Genetic Inheritance - Chp 16
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is a somatic cell?
all body cells that are not reproductive cells
Genetics
the study of inheritance
What scientist is known as ‘The Father of Genetics’?
Mendel
Species
a group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring
Inheritance/Heredity
passing on of traits from one generation to the next
Traits
physical/chemical characteristics that an orgnaism pocesses
Gene
a piece of DNA that contains the instructions to make a protein
Locus
the location of a gene on a chromosome
Allele
different forms of the same gene
Homozygous chromosomes
2 alleles are the same
Heterozygous chromosomes
2 alleles are different
Genotype
the genetic make-up of an organism
Phenotype
an organisms physical, visible traits
Dominant
only 1 allele needs to be present for the gene to be expressed
Recessive
a gene that is not expressed in the presence of a dominant allele, 2 recessive alleles are needed in order to be expressed
F1 Progeny
the first generation of offspring
Monohybrid cross
a cross between organisms involving 1 pair of traits
Dihybrid cross
a cross between 2 organisms that involve 2 traits
Incomplete dominance
neither allele is dominant or recessive over the other allele
Linked Cross
genes are located on the same chromosome
Sex Linked Cross
traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes
Mendel’s 1st Law: The Law of Segregation
states that at gamete formation pairs of alleles separate from each other, resulting in an allele in each gamete
Mendel’s 2nd Law: The Law of Independent Assortment
states that each allele separates at gamete formation and each allele is equally likely to combine with either member of another pair of alleles

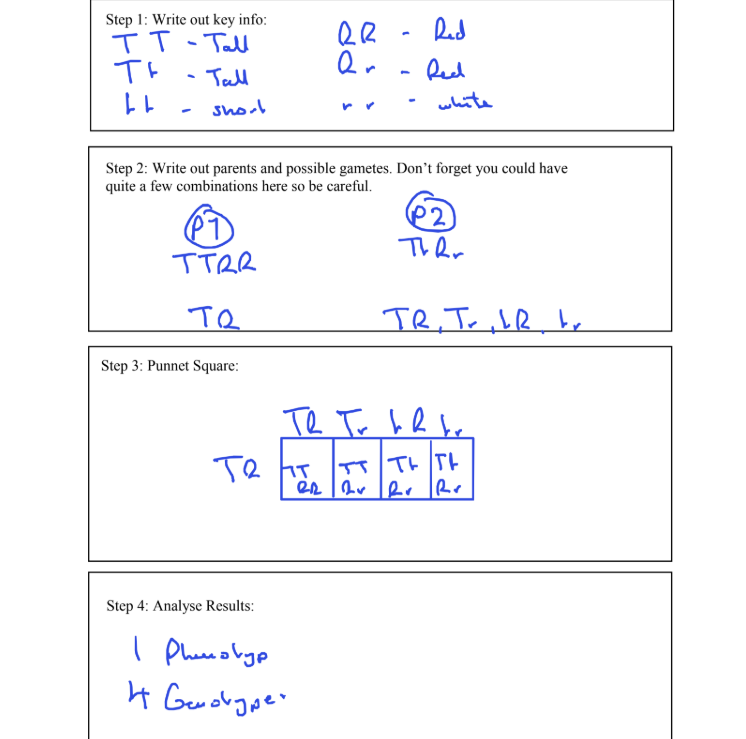




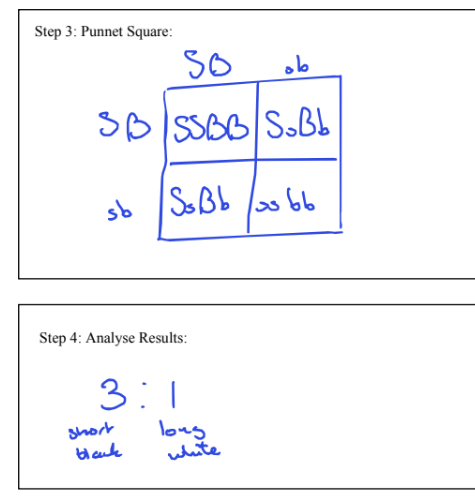
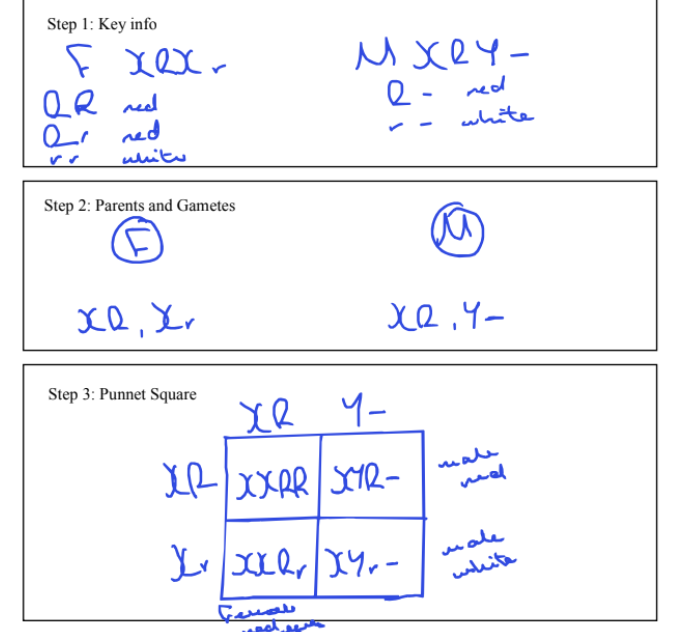
Why are recessive phenotypes expressed more frequently in males in a sex linked cross?
the Y chromosomes is shorter than the X genes, and contains less genes
if the X chromosome carries a recessive gene, there is no corresponding allele on the Y chromoeome that could preventi it from being expressed
as a result there is a ½ chance instead of a 1/3 chance of the male having the recessive phenotype


What is non-nuclear inheritance?
the inheritance of DNA via the mitochondria (and chloroplasts in plants)
this is always inherited meternally via the egg cell, as it is the cell that carry the cell organelles
What is a human disorder associated with non-nuclear inheritance:
Lack of ATP production - effects muscular and nervous system