Psych 3501 Exam 2: Psychoanalysis and Psychodynamic Therapy
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Freud's psychoanalytic theory
Emphasized the role of unconscious psychological conflicts and led to development of therapy to resolve those conflicts
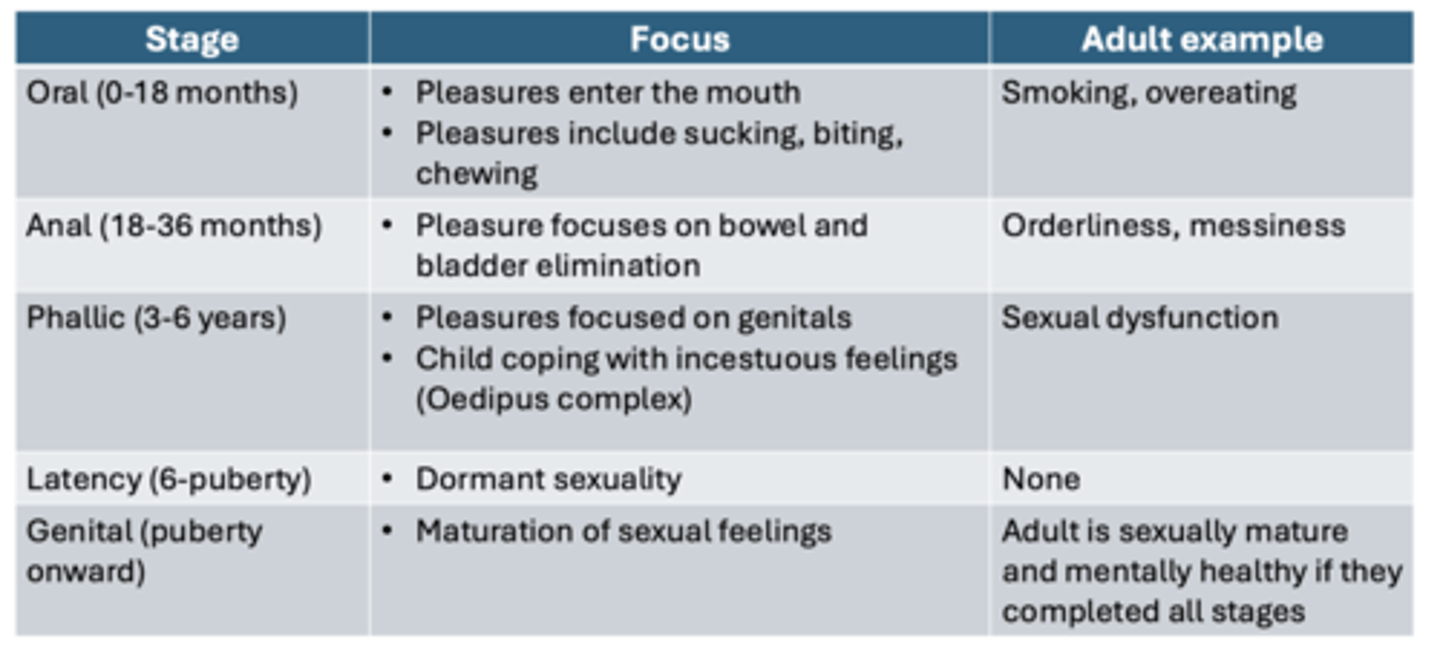
Freud's theory of psychosexual development
Oral
Anal
Phallic
Latency
Genital
Levels of consciousness
Conscious level
Full awareness
Preconscious level
Can become aware by directing attention
E.g.: can turn my attention to my stomach and realize that I’m hungry
Unconscious level
Unaware without psychoanalysis
Hidden, unspoken desires and thoughts
Day to day awareness only at conscious and preconscious level
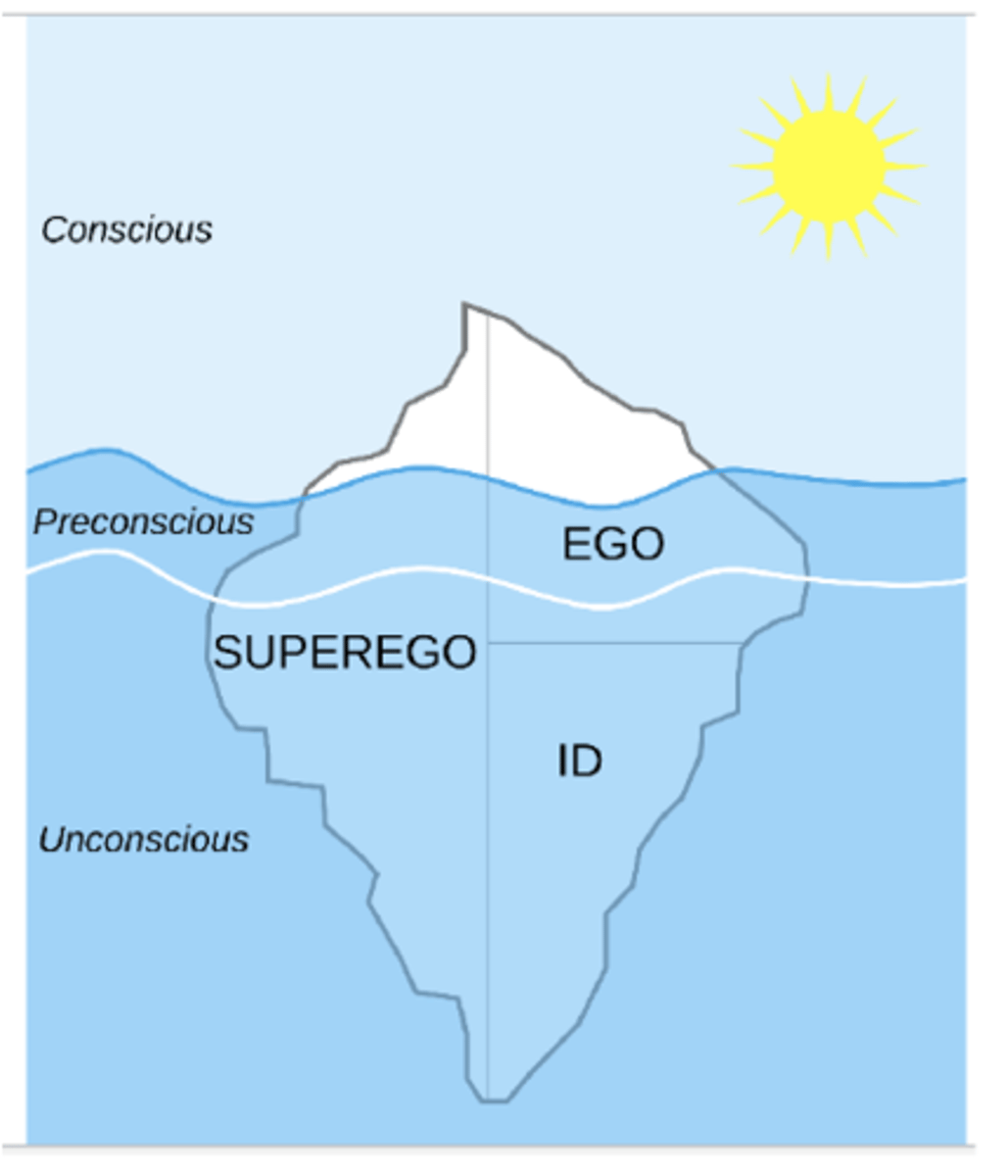
Freud's structural model of personality
Id
Unconscious
Operates on the pleasure principle: what feels good for me, what is best for me
Source of basic biological drives: sex and violence
Superego
Morals, perfection
Conscience: guilt we feel in response to an immoral act
Ego ideal: moral striving, pride we feel when we do something good
Ego
Mainly conscious
Operate on reality principle
Balances the impulses of the id and the superego
Responsive to external realities
E.g., I need to do certain things, I can’t do certain things
Topological map of the structural model
Ego: conscious & preconscious
Id: entirely unconscious
Superego: across all three levels
Neurosis
An umbrella term for all odd, unusual presentations of emotions and behaviors
Due to psychic conflicts between the id and superego
Usually occur in the unconscious
Anxiety occurs when unacceptable drives begin to enter the conscious mind
Ego responds by engaging a defense mechanism
Defense mechanisms
Unconscious strategies used to keep anxiety-provoking unconscious urges/desires from becoming conscious
Types of defense mechanism
denial
projection
repression
displacement
intellectualization
reaction formation
sublimation
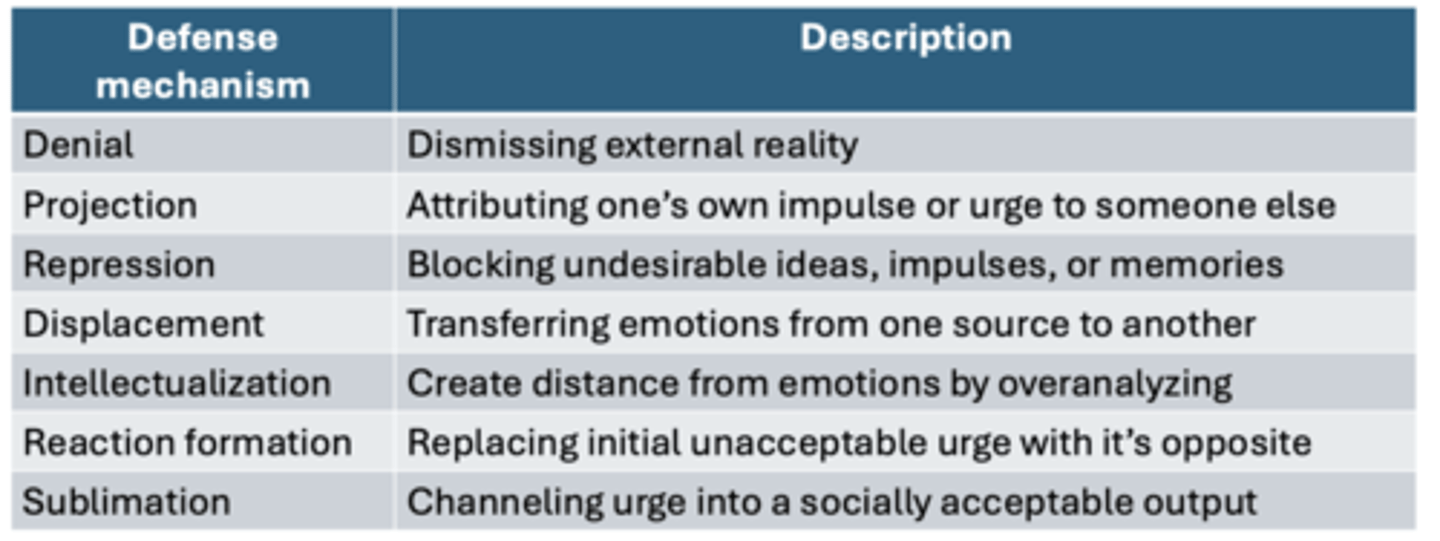
Denial
Dismissing external reality
E.g., continue to shop for luxury good despite in debt
Projection
Attributing one’s own impulse or urge to someone else
E.g., Someone cheating on their spouse accuse spouse of cheating
Repression
Blocking undesirable ideas, impulses, or memories
E.g., No recollection of a traumatic event
Displacement
Transferring emotions from one source to another
E.g., Get into a fight with roommate after a stressful day
Intellectualization
Create distance from emotions by overanalyzing
E.g., People diagnosed of a terminal illness started searching for papers but not engaging with the emotions
Reaction formation
Replacing initial unacceptable urge with its opposite
E.g., If you really dislike someone, you are excessively nice to this person
Sublimation
Channeling urge into a socially acceptable output
E.g., Playing sports to offset violent urges
Psychoanalysis goals
Goals: to help clients gain insight into and work through the unconscious thoughts and emotions underlying their neuroses and strengthen the ego’s control over the id and superego
Psychoanalysis 4 fundamental processes
Identifying relationships between psychosexual development and current issues
- What stages of psychosexual development did they get stuck in, how does early childhood experience influence their experience today
Lack of or limits in self-awareness causes neuroses
Talking about thoughts and emotions can be curative
The importance of the therapeutic relationship
Psychoanalytic techniques
free association
dream interpretation
transference
countertransference
psychic determinism
resistance
interpretation
insight
working through
Free association
The essential piece of psychoanalysis (Considered the sine qua non of psychoanalysis)
Expressing thoughts without censorship in order to reveal unconscious processes
Freud’s alternative to hypnosis
Dream interpretation
Probing content and imagery of dreams to reveal unconscious processes
Dreams generated by 2 processes
- Unconscious impulses that generate a desire or wish expressed in the dream
- A censorship process that distorts the expression of the wish
Dreams consist of 2 types of content
- Manifest content: narrative content that often reflects details of the prior day
- Latent content: unconscious urges in a disguised form
Disentangle the latent content from the manifest content and the censorship process that is distorting the latent content
Transference
Client's typical relationship patterns and defense mechanisms appear in therapy
Clients will repeat patterns of behavior in therapy
Freud believes these patterns reflect important early relationships (e.g., child-parent)
Creates an opportunity to bring awareness to the pattern and facilitate resolution
Countertransference
Therapist's reactions towards the client are impacted by their personal history
Can adversely affect therapy
Impetus for requiring therapy in trainees
Psychic determinism
Associations between memories, ideas, experiences are not random but reflect important underlying unconscious processes
Core assumption of psychoanalysis
“Freudian slips”, unexpected associations, memory failures, etc. are meaningful
Probing these will reveal an important unconscious meaning behind the connection
Resistance
Clients behave in ways that interfere with treatment
Not unique with psychoanalysis
As therapy progresses, unconscious conflicts become revealed, which provokes anxiety
Resistance behaviors to protect the conscious mind from unconscious impulses
E.g., forgetting appointments, emotionally detaching, disagreeing with the therapist, distracting from important conflicts
Interpretation
Insight
Working through
Interpretation
Therapist remarks on how thoughts, experiences, etc. might be related to an unconscious conflict; presented as hypotheses
Insight
Client gains conscious awareness of the underlying conflict
Occurs if an interpretation is accurate and client is ready to hear it
Working through
Insight is not sufficient
Exploring the implications of insights
Therapist encourages exploration of how the conflict drives problems in daily life
Criticisms of psychoanalytic theory and therapy
Vague and elusive concepts make theory difficult to test scientifically
Most of theory is based on case studies
Minimal evidence for efficacy of psychoanalysis
Excessive focus on sexuality
Intensive, long, and expensive
Psychodynamic therapies
“Neo-Freudians”
3 differences from original psychoanalytic theory
De-emphasized sexual/aggressive id, emphasized positive role of ego in promoting adaptive functions
de-emphasized sexuality in early experiences, emphasized attachment/bonding with caregivers
Emphasized the therapeutic relationship as healing itself
Alfred Adler's individual psychology
Striving for superiority: personality development driven by desire to overcome feelings of helplessness and gain control over environment
“Individual” refers to emphasis on the whole person
Emphasized personal fulfillment
Overprotection or neglect -> intense inferiority -> excessive striving, desperate and unhealthy efforts to enhance self-esteem
Emphasized the social context: vital for striving for the fulfillness
All behavior is goal-directed: not biological urge, but pursuing a specific goal
Fulfillment in the context of 3 basic life tasks
Work: realized when work is meaningful and satisfying
Friendship: realized by creating satisfying relationships with others
love/intimacy: realized when one can love oneself and partner
Adlerian psychodynamic techniques
Goal: explore and alter maladaptive lifestyles using strategies to promote growth and resilience
Interpretations focus on current problems and lifestyle patterns
- Still offer interpretation, but focus on current instead of early experiences
- Examine the purpose of a behavior
Create expectations for the client
- Ask clients to imagine how they would act if they were their ideal self
- Identify discrepancies between current self vs. the ideal self
Provide encouragement and empathy
- Help clients recognize their own strengths and increase their confidence
- Precursor to humanistic therapy
Object relations theory
Melanie Klein: one of first to adapt psychoanalysis to young children
Adult relationships are shaped by experiences of caregivers (objects) during infancy
Object: caregivers
Relations to objects are internalized early in life and unconsciously repeated in adult life
Emphasis on the relationship in contrast to discharging sexual and violent impulses
Object relations therapy
Therapist are more directive
Highlight patterns, conflicts rather than letting them be revealed naturally (e.g., through free association)
Focus on creating a nurturing relationship with the client
Criticisms of object relations theory
Relies on infant abstraction ability that exceeds cognitive capacity
- Can infants think abstractly at the stage of development?
Untestable
Short-term psychodynamic psychotherapy
1930-1940s: psychoanalysts begin questioning the necessity of year-long analysis
Argued daily sessions could create dependence (on the therapist) and monotony (bored)
Distinguished between clients who needed long-term traditional psychoanalysis and those who could be helped with shorter care
Intensive short-term dynamic psychotherapy
Developed by Habib Davanloo
Emphasizes concrete goals achievable in limited sessions
Insight and working through based on current problems
- Instead of exploration on past experiences & early experiences, focus on the present; no attention to past conflicts
Relatively fast-paced
Therapist is more active and directive
Identify problem, challenge to abandon defense mechanisms, highlight resistance as needed
~ 20 sessions
State of the science on psychodynamic approaches
Traditional psychoanalysis rarely practiced
Psychodynamic therapies are 2nd most common practiced
Less ideological than in past: many practitioners integrate elements of other approaches
Continues to be limited by insufficient evidence, though research is becoming more common
Efficacy of short-term psychodynamic psychotherapy in depressive disorders
Large effect compared to no treatment
Negligible effect compared to supportive therapy
Less effective than CBT but the effect size is small
Summary
