Carboxylic Acids
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Why are carboxylic acids soluble?
What happens to their solubility as chain length increases?
Polar C=O + O-H bonds
Form H bonds with water
As chain length increases solubility decreases as non-polar C has greater affect on overall polarity
Reaction of carboxylic acid with metals
example of propanoic acid and magnesium
Hydrogen gas + carboxylate salt
2CH3CH2COOH + MG —> (CH3CH2COO-)Mg2+ + H2
Reaction of carboxylic acids with metal oxides
Example using ethanoic acid and calcium oxide
Forms salt and water
2CH3COOH + CaO —> (CH3COO)2-Ca2+ + H2O
Reaction of carboxylic acids with alkali
Example using ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide
Forms salt and water
CH3COOH + NaOH —> CH3COO-NA+ + H2O
Reaction of carboxylic acids with carbonates
Example with ethanoic acid and sodium carbonate
Forms salt, water and CO2
2CH3CHOOH + NaCO3 —> 2CH3COO-Na+ + CO2 + H2O
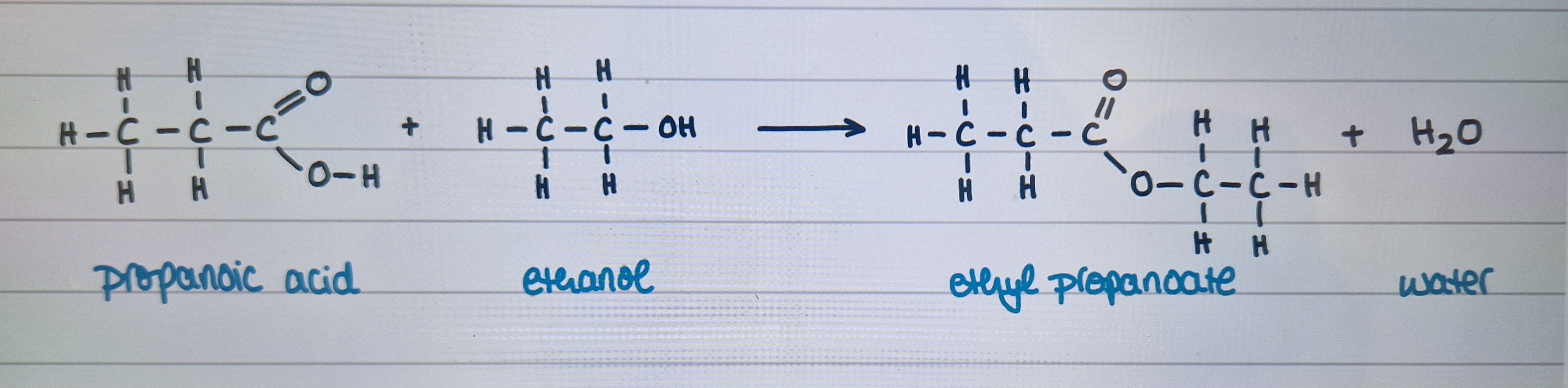
Describe esterification of carboxylic acids
Example using propanoic acid + ethanol
Happens when carboxylic acids react with alcohols in presence of concentrated H2SO4
produces ester + water
Describe alkaline hydrolysis of esters
Example using methyl enthanoate
Esters heated under reflux with aqeous OH- ions to form carboxylate ion and alcohol
CH3COOCH3 + NaOH- —> CH3COO-Na+ + CH3OH
Acid hydrolysis of esters
forms alcohol + carboxylic acids
What is rhe acyl chloride functional group?
COCl
Reaction of acyl chlorides with alcohols
using ethanoyl chloride + propan-1-ol as exmaple
form esters + HCl
CH3COCl + CH3CH2CH2OH —> CH3COOCH2CH2CH3 + HCl
Acyl chloride from carboxylic acids using ethanoic acid
R = SOCl2
Forms esters + SO2 + HCl
CH3COOH + SOCl2 —> CH3COOCl + SO2 + HCl
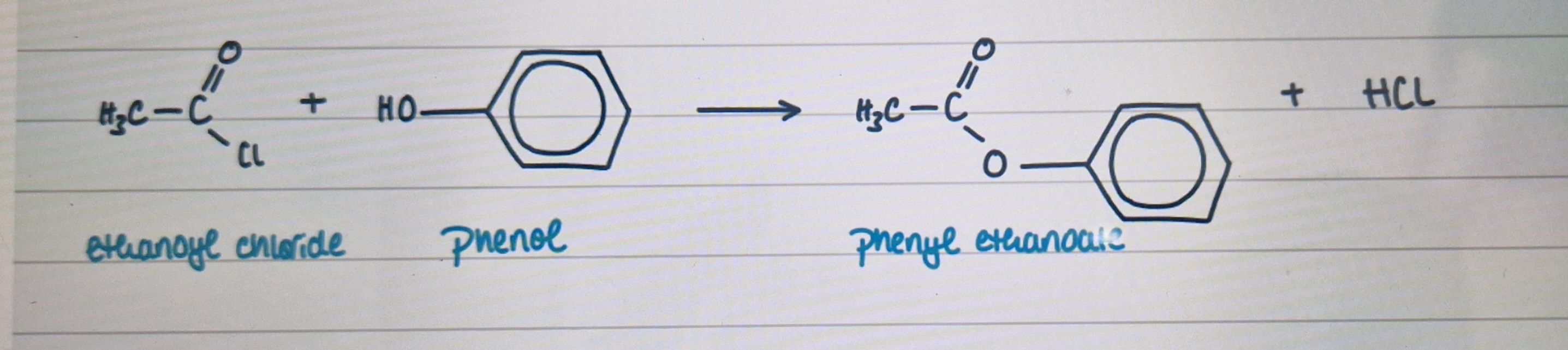
reaction of acyl chloride + phenol
example with ethanoyl chloride + phenol
forms ester + HCl
Acyl chloride + water using ethanoyl chloride
Forms carboxylic acid + HCl
CH3COCL + H2O —> CH3COOH + HCl
Why do acyl chlorides react with ammonia or amines
N on ammonia/amines acts as nucleophile and donates lone pair of electron to electron-deficient species
Acyl chloride + ammonia using ethanoyl chloride
Forms primary amide + NH4Cl
CH3COCl + 2NH2 —> CH3CONH2 + NH4Cl
Acyl chloride + primary amine using ethanoly chloride
Forms secondary amide
CH3COCl + CH3NH2 —> CH3CONHCH3 + CH3NH3+Cl-