Neuro Exam 3
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Vestibular System
A sensory system that maintains balance, posture, and spatial orientation.
Semicircular Canals
Three canals (anterior, posterior, lateral) in the inner ear that detect rotational movements.
Otolith Organs
Consist of the utricle and saccule that detect linear movements and gravitational forces.
Endolymph
Fluid found within the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear, essential for detecting motion.
Otoliths
Calcium carbonate crystals that rest on top of the gelatinous layer in the otolith organs.
Hair Cells
Sensory cells in the inner ear that transduce mechanical stimuli into neural signals.
Euler Angles
Angles used to describe the orientation of objects, specifically yaw, pitch, and roll.
Kinocilium
The single long cilium in hair cells that acts as a reference point for directional movement.
Cupula
A gelatinous diaphragm in the ampulla of the semicircular canals that is displaced by endolymph movement.
Striola
The reversal region in the utricle where hair cell polarity is organized.
Oculomotor Nucleus
Nucleus in the brain that coordinates eye movement and is connected to vestibular signals.
Bithermal Caloric Test
A test used to assess vestibuloocular reflexes by introducing cold or warm stimuli into the ear.
Vestibular Nuclei
Groups of neurons in the brain stem that process inputs from the vestibular system.
Multisensory Cortex
Regions that integrate information from multiple sensory modalities to create a comprehensive understanding of the environment.
Nystagmus
Involuntary eye movements often triggered by vestibular stimulation.
Bilateral Symmetry
The arrangement where paired structures (like semicircular canals) are similar on both sides of the body.
Perilymph
Fluid that fills the space between the bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth in the inner ear.
Vestibulospinal Tracts
Pathways that relay vestibular information to the spinal cord for motor control.
Equivalent Acceleration
A term referring to the linear acceleration that produces similar effects on the otolithic membrane as gravitational forces.
Ambiguous Information
The phenomenon where the postural system cannot distinguish between tilt and linear movements.
Reflexes
Rapid, automatic, and involuntary movements; stereotyped responses that occur the same way each time.
Rhythmic motor patterns
Movements initiated and terminated voluntarily but maintained through reflex mechanisms, like walking or chewing.
Voluntary movements
Purposeful and learned movements that improve with practice, such as writing or dancing.
Upper motor neurons
Located in higher motor centers like the cortex; they influence lower motor neuron circuits.
Lower motor neurons
Found in the brainstem and spinal cord; directly control skeletal muscles and regulated by local circuits.
Cerebellum
A brain structure that contributes essential and distinct roles to motor control by coordinating voluntary movements.
Basal ganglia
A group of nuclei in the brain associated with the control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, and routine behaviors.
Corticospinal tract
Pathway from the motor cortex to the spinal cord, crucial for voluntary motor control.
Reticulospinal tract
Regulates muscle tone and coordinates voluntary movements, adjusting muscle activity for balance.
Golgi tendon organs
Sensory receptors located at the junction of muscle and tendon that regulate muscle tension through feedback.
Muscle spindles
Sensory receptors arranged parallel to muscle fibers that detect changes in muscle length and the rate of that change.
Size principle of motor unit recruitment
Smaller motor neurons are activated before larger ones in response to increasing force demands.
Crossed extension reflex
A spinal reflex that causes the opposite limb to extend when one limb is flexed, providing balance.
Stretch reflex
A negative feedback mechanism that regulates muscle length by triggering contraction in response to stretch.
Presynaptic inhibition
Inhibition of neurotransmitter release from sensory axon terminals, allowing selective modulation of sensory input.
Renshaw cells
Interneurons that provide recurrent inhibition of motor neurons to stabilize firing rates.
Gamma motor neurons
Neurons that adjust the sensitivity of muscle spindles during muscle contraction.
Neural circuitry
Interconnected neurons that work together to control specific functions, such as locomotion or reflexes.
Basal Ganglia
A group of subcortical nuclei involved in the modulation and coordination of movement.
Striatum
Part of the basal ganglia that includes the caudate and putamen, responsible for receiving movement-related signals.
Globus Pallidus
A structure in the basal ganglia that plays a key role in regulating voluntary movement via its internal and external segments.
Substantia Nigra
A component of the basal ganglia, critical for movement regulation and affected in Parkinson's disease.
Dopaminergic Input
Neurotransmitter signals from dopaminergic neurons, crucial for the proper functioning of basal ganglia pathways.
Direct Pathway
Pathway in the basal ganglia that facilitates movement by inhibiting the globus pallidus, leading to increased excitation of the motor cortex.
Indirect Pathway
Pathway in the basal ganglia that inhibits movement by activating the globus pallidus external segment, which suppresses motor activity.
Parkinson’s Disease
A neurodegenerative disorder characterized by dopamine neuron loss in the substantia nigra, leading to movement impairments.
Huntington’s Disease
A genetic disorder resulting in the degeneration of basal ganglia, causing uncontrolled movements and cognitive decline.
Tourette’s Syndrome
A neurological disorder characterized by repetitive, involuntary movements and vocalizations known as tics.
Rheumatic Fever
An autoimmune response to a Streptococcus infection, causing inflammation in several body systems including the basal ganglia.
Wilson’s Disease
A genetic disorder resulting in copper accumulation in the body, particularly affecting the liver and brain.
Motor Learning
The process of improving and automating movements through practice, aided by the basal ganglia.
Cognitive Roles of Basal Ganglia
Functions related to decision making, learning, and reward processing, aside from movement.
Neural Plasticity
The ability of neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization.
Cerebellum
Part of the brain responsible for coordination, balance, motor learning, and cognitive functions.
Dysmetria
A condition in which the movement trajectory is inaccurate, often seen in cerebellar patients.
Decomposition of movement
Movement is performed in a series of discrete, separate motions, rather than as a smooth, fluid action.
Cerebellar Ataxia
A lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements, often caused by cerebellar damage.
Proprioception
The sense of body position and movement; impaired in cerebellar damage during active but not passive movement.
Cerebrocerebellum
The part of the cerebellum involved in planning and fine control of voluntary movements.
Spinocerebellum
Region of the cerebellum that receives sensory information, regulating posture and movement.
Vestibulocerebellum
Part of the cerebellum that maintains balance and controls eye movements.
Input Pathways
Paths through which sensory information is received by the cerebellum, including from the spinal cord and various brain regions.
Output Pathways
Paths through which signals are sent from the cerebellum to influence motor actions and coordination.
Learning in the cerebellum
Adaptive changes at synapses that refine motor responses based on experience, including classical conditioning and motor adaptation.
Mossy fibers
Fibers that carry sensory information to the cerebellum and excite granule cells.
Climbing fibers
Fibers originating from the inferior olivary nucleus that provide direct excitatory input to Purkinje cells.
Glomerulus (cerebellar)
A synaptic complex formed in the cerebellum involving mossy fibers and granule cells, integrating sensory input.
Plasticity
The ability of the brain to change and adapt as a result of experience, crucial for learning and memory.
Classical Conditioning
A learning process in which a conditioned stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response.
Vestibular System Diagram
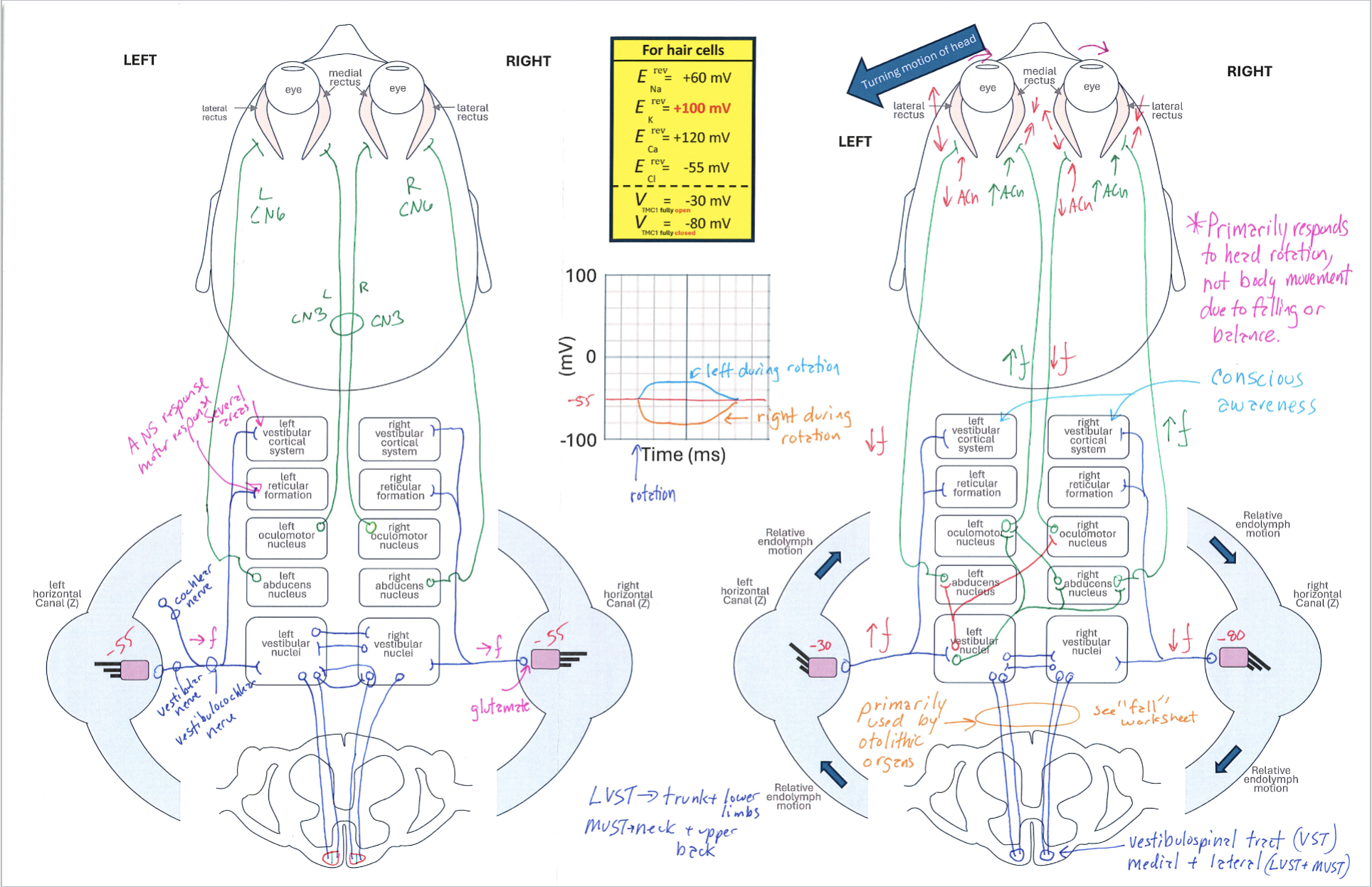
Correctly Drawn
Utricle Diagram
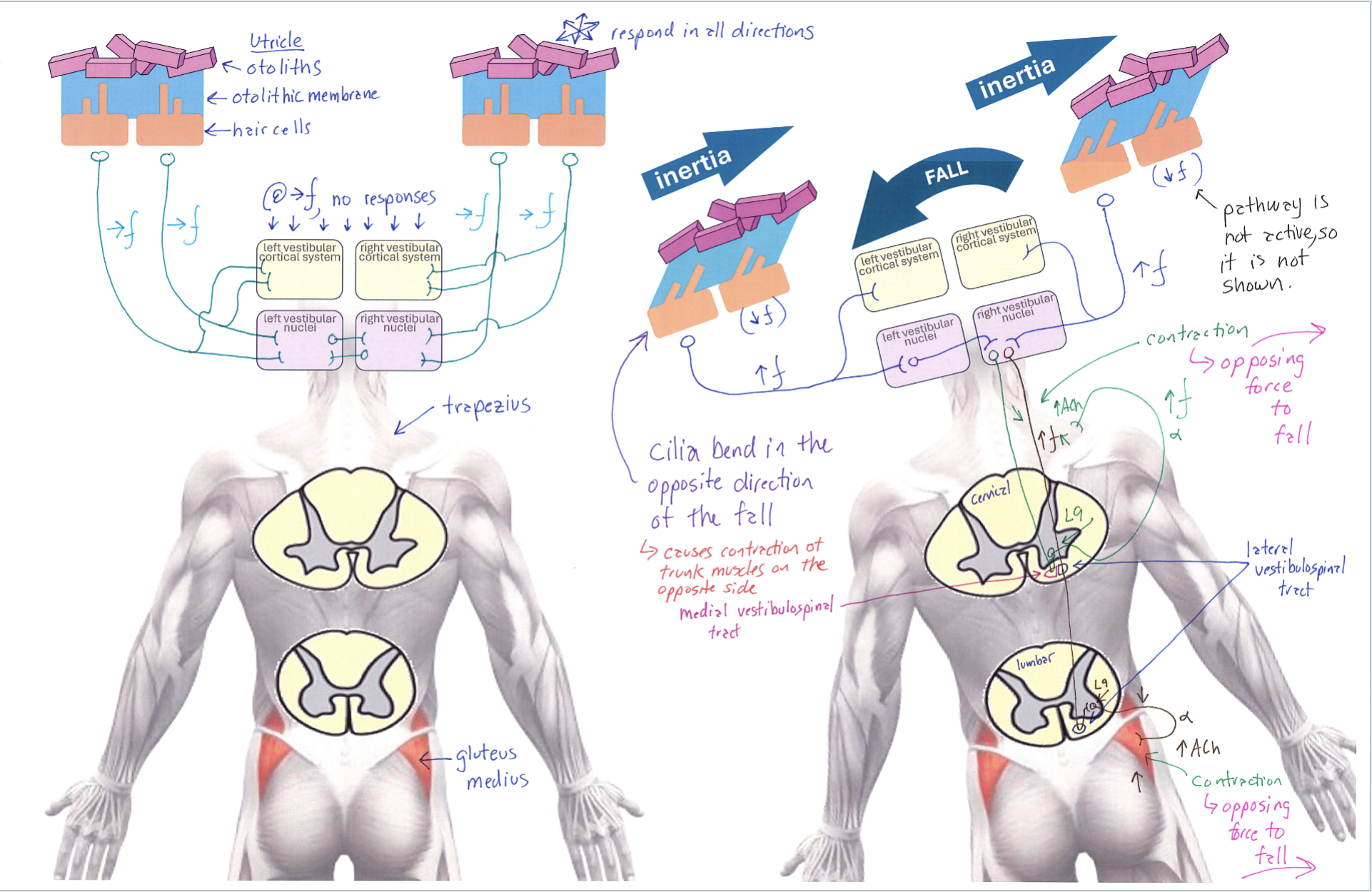
Correctly Drawn
Muscle Fiber Diagram
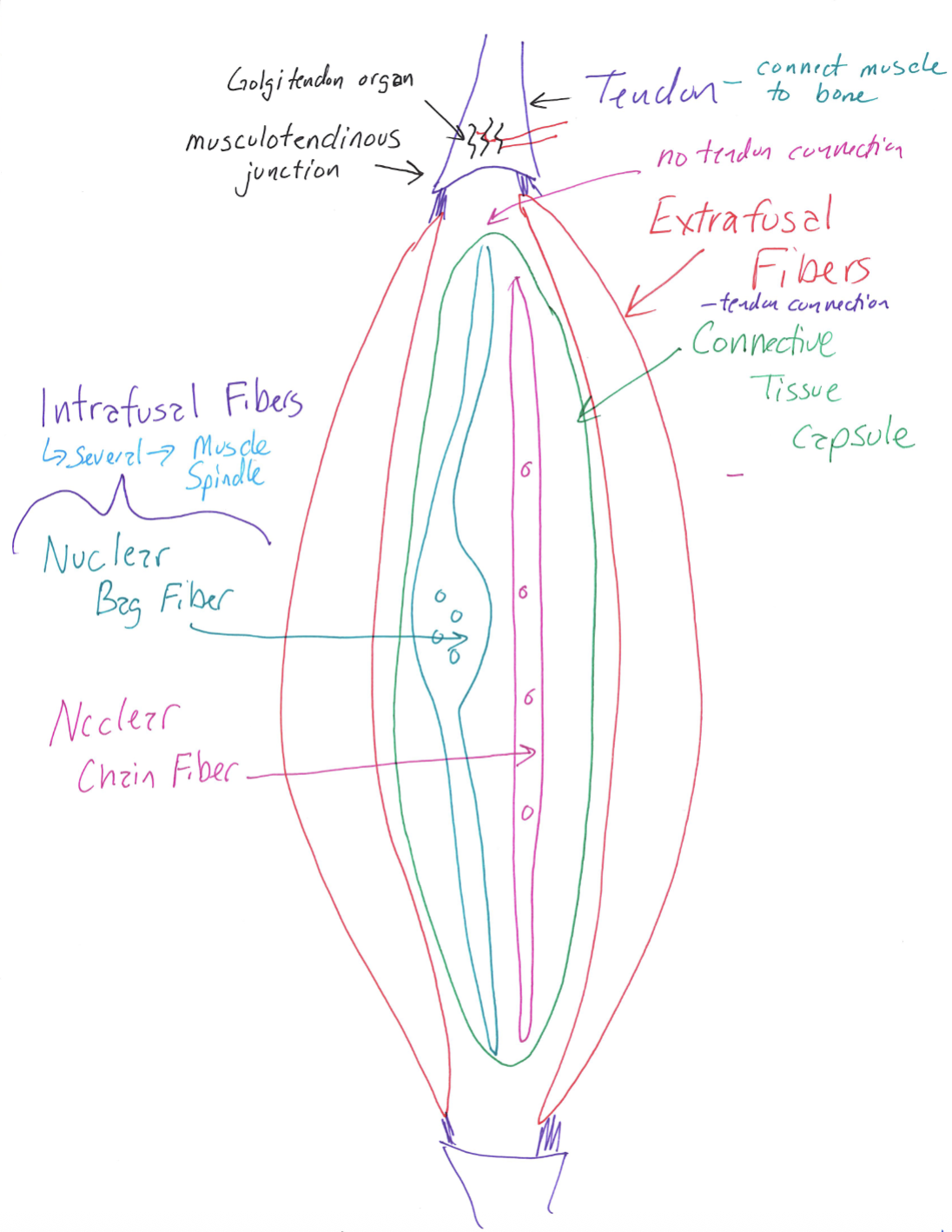
Correctly Drawn
Intrafusal and Extrafusal Fibers
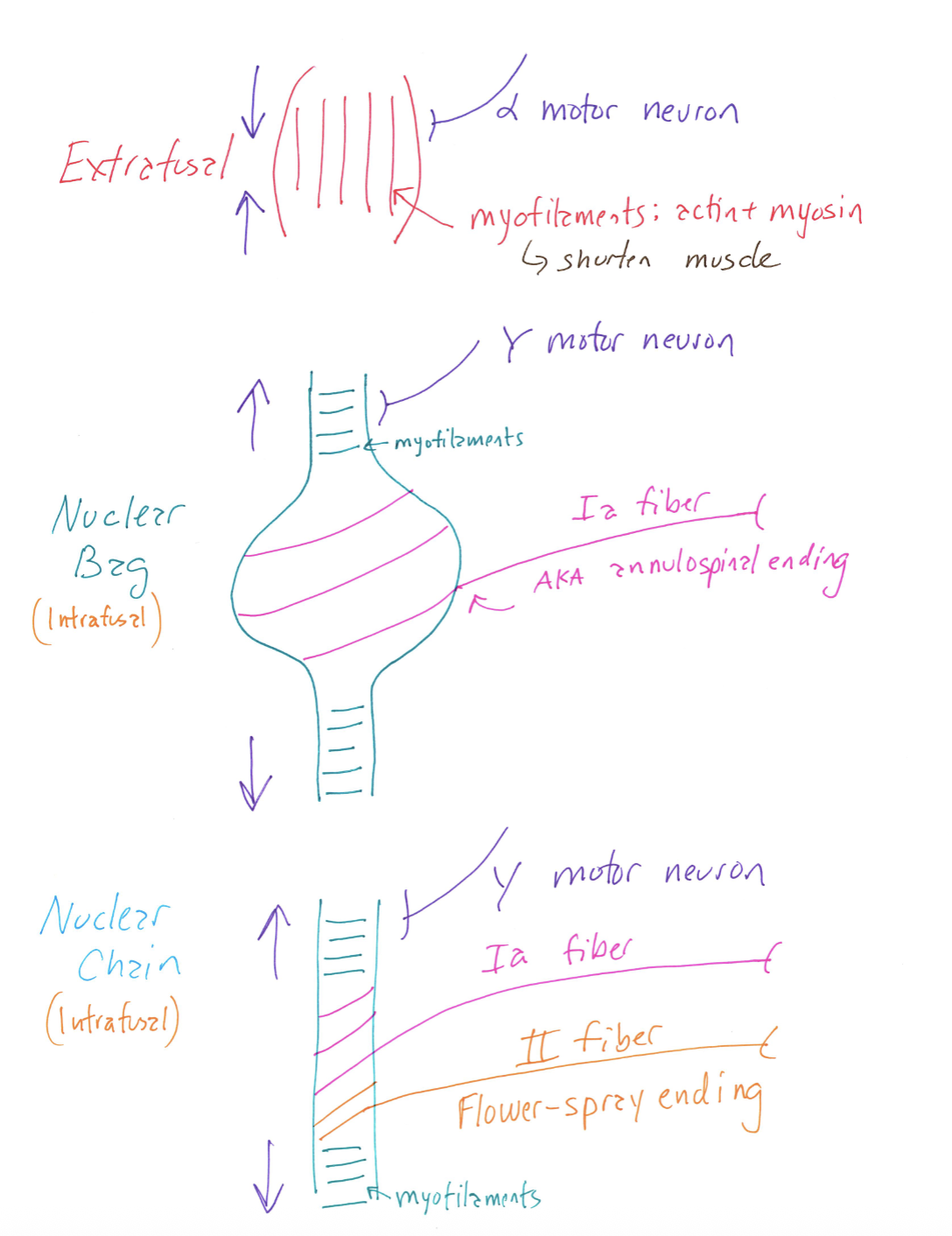
Correctly Drawn
Golgi Tendon Organ Anatomy
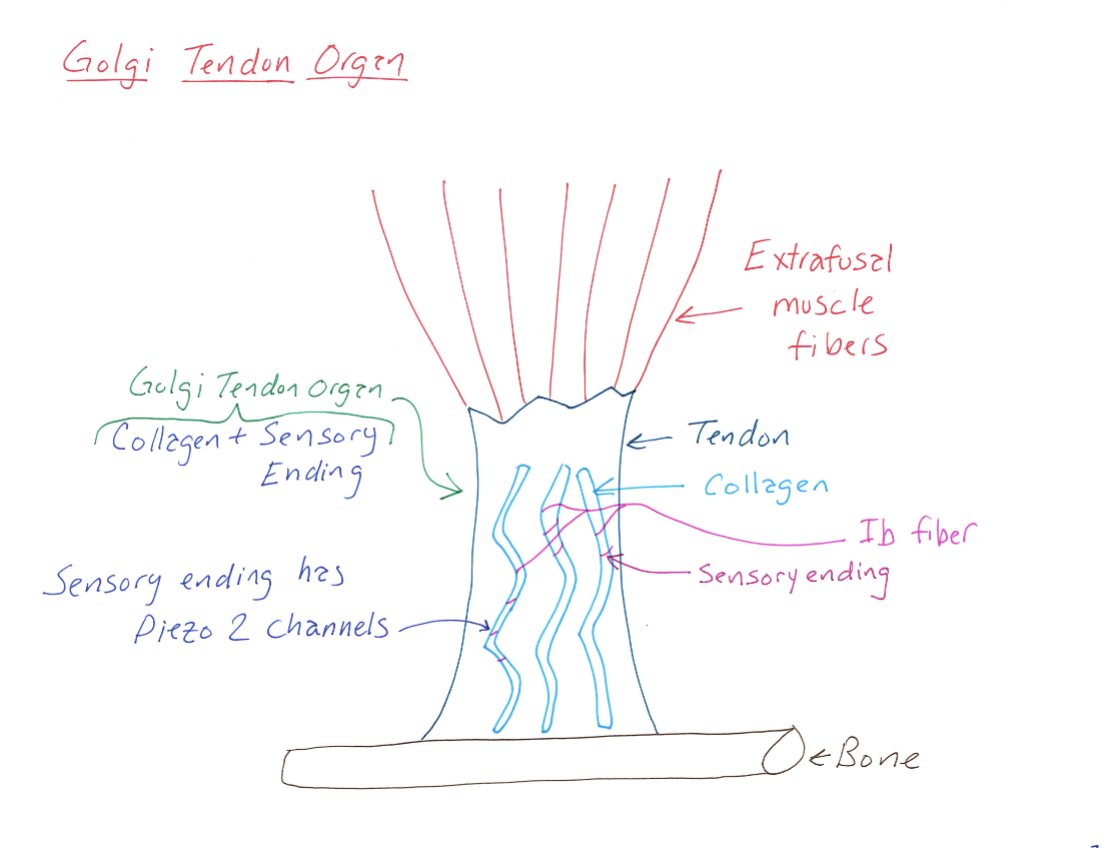
Correctly Drawn
Golgi Tendon Organ Reflex
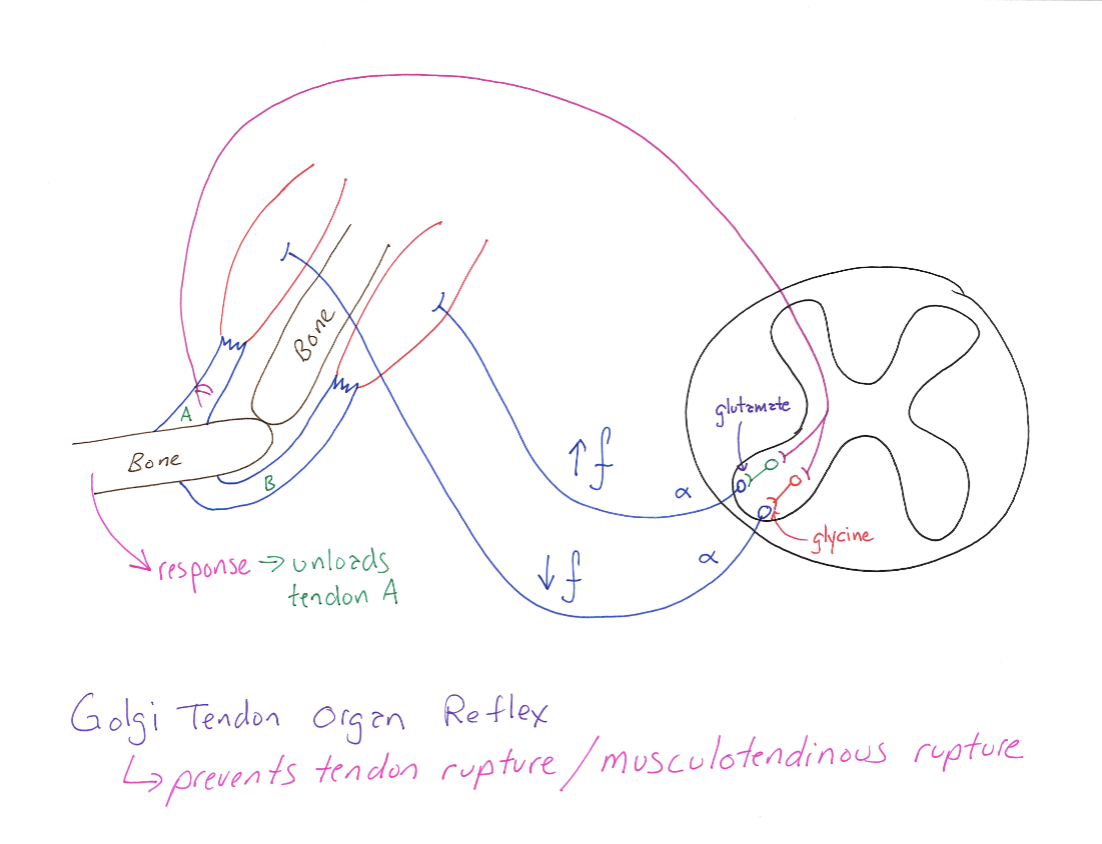
Correctly Drawn
Alpha-Gamma Coactivation
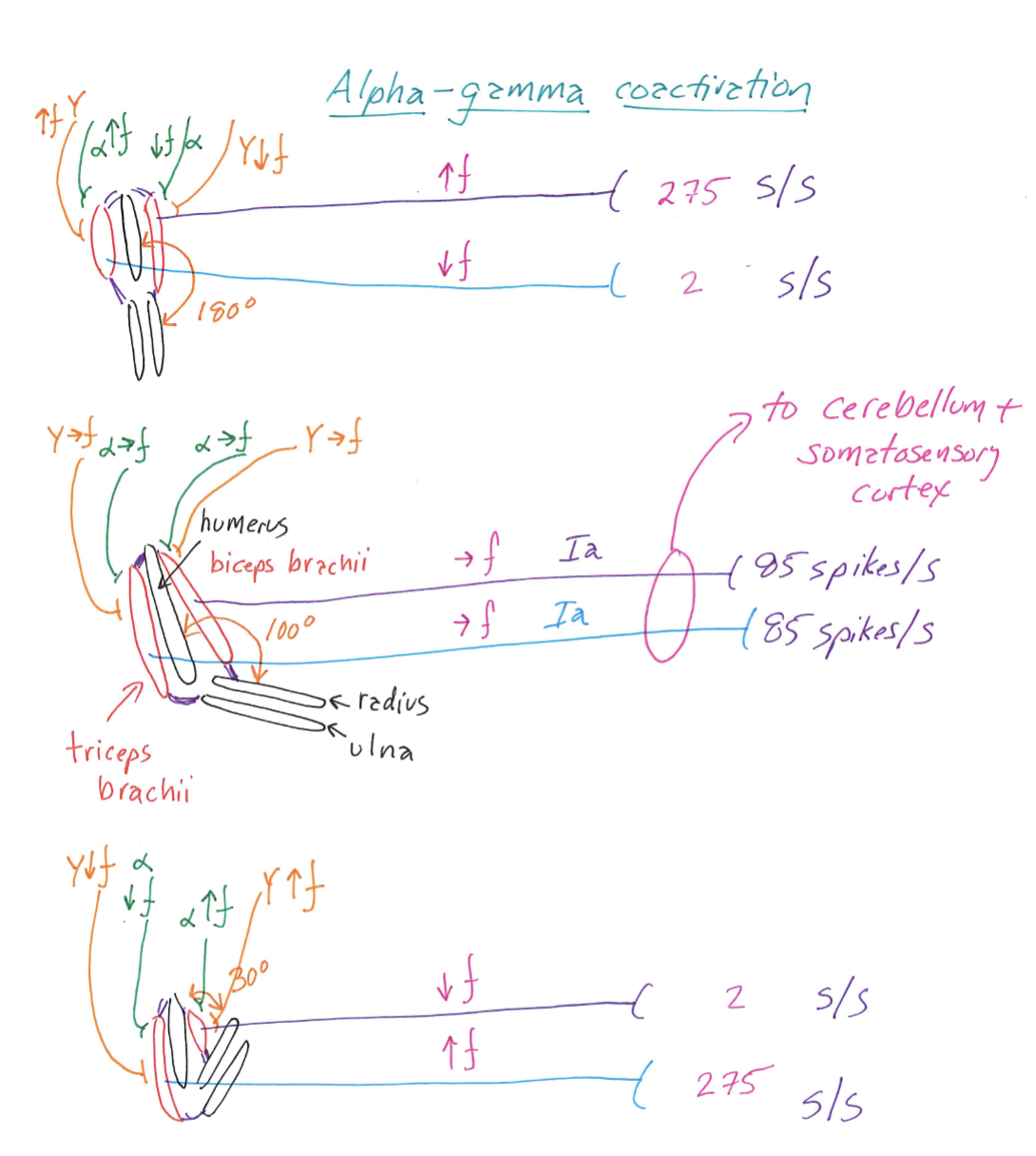
Correctly Drawn
Big Diagram
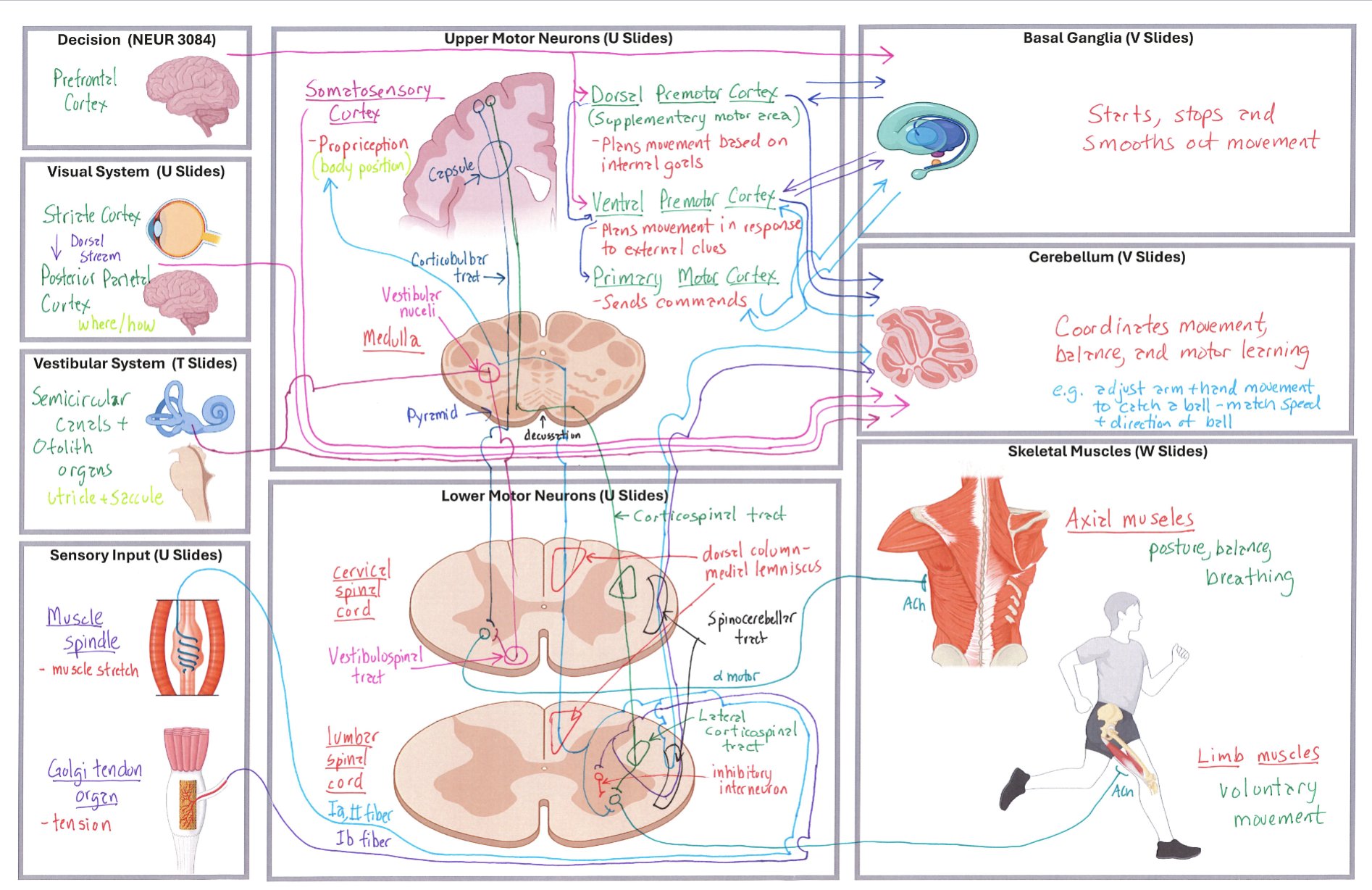
Correctly Drawn
Knee-Jerk Reflex Diagram
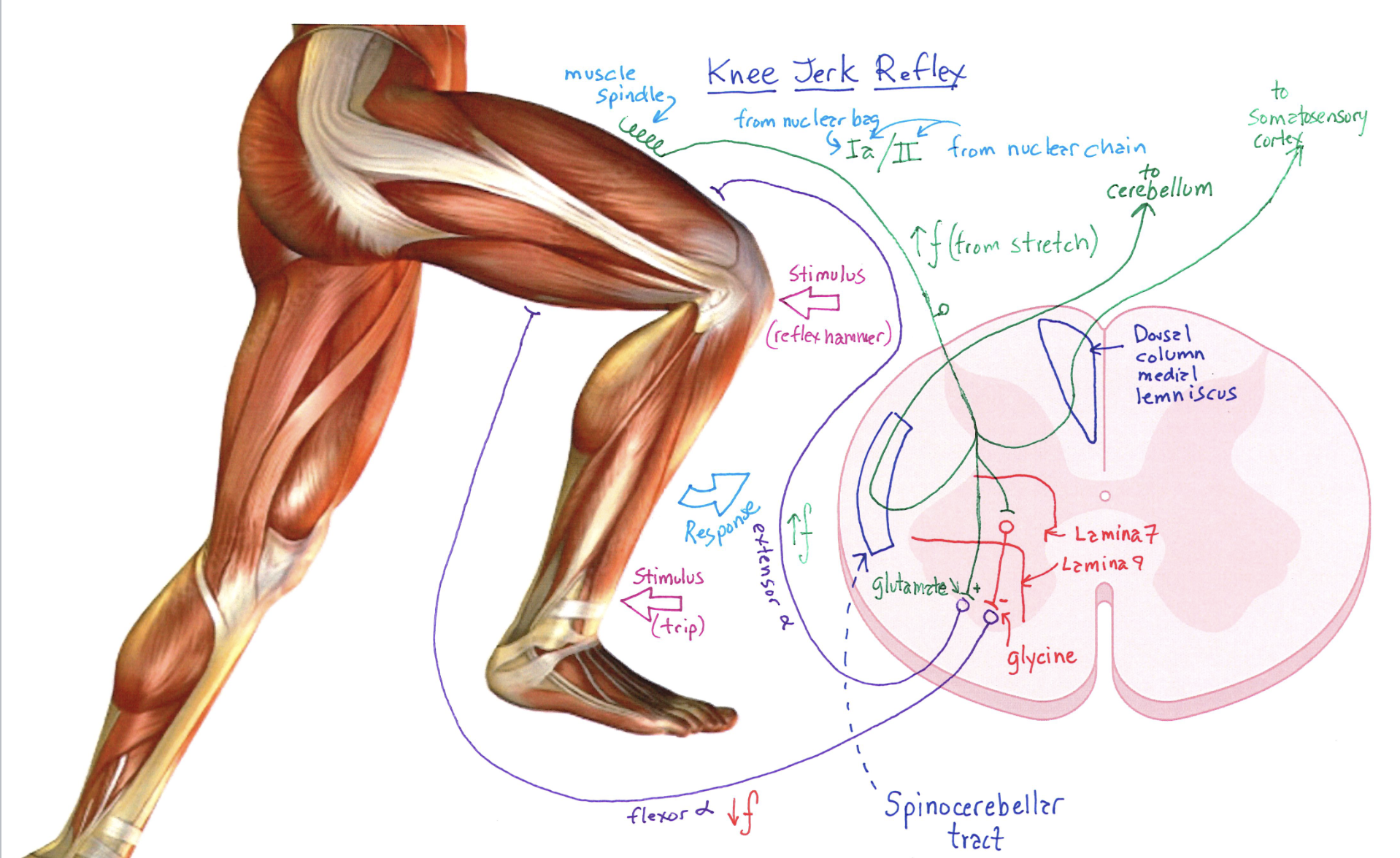
Correctly Drawn
Crossed Extension Reflex Diagram
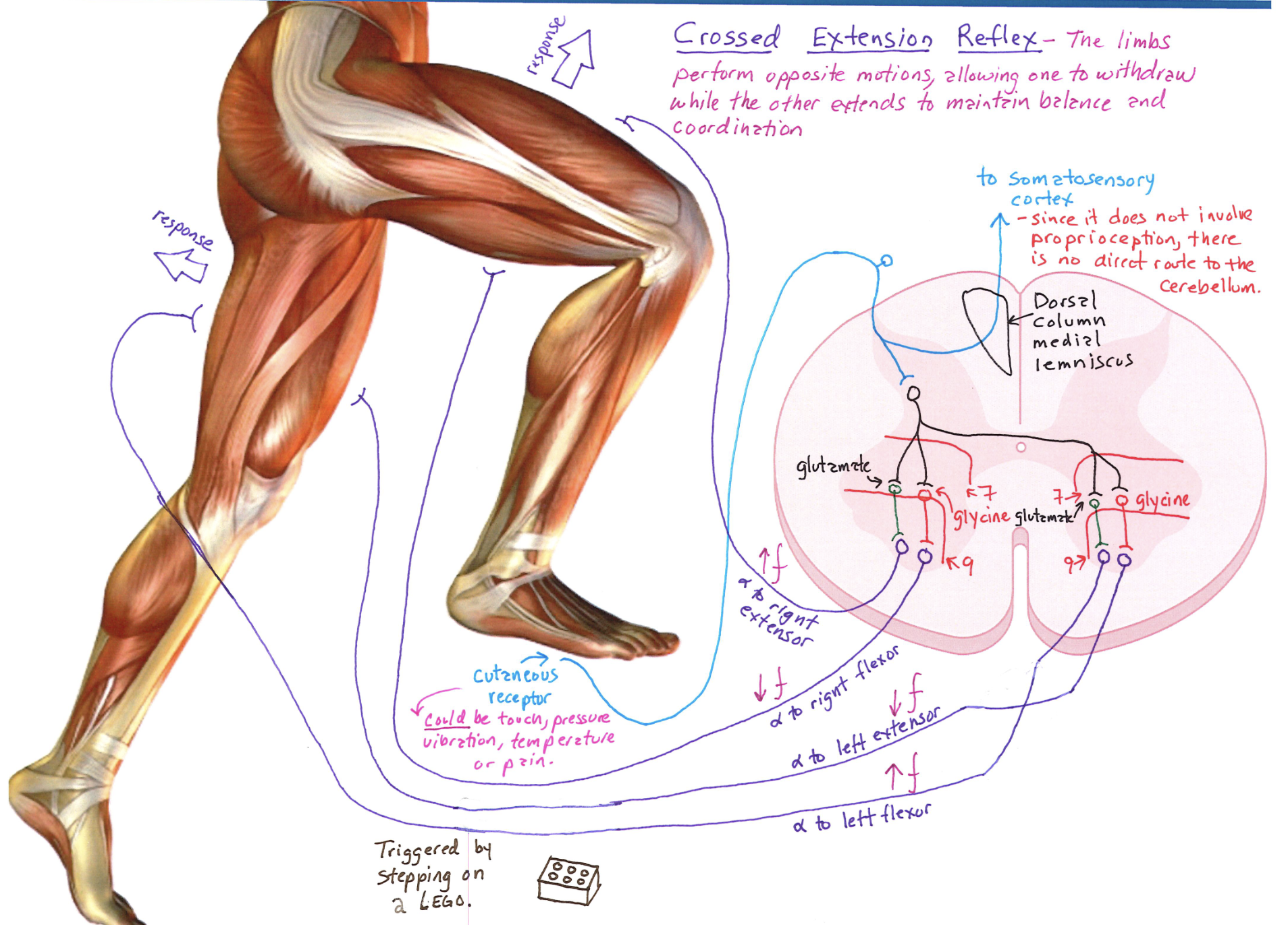
Correctly Drawn
Big vs. Small Neurons
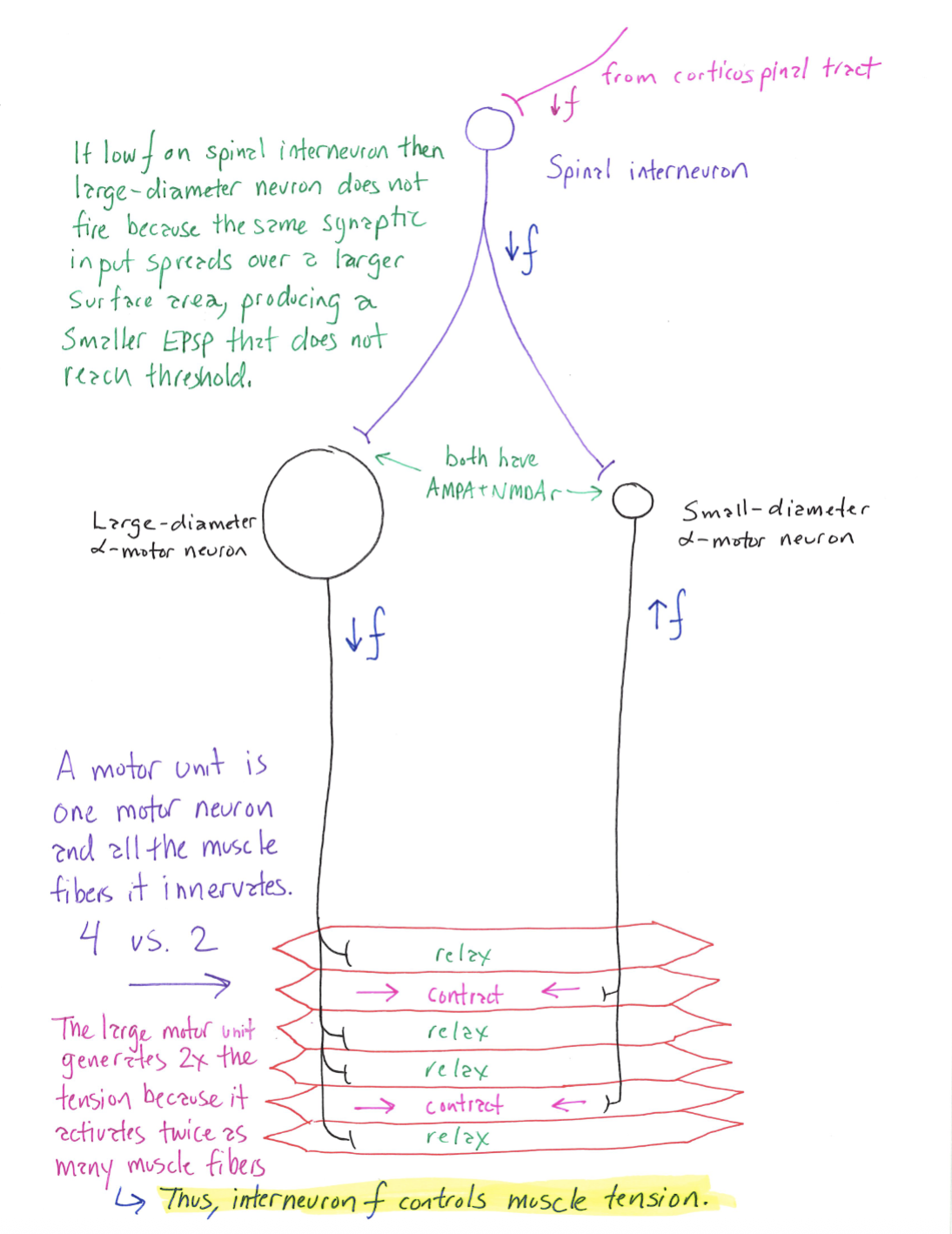
Correctly Drawn
Muscle Neurons Circuit (Extensor Muscle Contracted)
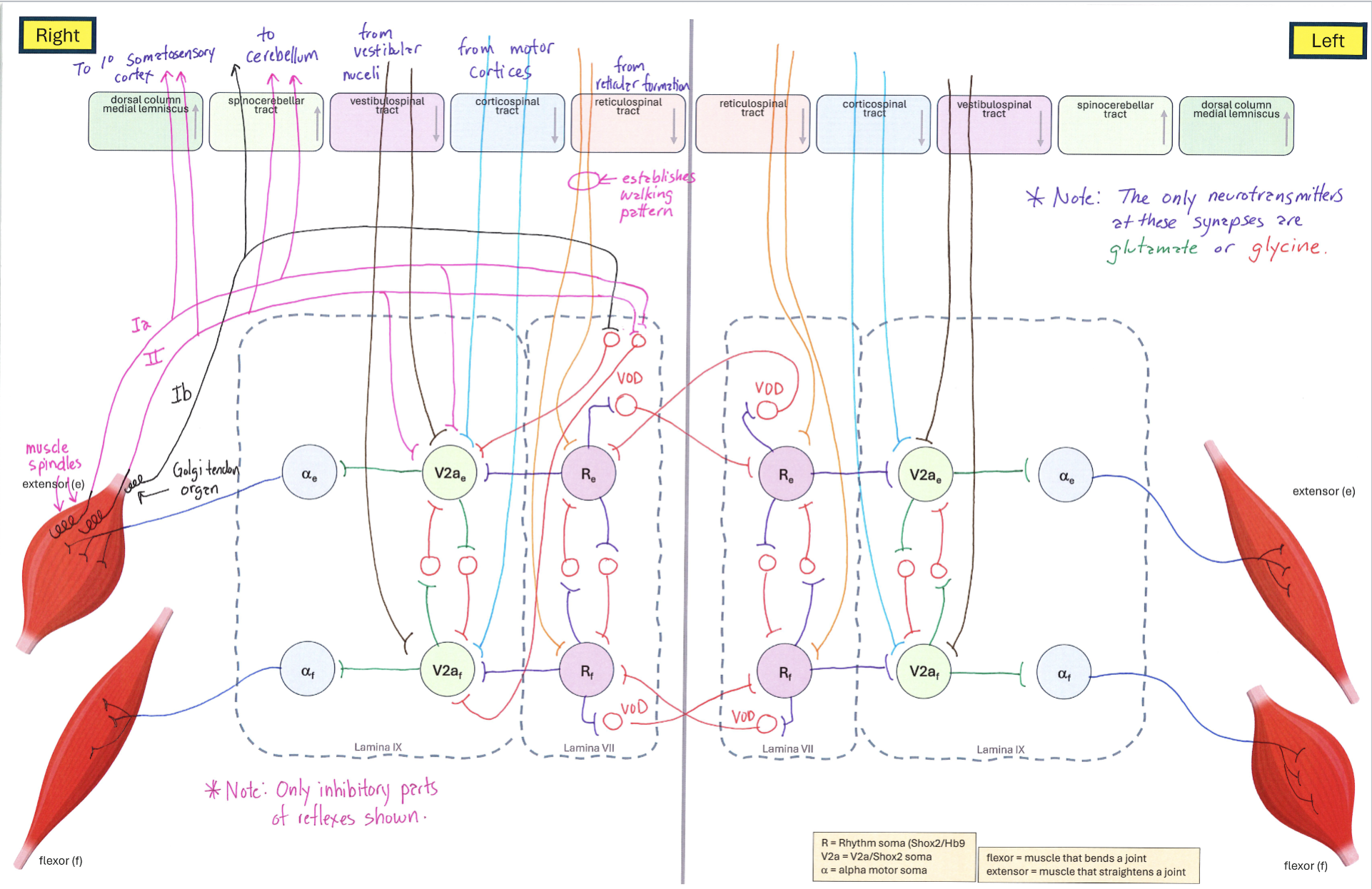
Correctly Drawn
Muscle Neurons Circuit (Flexor Muscle Contracted)
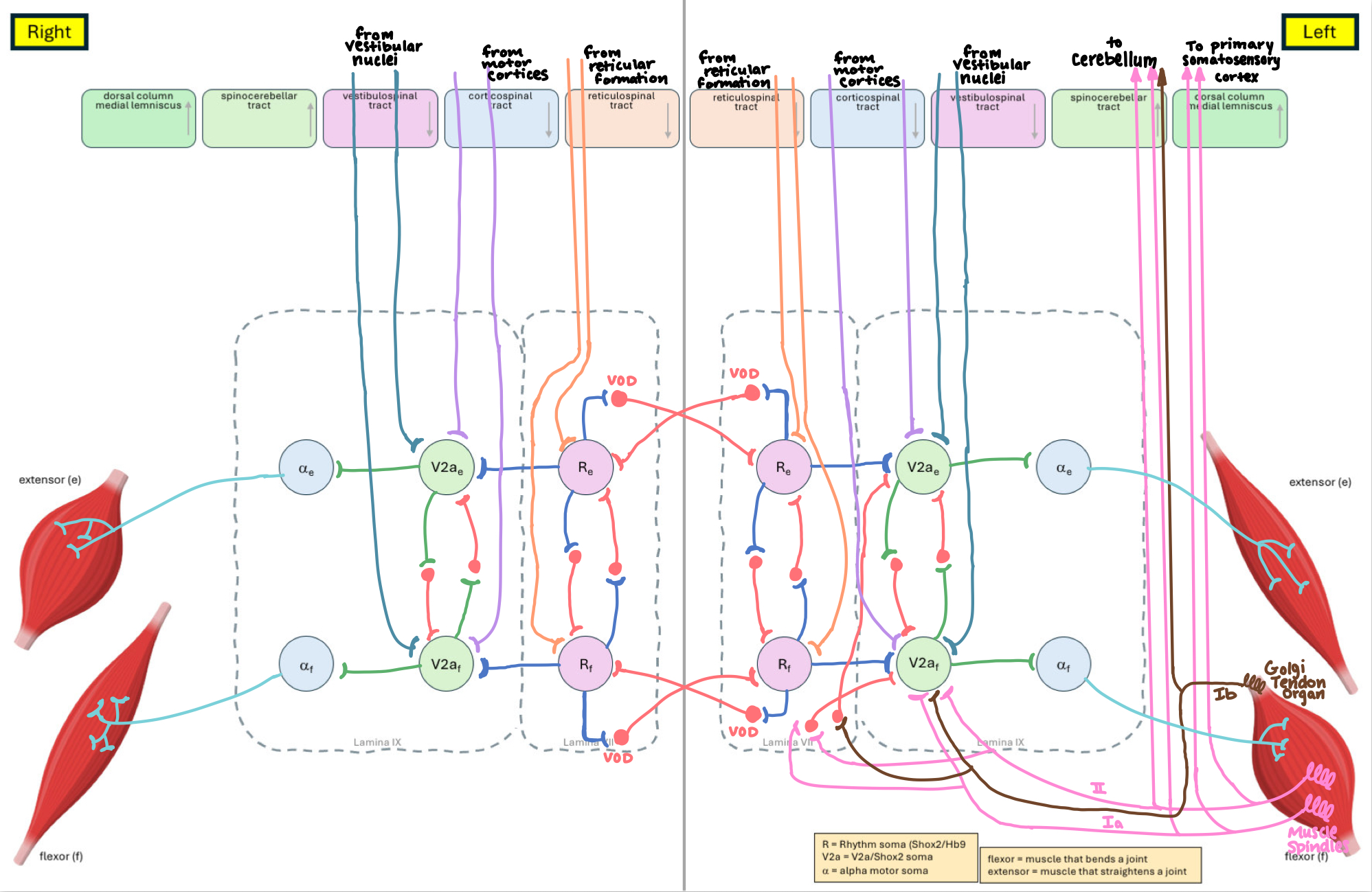
Correctly Drawn
Basal Ganglia Direct Pathway
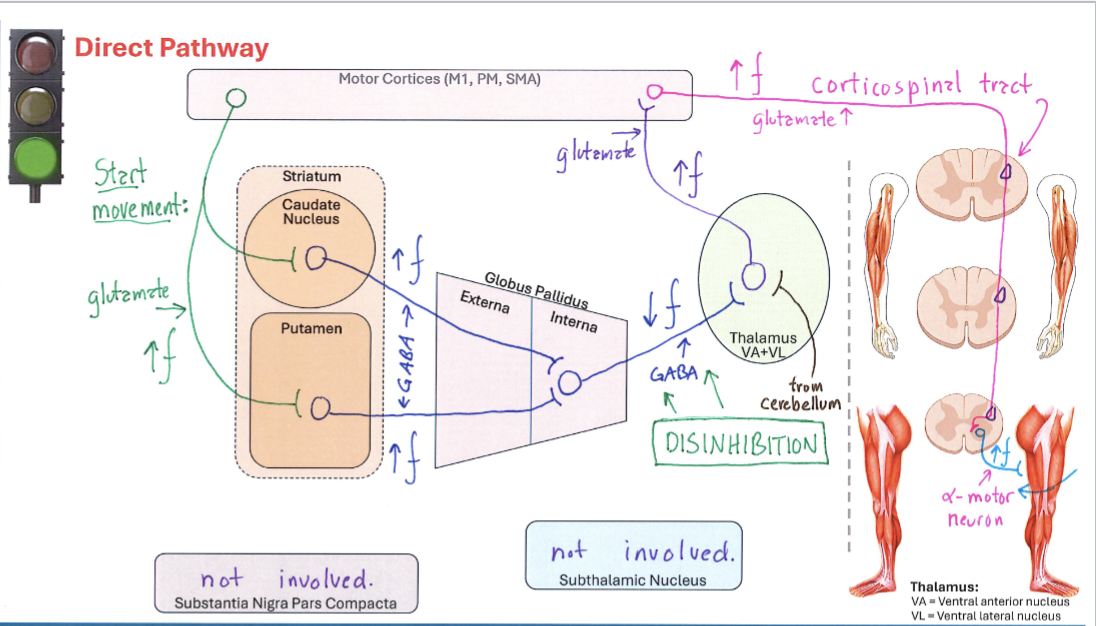
Correctly Drawn
Basal Ganglia Indirect Pathway
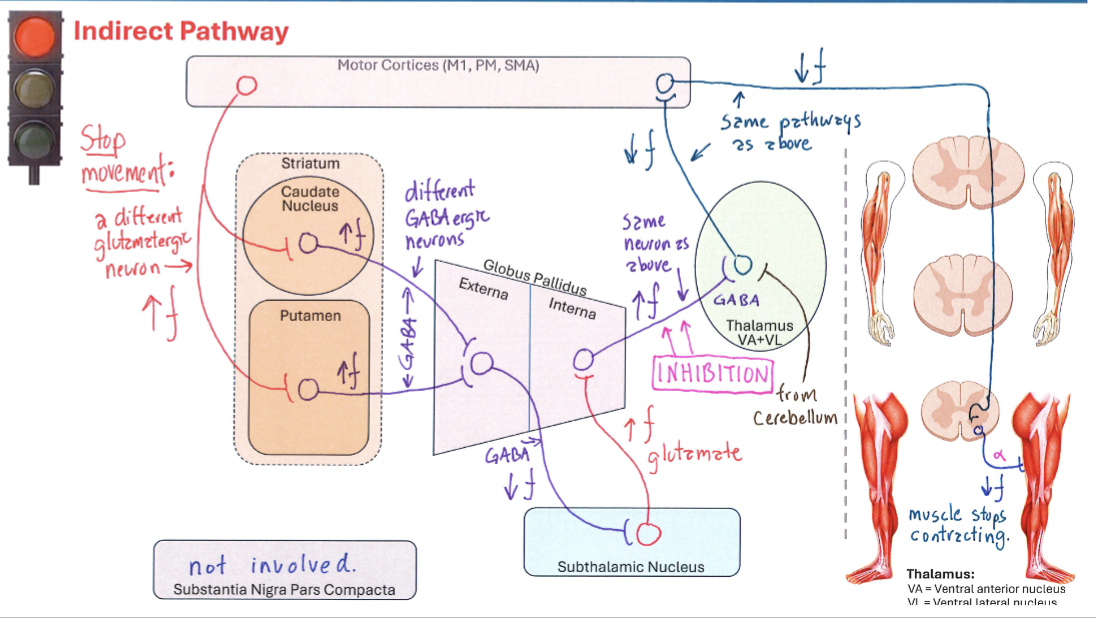
Correctly Drawn
Nigrostriatal Pathway Modulation of Direct Pathway

Correctly Drawn
Nigrostriatal Pathway Modulation of Indirect Pathway

Correctly Drawn
D1r Membrane
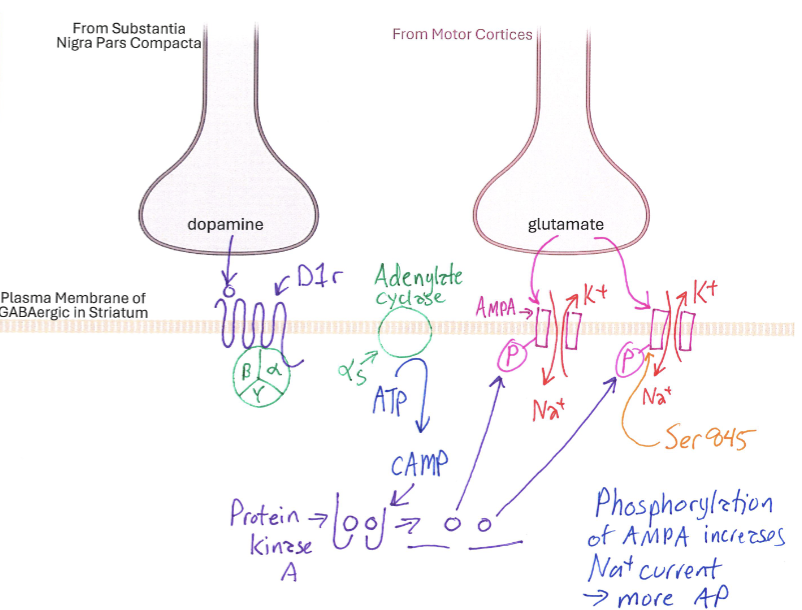
Correctly Drawn
D2r Membrane
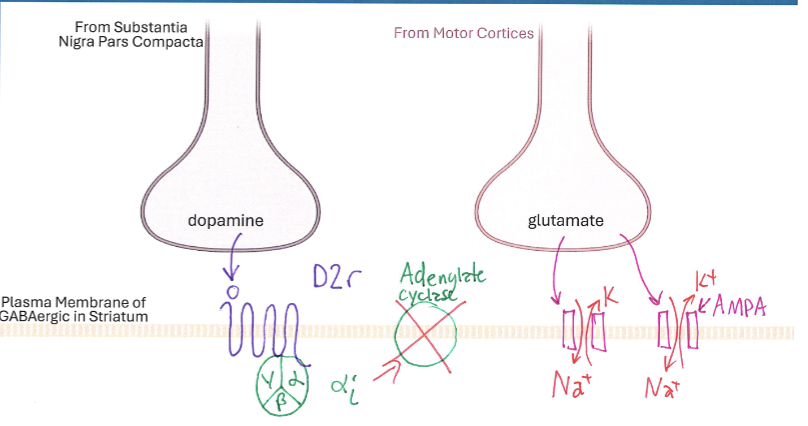
Correctly Drawn
Cerebellum Overall Anatomy
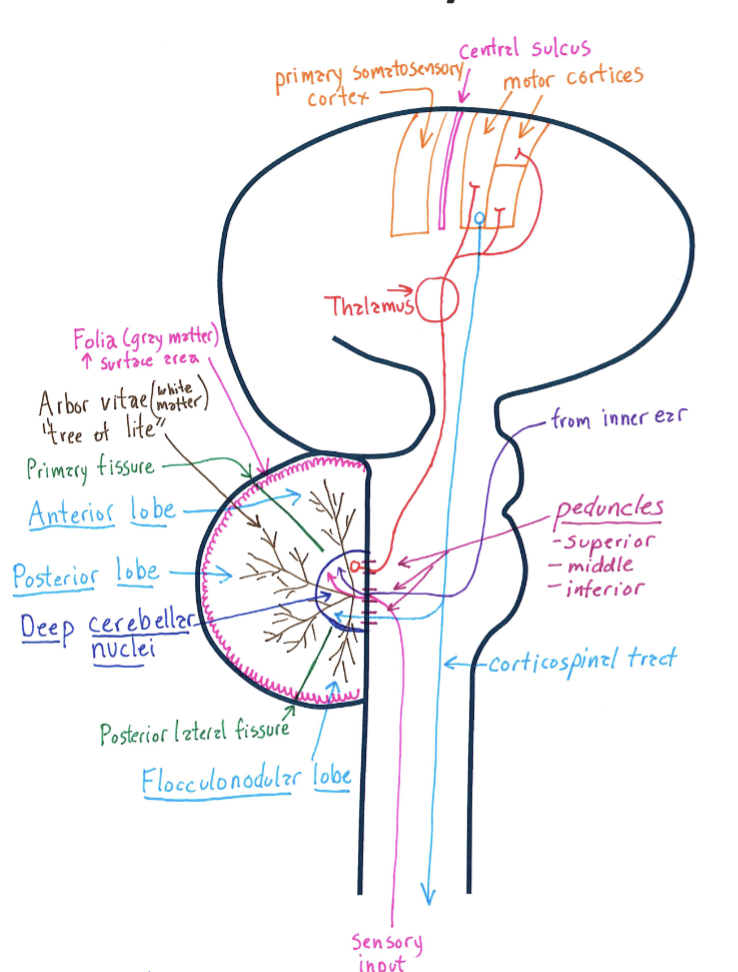
Correctly Drawn & Labelled
Cerebellum Lobe Anatomy
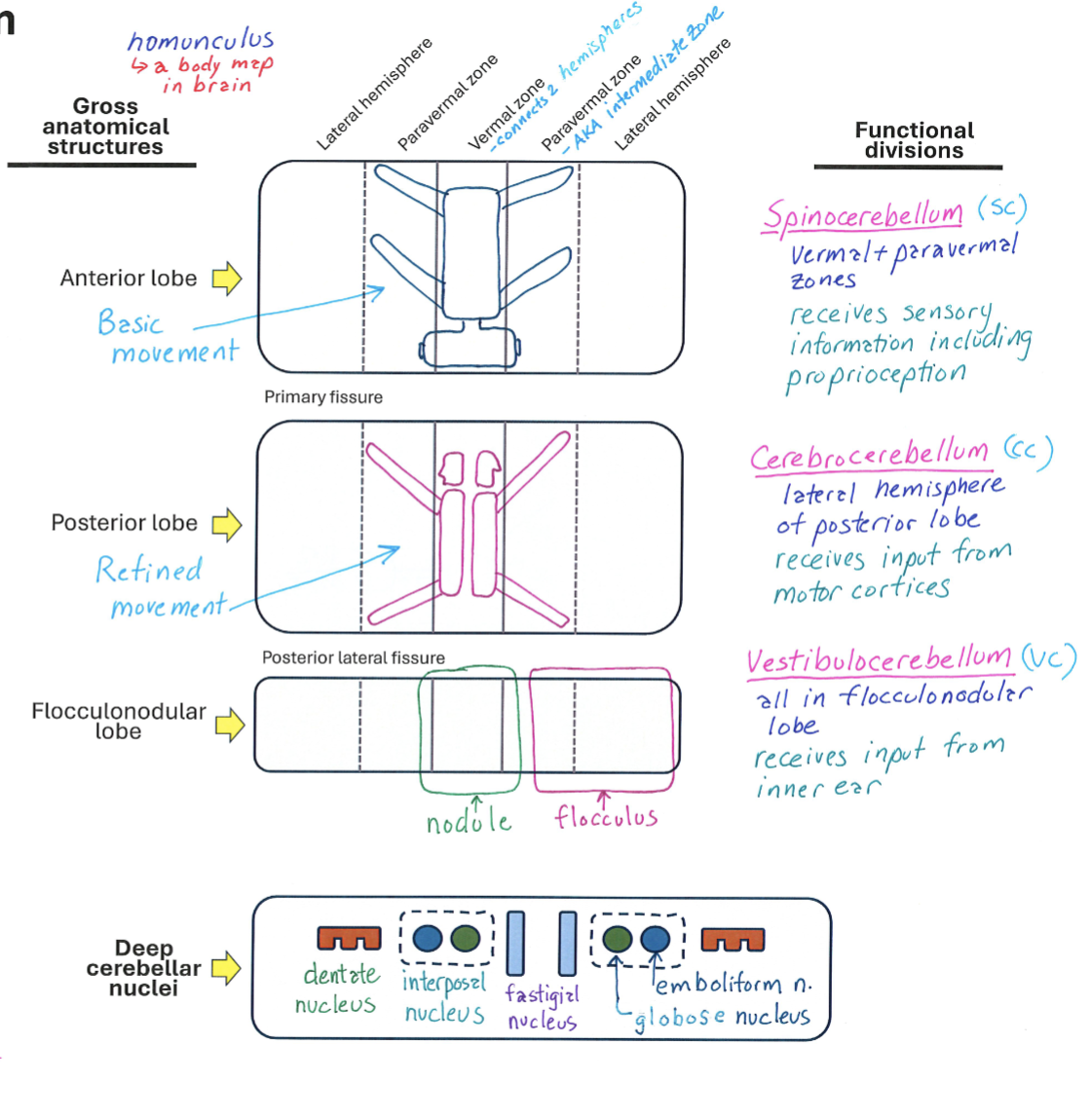
Correctly Drawn & Labelled
Cerebellum Neural Sharpening
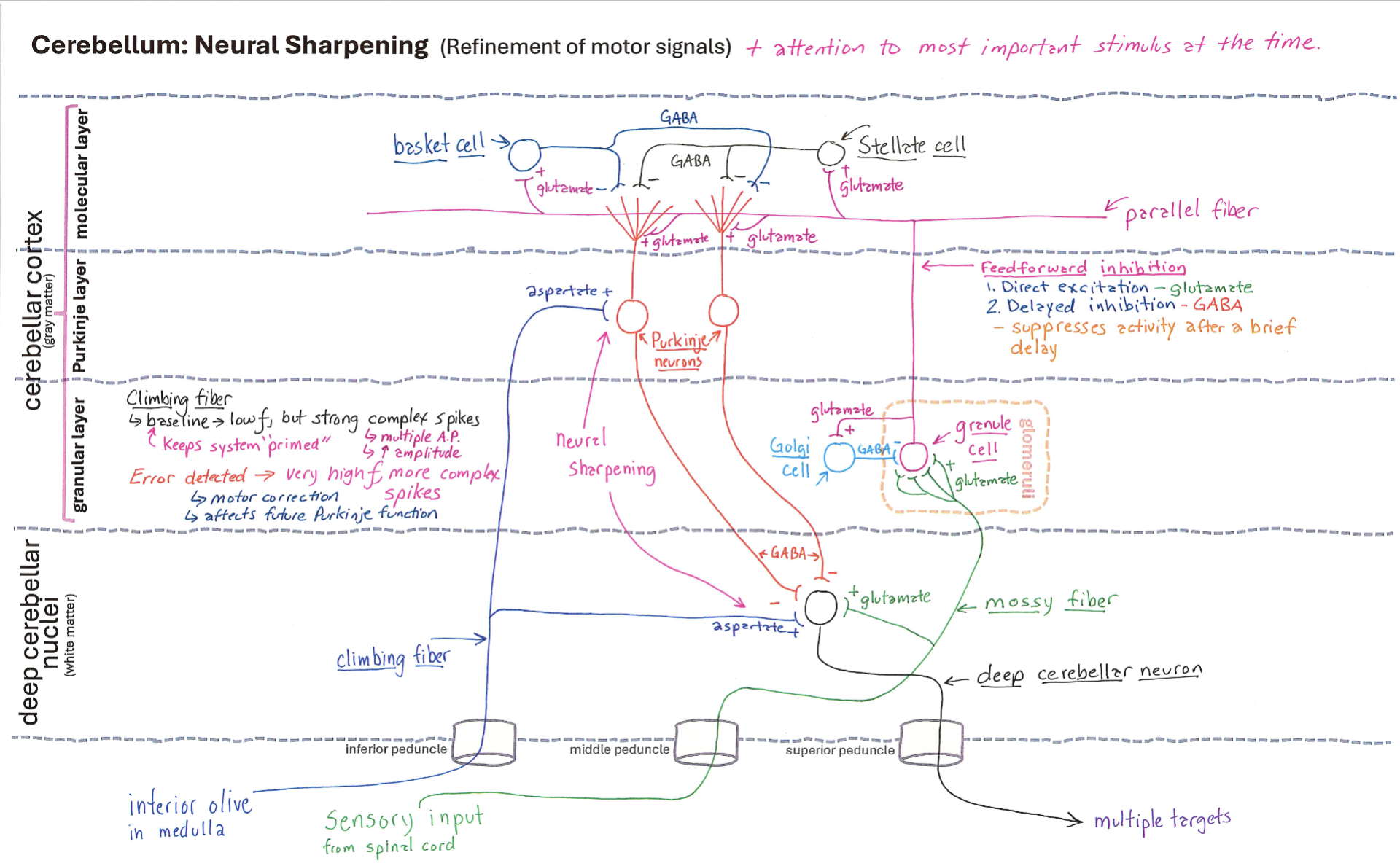
Correctly Drawn
Dentothalmic / Dento-Rubro-Thalamic Pathway
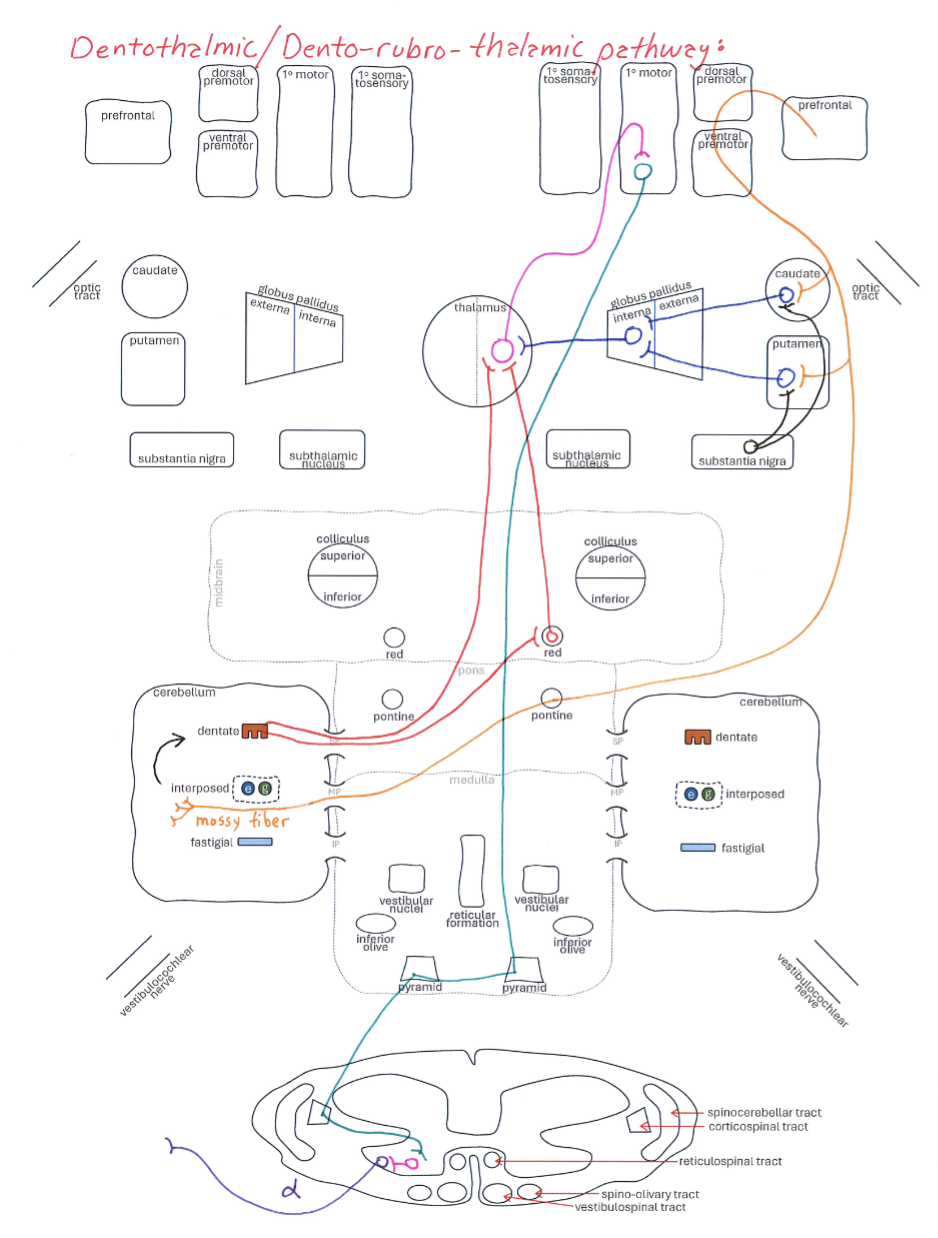
Correctly Drawn
Interposed-Rubriospinal / Interposed-Thalamic-Cortical Pathway
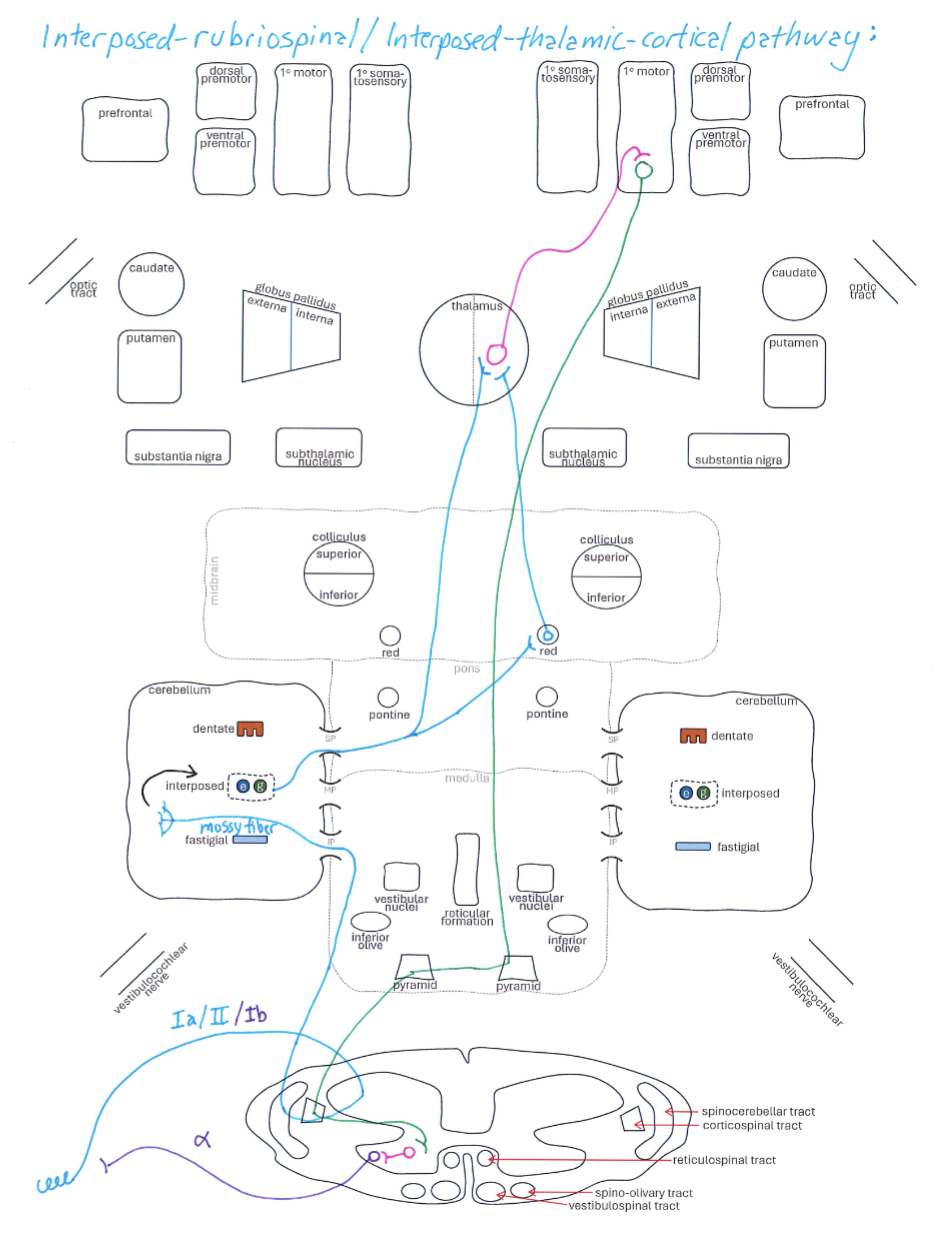
Correctly Drawn
Fastigal-Reticular / Fastigal-Vestibular / Fastigal-Thalamic Pathways
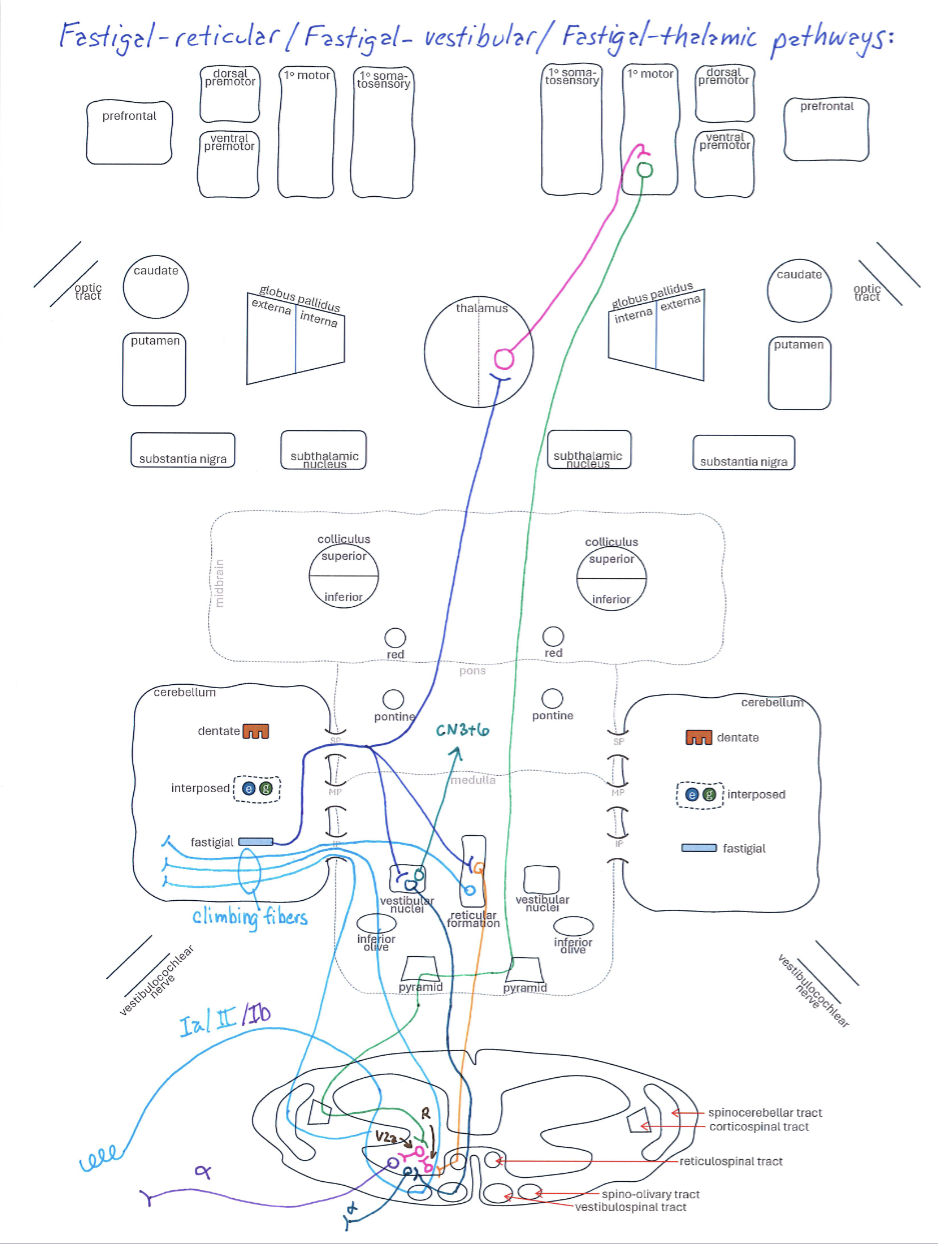
Correctly Drawn
Visual and Vestibular Inputs
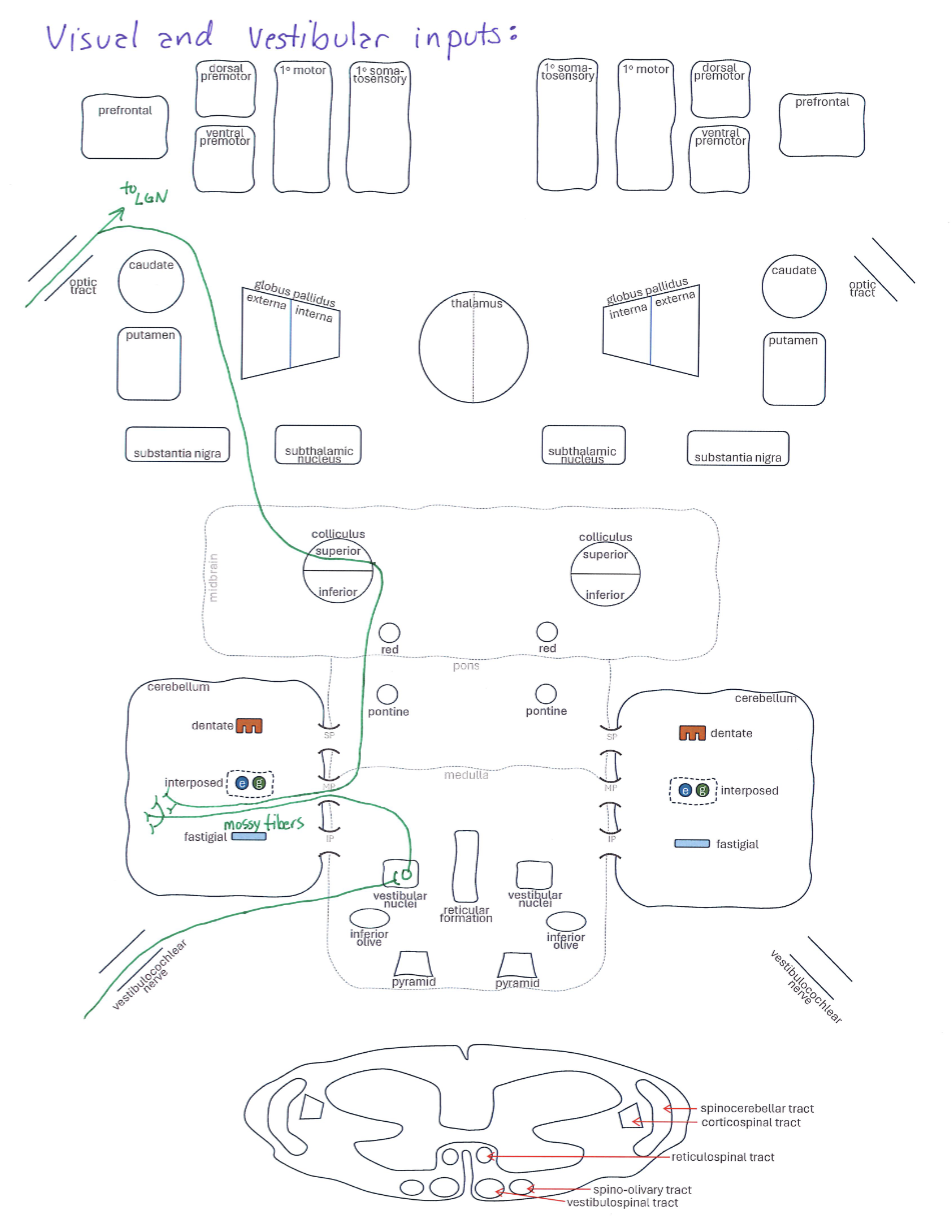
Correctly Drawn