Eyes & Ears
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Eyes & Ears
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
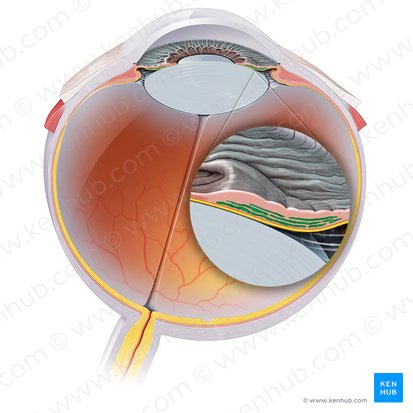
Lacrimal Apparatus
Produces tears, channels them to the surface of the eye where they maintain moisture, and flushes debris and waste material from the ocular surface. The control of tears is under a multitude of inputs and sensory responses.
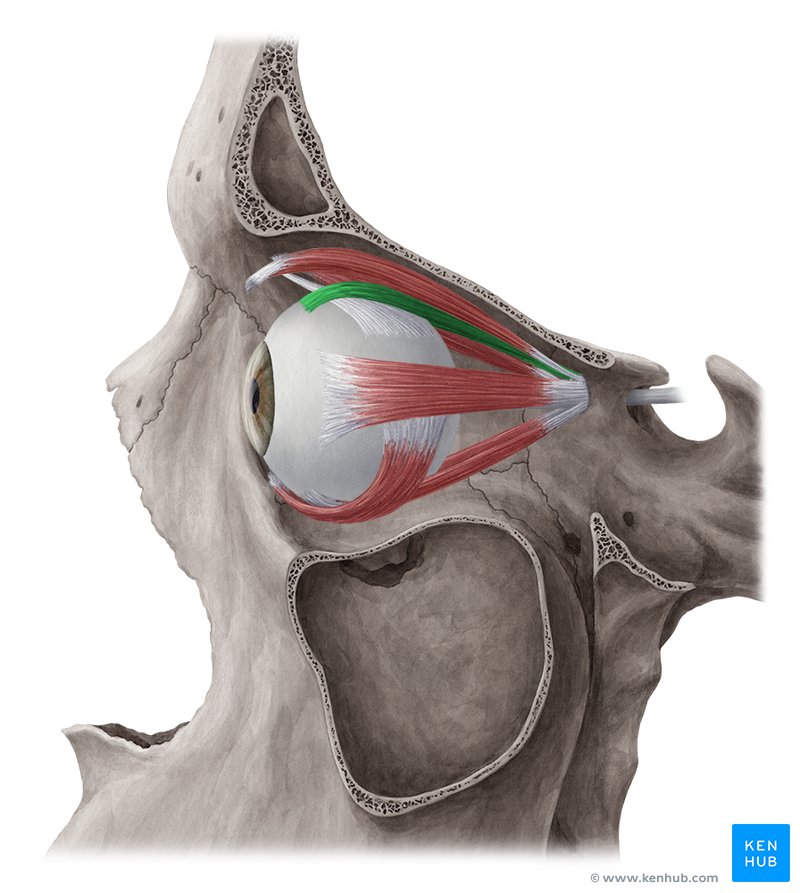
Superior Rectus Muscle
One of the extrinsic muscles of the eye, located outside the eyeball but within the superior orbit, it belongs to a group called the extraocular muscles. This group of muscles serves to move the eyes within the orbit.
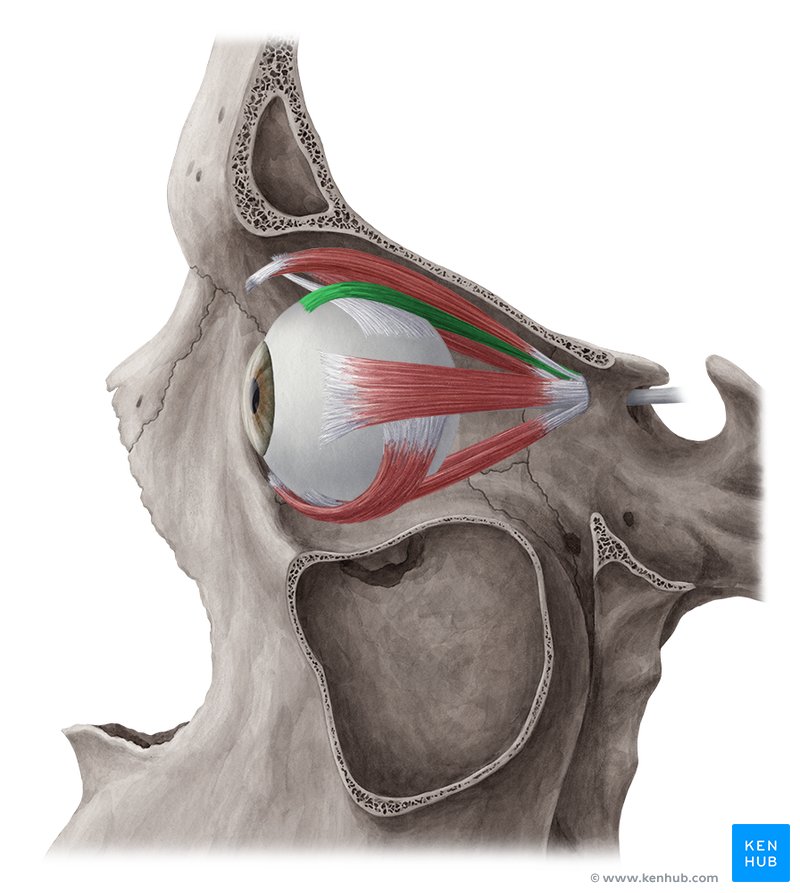
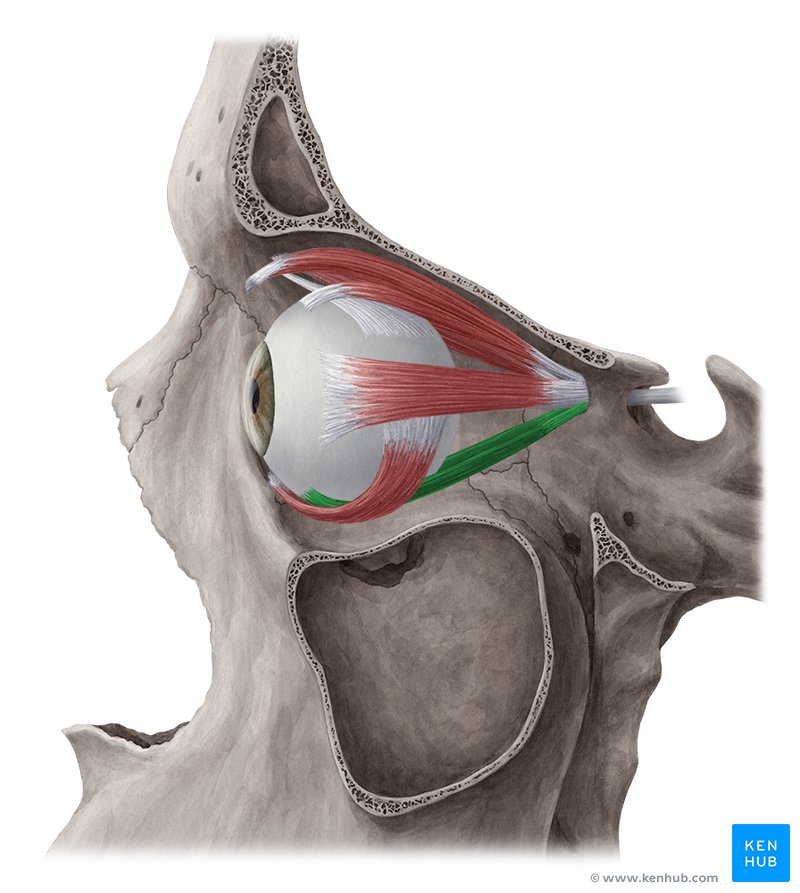
Inferior Rectus Muscle
One of the extrinsic muscles of the eye, located outside the eyeball but within the inferior orbit, it belongs to a group called the extraocular muscles. This group of muscles serves to move the eyes within the orbit.
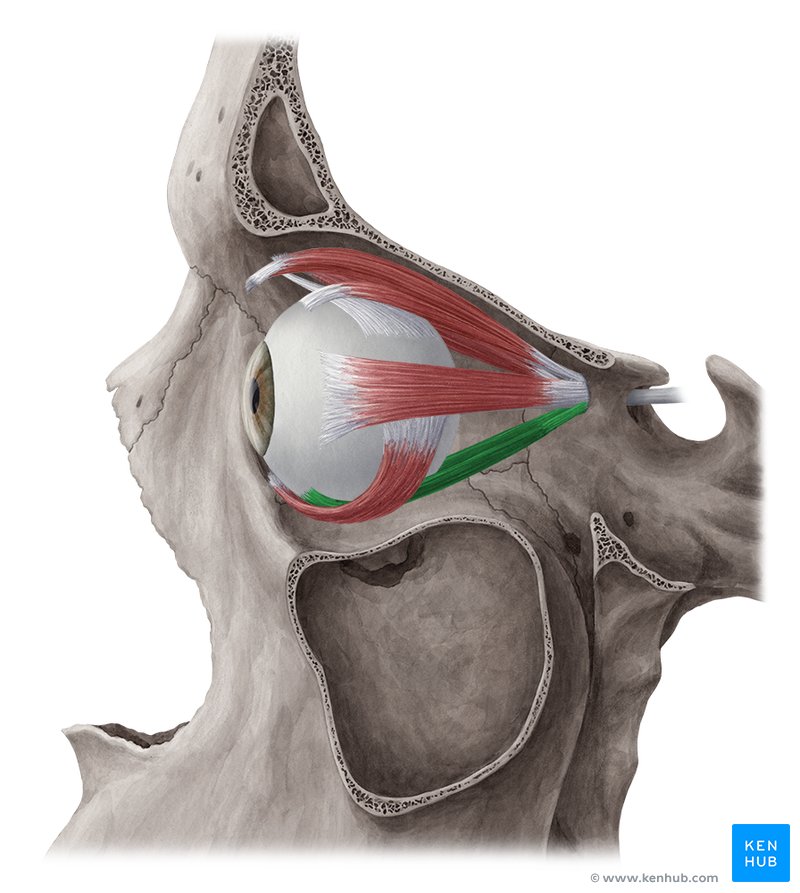
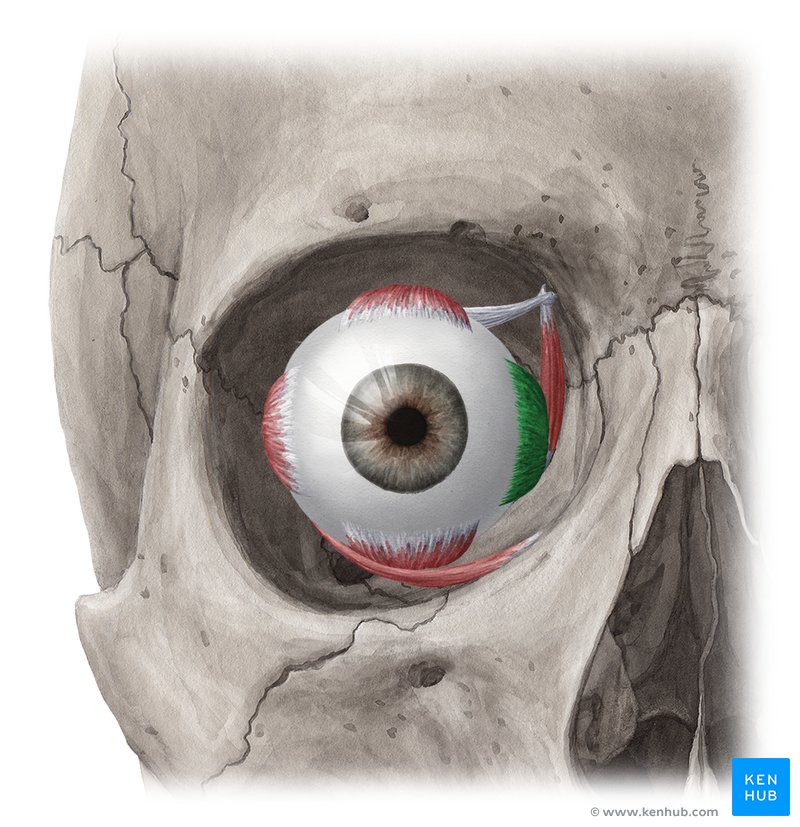
Medial Rectus Muscle
One of the extrinsic muscles of the eye, located outside the eyeball but within the medial orbit, it belongs to a group called the extraocular muscles. This group of muscles serves to move the eyes within the orbit.

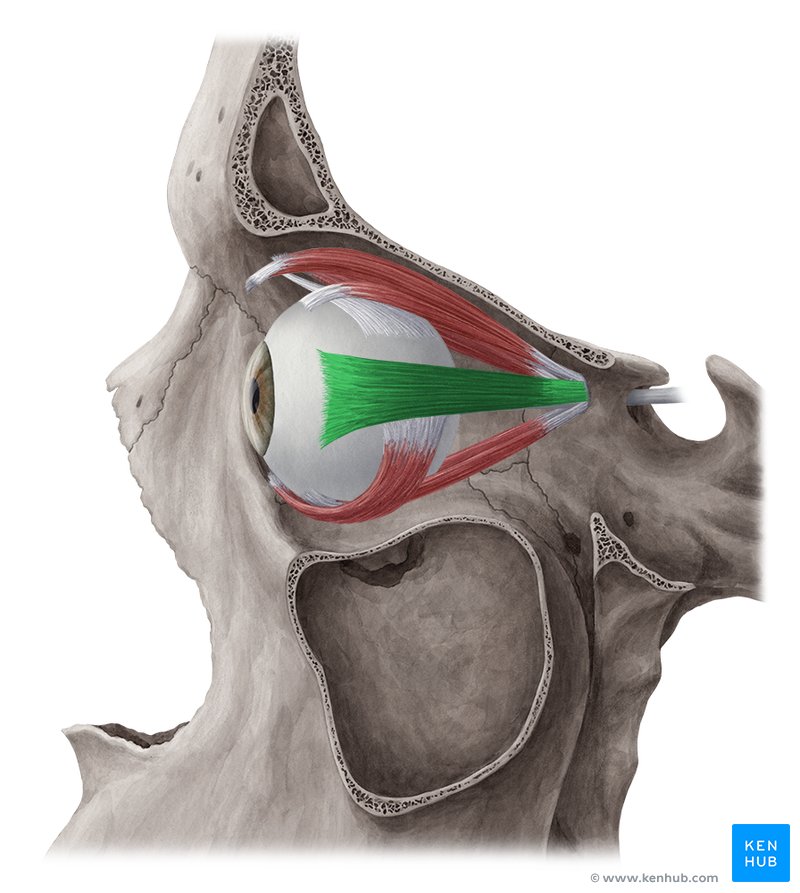
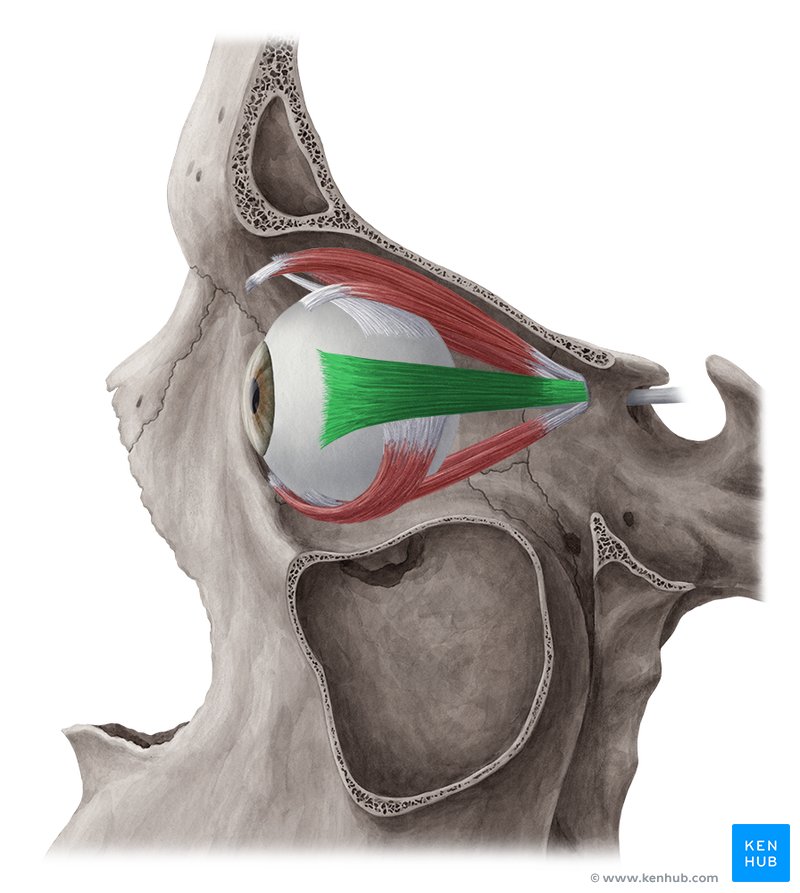
Lateral Rectus Muscle
One of the extrinsic muscles of the eye, located outside the eyeball but within the lateral orbit, it belongs to a group called the extraocular muscles. This group of muscles serves to move the eyes within the orbit.
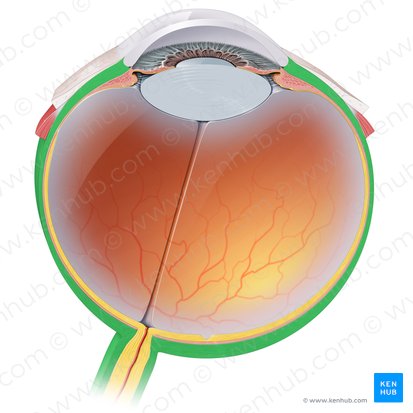
Sclera
The opaque white posterior part of this outer layer. It protects the inner eye contents and gives structural integrity to the eye.
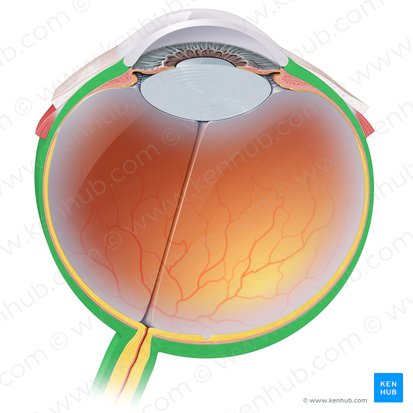
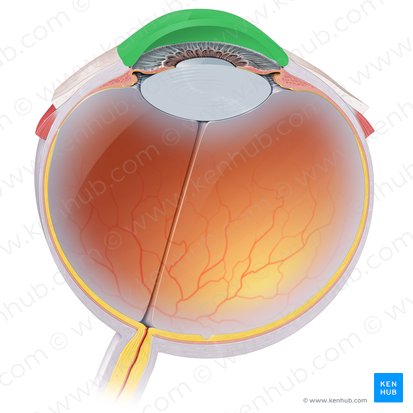
Cornea
Forms the anterior transparent layer of the outer coat. It is a dome shaped elevation which projects from the sclera at the corneoscleral junction. It is an avascular structure, containing no blood vessels except at its margins. It is however highly innervated and is very sensitive to pain and touch.
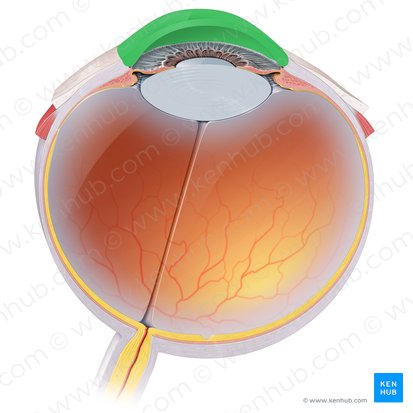
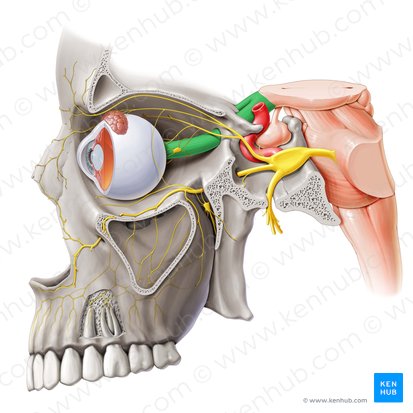
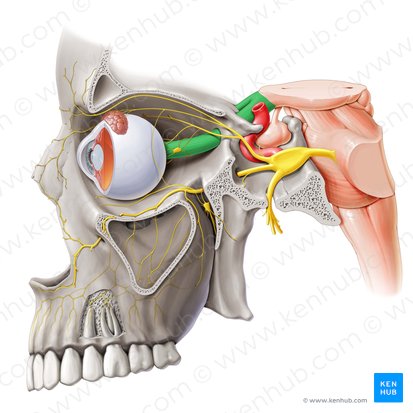
Optic Nerve
Cylindrical structures that extend from the posterior part of the eyeball to the suprasellar space in the middle cranial fossa. Has the responsibility of transmitting special afferent impulses of light to the brain. It is also involved in several reflex arcs related to the ocular system.
Iris
The circular colored part of the eye.
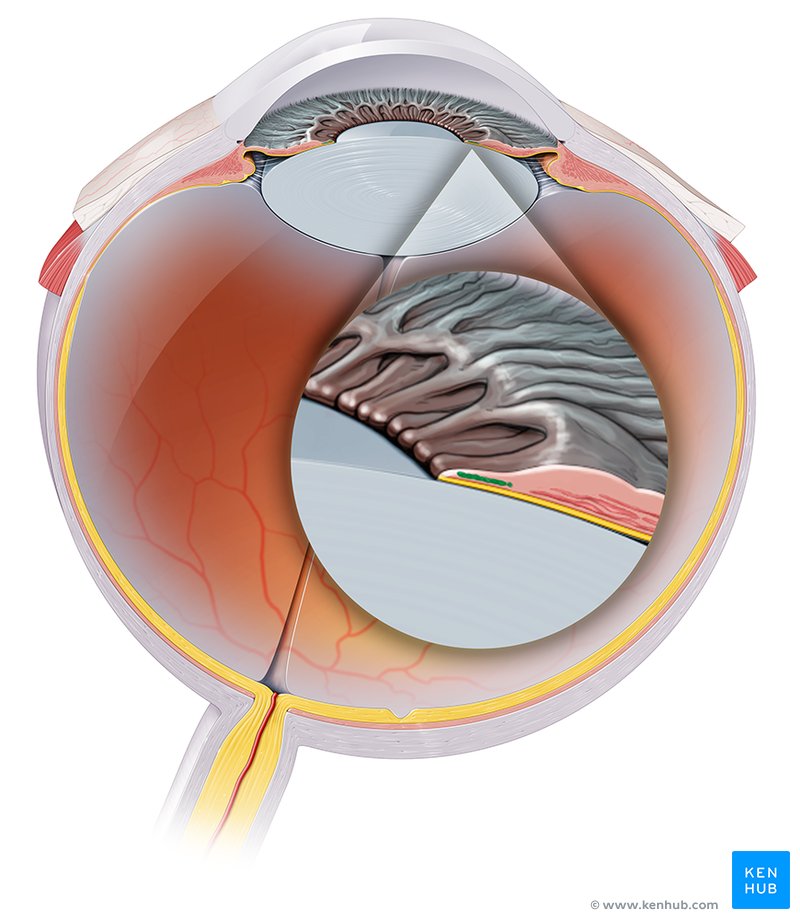
Sphincter Pupillae
Muscle responsible for constricting the pupil.
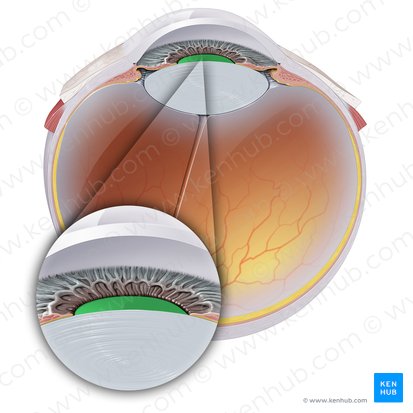
Pupil
The small black circle located in the center of the eyeball.
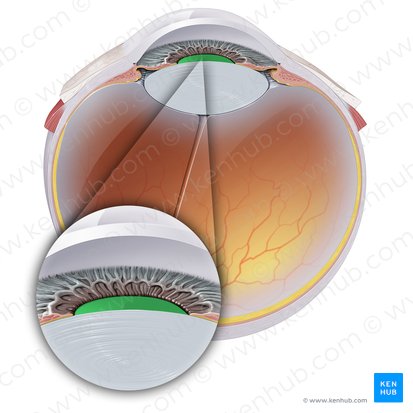
Uvea
The eye's middle layer, situated between the white sclera and inner retina, comprising the iris, ciliary body, and choroid.
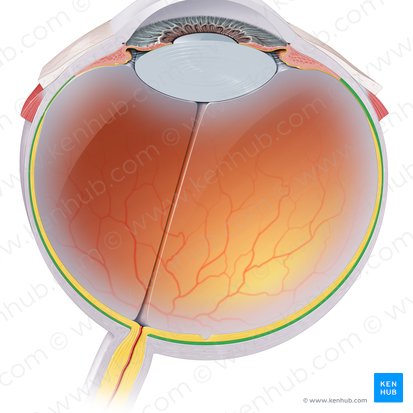
Choroid
Forms part of the vascular layer of the eyeball, along with the ciliary body and iris. It is a thin, pigmented vascular connective tissue layer of the eyeball that extends from the ora serrata to the optic nerve (CN II). It is located between the fibrous outer sclera and inner retina, extending from the optic nerve posteriorly.
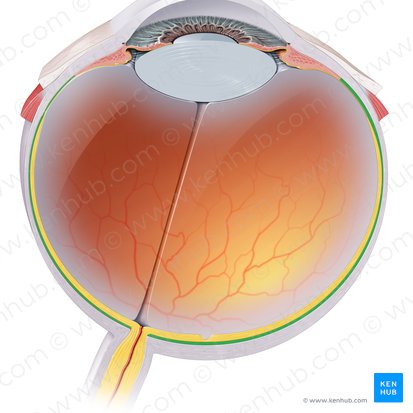
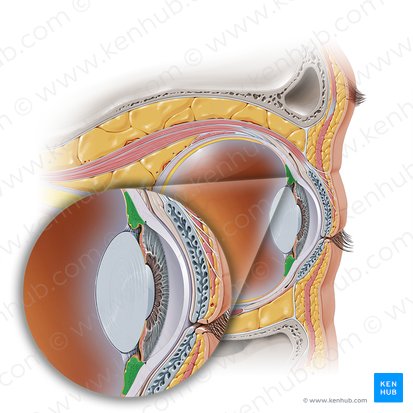
Ciliary Body
An inner eye structure, located at the border between the choroid and the iris. It is composed of several unique structures that give the it its unique shape and function. These structures include the ciliary muscle, ciliary processes, ciliary vessels and ciliary epithelia.
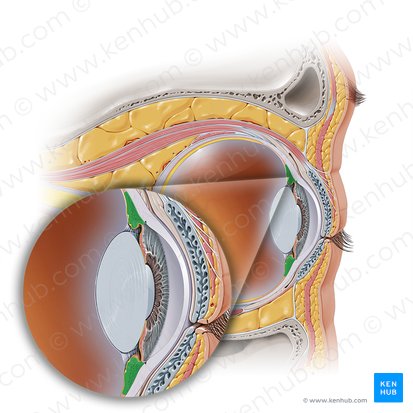
Ciliary Muscles
Muscles that control the movements of the lens and pupil and thus participate in the accommodation of vision. There are three smooth muscles that comprise this group; ciliary, dilatator pupillae and sphincter pupillae muscles.

Zonule
Tiny, thread-like fibers in the eye that suspend the lens, connecting it to the ciliary body, acting like tiny springs to change the lens shape for focusing (accommodation).
Lens Capsule
A clear, elastic membrane encasing the eye's natural lens, providing shape, support, and protection, acting like a clear bag that holds the lens and connects to the eye's focusing system (zonules).

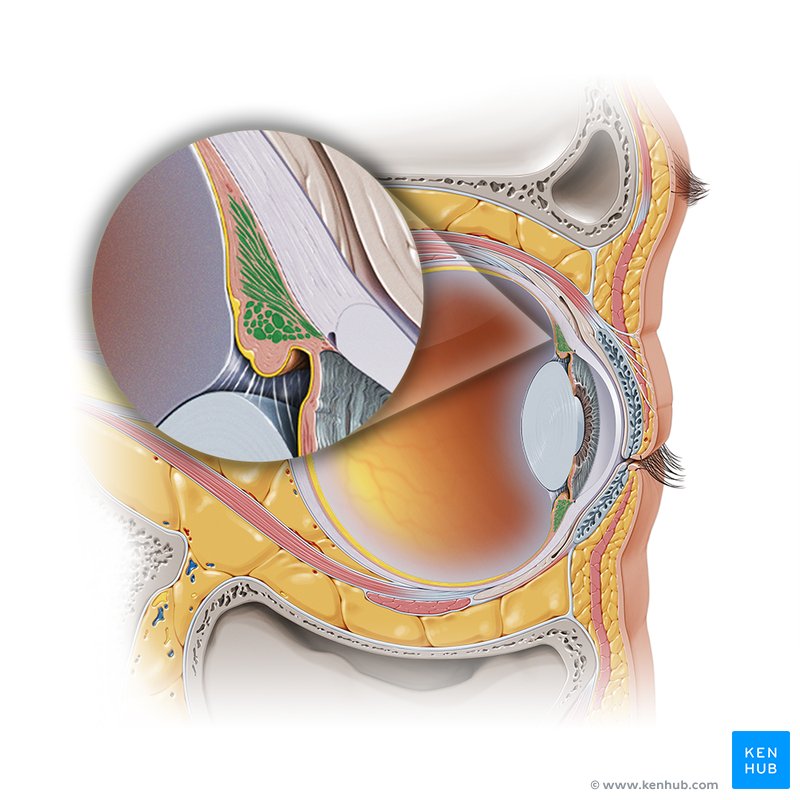
Ora Serrata
Marks the junction between the posterior, photosensitive optic region of the retina (neural retina) and the anterior nonphotosensitive (nonvisual) region, which extends over the internal surface of the ciliary body and the iris.
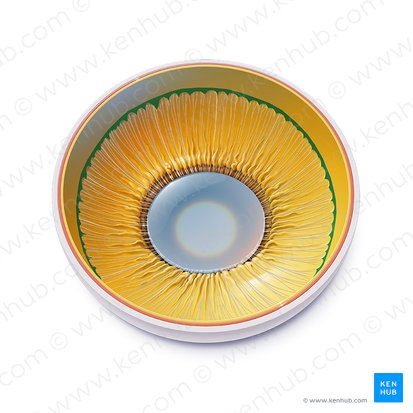

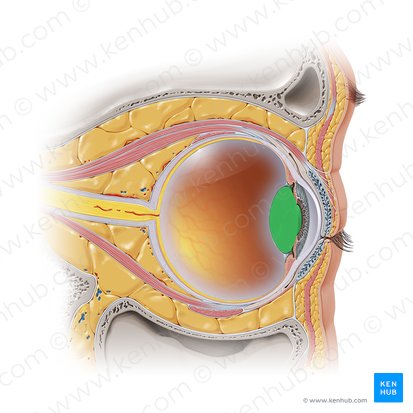
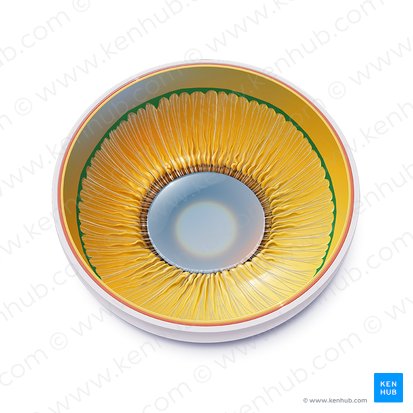
Lens
Transmits and focuses light onto the retina in order to create clear images of observed objects at various distances. It is also the main structure of the accommodation reflex.
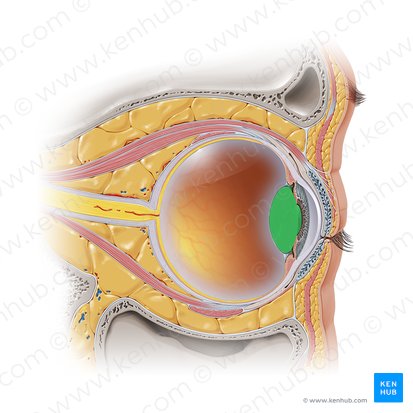
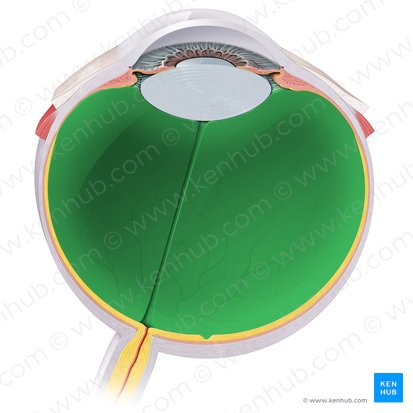
Vitreous Body
The largest structure of the eyeball, occupying the four-fifths of the entire eye. It fits into the concavity of the retina, being posterior to the lens. The anterior concavity that is adapted to fit with the convexity of the lens is called the hyaloid fossa.
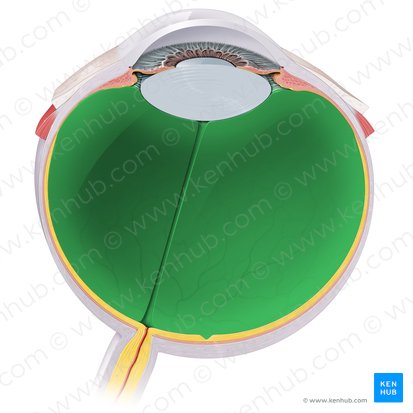
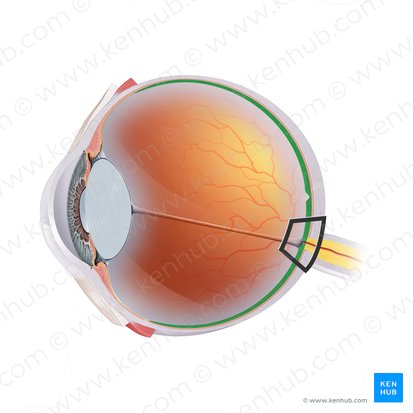
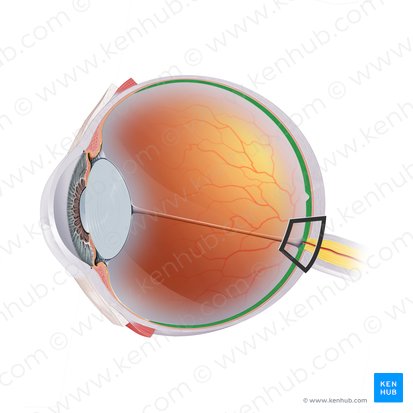
Retina
Composed of epithelial, glial, and neural cells that are organized into 10 distinctive layers. Out of these, the first 9 layers belong to the inner neurosensory retina, one of which are the photoreceptors that are sensitive to light.
Pinna of Ear
The visible, cartilage-supported flap on the side of your head that collects and funnels sound waves into the ear canal.
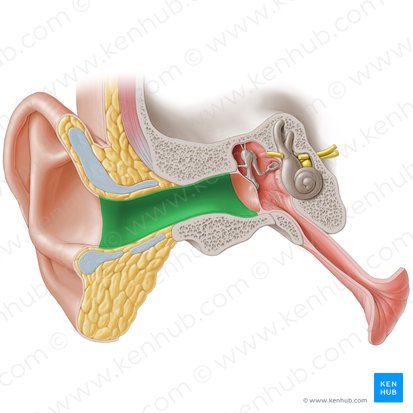
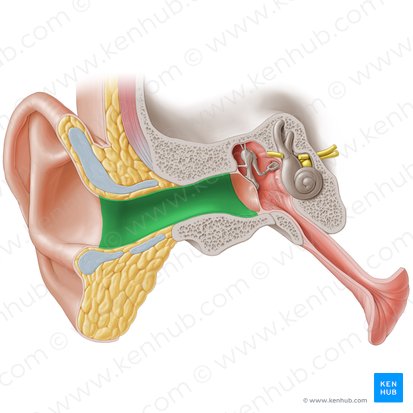
External Acoustic Meatus
The ear canal; a slightly S-shaped tube situated within the tympanic portion of the temporal bone. Its entrance is lies just in front of the mastoid process of the temporal bone.
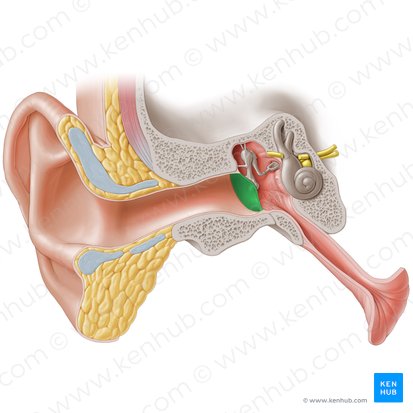
Tympanic Membrane
An oval, semi-transparent structure situated between the external auditory meatus and the tympanic cavity of the middle ear.
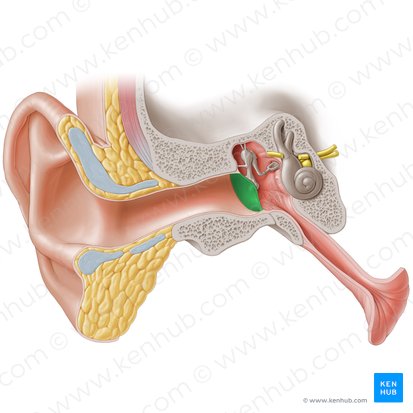
Malleus
One of three tiny interconnected bones in the middle ear cavity (tympanic cavity) which are collectively called the auditory ossicles. Is Latin for 'hammer' and is so called due to its mallet shape.
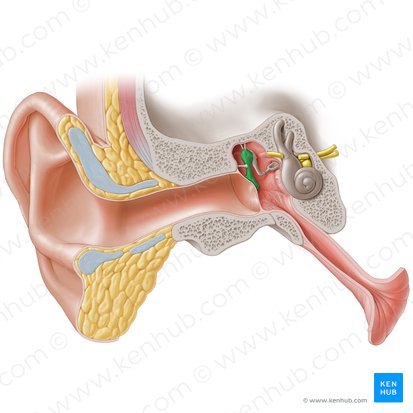
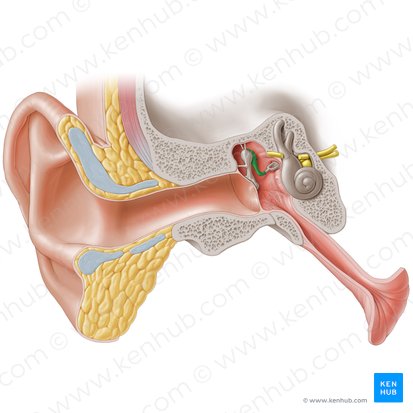
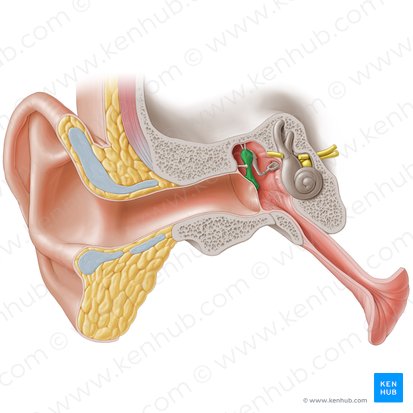
Incus
The anvil-shaped central auditory ossicle which connects the malleus to the stapes.
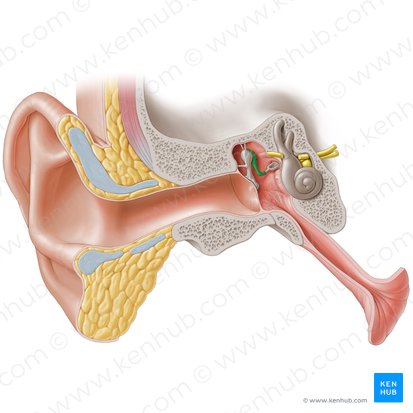
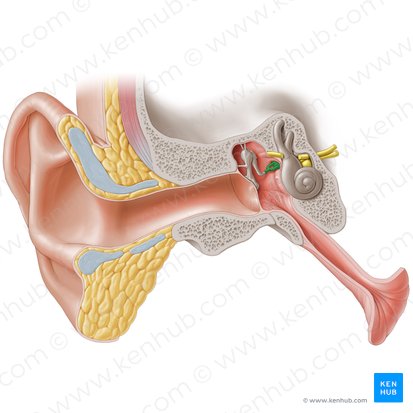
Stapes
The smallest and the lightest bone of the human body; one of three bones of the middle ear along with the malleus and incus. These three bones are collectively called auditory ossicles. They are primarily responsible for sound conduction from the tympanic membrane to the middle ear.
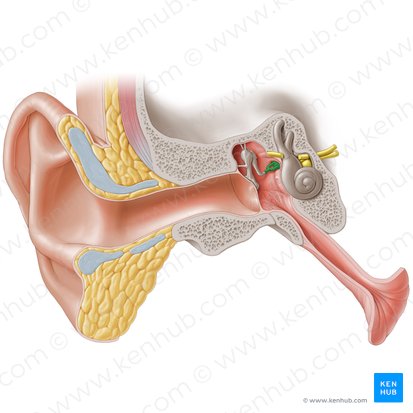
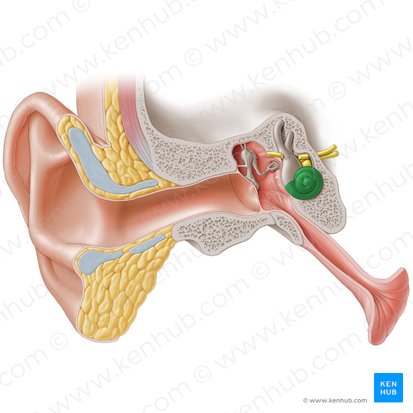
Conchlea
A component of the labyrinth of the internal ear that is responsible for hearing. It is a hollow, spirally coiled chamber inside the temporal bone that makes 2.75 turns around its axis, which is called the modiolus.
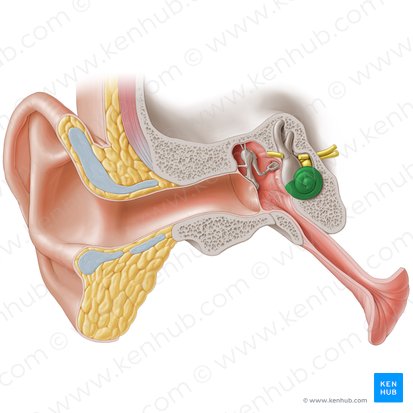
Organ of Corti
A spiral-shaped structure in the cochlea of the inner ear which produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations.
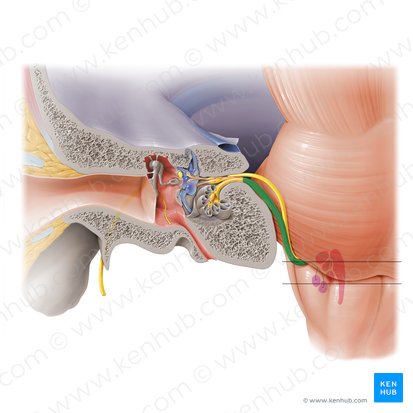
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
The eighth cranial nerve (CN VIII), is the sensory nerve which consists of two divisions. Each emerge from their respective roots:
The vestibular root (gives rise to the vestibular nerve)
The cochlear root (gives rise to the cochlear nerve)
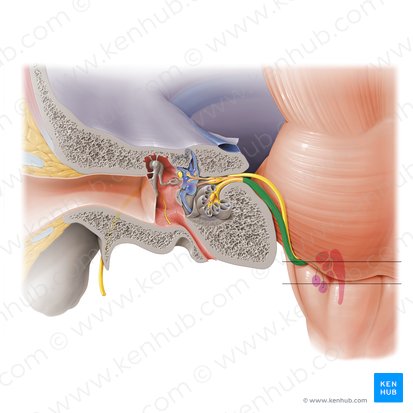
Macula
Sensory patches, one in the utricle (horizontal) and one in the saccule (vertical), that detect head position and linear acceleration, essential for balance, using hair cells and heavy calcium carbonate crystals (otoconia) in a gel-like membrane to sense gravity and motion.
Cupula
A small, dome-shaped structures, most notably the gelatinous sensory organ in the inner ear that detects head movement for balance.
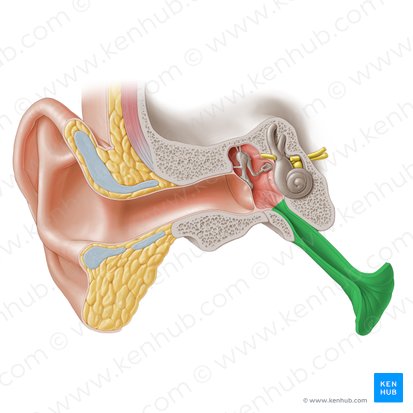
Eustachian Tube
A part bony, part fibrocartilaginous tube which connects the middle ear with the nasopharynx. It is also known as the pharyngotympanic tube.
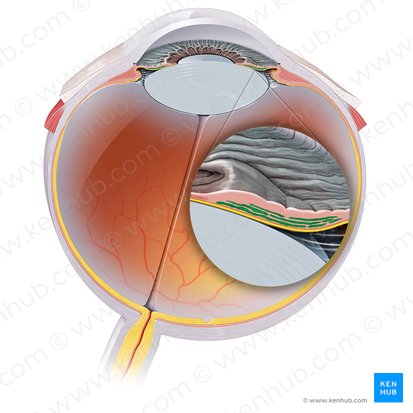
Dilator Pupillae
Muscle responsible for expanding the pupil.