2. Sensory and Edocrine
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Wavelength we can and cant detect
Can detect 380-750nm through photoreceptors
3 types of cones (red, green, blue)
1 type of rod
Cant detect
Infrared (700+)
Unltraviolet(400-)
Functional properties of peripheral retina and fovea
Peripheral retina
Mainly rods
peripheral and night vision
Fovea
Mainly cones
High acute vision
Human vs Dog Apple
Humans evolved from primates who had (3 cones)
They ate RED fruits
Dogs evolved from wolves (2 cones)
Didnt need to see RED to hunt
Ear canal
Sound waves enter ear canal → strike tympanic membrane → become vibrations
3 bones of middle ear vibrate (malleus, Incus, Stapes)
Oval window in vetibular duct passes vibration from stapes into fluid waves
Fluid waves cause vibration in basil membrane which bend inner hair cells
The tympanic duct get hit with vibration that dissipate at round window
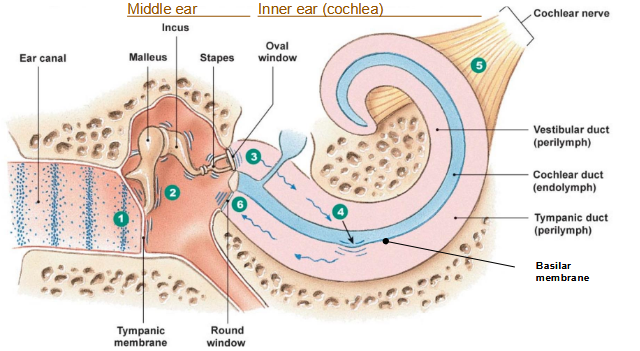
Stiffness of the Basilar membrane
Low frequency sounds cause vibrations at the distal end
High frequency sounds cause vibrations in proximal regions (close to the oval window) (stiff area)
Wherever the vibrations occur the cilia of the IHC’s in that same region will bend and send neutral signals to the brain
3 functions of the taste system
Prepares body for digestion
Motivates or inhibits feeding
Identified the different chemicals in foods
Umami, salt, butter, sour, sweet, or fat?
Proprioceptive vs Vestibular system contribution to movement, body awareness, and balance
Proprioception (Body position awareness)
Stretch receptors in muscles and joints
Control our movement and keep track of where our body is located.
“Know ur hand is on a desk without looking)
Vestibular System (Balance and spatial orientation)
Inner ear (semicircular canal)
detects head position and movement
“Know which way is up when spinning)
Functions of internal chemoreceptors and baroreceptors in the body
Chemoreceptors
Allow us to track changes in pH, PCO2, and PO2 of the blood and the spinal fluid in brain and spinal cord.
Trigger changes in breathing and cariodiovascular activity
Baroreceptors
Allow us to monitor degree of stretch of internal cavities
Ex) Carotid sinus and aortic sinus (info on blood pressure and respiratory control centers)
Ex) lungs (info on respiratory rate)
4 somatic senses
Somatic sensory cells/neurons
Proprioception
Baroreceptors
Internal chemoreceptors
Which oral sensations are mediated by Somatic sensory receptors
Crispness
Oiliness
Astringency (wine)
Sharpness/pain
Smoothness/Lumpiness
Carbination
Coldness/heat
Spicy, pungent/tingling (spinces)
How the peripheral olfactory system discriminates odors
Odor molecules enter the epithelum and stimulate specific types of olfactory sensory neurons
Green, red, or purple
Each odor causes a unique pattern of activation of the receptor neurons
Glomeruli in the olfactory bulb
Action potentials travel through the neurons and to the olfactory bulb in the brain
Comparison of nervous and endocrine systems
Nervous:
Wierd
Neurotransmitters diffuse over short distances
Fast and Short lasting
Coordinate rapid and specific responses
Endocrine:
Wireless
Hormones are transported over long distances in blood
Slow and Long lasting
Produce slower more general responses
Anterior vs Posterior pituitary gland
Posteriror Pituitary
Secretes 2 neurohormones made by hypothalmic neurons to the blood stream
ADH and oxytocin-
Anterior pituitary glands
Secreates many endocrine hormone
Made in pituitary and controled by releasing hormones from hypothalmus
GH, TSH, ACTH
Hypthamic neurons
Neurons in the brain
Make neurohormone
Sends release and inhibitory signal to anterior pituitary
Sends neural signals to the pituitary gland to control hormone release.
Releasing hormone vs Regular Hormone
Releasing hormone
Come from hypthalamus
Tells anterior pituitary cell to release another hormone
Travels through veins
Hormones
Produced by endocrine cells
Acts directly on target organs/tissues
Travels through blood
Negative feedback regulating secretion of thyroid hormones
When cortisol and thyroid hormone levels are high enough
They signal the hypothalamus and pituitary to stop releasing their stimulating hormones
How the body terminates hormone action
Destroyed by enzymes in the blood or inside cells
Reabsorbed by the secretory cells
Excreted in urine
Target cells
Posses specific protein receptors that bind to a hormone
target tissues for epinephrine
lungs
heart
muscles
fatty acid releae
intestines
liver
brain