarithm of transmittance.
Transmittance (T)
The ratio of the intensity of light that passes through a sample to the intensity of the light that was incident on the sample.
Molar Absorptivity (epsilon)
A constant that indicates how strongly a substance absorbs light at a given wavelength, used in conjunction with Beer-Lambert Law.
Path Length (l)
The distance that light travels through a sample in a cuvette, typically measured in centimeters.
Wavelength (lambda)
The distance between successive peaks of a wave, particularly in the context of light, crucial in determining absorbance in spectrophotometry.
Beer Law
A relationship that relates the absorbance of light to the concentration of the absorbing species in a sample, used in spectrophotometry. A = l e c
Absorption Spectrum
A plot showing the absorbance of light by a sample at different wavelengths, providing information about the sample’s composition and concentration.
Standard Solution
A solution with a precisely known concentration, used as a reference in analytical methods like spectrophotometry.
Calibration Curve
A graph plotting known concentrations of a substance against their corresponding absorbance, used to determine the concentration of unknown samples.
Dilution
The process of reducing the concentration of a solute in a solution, often necessary in analytical procedures to ensure accurate measurements.
Blank Solution
A solution that contains all the components except the analyte of interest, used as a reference to zero the spectrophotometer before sample measurements.