Entropy
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
entropy (S)
the distribution of energy and/or matter in a system
the more ways energy can be distributed, the higher the entropy
how chaotic a system is
what can increase entropy:
change in state (gas has the highest entropy)
increased movement of particles e,g through heating
increased number of particles e.g. 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2(g)
greatest increase usually results from an increase in the number of gaseous particles
higher entropy is energetically favourable as energy of the system is more spread out in a disordered state
the entropy of a perfect crystal at 0K is 0 because:
there is a perfectly ordered arrangement of the constituent particle of a pure crystalline substance and there is no disorder at all
calculating standard entropy changes
units of entropy are in J K-1 mol–1
entropy changes depending on state of matter (gas has the highest entropy)
coefficients used to balance equation must be used when calculating overall entropy change

what is free energy
what’s left over to do useful work after a reaction is carried out
enthalpy change is difference between energy put in to break bonds and energy out when making bonds
entropy change is the cost of carrying out the reaction, so free energy is what you’re left with
gibbs free energy equation
units of ΔGꝋ are in kJ mol–1
ΔHrꝋ are in kJ mol–1
units of T are in K
units of ΔSsystemꝋ are in J K-1 mol–1. so usually must be converted to kJ K–1 mol–1 by dividing by 1000

calculating ΔGꝋ from other ΔGꝋ values
ΔGꝋ = ΣΔGproductsꝋ – ΣΔGreactantsꝋ
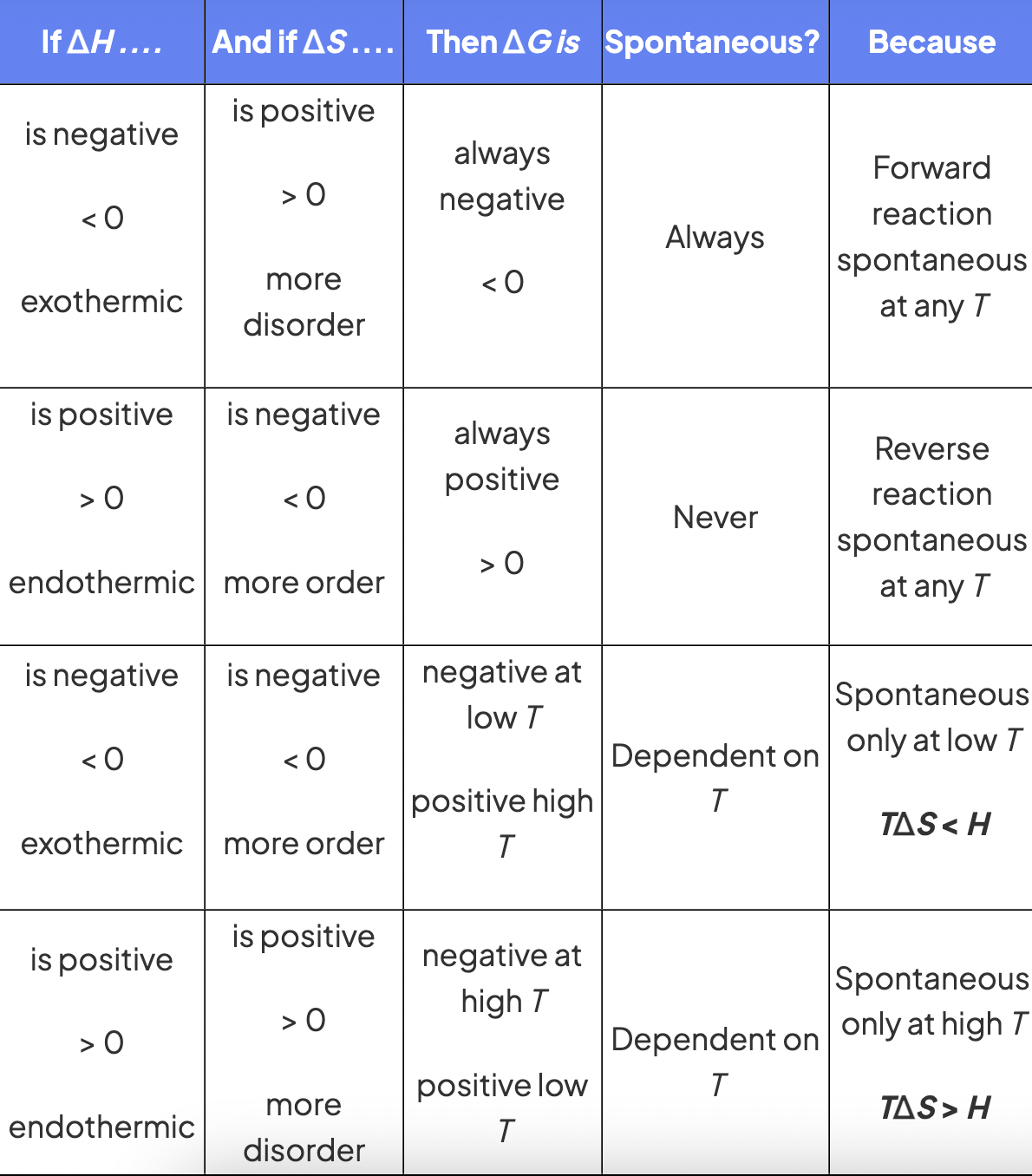
spontaneous reactions
spontaneous = feasible
for a reaction to be spontaneous ΔGꝋ must be negative or zero
summary of factors affecting gibbs free energy