Gross Anatomy Lab Exam 1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Terms to identify in lab:
deep fascia
superficial fascia
neurovascular bundle
upper limb
forearm
arm
lower limb
thigh
leg
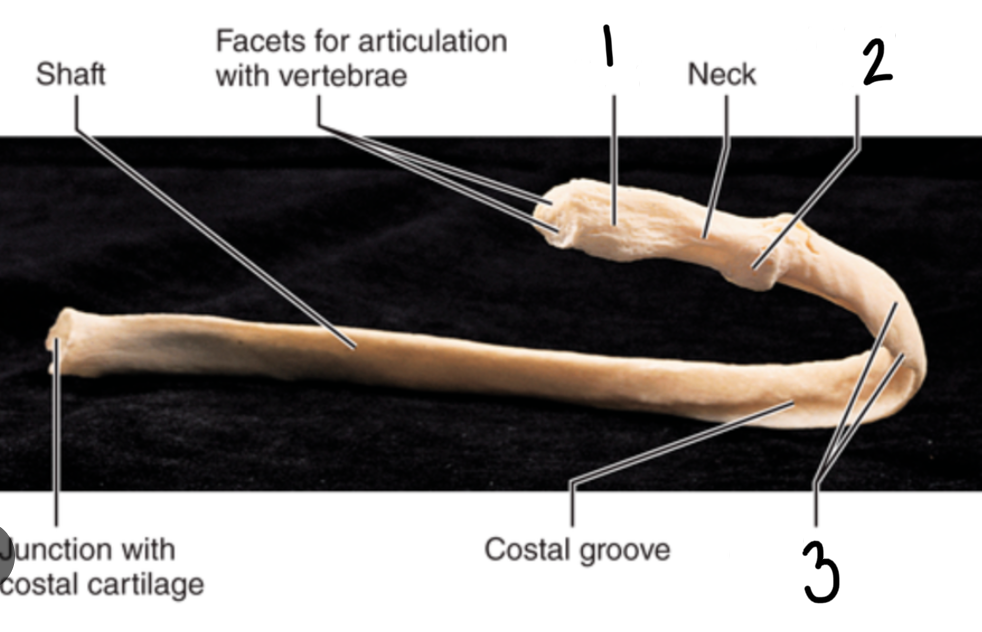
Parts of the rib
head
tubercle
angle
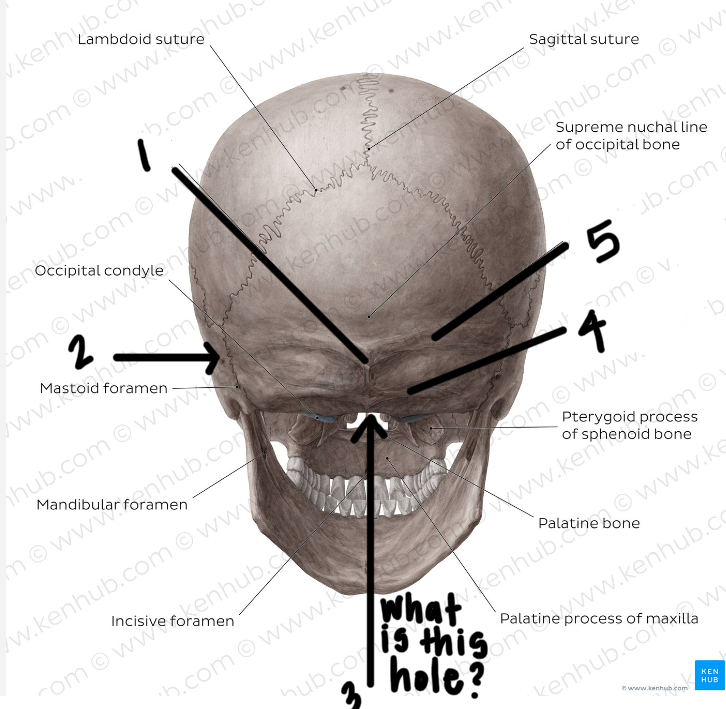
Label the posterior skull
external occipital protuberance
temporal bone
foramen magnum
inferior nuchal line
superior nuchal line
*also remember occipital bone
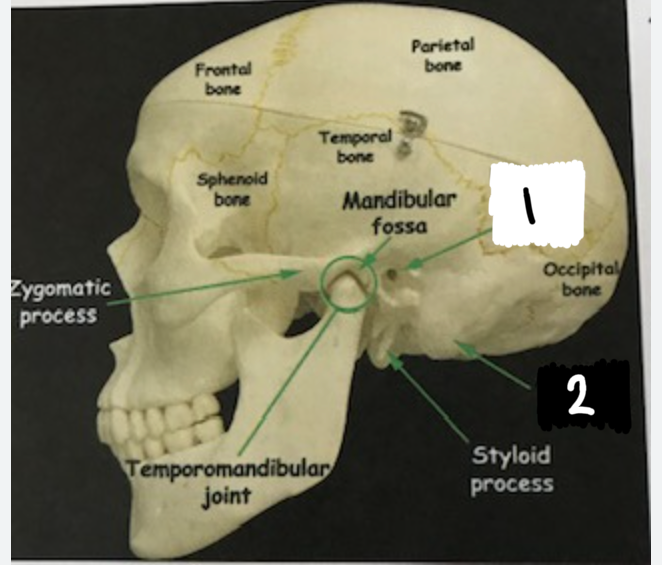
Label these two structures that are apart of the skull
external acoustic meatus
mastoid process
Know the differences between the structures of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae.
The cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae differ in location, shape, and function.
Cervical Vertebrae: Found in the neck region, they are smaller and more mobile (C1-C7). They have a small body, a large vertebral foramen, and a bifid spinous process.
Thoracic Vertebrae: Located in the upper back (T1-T12), they are larger and more rigid. They articulate with the ribs and have downward-pointing long spinous processes.
Lumbar Vertebrae: Situated in the lower back (L1-L5), they are the largest and strongest. They have a thick body, a triangular vertebral foramen, and short, thick spinous processes.
Vertebra prominens
SP of C7
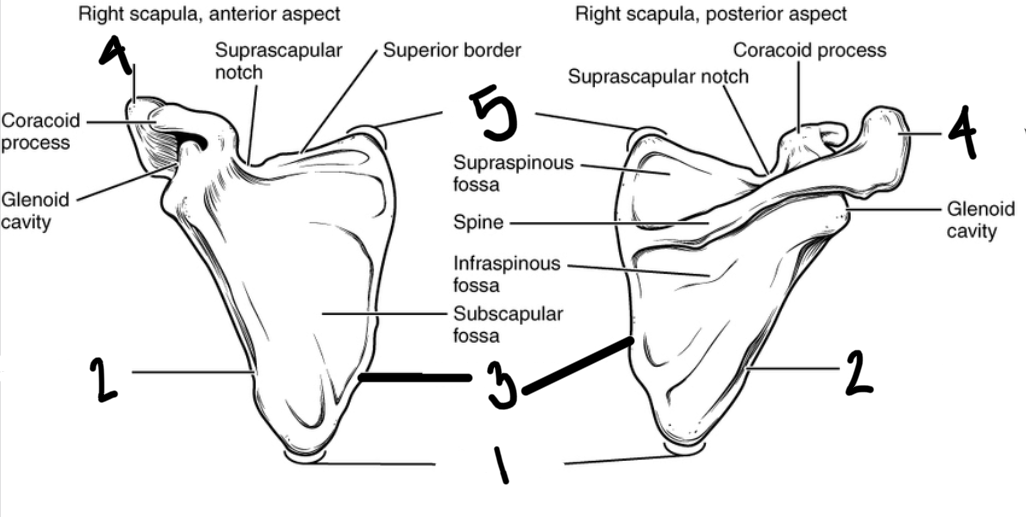
Label the Scapula
Inferior angle of scapula
Lateral boarder of scapula
medial boarder of scapula
acromion
superior angle of scapula
Know the structures on the vertebrae
body
transverse processes
transverse costal facets
demi facets
superior costal facets
inferior costal facets
IV disc
superior articular process
inferior articular process
inferior vertebral notch
superior verterbral notch
IV foramen
vertebral arch
pedicle
laminae
vertebral foramen
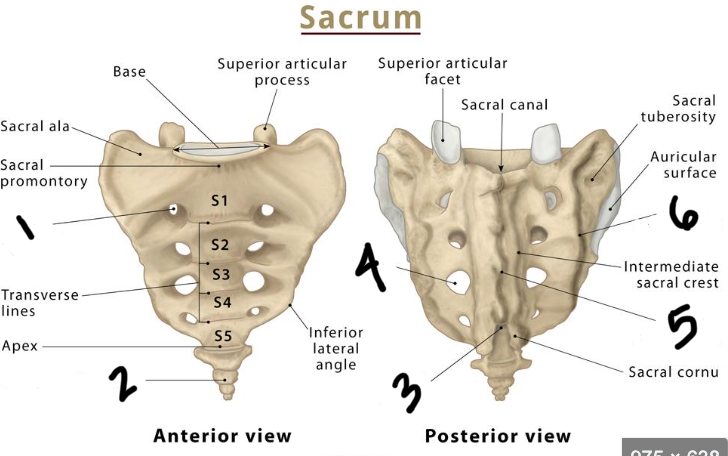
Label the sacrum
anterior sacral foramen
coccyx
sacral hiatus
posterior sacral foramen
medial sacral rest
lateral sacral crest
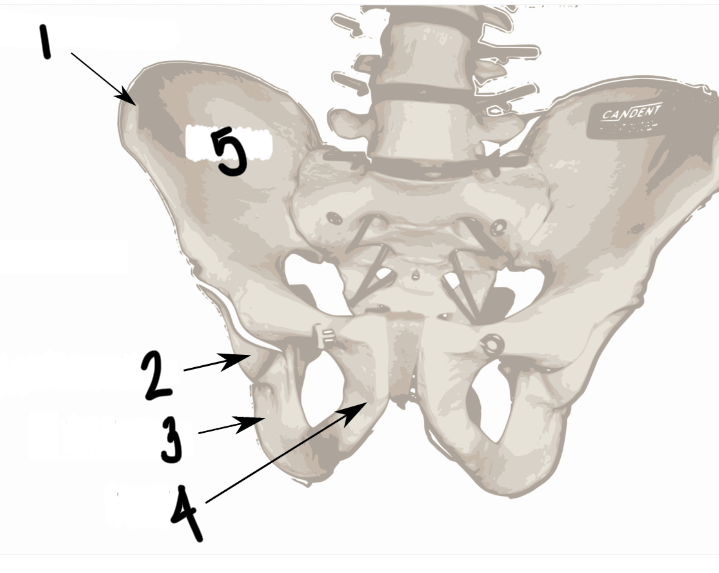
Label these structures
iliac crest
acetabulum (the socket of the ball and socket joint of the hip)
ischium
pubis
ilium
What is the os coxae?
the hip bone
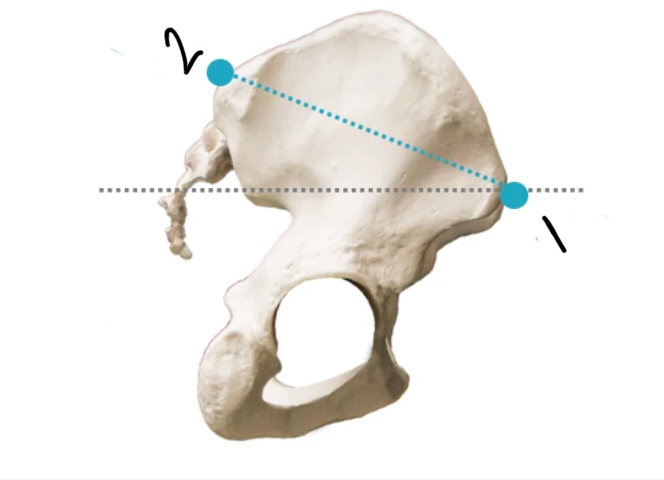
Label these 2 structures.
Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
Posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS)
Where is the superior boarder of the trapezius muscle?
The superior border of the trapezius muscle is located at the base of the skull, near the occipital bone. (superior nuchal line)
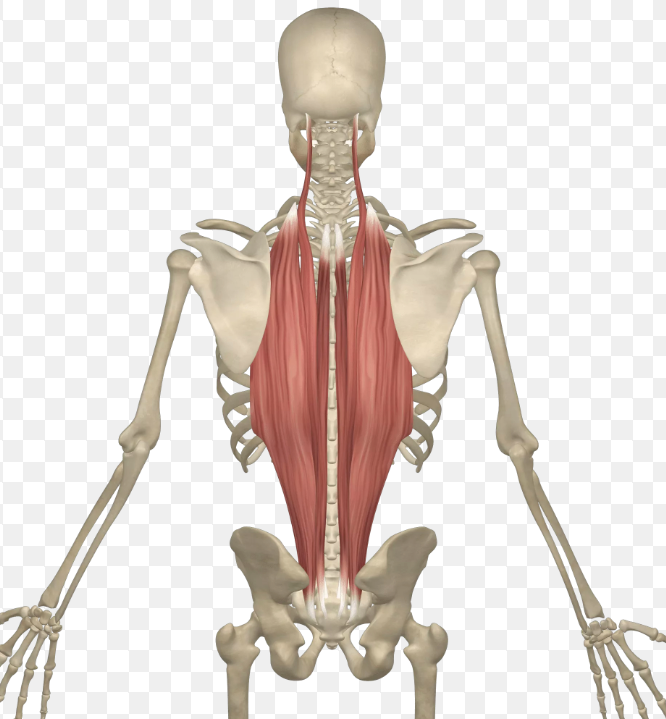
What muscles are these? and what are the attachments?
Erector spinae
inferior- thoracolumbar fascia, posterior sacrum, posterior iliac crest, sacral and lumbar SP
What is the lateral boarder of the latissimus dorsi muscle?
outer edge of the muscle that runs along the side of the back and attaches to the anterior proximal humerus.
Where is the posterior axillary fold?
In the axilla (armpit)
What muscle does the spinal accessory nerve innervate? and where is the nerve located.
Trapezius
on the deep surface of the reflected trapezius muscle
What is the superficial branch of the transverse cervical artery?
accompanies the plexus of nerves on the deep surface of the trapezius.
What muscle does the thoracodorsal nerve and artery supply? where will you find it?
Latissimus dorsi
you will find this bundle on the anterior surface near the lateral attachment on the humerus
Where are the rhomboid muscles? Which one is superior?
Rhomboid minor is superior to rhomboid major
Where do you find the dorsal scapular nerve and vessels in the rhomboid muscles?
the deep surface near their lateral attachments on the medial boarder of the scapula
Where will you find the levator scapulae? What are its attachments?
Superior to the rhomboid minor
superior: TP C1-C4
inferior: superior angle of the scapula
What nerve and vessels supply the levator scapulae and where will you find them in the dissection?
dorsal scapular nerve and vessels and you will find it deep and towards the inferior end of the muscle
Where is the serratus posterior superior muscle?
deep to the rhomboid muscles
Where is the serratus posterior inferior muscle?
deep to the latissimus dorsi
Where is the splenius muscle and what are the parts?
deep to the serratus posterior superior muscle
splenius capitus (superior)
splenius cervicis (inferior)
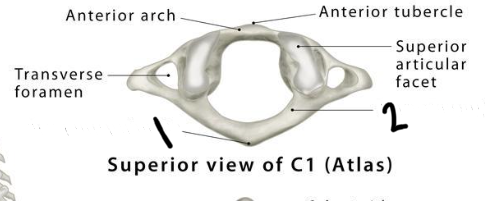
Atlas (+ 2 identifiable structures on the vertebrae)
C1
posterior tubercle
posterior arch
*has no body
Axis
C2
has dens
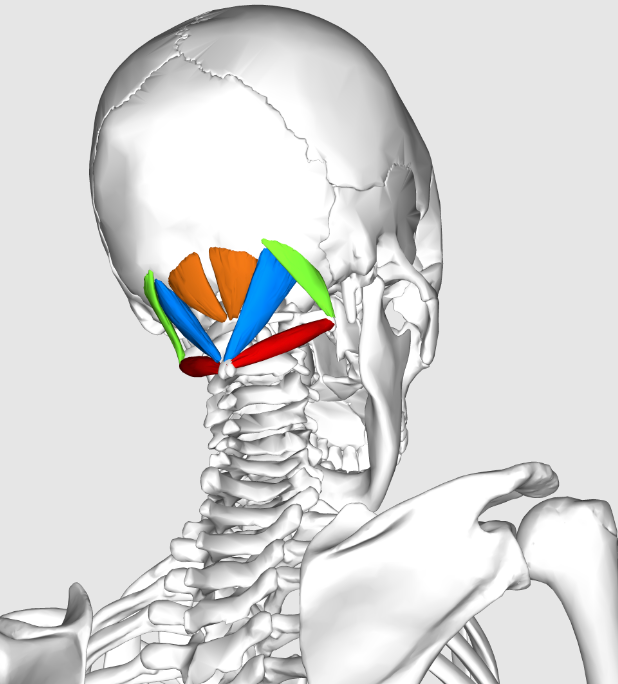
Suboccipital muscles
green- obliquus capitus superior
orange- rectus capitus posterior minor
blue- rectus capitus posterior major
red- obliquus capitus inferior
Contents of the subocciptal triangle
rectus capitus posterior major
obliquus capitus superior
oliquus capitus inferior
occipital bone
semispinalis
Know these structures
suboccipitial nerve
vertebral artery
Interspinous ligament
The interspinous ligament is a type of ligament found between the spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae in the spine. Its main function is to limit excessive flexion (forward bending) of the spine and provide stability to the vertebral column.
ligamenta flava
The ligamenta flava, also known as the ligamentum flavum, are a series of ligaments found in the spinal column. They connect the laminae of adjacent vertebrae and help to maintain the stability of the spine. The ligamenta flava are composed of elastic fibers, which allow them to stretch and recoil during movement of the spine.
supraspinous ligament
The supraspinous ligament is a strong fibrous band that runs along the posterior aspect of the vertebral column, connecting the spinous processes of the vertebrae. It helps to stabilize the spine and limit excessive flexion (forward bending) of the vertebral column.
contents of the epidural space
epidural fat and veins
know these structures
know how to identify these structures
dura mater
dural sac
arachnoid mater
subarachnoid space
spinal cord
pia mater
lumbar enlargement
conus medullaris
cauda equina
filum terminale internum
filum terminale externum
denticulate ligaments
posterior roots
anterior roots
IV foramen
posterior rootlets
anterior rootlets
spinal nerve
spinal ganglion/ dorsal root ganglion
posterior ramus
anterior ramus
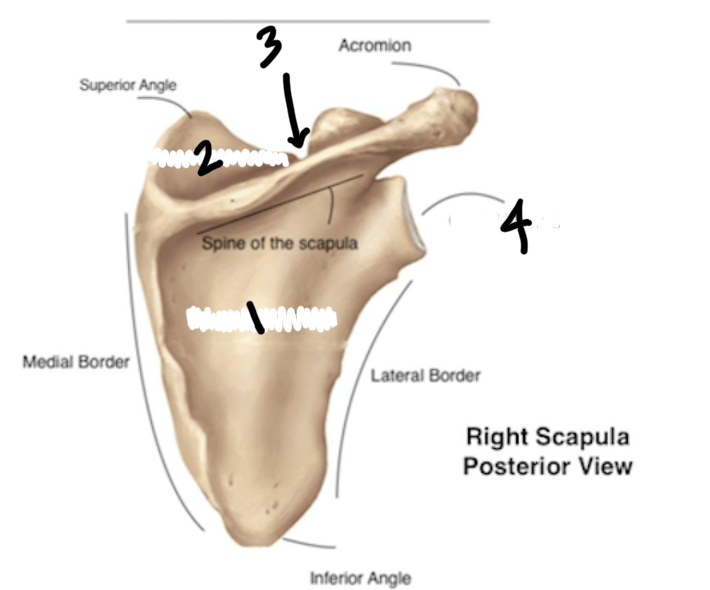
Label the parts of the scapula
infraspinous fossa
supraspinous fossa
suprascapular notch
glenoid cavity