Clin Lab Med Exam 3 Review
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
3 lines of defense
1. nonspecific/innate = physical, chemical, & genetic barriers
2. nonspecific/innate = inflammatory response, interferons, phagocytosis
3. specific to a particular microbe = acquired immunity; B & T lymphocytes, antibodies, cytotoxicity
acquired immunity
immunity that the body develops after it overcomes a disease (natural), or through vaccination (artificial)
4 body compartments involved in immune function
1. reticulonendothelial system
2. blood stream
3. lymphatic system
4. extracellular fluid
reticuloendothelial system (RES) role in immunity
= fibrous network enmeshing each cells which connects one well to another tissue or organ
*provides a niche for phagocytic WBCs to crawl
circulatory system role in immunity
blood stream = blood cells + plasma
lymphatic system = vessels, lymph fluid, & lymph nodes
WBCs differentiate into specialized cells: granulocytes & agranulocytes
WBC granulocytes
-neutrophils: phagocytes
-eosinophils: destroy parasites, involved in allergic reactions
-basophils: release potent chemical mediators, involved with allergic reactions
WBC agranulocytes
-lymphocytes: B & T cells involved in specific immune response (key to 3rd line of defense)
-monocytes: phagocytes
B cell maturation
bone marrow
-when stimulated by antigens and cytokines from T-helper cells, they differentiate into plasma cells (which produce antibodies)
activated T cells can become what 4 cell types & what is their function?
= provide cell-mediated immunity
1. helper cells
2. supressor cells
3. killer cells
4. delayed allergy cells
*attack infected host cells, cancer cells, & foreign cells marked by antibodies
activated T helper cells
CD4
= signal B lymphocytes to produce antibodies and signal cytotoxic/killer T cells to kill tagged cells
stimulated cytotoxic T cells
CD8
= kill cells tagged for destruction
mature dendritic cells
= mature into highly effective processors and presenters of foreign proteins
*process antigens and present them to T helper cells
advantage of memory B cells
= remember the antigen and respond very rapidly on subsequent exposures
B cells become _____ when activated by an _____
plasma cells
antigen
= humoral immunity
plasma cells secrete _____
antibodies
IgG
= most prevalent antibody with numerous functions
-produced by memory B cells in response to second exposure
**only antibody capable of crossing the placenta
IgA
= secretory component of mucus and serous secretions
-confers specific local immunity to enteric, respiratory, & GU pathogens
-produced by plasma cells
-protects newborns passively from breast milk
IgM
= first class synthesized by plasma cells following the initial encounter with an antigen
-largest immunoglobulin
IgD
= serve as a receptor for antigens on B cells along with IgM
-may be the trigger for B cell activation
IgE
= interacts with receptors on mast cells and basophils
-involved with allergic reactions & parasitic infections
what is the only type of immunoglobulin that can cross the placenta?
IgG
opsonization
= a process in which microorganisms are coated with specific antibodies so that they will be more readily recognized by phagocytes to dispose of them
neutralization
= antibodies fill the surface receptors on a microorganism to prevent it from functioning normally
agglutination
= cross-linking antigens into larger clumps so that they are more easily found by antibodies
complement fixation
= interaction of an antibody with complement results in specific rupturing of cells & some viruses
4 types of immunodeficiency
1. B cell deficiency
2. T cell deficiency
3. combined immunodeficiency
4. acquired immunodeficiency
B cell deficiency
= inability of B cells to produce viable antibodies
T cell deficiency
= developmental failure of the thymus results in a few (if any) T cells and poor cell-mediated immunity
combined immunodeficiency
= lack of enzymes that produce T cell and B cell receptors leads to combined immunodeficiency
*rapidly fatal if severe
acquired immunodeficiency
= immune deficiency due to viruses (HIV), exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, or chronic diseases
what is the screening test you can quickly order in clinic to diagnose strep throat? What routinely needs to be sent out afterward to confirm the result?
1. rapid strep test - strep Group A
2. culture
what blood test can you order if a patient has a history of strep that you think may have gone untreated and turned into rheumatic fever, post-strep glomerulonephritis, or post-strep infection?
anti-streptolysin O titer (ASO titer)
what would you expect to see on a positive PPD test?
induration is > 2 cm in diameter
-larger erythema
what skin test can you order if you suspect your patient may have an immunodeficiency? what result would you see if your suspicion was right?
Candida albicans skin test
negative reaction = immunocompromised
how large of an increase from an acute to convalescent viral antibody titer would there be to suspect a viral infection?
4x or 4-fold increase
*you did have a prior infection
what screening test would you order to test for mononucleosis?
mono-spot
-detects heterophiles antibodies against the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in patient's serum
+ result = agglutination
interpret the following Mono-spot results
VCA-IgM: positive
VCA-IgG: positive
EA-D IgG: negative
EBNA, IgG: negative
= early, primary mono infection
interpret the following hep A virus (HAV) results
IgM anti-HAV: positive
= presence in blood indicates acute infection
interpret the following hep A virus (HAV) results
IgG anti-HAV: positive
= presence in blood indicates past infection (months-years) & immunity
what is the confirmatory test for a positive anti-HCV?
anti-HCV (RIBA)
-type of Western blot
what is the best screening test for syphilis?
rapid plasmin reagin (RPR) test
+ test = agglutination
what is the confirmatory test for syphilis?
FTA-ABS test (fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test)
when would it be best to use an RPR test to screen for syphilis?
= useful to detect AND can help monitor treatment
-test becomes reactive within 1-4 week of infection
-becomes non-reactive/negative within 1 year of treatment
what test can you run from a CSF sample when you suspect late stage neuro-syphilis?
VDRL test (venereal disease research laboratory)
+ test = flocculation
what test can you order for suspected chlamydia?
EIA (enzyme immunoassay)
-urethral swab or urine sample that uses an antibody specific enzyme to detect the presence of an antigen
+ test = color change
what is the preferred method testing for HSV?
PCR test (polymerase chain reaction)
-fast & inexpensive that amplifies small segments of DNA
what is the downfall of ordering a Tzanck smear vs antibody testing for suspected HSV?
Tzanck - rapid diagnosis but CANNOT distinguish between HSV 1 and 2
antibody testing - CAN distinguish between HSV 1 and 2
what is the screening test for HIV?
EIA test
what is the confirmatory test for HIV?
Western blot test
antibodies in Type A blood
anti-B antibodies
antibodies in Type B blood
anti-A antibodies
antibodies in type O blood
anti-A and anti-B antibodies
antibodies in type AB blood
none
forward typing
= adding antibodies to the RBC sample to look for the antigen
type A: positive anti-A
type B: positive anti-B
type AB: positive anti-A & anti-B
type O: no antigens
interpret the following forward typing results:
anti-A: positive
anti-B: negative
anti-D: positive
Type A+ blood
reverse typing
= adding antigens/RBCs to the serum sample that contains antibodies
type A: positive for B cells
type B: positive for A cells
type AB: no cells
type O: positive for A & B cells
D-antigen
= Rh factor
Rh + means you have the D antigen (& anti-D antibodies)
Rh - means you lack the D antigen
what will happen to an Rh- mother when she is exposed to D-antigens from an Rh+ fetus during pregnancy?
her blood will develop anti-D antibodies
what is the most common cause of hemolytic disease of the newborn?
= Kell (K,k), Duffy (Fya, Fyb), & Kidd (Jka, Jkb) antigens
DAT or Coombs serum test is looking for the presence of what on the surface of RBCs?
= antibodies
DAT/Coombs test can help diagnose what conditions
1. hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)
2. investigation of hemolytic transfusion reactions
3. diagnosis of immune hemolytic anemias
type & screen
= used when the patient is not as likely to need a transfusion/blood products
-testing the patient's plasma for ABO, Rh factor, & unexpected antibodies
type & cross
= utilized when you know a transfusion is necessary
-patient/recipient serum is also crossmatched against donor RBCs
what type of blood can each blood type receive? universal donor & acceptor?
type A: can receive type A or O
type B: can receive type B or O
type AB: can receive type A, B, O, or AB = universal recipient
type O: can only receive type O = universal donor
when are washed RBCs given?
to patients who have serve reactions to plasma
-severe allergies, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, IgA immunization
when is fresh frozen plasma given?
= unconcentrated source of all clotting factors without platelets
to correct bleeding secondary to clotting factor deficiencies or in multifactor deficiency states
-massive transfusion, DIC, liver failure
when is cyroprecipitate given?
= concentrated FFP
used as a source of fibrinogen in acute DIC with bleeding & in other severe bleeding disorders
when is recombinant factor VII given?
for the treatment of hemophilia A
what is the first thing you should do when you suspect your patient is having a transfusion reaction?
STOP the transfusion
acute hemolytic transfusion reaction
= causes acute hemolytic anemia
signs & symptoms:
*pain at infusion site
-chest/back pain
-restlessness or anxiety
-nausea or diarrhea
febrile non-hemolytic transfusion reactions
*most common
= defined by a temp increase of 1 C or 1.8 F; antibodies in recipient's plasma react against antigens present on cell membranes of transfused granulocytes
signs & symptoms:
-temp increase, chills, headache, malaise, confusion
anaphylactic transfusion reaction
= reaction with recipient anti-IgA that occurs after infusion of only a few milliliters of blood/plasma
signs & symptoms:
-tachycardia, flushing, headache, chest pain, dyspnea
urticarial transfusion reaction
= occurs after febrile non hemolytic reactions; suspected allergy to donor plasma substances
signs & symptoms:
-local erythema, hives, itching, usually without fever
delayed hemolytic reaction
= high antibody levels 3-7 days after the transfusion (while initial screen was negative)
signs & symptoms:
-malaise, jaundice, fever, unexplained decrease in Hgb level, hemoglobinuria
CSF is analyzed in 4 tubes for what and in what order?
1. protein & glucose levels (chemistry)
2. Gram stain, meningitis PCR panel, cultures
3. cell count & differential
4. VDRL test (syphilis) or India ink stain
difference in findings between a traumatic LP & brain bleed
traumatic tap: red color is most intense in first tube
brain bleed/cerebral hemorrhage: even amount od red in ALL tubes
difference in findings between viral & bacterial meningitis
viral: high levels of lymphocytes
bacterial: high levels of neutrophils
what test can you utilize to assess the impairment of the blood-brain barrier and what results would indicate an impairment?
= CSF albumin index
impairment: index value > 9 (higher values are more severe)
what type of protein in the CSF would be indicative of MS? what other findings can support the diagnosis of MS?
= IgG (tested through CSF IgG index from a CSF total protein test)
-increased myelin basic protein (MBP)
-detection of oligoclonal bands (CNS IgG bands) using electrophoresis
-elevated lactate
what microbiology tests can be orders for CSF samples?
a) gram stain - bacterial & fungal meningitis
b) acid-fast stain - mycobacterial meningitis
c) india ink preparation - fungal meningitis caused by Cryptococcus neoformans
d) cultures - cases of meningitis
normal appearance of synovial fluid
clear, colorless to straw, does not clot
abnormal variants of synovial fluid
dark yellow: inflammation
green/yellow: bacterial infection
cloudy: elevated # of cells, organisms, or crystals
red: elevated # of RBCs
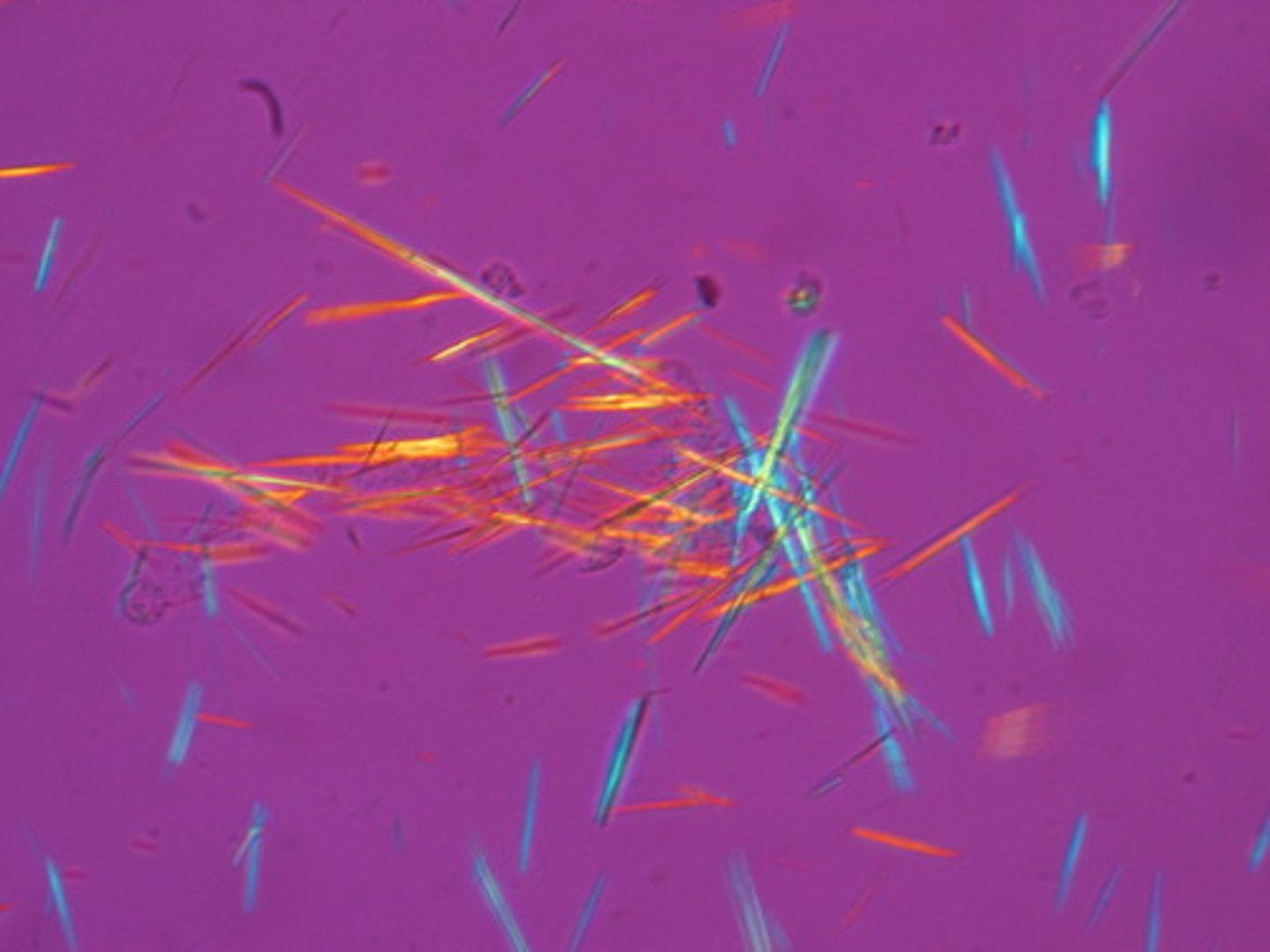
gout findings
= uric acid needle-like crystals
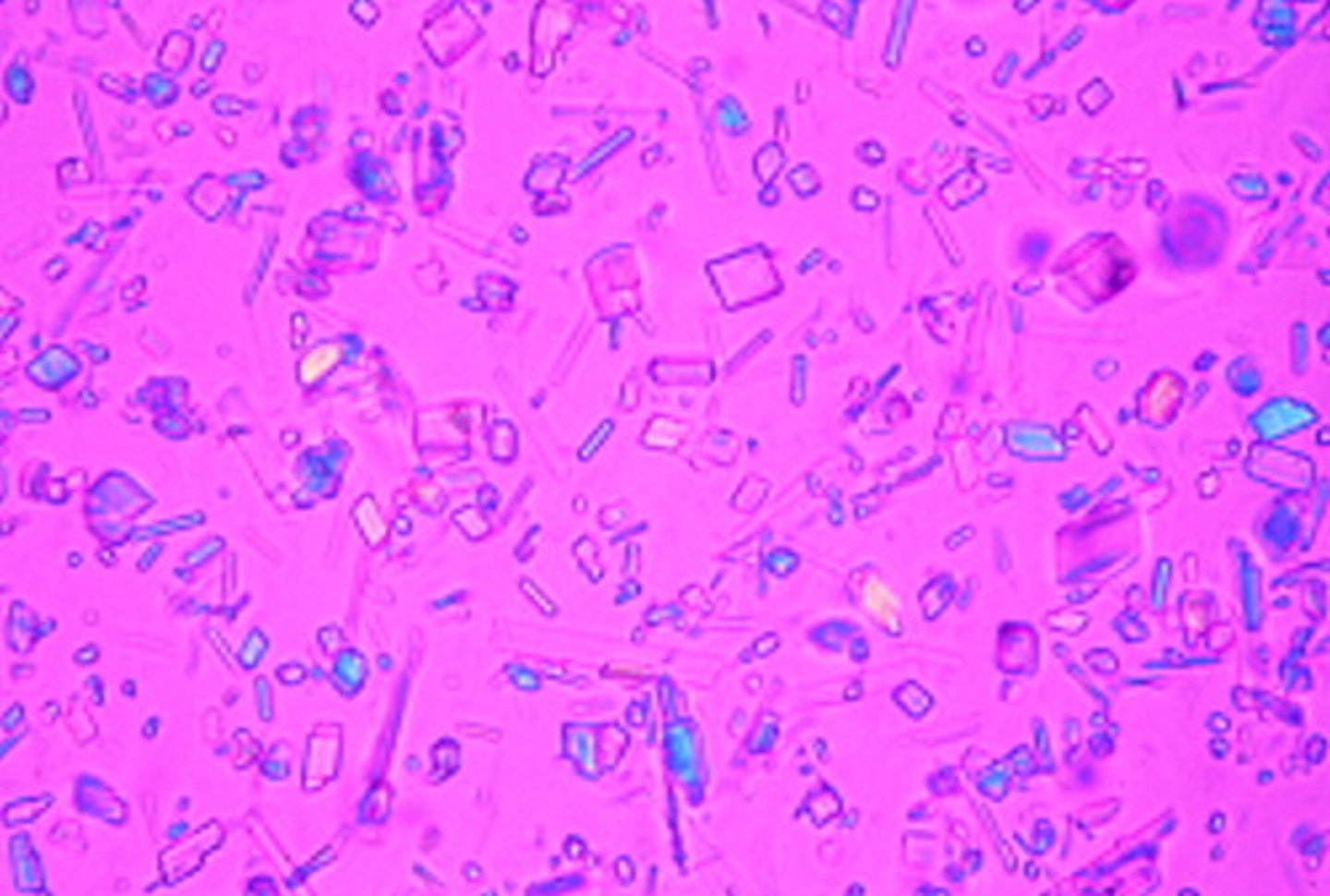
pseudogout findings
= calcium pyrophosphate rod-like or rhombic crystals
septic joint findings from a bacterial infection
= decreased glucose levels (they are using the glucose as food)
what information can you acertain from amniotic fluid examination?
-chromosomal defects
-neural tube defects (alpha-fetoprotein)
-hemolytic disease
-fetal pulmonary development (measures alveolar surfactant)
when/why is a Lecithin/Sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio test done?
= ratio estimates fetal lung maturity
-lethicin levels increase dramatically at gestational week 34 to develop/mature the lungs
-if there is a planned early delivery, L/S ratio > 2.0 is considered safe, otherwise the delivery is unsafe & meds may need to be given
transudative serous fluid
= body wide problem; an effusion that forms because of a systemic disorder that disrupts the balance in regulation of fluid filtration/reabsorption
ex. ascites
-SAAG > 1.1
-generally low WBC count
exudative serous fluid
= problem in the lining; an effusion that forms because of disorders that directly involve the membrane of the cavity that increases capillary permeability
ex. bacterial pneumonia, malignancies
-SAAG < 1.1
-generally high WBC count
normal semen results in an infertility work up
color: grayish-white & opalescent
volume: 2-5 mL
viscosity: initially viscous, but will become water within 60 mins
motility: > 50% motile sperm with moderate to rapid linear progression
count: 20-250 million sperm/mL
morphology: > 50% normal
pH: 7.2-7.8
when would you utilize a hemoccult test?
= when screening for increased amounts of blood in the stool (detects Hgb)
-utilizes guaiac impregnated filter paper
+ test: color change to blue/purple
*false + can appear after eating rare cooked meats/fish, vegetables (broccoli, turnips, cauliflower), fruits (cantaloup, bananas, pears, plums), or drugs that irritate the GI tract (aspirin, iron)
inflammatory vs non-inflammatory diarrhea
= microscopic examination of feces for presence of WBCs helps distinguish these
inflammatory: 1-3 cells per high power field
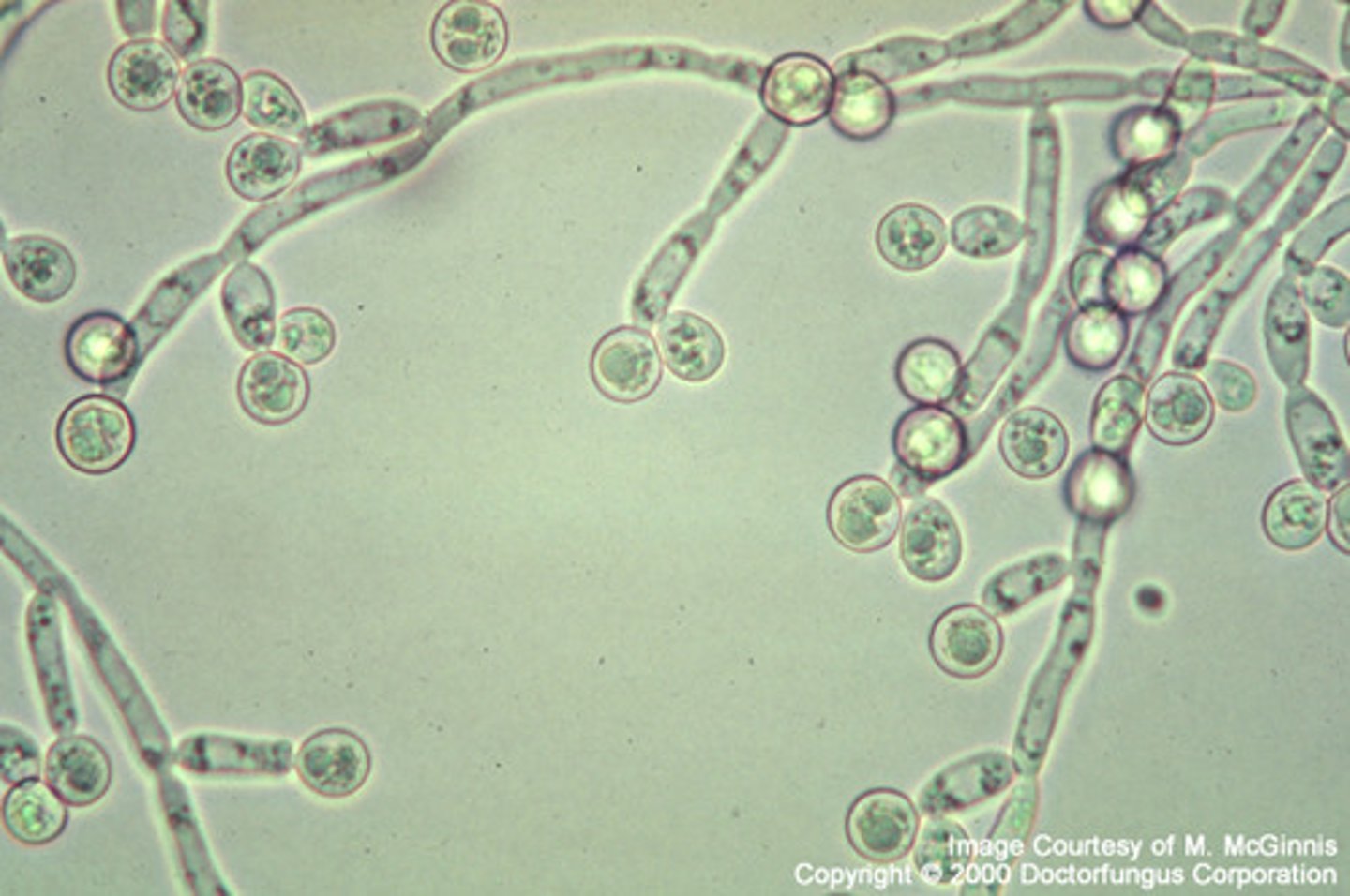
how do you test for candidiasis?
= tests for yeast infection by adding a drop of KOH to a smear of vaginal secretions
+ test: branching/budding organisms
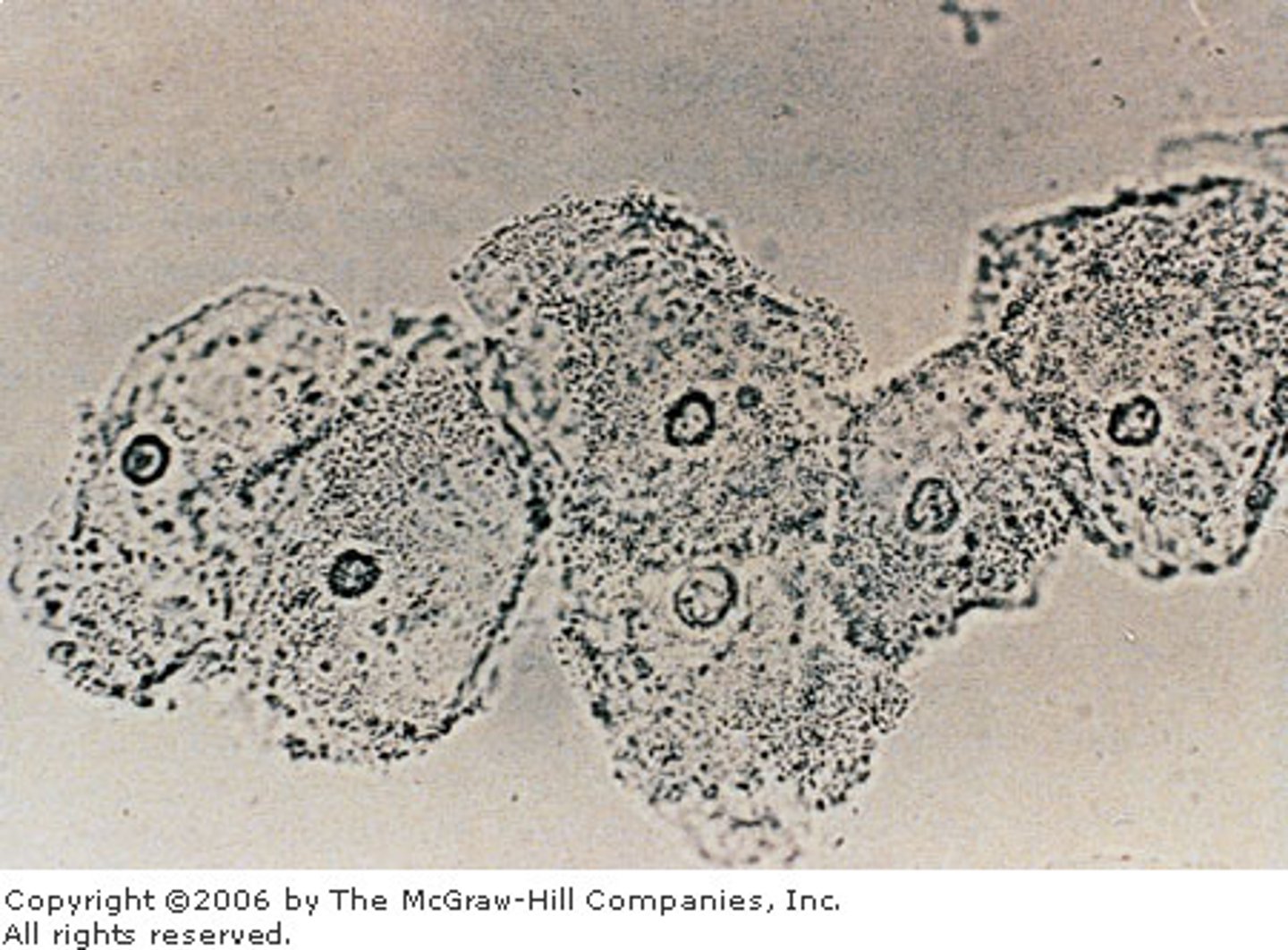
how do you test for bacteria vaginosis (BV)?
= a drop of normal saline is added to a smear of vaginal secretions
+ test: "clue cells" or large squamous epithelial cells that are covered with bacteria
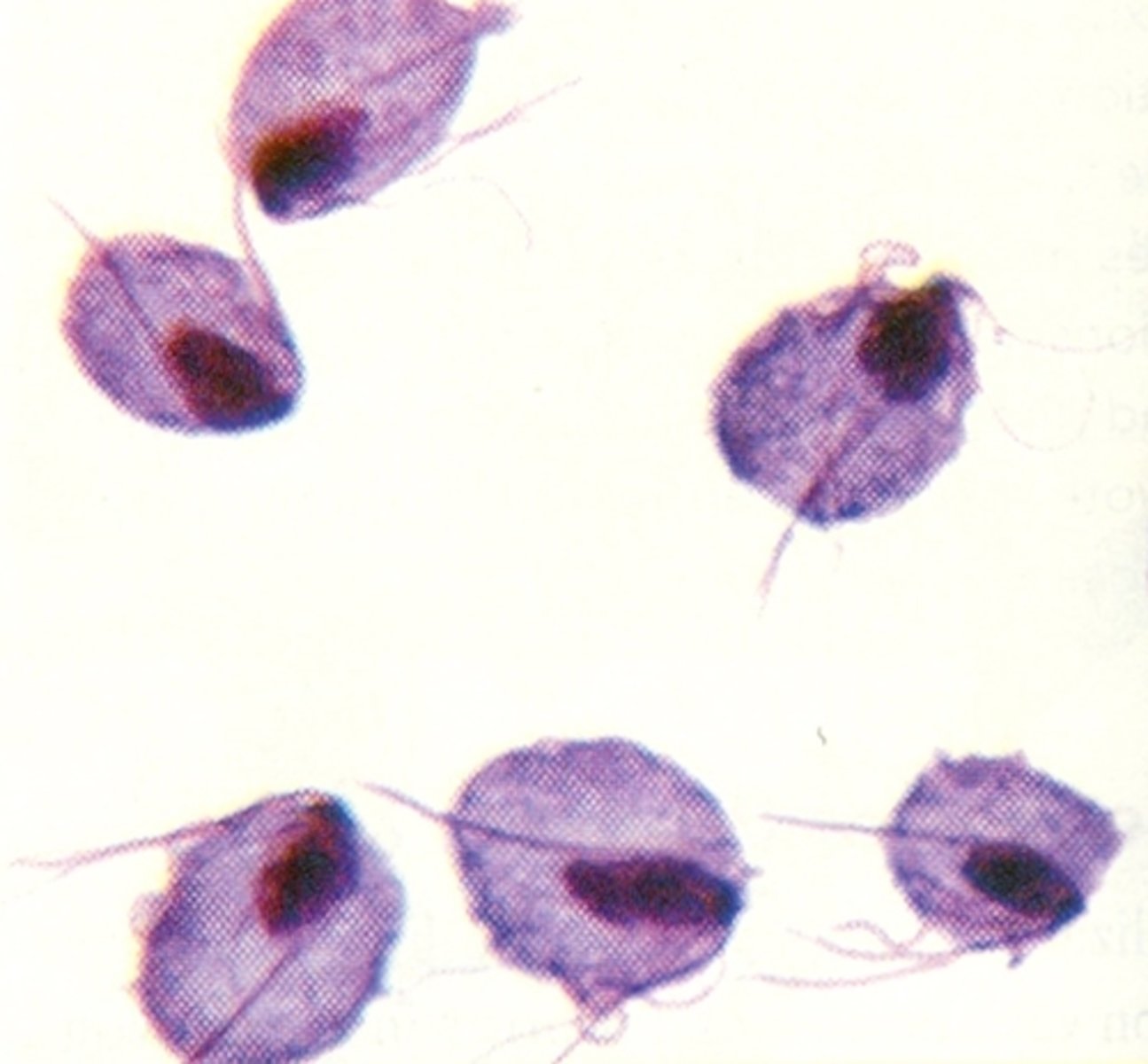
how do you test for trichomoniasis?
= a drop of normal saline is added to a smear of vaginal secretions
+ test: large, round or slightly oval organism with flagella that are usually motile
therapeutic range
blood level of a drug that correlates with the desired therapeutic effect in most patients
minimum effective concentration
below this level therapeutic effect is not achieved
minimum toxic concentration
above this level symptoms of toxicity appear
trough values of medications
= lowest concentration achieved during a dosing cycle
*most specimens drawn for therapeutic drug monitoring are trough specimens
peak values of medications
= highest concentration achieved during a dosing cycle
-should be below minimum toxic concentration